Let's start with concepts and meanings
Accounting profit (BP) is a key economic indicator. It characterizes production efficiency, rational use of resources and the overall productivity of the company’s financial and economic activities. The calculated value of accounting profit is determined through income and expenses - their difference shows the real economic situation of the enterprise.
| Bukhpribyl | Meaning |
| Positive | Revenues exceed expenses. The work is going in the right direction, capacity is growing, and the company is benefiting. |
| Zero | Equality of income and expenses. The company has no profit or loss - this is the break-even point. |
| Negative | Profitability is lower than costs. For profitability, such a situation is impossible. |
The result obtained is always either positive or zero. If the difference between income and expenses is negative, the economic situation of the organization is unsatisfactory, and we are talking about accounting losses. Consequently, the company will receive a positive accounting profit if the total revenues from all types of activities exceed the total costs for the same period of time.
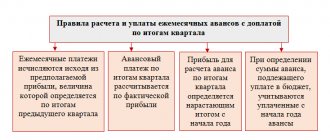
After the calculation, analyze the main indicators of financial and economic activity. For each index, profitability per ruble of added material costs is calculated. Here's how to find accounting profit and check your investment's performance:
Step 1. Determine income and expenses.
Step 2. Calculate accounting profit: find the difference between profitability and costs.
Step 3. Select the financial indicator of interest and calculate the coefficient using the formula:
K = P / MZ,
Where:
- P - profit received from core activities;
- MZ is the amount of material costs.
If the index is positive and continues to grow over a given time period, the company's core business is productive. A negative value characterizes the ineffectiveness of investments and an unfavorable economic situation for the enterprise.
Meaning
The indicator under consideration, among other things, characterizes the rational use of material and labor resources. In general, accounting profit is the difference between the income and expenses of an enterprise.
| Profit indicator | Explanation |
| Positive | Evidence that the company has received financial benefits from its activities |
| Income equals expenses | The break-even point has been reached: no profit or loss has been made |
| "Negative profit" | There shouldn't be such a thing. After all, when expenses exceed income, we cannot talk about any profit. |
Based on the value of the PWB, calculations are made to assess the effectiveness of the activity. For example, analysis is carried out in relation to material resources using various indicators. But the general one for them is profit per 1 ruble. material costs . The resulting coefficient is equal to the quotient of the extracted profit from the main activity (P) to the amount of material costs (MZ):
The growth of this value positively characterizes the activity of the enterprise. In practice, specialists conduct such analysis in more depth, using various factor models and establishing the reasons for changes.
Types of accounting profit
Experts identify several key types of accounting profits. The classification is:
- Gross - is defined as the arithmetic difference between the gross revenue receipts of the institution and the cost of production costs. Mandatory tax payments, such as VAT, excise duty and other fees, are deducted from the income portion.
- Interim and final - calculated as income minus expenses. The final value is determined based on the results for the year, and the intermediate value is determined for a specific period of time.
- From sales - calculated as the difference between gross profitability and selling expenses. If the company has management costs, they should be deducted.
- Margin is a type of accounting profit, which is calculated as the difference between gross receipts and variable costs. Moreover, fixed costs are not included in the calculation. This indicator allows you to determine profitability for individual areas of activity (categories of goods, types of work, items).
- Balance sheet - an indicator equal to total revenue reduced by the cost of production.
- Net is the balance sheet profitability reduced by the amount of calculated company income tax, which is subject to payment to the relevant budgets. Deferred tax assets should be included in the calculation.
How is the calculation of current income tax regulated?
The legislator pays serious attention to the calculation of income tax. The rules by which tax is calculated are contained in PBU 18/02. Changes to this document were made by the Ministry of Finance by order No. 236n dated 11/20/18. Income tax is reflected in the financial statements, in the income statement, so its form was also changed by order of the Ministry of Finance No. 61n dated 04/19/19.
Let us recall that the income tax of legal entities is direct, in other words, directly dependent on the final financial results of the work for the reporting period. It is accrued on the amount of profit, which is the difference between income and expenses, which is the object of taxation.
Important! Taxation is determined by the rules of Chapter. 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The reason for such close attention to tax calculation is obvious: in the country’s budget system it is one of the main income-generating factors. Income tax is equally important for federal and regional budgets.
The main difference from the previous edition of the PBU is the following: the current income tax is calculated in accordance with the Tax Code. Previously, it was calculated based on profit according to accounting data, adjusted for the amount of deferred tax liabilities, assets, permanent tax liabilities, and assets.
Now only the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are taken as a basis. The difference between accounting and tax accounting when calculating income tax is reduced to zero.
PBU 18/02 declares two options by which the amount of tax can be determined:
- according to BU data;
- according to the data reflected in the tax return.
Whatever method of calculation the taxpayer uses, the amount of the current income tax must be equal to the amount entered in the tax return.
Note! For a group of consolidated taxpayers (CGT), the tax is reflected in a separate account for the group as a whole. This account of settlements with members of the consolidated group is maintained in the accounting department of the responsible participant of the consolidated group (PBU 18/02, clause 22).
We have analyzed the general algorithm for calculating the current income tax and the documents regulating it. Let us now find out how to apply the formula for calculating the current income tax and reflect the amount in the income statement.
Let's calculate profit using the formula
Accounting profit is the final financial result for the reporting period - a year (clause 79 of Order No. 34n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998). The general formula for accounting profit is:
BP = D - R,
Where:
- D - income for the period;
- R - consumption.
Only explicit (direct) costs are used for calculations. If necessary, accounting profits are also calculated for one calendar month or quarter, six months, or 9 months. This value is reflected in the financial statements - in Form 2 “Report on Financial Results” (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 66n dated July 2, 2010).
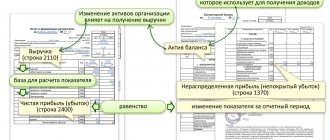
The values of formula indicators are in interim and final reports and in balance sheet items. Here's how to determine accounting profit:
- Open balance.
- Find the required values in the balance sheets.
- Substitute the numbers into the formula.
Calculation based on the resulting indicators will give more accurate profitability values. On the balance sheet, the company's accounting profit is calculated using the formula:
BP = revenue (line 2110) + income received from participation in enterprises (line 2310) + amount of % receivable (line 2320) + other income (line 2340) – cost price (line 2120) – commercial expenses (line 2210) – administrative expenses (line 2220) – amount of % payable (line 2330) – other expenses (line 2350).
Reflection of profit in accounting
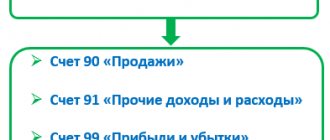
In accounting, accounting profit is formed on account 99 as a result of reflecting on it the results formed on accounts 90 and 91. In relation to the lines of the financial results report, it will look like this:
- line 2110 reflects the amount of revenue generated on the credit of account 90, minus the amount of VAT included in the debit of the same account;
- in line 2120 the amounts are entered from the debit of account 90 in relation to accounts 20, 23, 41, 43 (cost);
- page 2210 shows the amounts reflected in the debit of account 90 in relation to account 44 (business expenses);
- in line 2220 the amount debited from account 90 from account 26 (administrative expenses) is entered;
- on page 2200, an amount is formed that goes from account 90 to account 99 (profit from sales);
- in lines 2310, 2320, 2330, 2340, 2350, according to the analytics specified in them, data on account 91 is entered (other income and expenses minus VAT, if this tax is present in other income);
- on page 2300, the result obtained on account 99 will be reflected as a result of the receipt of amounts from accounts 90 and 91 (accounting profit).
Thus, the accounting profit that appears in the financial results statement is correlated with the accounting data at all stages of its reflection in it.
Let's give an example
Financial results for 2022 for the organization: income - 15,000,000.00 rubles, expenses - 10,000,000.00 rubles. According to the rules, only explicit costs are taken into account when calculating accounting profit. The items of such costs are presented in the table:
| Expense item | Amount, rub. |
| Wage | 3 500 000,00 |
| Taxes | 2 500 000,00 |
| Communal payments | 500 000,00 |
| Building maintenance costs | 1 500 000,00 |
| Other costs | 2 000 000,00 |
| Total | 10 000 000,00 |
Let's calculate profitability for 2022. BP = 15,000,000.00 - 10,000,000.00 rubles = 5,000,000.00 rubles. This is a positive value, which means production efficiency and productivity of financial and economic activities.
Accounting and economic profit: what is the difference?
When analyzing business activities, experts often identify so-called lost profits and implicit costs. These include funds that could be obtained, for example, by using a different strategy or making a different management decision.
It is important to understand that accounting profit is a measure that excludes implicit costs.
Another value takes them into account - economic profit. It helps compare the desired profitability with the minimum required to meet all expectations and represents the difference between total income and all types of costs. Mathematically, the equation looks like this: Accounting profit = economic profit - implicit costs
When assessing efficiency, economic profit gives a complete picture of the use of enterprise assets, since it compares the actual result with rejected opportunities. A positive result indicates the rational use of resources. A negative or zero value may indicate a loss of funds from capital.
Also see “Retained earnings on the balance sheet, what is it?”
We will reflect it in accounting
For intermediate calculations, data from synthetic accounts is used. To determine what the accounting profit is equal to in the reporting period, the accountant analyzes accounting account 99 (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 94n dated October 31, 2000).
Account 99 reflects profitability or losses from the main and other activities of the enterprise every month. It also forms the final accounting records. Here are the main wiring:
| Wiring | Operation description |
| Dt 90.9 Kt 99 | Accounting profit from main activities is taken into account |
| Dt 99 Kt 90.9 | Loss from core activities |
| Dt 91.9 Kt 99 | Profitability from other income and expenses |
| Dt 99 Kt 91.9 | Loss from other income and expenses |
| Dt 99 Kt 84 | Total accounting profit for the year |
| Dt 84 Kt 99 | Total loss for the year |
Profitability for the selected period (as of the date of report generation) is calculated as follows: BP = balance of account 99 + balance of account 84.
The relationship between profitability and costs
To identify a holistic picture of the functioning of any enterprise, it is necessary to identify the relationship between the values of EP, BP and explicit and implicit costs.
Explicit (external) costs refer to expenses actually incurred by the institution and expressed in current market value. This type of cost includes expense transactions related to the main activities of any organization:
- wage;
- acquisition of inventory items;
- payment for services;
- rent;
- payments on loans and borrowings;
- general production and general business expenses.
Implicit, or internal, costs are the amount of lost costs, alternative costs that the enterprise would have had if it had operated in a different area or in a different direction of development.
Thus, as mentioned above, economic profit is less than accounting profit by the amount of implicit costs.
Expenses and income
A company that operates and pays taxes obviously has some revenue and expenses. The latter are usually divided into two large groups:
- Explicit costs (external costs) are the costs actually incurred by the company in monetary terms. They include: rental costs, utilities, maintenance of the administrative apparatus, wages of employees, cost of purchased raw materials, materials, goods, depreciation, servicing of borrowed funds, transport and delivery costs, equipment operation, etc.
- Implicit costs (internal costs) are monetary costs planned under certain conditions. For example, those that could arise during the implementation of any projects or the development of a company.
Usually, in addition to costs, they also plan the income that can be received from placing a similar amount of funds in another area. Most often, an example is the placement of funds in a bank at interest. This is an indicator of the profitability that business owners can get from using their funds. For example, if a bank offers a deposit at 10% per year, then when placing 1 billion rubles in this way, a businessman is guaranteed to receive 1 million rubles. In this case, he will not incur any costs. This means that in his case, a business in which he can get no less financial results, taking into account all possible expenses, will be profitable.