A cash register inventory is carried out to check whether the actual cash balances in the cash register correspond to accounting data. Additionally, during the cash register inventory, cash documents, financial statements and securities are checked. Verification can be mandatory or voluntary. How to complete an inventory, who should carry out the inspection and how to do it - we will tell you in the article.
When is a cash register inventory needed?
Inventory can be mandatory or voluntary. There are five main cases when verification is required:
- preparation of annual accounting reports;
- change of financially responsible person (cashier);
- identifying discrepancies in accounting, theft and abuse;
- natural disasters or emergencies (fire, hurricane, robbery);
- reorganization or liquidation.
The manager can conduct an inventory by his own decision, if there are no reasons for a mandatory inspection. This is necessary for additional control: for example, to find the causes of errors in accounting or to see that an employee is taking money from the cash register. There are no restrictions on the frequency of such checks - you can check the cash register at least once a month, at least once a week.
There are two more types of inspections: scheduled and unscheduled. As a rule, they prepare for scheduled inspections in advance and conduct them more thoroughly, but during unscheduled inspections more violations are found.
The organization can independently set the timing of unscheduled inventories. The order for such an inspection should indicate the reason why it was initiated.
Who is involved in the inventory?
The inspection is carried out by a special commission - the inventory commission. The list of participants is determined by the head in his order. Typically this includes the following employees:
- from the administration of the organization;
- from accounting;
- from the internal audit service;
- from the economic or legal department.
The number of inspectors is not established by law, but there must be at least two people on the commission. So, if the company’s staff includes only a director, there is no need to issue an order approving the composition of the inventory commission.
One person from the commission is appointed chairman. This can be any employee appointed by the general director, but usually this is a deputy director or head of a department. The chairman manages the inventory commission, endorses incoming and outgoing documents, signs inventories, acts, and accepts applications from financially responsible persons.
If the amount of work is small, for example, you only need to check the cash register of a micro-enterprise, then you can get by with the help of the audit commission (if the organization has one).
Another mandatory participant in the inventory is the financially responsible person (MRP). In our case, this is the cashier. He is not part of the inventory commission, but is required to be present during the inspection. With collective financial responsibility, all MOLs must be present at the inventory.
If the cashier is not present at the inspection, interested parties will be able to challenge the inventory results. Without it, an inventory can be carried out only in exceptional cases: when the MOL is seriously ill or for other reasons will not be able to come to work for a long time, and also when the MOL deliberately avoids participation. In such cases, before the inspection, a report is drawn up indicating the reasons for its absence.
During the inventory, a shortage of BSO was discovered
When taking inventory of BSO, their shortage may be revealed. In this case, it is necessary to find out the reason for the shortage. An appropriate explanation should be obtained from the person responsible for these documents. Guilty persons are subject to punishment in the form of penalties.
Let's look at an example. Continent LLC carried out an inventory of the BSO, during which a shortage of the BSO on payment for services was identified. The person responsible for this document is accountant O.P. Petrova, from whom an explanation was received about the reasons for what happened. She explained that the shortage of the form was due to its damage without drawing up an act of writing off the document.
What is checked during a cash register inventory?
The cash register inventory can be continuous or selective. The following values are checked on a continuous basis:
- Cash at the till. They count all the money in the cash register and compare it with the data in the cash book. If a cash register is used, the check should begin with operating cash registers: check the cash amounts with the data in the cashier-operator’s book, cash register tape indicators and cash register counters.
- Monetary documents. This group includes stamps, train and plane tickets, vouchers to sanatoriums, fuel cards, etc. It is enough to check the actual availability by type, as well as check the details and cost with the registration data.
- Securities. They check series and numbers, nominal and actual values, and maturity dates. Conduct a reconciliation with inventory data.
- Strict reporting forms (SSR). They check the actual availability - look at the types and numbers of forms. The number of BSOs is verified with the data on off-balance sheet account 006 reflected in the inventory.
If the inventory is selective, then the manager indicates in the order what exactly he wants to check. For example, you can take inventory of only the cash on hand.
Procedure for using and accounting for BSO
BSO must be printed in a printing house and have the required details, six-digit numbering, as well as the necessary degree of protection. Control over the use of forms is carried out by name, series and numbers of documents. They are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 006. Registration of BSO is carried out in a special book, which must be laced and numbered. After this, the book is certified by the signatures of the director and chief accountant, as well as the company seal. As a sample, you can use the OKUD form 0504045, developed for government agencies.
Important! BSO should be stored under certain conditions to avoid damage or theft.
The responsibility of the head of the company is to organize the safety of the BSO. To do this, he must create certain storage conditions that will protect the forms from damage and theft. Metal safes, cabinets, or a special room can be allocated for storing BSO. At the end of the work shift, the place where the forms are stored must be sealed or sealed.
Inventory procedure
Let's immediately say about the mandatory restriction - during the inventory of the cash register, you cannot accept or issue money or other valuables that are stored in the cash register and are being checked.
The procedure for conducting the inventory itself is as follows:
Step 1. The manager issues an order to conduct an inventory, in which he approves the composition of the inventory commission and specifies the reason for the inspection (change of cashier, emergency, reconciliation of cash balances).
If an annual inventory of the cash register is carried out before preparing financial statements, there is no need to issue an order.
Step 2. Before checking, the cashier submits all documents for expenses and receipts to the accounting department. Then he draws up a receipt stating that he handed over everything, capitalized the valuables received at the cash desk and wrote off those that were disposed of.
Step 3. The commission checks all the property declared in the order: cash, monetary documents, financial statements, etc. We described above how individual groups check. At this stage of inventory, the presence of a cashier is mandatory.
Step 4. The commission formalizes the inventory results and draws up an inventory list. In total, the audit can have three options for results: surpluses, shortages, and compliance of the fact with accounting data.
Cheat sheet for an accountant: BSO inventory
In order to check the actual availability of document forms with a certain degree of security (hereinafter referred to as BSO) , as well as to confirm the correspondence of their actual availability with accounting data, an inventory is periodically carried out. The process of conducting such a check must be carried out according to certain rules provided for by accounting practices and regulatory documents. How and when to carry out an inventory of BSO, we will consider in the material.
Inventory of BSO in places of their storage is carried out by the organization’s commission in accordance with the Instructions for the inventory of assets and liabilities, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated November 30, 2007 No. 180 (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 180).
The frequency of the BSO inventory is at least once a year (clause 8 of Instruction No. 180).
Note. By decision of the head of the organization, the number of mandatory inventories carried out during the year may be increased.
The timing of the BSO inventory is established by the head of the organization.
Before drawing up the annual financial statements, the BSO inventory is carried out no earlier than November 1 (clause 7 of Instruction No. 180).
Carrying out an inventory is mandatory, incl. (Clause 2 of Article 13 of the Law of the Republic of Belarus dated July 12, 2013 No. 57-Z “On Accounting and Reporting”; hereinafter referred to as Law No. 57-Z):
– during reorganization or liquidation of the organization;
– when changing materially responsible persons (hereinafter referred to as MOL);
– when facts of theft and (or) damage to property are revealed;
– in case of emergency situations;
– in other cases provided for by the legislation of the Republic of Belarus.
To carry out an inventory, the head of the organization issues an order in an approximate form in accordance with Appendix 1 to Instruction No. 180, which appoints the chairman and members of the inventory commission, determines the timing of the inventory and the reason for its implementation.
Before checking the actual availability of assets, incoming and outgoing documents or reports on the movement of financial assets must be submitted to the accounting department (accountant).
The chairman of the inventory commission endorses all receipts and expenditure documents attached to the registers (reports), indicating “before the inventory on “_________” (date),” which is the basis for determining the balance of assets by the beginning of the inventory according to the accounting data (clause 21 of the Instructions No. 180).
The MOL gives a receipt stating that by the beginning of the inventory, all expenditure and receipt documents for assets were submitted to the accounting department or transferred to the working inventory commission and all assets received under their responsibility were capitalized, and those disposed of were written off as expenses.
Situation. When changing the MOL, an inventory of the BSO was carried out
In the organization, a computer operator quits on October 29, 2020 (last working day). This person was the MOL for accounting for BSO.
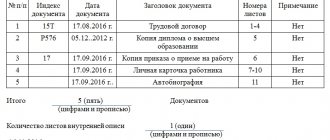
On 10/01/2020 he was issued the following BSO:
– TN-2 (PC) series AB from No. 5032451 to No. 5032700 (in the amount of 250 numbers);
– TTN-1 (PC) series NV from No. 2792631 to No. 2792800 (170 numbers).
When changing the MOL, the manager ordered an inventory of the BSO as of October 28, 2020. Inventory is carried out from 09:00 to 12:00.
Before the start of the inventory, the MOL indicated that as of 09:00 on October 28, 2020, the following BSOs were used:
– TN-2 (PC) series AB from No. 5032451 to No. 5032503 (53 numbers);
– TTN-1 (PC) series NV from No. 2792631 to No. 2792658 (28 numbers).
The discrepancy between the actual availability of BSO and accounting data has not been established.
The actual presence of SSO is checked (clause 59 of Instruction No. 180 of the SSO Instructions):
1) by type of form, taking into account the starting and ending numbers;
2) for each storage location for which the MOL is responsible.
Data on the presence of BSO is entered into the inventory list. The form of this document is given in Appendix 18 to Instruction No. 180. However, if there is a lack of information contained in the approved form, the organization can accept for accounting an independently developed and approved form in accordance with the law (part three, clause 23 of Instruction No. 180).
The inventory list is signed by the accountant and members of the inventory commission.
Let's consider documenting the inventory list of BSO in accordance with Appendix 18 to Instruction No. 180 (see example of filling).
BSO accounting is maintained by the organization's accounting department in monetary and quantitative terms. Commercial organizations that maintain accounting records must reflect BSO on account 10 “Materials” and at the same time on off-balance sheet account 006 “Document forms with a certain degree of protection.”
If there are guilty persons who did not ensure the safety of the BSO in storage areas, the cost of damaged and (or) canceled BSO is reflected in the following accounting entries (clause 25 of the Instructions on the procedure for the use and accounting of strict reporting forms, approved by the resolution of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated December 18, 2008 No. 196):
– Dt 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” – Kt 10 “Materials”, 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, 20 “Main production”, 23 “Auxiliary production”, 26 “General expenses”, 29 “Servicing production and economy", 44 "Sales costs", etc.;
– at the same time, the write-off of forms of specific series and numbers is reflected as an expense in off-balance sheet account 006.
The cost of damaged and (or) canceled BSO is reflected as follows:
Dt 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” – Dt 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.”
For reference: document forms with a certain degree of protection include:
- receipt of cash receipt for the sale of goods (performance of work, provision of services) without the use of cash register equipment and payment terminals;
- waybill;
- packing list;
- invoice certificate.
Documents with a certain degree of protection include:
– excise stamp for marking alcoholic beverages;
– excise stamp for marking tobacco products;
– excise stamp for re-labeling alcoholic beverages with damaged excise stamps;
– control stamp for labeling alcoholic beverages marked with excise stamps being withdrawn from circulation;
– control (identification) sign;
– a control mark intended for marking accompanying documents for imported (exported) alcoholic products, non-edible alcohol-containing products and non-edible ethyl alcohol;
– a control mark intended for marking accompanying documents drawn up in accordance with the legislation on petroleum liquid fuels;
– a special brand for marking tobacco products converted into state revenue;
– a special stamp intended for marking alcoholic beverages detained or seized by law enforcement and regulatory authorities, as well as confiscated or converted into state revenue in another way.
Printed products include:
1) a book of comments and suggestions;
2) book of inspections.
The list of document forms and documents with a certain degree of protection and printed products, information about which is subject to inclusion in the electronic data bank of document forms and documents with a certain degree of protection and printed products, was approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated July 6, 2011 No. 912.
Natalya Kurskaya, economist
Registration of results
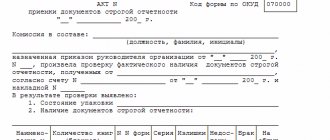
Based on the results of the inspection, the commission draws up inventories (inventory acts). They are signed by all members of the commission and the cashier. You can develop the forms of acts yourself or use ready-made ones:
- form No. INV-15 - for cash and monetary documents;
- Form No. INV-16 - for securities and BSO.
Draw up the acts in two copies - give one to the cashier, and give the other to the accountants. When the inventory is associated with a change of MOL, you will need another copy for the new cashier.
If surpluses or shortages are found in the inventory, comparison sheets must be drawn up. They will not be needed if you use unified acts No. INV-15 and No. INV-16, since there is already a place for information about deviations. Additionally, you need to request a written explanation of the discrepancies from the cashier.
The commission gives the manager all inventory documents. He checks them, analyzes them and issues an order approving the inventory results. The form is arbitrary, but it must contain instructions on how to eliminate discrepancies. If there are no discrepancies, you can do without an order.
How to reflect cash register inventory in accounting
The results of the inventory should be reflected in accounting in the reporting period to which the date as of which the inspection was carried out is attributed. Thus, the results of the annual inventory form the indicators of the annual financial statements.
The postings depend on the result of the check:
| Debit | Credit | The essence of the operation |
| 50 | 91.1 | Showed surplus at the cash register |
| 94 | 50 | Showed shortages at the cash register |
| 73 | 94 | The shortage was attributed to the cashier and another responsible employee |
| 70 | 94 | We paid off the shortfall from the salaries of those responsible |
| 91.2 | 94 | The shortage was included in other expenses (in case there are no culprits or they have not been found) |
Keep records of cash, BSO, securities, tickets, fuel cards and other documents in Kontur.Accounting. Draw up cash receipts and expenditures and prepare documents for inventory. In the service, you can also make payments to employees, submit reports via the Internet, and even connect integration with a cash register program. Try all the features of Kontur.Accounting during the test period - 14 days as a gift for all new users.
Accounting for strict reporting forms and the new KOSGU code
In accordance with the Procedure for applying the classification of operations of the public administration sector, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 29, 2017 No. 209n (hereinafter referred to as Procedure No. 209n), from January 1, 2019, costs for the acquisition (production) of strict reporting forms in an institution are included in subarticle 349 “ Increase in the cost of other single-use material reserves" (previously - under subarticle 226 "Other work, services") of KOSGU.
Thus, the application of the new sub-article assumes that BSO are objects of material reserves, while Instruction No. 157n, on the contrary, excludes them from the composition of material reserves.