Basis and legal basis
Income tax is one of the main taxes paid by an organization, provided that it does not apply special tax regimes.
The legal basis of the tax is set out in Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in articles 246 to 333.
There are also regional laws regulating the payment of income tax in terms of the application of tax benefits.
There are also numerous explanations from the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service, which, although not of a regulatory nature, are of great importance and are actively used for the work of accountants and lawyers.
Results
So, we found out that income tax payers are organizations and not individual entrepreneurs.
All Russian organizations must pay income tax, with the exception of those that:
- exempt from its payment due to the use of special tax regimes;
- use the Skolkovo exemption.
Also, some foreign organizations are payers, for some of which there are also a number of preferences.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Taxpayers
Payers of income tax are:
- Russian organizations, in addition to those that have switched to special tax regimes - simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax, those involved in the gambling business and a number of others.
- Foreign organizations operating through permanent representative offices in the Russian Federation and (or) receiving income from sources in the Russian Federation.
Organizations that are responsible participants in a consolidated group of taxpayers are recognized as taxpayers with respect to corporate income tax for this consolidated group of taxpayers.
The following are exempt from income tax:
- Organizations on UTII or engaged in the gambling business (if their activities are broader, then they calculate and pay income tax on it in the general manner).
- Organizations on the simplified taxation system (simplified taxation system) and unified agricultural tax (agricultural producers) (but they are required to pay tax on income in the form of dividends and interest on state and municipal securities).
- Organizations related to the preparation and holding of the 2022 FIFA World Cup and the 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup in the Russian Federation: FIFA itself and its subsidiaries, as well as national football associations, confederations, suppliers of goods (works, services) to FIFA and media information providers.
Freeing up to innovate
Organizations that have received the status of participants in a project to carry out research, development and commercialization of their results in accordance with Federal Law dated September 28, 2010 No. 244-FZ “On Innovation” can apply an exemption from the duties of income tax payers. The exemption is valid for 10 years from the date of receipt of project participant status. The procedure and conditions for applying the exemption are established by Art. 246.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The exemption can be used from the first day of the month following the month in which the status of a project participant was obtained (clause 4 of Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The tax authority must be notified of its use. To do this, no later than the 20th day of the month following the month from which the exemption is used, the following must be sent to the inspectorate at the place of registration (clauses 4, 7 of Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- written notification (in the form approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 2010 No. 196n, Appendix No. 1);
- documents confirming the status of a participant in the Skolkovo project;
- an extract from the book of income and expenses (financial performance report), confirming the annual volume of revenue from the sale of goods (work, services, property rights). The volume of revenue should not exceed 1 billion rubles (clause 2 of Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The same documents should be submitted to the inspectorate at the end of the tax period in which the exemption was used, along with a notice of extension of the use of the right to exemption for the next period or refusal of the exemption. The deadline for sending is no later than the 20th day of the month following the tax period in which the exemption was applied (clause 6 of Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the documents are not sent or contain false information, you need to restore the income tax, pay it to the budget, and also transfer penalties. According to the Ministry of Finance, organizations that submit documents later than the deadline should do the same (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 20, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/316).
See also “How to calculate and reflect penalties for income tax?”
The right to release can be lost for 2 reasons (clause 2 of article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- in case of loss of the status of a project participant - from the first day of the tax period in which such status was lost;
- if the annual revenue exceeds 1 billion rubles - from the first day of the tax period in which the specified excess occurred.
The tax for the tax period in which the status of a project participant was lost or the total amount of profit received by a project participant exceeded 300 million rubles will have to be restored and paid to the budget with the corresponding penalties (clause 3 of Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Voluntary refusal of release is also possible (clause 5 of Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To refuse it, you need to send to the inspectorate the notification provided for by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2010 No. 196n (Appendix No. 1). This should be done no later than the first day of the tax period from which the waiver of exemption is planned. However, it must be remembered that someone who has repeatedly refused it will no longer be able to obtain exemption.
In 2012-2018, certain categories of taxpayers were exempt from paying income tax. These included organizations associated with:
- holding the XXII Olympic and XI Paralympic Games 2014 in Sochi;
- holding the 2022 FIFA World Cup and the 2022 FIFA Confederations Cup in the Russian Federation.
Let's consider this point in more detail.
Object of taxation
The object of taxation is the profit that the organization received in the course of its activities, as the name implies.
According to Article 247 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, profit is:
- for Russian organizations that are not members of the consolidated group of taxpayers - income received, reduced by the amount of expenses incurred;
- for organizations participating in a consolidated group of taxpayers - the amount of total profit of the group attributable to this participant;
- for foreign organizations operating in the Russian Federation through permanent missions - income received through these permanent missions, reduced by the amount of expenses incurred by these permanent missions;
- for other foreign organizations - income received from sources in the Russian Federation (defined by Article 309 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What are income and expenses?
Income is an economic benefit in cash or in kind. It is assessed and determined in accordance with the rules of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code.
For income tax purposes, income refers to the total receipts of an organization (in cash and in kind) without taking into account expenses incurred by the organization. There is only one exception to this rule - taxes that the organization imposes on customers are excluded from the amount of income (for example, the amount of VAT in the invoice to the buyer).
The amount of income is determined on the basis of any documents that in one way or another confirm its receipt. These include primary accounting documents, tax accounting documents, settlement documents, contracts, etc.
Income that is taken into account when taxing profits is divided into:
- income from sales (revenue from the sale of goods, works, services and property rights);
- non-operating income (all other income, for example, dividends received by the organization, penalties, penalties, income from rental property, interest on loans and borrowings, etc.).
The following types of income are not taken into account when taxing profits:
- property or property rights received in the form of a pledge or deposit;
- property received free of charge from a Russian organization or individual owning more than 50% of the share of the company to which this property was transferred;
- contributions to the authorized capital of the organization;
- property received under credit or loan agreements;
- capital investments in the form of inseparable improvements to leased (received for free use) property made by the lessee (borrower);
- property received as part of targeted financing;
- other income provided for in Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Expenses are recognized as justified (economically justified) and documented expenses incurred by the taxpayer. Expenses must be incurred for activities aimed at generating income.
An expense is the amount by which an organization can reduce its income.
The following types of expenses are not taken into account when taxing profits:
- amounts of penalties, fines and other sanctions transferred to the budget;
- dividends;
- tax amounts, as well as payments for excess emissions of pollutants into the environment;
- expenses for voluntary insurance and non-state pension provision;
- financial assistance to employees, pension supplements
- etc.
This list is quite long (several dozen items), but it is exhaustive. It is established by Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Some expenses may be accepted to reduce the tax base not completely, but partially - within the limits of specially established norms (Articles 254, 255, 262, 264-267, 269, 279 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). They are called “standardized expenses”.
Please pay attention!
From January 1, 2022, amounts spent on assessing the qualifications of employees can be included in expenses. Since 2022, the Law on Independent Assessment of Qualifications has come into force. To encourage participation in the assessment, provisions will be introduced, for example, to take into account the cost of assessment in income tax expenses (clause 23, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To conduct an independent assessment of an employee's qualifications, his written consent is required. An organization can take expenses into account if the assessment was carried out on the basis of an agreement for the provision of relevant services and was carried out by a person who entered into an employment contract with the taxpayer. The storage periods for documents confirming the costs of an independent assessment of an employee’s qualifications are established in the new paragraph. 5 paragraph 3 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The changes are provided for by Federal Law No. 251-FZ of July 3, 2016.
What expenses are not taken into account when calculating?
When calculating income tax, the following costs are not taken into account:
- contributions to the authorized capital;
- penalties and fines;
- property and funds transferred to pay for loans and borrowings;
- advance payment for goods or services;
- the cost of property transferred free of charge and the costs of transfer;
- pension benefits;
- vouchers for treatment and rest of employees, etc.
A complete list of expenses that are not taken into account in the calculation is given in Art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax and reporting periods
The tax period for paying income tax is a calendar year.
Reporting periods:
- I quarter
- half year
- 9 months of the calendar year
Reporting periods for taxpayers who calculate monthly advance payments based on actual profit received are one month, two months, three months, and so on until the end of the calendar year.
From January 1, 2016, there were changes to the limit on the average quarterly amount of sales income, which is determined for the previous four quarters. This limit has been increased from 10 to 15 million rubles.
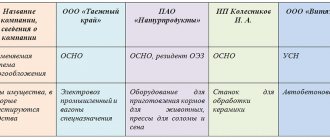
Who fills out which sheets?
From the following table you can find out which sheets of the income tax return a company should fill out.
Table 2. Filling out declaration sheets for common operations
| Filling conditions | Sections and sheets of the declaration |
| Required to be completed by all taxpayers | Title page Subsection 1.1 Section 1 Sheet 02 Appendices No. 1 and 2 to Sheet 02 |
| Advance payments are made monthly based on the actual profit received | Subsection 1.2 Section 1 |
| Information is provided only for the first quarter and at the end of the year | Appendix No. 4 to Sheet 02 |
The remaining sheets of the declaration are filled out if the organization has the relevant data.
Less often than others, due to their narrow focus, organizations fill out:
- Appendix No. 5 to sheet 02
- sheets from 03 to 09
- Appendix No. 2 to the declaration
Tax base for income tax
The tax base is the monetary value of profit subject to taxation.
As a general rule, profit is the income received minus the expenses taken into account in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If income is less than expenses, the tax base is zero.
Profit is determined on an accrual basis from the beginning of the tax period (calendar year).
The tax base for business transactions is determined in total, the profit from which is subject to a general rate of 20%.
Tax bases are determined separately for each type of business transaction, the profit from which is taxed at different rates. According to them, the taxpayer keeps separate records of income and expenses.
The financial result for transactions that are accounted for in a special manner is determined separately. Accounting for income and expenses is also kept separately.
Certain categories of taxpayers have their own specifics for determining the tax base for income tax. This:
- banks (NC, articles 290-292);
- insurance organizations (TC, articles 293, 294);
- non-state pension funds (NC, articles 295, 296);
- consumer cooperatives and microfinance organizations (NC, articles 297.1 - 297.3);
- professional participants in the securities market (TC, articles 298, 299);
- transactions with securities (TK, articles 280 - 282, letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 3, 2005 N MM-6-02/934);
- operations with financial instruments of futures transactions (TC, articles 301-305);
- clearing organizations (TC, articles 299.1, 299.2)
Taxpayers who apply special tax regimes (STS, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax, Patent) do not take into account income and expenses related to such regimes when calculating the tax base.
Gambling business organizations, as well as organizations that have switched to UTII, keep separate records of income and expenses. For tax purposes, only those expenses are taken into account that are economically justified, documented and incurred in the implementation of activities aimed at generating income.
The procedure for recognizing income provides for 2 methods: the accrual method and the cash method (Articles 271, 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Enrollment in the budget
The amount of income tax as a percentage is credited to the federal and regional budgets.
However, in 2022, there were changes in the distribution of interest. In 2022 - 2022, it is necessary to credit the amount of income tax calculated at the rate of 3% to the federal budget, to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - at the rate of 17%, and not at the usual 2% and 18%, respectively (paragraph 2, 3, paragraph 1 Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). As you can see, the general rate of 20% for income tax has not changed, but the funds received are distributed between budgets differently.
For certain categories of taxpayers, regional authorities have the right to reduce the rate at which the tax is credited to the budget of the subject. As a general rule, it should not be less than 13.5%, but for 2017 - 2022 this limit is reduced to 12.5%.
It is important to take these changes into account when filling out tax returns and payment orders.
The changes are provided for by Federal Law No. 401-FZ of November 30, 2016.
Example
The taxable profit of the Organization based on the results of the first quarter amounted to 1,000,000 rubles. The declaration for 9 months for the previous period indicates advance payments payable in the first quarter - 20,000 rubles, including:
- to the federal budget - 3,000 rubles;
- to the regional budget - 17,000 rubles.
For the first quarter, a trading fee in the amount of 30,000 rubles was accrued and transferred to the budget.
It is necessary to calculate advance payments payable for the first quarter and monthly advance payments for the second quarter.
Tax rates
The general tax rate is 20%, of which from 2022 to 2022 3% is credited to the federal budget, 17% to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
According to the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the rate may be reduced for certain categories of taxpayers in terms of tax amounts subject to credit to regional budgets. In this case, as a general rule, the rate cannot be lower than 13.5%. However, for 2017 - 2022 this limit is reduced to 12.5%.
Special tax rates are established for certain types of income:
| Type of income | Tax rate | Budget | Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Income of foreign organizations not related to activities in the Russian Federation through a permanent representative office (except for the income listed in paragraph 2, paragraph 2, paragraphs 3 and 4 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | 20% | federal | 1 item 2 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Income of foreign organizations not related to activities in the Russian Federation through a permanent establishment, from the use, maintenance or rental of mobile vehicles or containers in connection with international transportation | 10% | federal | 2 p. 2 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Income received in the form of dividends by Russian organizations from Russian and foreign organizations: - total rate - rate subject to certain conditions | 13% 0% | federal | pp. 2 p. 3 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation pp. 1 clause 3 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Income received in the form of dividends by foreign organizations from Russian organizations | 15% | federal | pp. 3 p. 3 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Income in the form of interest on state and municipal securities specified in paragraphs. 1 clause 4 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | 15% | federal | pp. 2 clause 4 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Income in the form of interest on municipal securities issued for a period of at least three years before January 1, 2007, as well as other income specified in paragraphs. 2 clause 4 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | 9% | federal | |
| Income in the form of interest on state and municipal bonds issued before January 20, 1997 inclusive, and other income specified in paragraphs. 3 p. 4 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | 0% | — | pp. 3 p. 4 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Income from securities (except for income in the form of dividends) issued by Russian organizations and accounted for in securities accounts: foreign nominee holder, foreign authorized holder and (or) depository programs, during the payment of which the procedure for submitting information to the tax agent in accordance with paragraph. clauses 7, 8, 10, 12, 13 art. 310.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | 30% | — | clause 4.2 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Profit received by the Bank of Russia from activities related to the performance of functions provided for by the Federal Law “On the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Bank of Russia)” | 0% | — | clause 5 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Profits of agricultural producers who have not switched to paying the Unified Agricultural Tax | 0% | — | clause 1.3 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 3 of Art. 1, paragraph 1 art. 2, part 1 art. 3 of Law No. 161-FZ, art. 2.1 Federal Law dated 06.08.2001 N 110-FZ |
| Profits of Skolkovo project participants who have ceased to exercise the right to be exempt from income tax obligations | 0% | — | Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Tax base of organizations engaged in medical and (or) educational activities (except for tax bases for dividends and transactions with certain types of debt obligations) | 0% | — | clauses 1.1, 3, 4 art. 284, art. 284.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Tax base for transactions related to the sale or other disposal (including redemption) of shares in the authorized capital of Russian organizations, as well as certain categories of shares of Russian organizations | 0% | — | clause 4.1 art. 284, art. 284.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Profit from activities carried out in a technology-innovation special economic zone, as well as in tourist and recreational special economic zones united in a cluster, subject to separate accounting of income and expenses by type of activity | 0% | federal | clause 1.2 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| The tax base of participants in a regional investment project, provided that income from the sale of goods produced within the project constitutes at least 90% of all income taken into account when determining the tax base | 0% | federal | clause 1.5 art. 284, paragraph 1, art. 284.3 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Tax base of residents of the territory of rapid socio-economic development | 0% | federal | clause 1.8 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
Income tax reporting. Declaration
At the end of each reporting and tax period, the organization is obliged to submit an income tax return to the tax authorities.
The income tax return form and the rules for filling it out were approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 26, 2014 N ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
The declaration is submitted to the tax office:
- at the location of the organization;
- at the location of each separate division of the organization.
If separate divisions of an organization are located on the territory of one subject of the Russian Federation, then income tax to the budget of this subject of the Russian Federation can be paid through one separate division, which the organization determines independently.
In what form is the declaration submitted - paper or electronic?
The following are required to submit a declaration electronically:
- largest taxpayers;
- organizations in which the average number of employees for the previous calendar year was 100 people or more;
- newly created organizations with more than 100 employees.
Other taxpayers may submit a return in paper form.