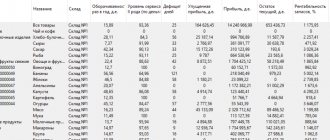
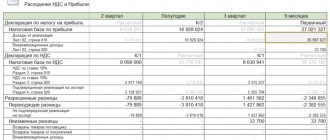
What is profit
Profit is an indicator that determines the financial success of a business, the goal of entrepreneurial activity. This concept is used to evaluate the profitability of a business and its economic efficiency. Revenue and profit are related phenomena, but not equivalent.
Attention!
Profit is the difference between revenue (financial benefit) and the costs required to obtain it.
Expenses include all costs incurred in the course of business activities. Such as: purchase or production of goods, rental of premises, utilities, wages to employees, delivery, etc.
Profit is calculated using the formula: Income (Revenue) – Expenses (Costs) = Profit.
Calculation example: Alexander Petrov produces homemade cheese. In one month, revenue from the sale of his products amounted to 100,000 rubles. During this time spent:
- for the purchase of homemade milk 30,000 rubles;
- for cheese production 5,000 rubles;
- for utilities – 5,000 rub.,
- for salary - 2,0000 rubles;
- for delivery to the buyer - 10,000 rubles.
The amount of expenses was: 30,000 + 5,000 + 5,000 + 20,000 + 10,000 = 70,000 rubles.
Profit amounted to: 10,0000 rubles. – 70,000 rub. = 30,000 rub.
Calculation of profit before tax
It is easy to determine this indicator if the necessary calculations have previously been made. For this, the formula is used:
PDN = PP + other income + interest receivable – other expenses – interest payable
Additionally, income received by the enterprise in the process of participation in the activities of other companies is added. If a loss is detected, the value is taken with a “-” sign. This result indicates a lack of efficiency, so management is forced to reconsider its work strategy.
Watch the video about income tax tricks:
Functions and role of profit received
The main function of profit is an indicator of the economic effect of the enterprise's activities. Additional functions:
- Estimated. Shows the level of development of the enterprise, gives an assessment of economic activity as a whole.
- Stimulating. Stimulates the growth of enterprise efficiency.
- Reproductive. Illustrates the difference between income and expenses.
- Test. Criterion for assessing the activities of an enterprise.
- Fiscal. Contributions to the state budget are made from profits.
The main role of profit is to show the result of the operation of an economic entity in monetary terms. This is a marker of the level of quality, demand and success of promotion of manufactured products. The profit received is distributed to expand production, improve working conditions, encourage employees, and improve the well-being of owners.
Cost and non-production expenses
When calculating profit (before tax, operating profit), the cost of manufactured products (services) is used. It characterizes the valuation of those actual current expenses that went into the production and sale of goods, and may include:
- Production costs (product manufacturing + general production overhead): for the purchase of raw materials, materials, depreciation, staff salaries, deductions for mandatory insurance premiums, etc.
- Non-production costs (costs not related to the production of products): marketing, general business, after-sales such as loading and unloading, transportation, storage, etc.
Income and expenses in accounting are formed in accordance with PBU 9/99 (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 32n), as well as PBU 10/99 (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 33n).
Types of profit
Profit can be made in different ways. Depending on the conditions of formation, several types of this concept are distinguished:
- Gross profit. The difference between the cost of production and the income from its sale. Includes the cost of paying tax contributions.
- Operating room. The financial result remaining after deducting all operating expenses, including equipment depreciation and operating expenses.
- Clean. The funds remaining after taxes, debt obligations, and manufacturing and selling expenses have been paid.
- Marginal. The company's income, which ensures its break-even operation. The calculation does not take into account VAT and unplanned costs.
- Unallocated. The profit remaining after subtracting all expenses, paying taxes, and paying other financial obligations, including stock dividends. It is not spent, but accumulated in the accounts of the enterprise.
- Balance sheet. Total profit before taxes. Used as a basis for taxation.
- Accounting. The difference between confirmed income and manifest expenses. The concept is used to balance the balance sheet.
- Economic. The amount remaining after subtracting implicit expenses from net income. Implicit expenses include lost income and unplanned expenses.
In addition, according to the final result, profit can be:
- provided (planned);
- maximum or minimum permissible;
- lost and negative (unprofitable).
Depending on the methods of earning, profit is divided into:
- Income from financial activities. Capital investments with favorable conditions.
- The result of the production and marketing of goods.
- Funds received through investments. Investments in securities and bank deposits.
Depending on the frequency of receipt of profit, it is:
- normalized;
- seasonal;
- excessive;
- marginal or additional.
In order to understand the main types of profit, it is worth considering them in more detail.
Determination of profit from sales
This indicator allows you to find out how effective and appropriate the strategy chosen by the company is. Organizational leaders must strive to increase this value in order to continue to operate in the market.
The analysis takes into account the contents of the profit and loss statement, as well as the balance sheet. Additionally, the financial plan is examined to determine whether the planned values have been achieved. To calculate the indicator, the formula is used:
PP = VP - administrative and commercial expenses
Costs associated with commercial work or managerial decisions are recorded in official documents.
Gross profit
Gross profit (GP) is the balance between income from sales of a product and the cost of this product. VP is considered until debt and tax obligations are paid off. The indicator is influenced by factors that depend and do not depend on the actions of management and the team:
- growth in production volumes;
- implementation methods;
- improving product quality;
- expansion of the range;
- reduction in cost;
- advertising company;
- location of the company;
- ecology of the location area;
- features of current legislation;
- unforeseen situations affecting logistics;
- economic situation in the country and in the world.
Attention!
Formula for calculating gross profit: VP = PE – S.
Where C is the cost of a unit of goods, and PE is net profit minus the costs of returning goods and discounts on products.
Total revenue value
Revenue shows how much money a company earned over a certain period of time. If the indicator grows from year to year, it means that the company is developing successfully. If revenue decreases, something needs to change.
Total revenue includes only income from product sales. If a company invests part of its profits or rents out an office, income from these activities is not included in the revenue figure.
What is gross revenue
Gross revenue is the result of the financial activities of an enterprise or company. The indicator includes income from any type of commercial activity, from the sale of manufactured products and any services. Let's consider the VP of a company that has a basis and additional sources of income.
Calculation example: The company produces and sells T-shirts with original inscriptions. The cost of the product is 500 rubles. Production costs:
- purchase of material, paints - 100,000 rubles. for 12 months of work;
- expenses for obtaining copyrights for drawings – 10,000 rubles. in year.;
- salary fund - 1 million rubles. in year;
- advertising expenses – 50,000 for 12 months;
- delivery – 40,000 rub. year.
Enterprise income (gross revenue) is formed from several sources:
- sale of fashionable T-shirts – 1 million rubles. in year;
- income from the rental of real estate - 50,000 rubles. in year;
- receipt of funds from investments RUB 20,0000. in year.
Amount spent: 100,000+10,000+1,000,000+50,000+40,000=1,200,000 rub.
Amount received: 1,000,000+300,000+200,000=1,500,000 rub.
VP = 1,500,000-1,200,000=300,000 rub.
An analysis of expenses and income showed that it was necessary to increase gross profit. You may have to reduce your salary fund or use the amount allocated for investments more rationally.
Advance payments
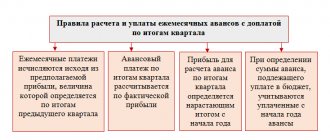
Income tax is paid in advance payments every month or quarter, and then at the end of the year. Transferring advances quarterly in 2022 is allowed to those companies whose sales revenues do not exceed 15 million rubles per quarter over the previous 4 quarters. Other legal entities pay advances monthly. We described how to calculate advances for income tax in a separate article. Quarterly advances are calculated from actual income, and monthly advances are calculated from estimated income (based on data for the previous quarter).
Operating profit
Operating profit takes into account absolutely all types of costs that support the operation of the enterprise, but differ from the expenses that make up the cost of the product. Including: depreciation of equipment, rent, unplanned expenses and other types of expenses.
Attention!
Operating profit is calculated using the formula: OP = VP - OR
Where VP is gross profit, and OP is operating expenses. Operating expenses include commercial and administrative expenses.
Calculation example:
The company buys small household appliances from the manufacturer and sells them in a store located in a shopping center. During the reporting period, goods worth 150,000 rubles were purchased. Sales revenue amounted to 300,000 rubles.
Expenses for the store's activities amounted to:
- rent – 25,000 rub.;
- salary - 50,000 rubles;
- wear and tear of the cash register and display cases – 2,000 rubles;
- other expenses – 3,000 rub.
Operating profit = 300,000 – 150,000 – 25,000 – 50,000 – 2,000 – 3,000.
Total OP = 70,000 rub.
Determination of profit before tax
There are several types of profit, the determination of which uses different data.
Table 1. What they include
| Name | Description |
| Gross (VP) | Difference between revenue and cost excluding VAT |
| From sales (PP) | Gross minus selling and administrative expenses |
| Before tax (PDN) | Profit from sales plus interest and other cash receipts and expenses |
| Clean | Financial result of the enterprise |
Schematic explanations in the video:
Net profit is considered a significant coefficient for any entrepreneur, but each line of the balance sheet is subject to analysis. With the help of competent accounting, it is determined which factors positively or negatively affect the result.
Net profit. How to calculate
The definition of net profit (NP) includes an additional parameter - mandatory payments, including tax and other payments.
Attention!
Formula for calculating net profit. PE = GR (gross income) – P (explicit expenses, including tax and debt obligations).
Calculation example:
Entrepreneur Kuznetsova sells fresh baked goods. The cost of a bun is 20 rubles, the cost price is 10 rubles. Other expenses amount to 3 rubles. on a bun. In order to calculate the net profit from the sale of 1 confectionery product, you need to sum up the expenses 10 + 3 = 13 rubles. and deduct them from your income. 20 – 13 = 7 rub.
If an individual entrepreneur sells 50,000 buns in a year, the state of emergency will be: 50,000 * 7 = 350,000 rubles.
Marginal profit rate
To determine when a company will reach the break-even point, it is necessary to calculate the marginal profit rate (MPR). The NPP indicator helps to understand what type of costs need to be reduced in order to improve business efficiency.
NPP is profit taking into account all types of costs.
Attention!
Calculation of NPP is possible using the formula: B – PI/B*100%. Where B is sales revenue, PI is variable costs.
The rate of marginal profit is expressed as a percentage and means the portion of profit that remains from revenue minus variable costs.
Calculation example:
The company sold the goods it produced in the amount of RUR 5,000,000. Variable costs for products sold amounted to half of the revenue, i.e. RUB 2,500,000
NPP = (10,000,000 – 5,500,000)/10,000,000*100% = 4,500,000/10*100% = 45%
A high marginal profit margin does not guarantee a high net profit because, in practice, profit markers are affected by fixed and variable costs.
In their book, MBA Short Course, Neil Thomas and Barry Pearson gave the example of a company that was forced to produce products at a very high cost level.
A large electronics company has adopted a small organization that produces electronic chips. Significant sums were spent on production and trained personnel. In the third year of operation, the NPP reached 74%, with the variable costs indicator being 24%. But the enterprise’s capacity was not fully utilized; fixed costs reached the level of 205% of revenue. The company spent 2.5 rubles. more money than she earned. The following year, demand for products using chips produced by the company increased. Sales increased 3 times, profit appeared.
Knowledge of GMP for each type of product/service allows you to increase profits in the following ways:
- If a certain type of product or service shows a high marginal profit margin, it is necessary to promote this particular product/service.
- Reduce costs in the production of goods that provide a low GMP indicator.
- Ensuring an average level of GMP for new products launched into production.
Important components of competent profit management:
- Orientation to the payback point of the enterprise/company.
- Managing the profitability (profitability) of the products or services produced.
- Monitoring the level of profitability achieved with key clients.
- It is inadmissible to set extremely low prices.
For more effective business management, it is necessary to consider the above points in detail.
Payback point and break-even point
The break-even point is the point at which revenue from the sale of a product equals costs. That is, the level of sales at which the company has neither loss nor profit. To determine the indicator, you must have the following information:
- amount of revenue;
- the amount of basic expenses;
- level of fixed and variable costs.
The payback point shows at what income the funds invested in the business will pay off. To calculate the payback point, you need to know the size of investments, income and expenses for a certain calendar period. For example, for a year.
Profitability of a product or service
In practice, the calculation of the profitability of production of a certain type of goods/services is carried out taking into account assumptions. The calculation may be inaccurate due to the fact that the activities of workers or production facilities relate to the production of several goods or services. For accounting, I use approximate data based on actual or “allocated” costs.
Profitability by key clients
As the company develops, the level of customer concentration increases. Large customers appear, purchasing about 5% of the products produced. Regular customers are more demanding. Their maintenance often requires additional costs. Competent sales management involves calculating the marginal profit rate for each wholesale or regular customer.
Negative consequences of setting low prices
When sales are unsatisfactory, some entrepreneurs reduce prices in order to attract buyers. But a significant price reduction does not lead to an increase, but to a sharp drop in business profitability.
The consequences of such actions by entrepreneurs are as follows:
- sales at low prices undermine the efficiency of a business based on correct pricing;
- Dumping and price fights with competitors are possible.
If production capacity is idle, there is a temptation to lower prices. That is, increase the efficiency of excess capacity. In this case, several conditions must be met:
- limiting the period of sales at reduced prices. Carrying out promotions and discounts for a limited period. Otherwise, buyers will like low prices, and business profitability will fall;
- sell goods whose cost is lower than that of conventional products;
- reduce prices for selling goods to other regions, countries or new segments of the target audience.
If the conditions are not met, there is a danger of destroying your own business.
What are financial results
Financial results are profits and losses (Profit and Loss) from the company's activities. To determine them, you need to subtract expenses from income. If the difference is positive, the company made a profit. If negative - loss. Financial results can be determined when income and expenses for the period are known. In accounting, profits and losses are determined for a month. But no one bothers to determine the financial result for each operation. It is only important to correctly determine the income and expenses for it.
There are several types of profit that are calculated in accounting to understand the effectiveness of various business processes of a company.
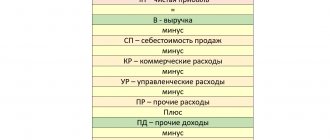
Gross Profit is the difference between income from the sale of products (revenue) and the costs of its production (cost).
It shows the effect of the company's production activities. By the way, in the word “gross” the stress on the last syllable is like “dear”. And she is really valuable to the company. If gross profit is zero or negative, it’s time to close down or seriously reconsider the production process. Neither competent management nor excellent marketing and sales can save inefficient production. Operating Income is gross profit minus the costs of storing and selling products (selling expenses) minus the costs of running the company (administrative expenses). It shows the effect of the company's main activity - selling what it produced. A loss on sales is an unpleasant thing, but it can often be avoided by increasing production volumes. This is called economies of scale.
Example 1.
LLC "Horns and Hooves" buys horns for 8 rubles and sells them for 10. Last month, 50 horns were sold. Gross profit was 50 * (10 rubles - 8 rubles) = 100 rubles. At the same time, the seller’s salary is 150 rubles. per month. That is, the profit from sales amounted to 100 rubles. — 150 rub. = - 50 rub. If the company manages to sell 100 horns this month, then the gross profit will be 100 * (10 rubles - 8 rubles) = 200 rubles, and the profit from sales is already 200 rubles. — 150 rub. = 50 rub.
Income Before Tax is profit from sales plus other income minus other expenses. Other income and expenses are not related to the main activities of the company. If a company sells horns and hooves, then the interest on placing free money on deposit is other income, and the cost of the New Year's corporate party is another expense. Profit before tax characterizes the effect of all the company’s activities, to which not only the main, but also other activities contribute.
Net Income is profit before tax minus income tax. This is what remains for the company after Mishustin and his team. For special regime employees, instead of income tax, tax is deducted according to the simplified tax system or UTII.
Retained Earnings - net profit minus dividends to founders. Part of the net profit must be given to the founders for contributing their assets to the authorized capital. This procedure is called profit distribution. From the founders' point of view, this is the whole point of the company's existence. But in the first years, the founders may not withdraw dividends into their pockets, leaving profits for the development of the company. Then the net profit of the current year increases the retained earnings remaining from previous years.
The owner can see the first four types of year-to-date profits on the income statement. Retained earnings for the entire existence of the company are in the balance sheet.
Outside of accounting, other options for financial results can be considered. For example, EBIT and EBITDA, which I talked about in detail on vc.ru. But it is useless to count any financial resources if its components—income and expenses—are incorrectly determined.
Earnings before taxes and interest
Earnings before taxes and interest are an important indicator of business profitability. Illustrates the profit generated by a company. The concept is synonymous with operating profit. Ignoring variables such as capital structure and tax burden, the indicator shows what a company is capable of. The ratio of pre-tax profit to sales varies depending on the industry. In the construction segment - 2-3%, in food trade - 4-5%. In companies providing services to the public, the figure can reach 15%.
The average earnings before interest and taxes is about 10%.
Important!
If your gross profit drops by a few points, you need to check the percentage of expenses versus sales. If it has not changed, then the fall will lead to a decrease in the rate of profit.
If sales levels sharply decline, it is necessary to partially compensate for losses by reducing overhead costs.
Marginal profit
Marginal profit (MP) allows you to find out the profitability of production and assess whether the “margin” can cover costs. The calculation includes such variables as:
- cost of raw materials;
- salaries and bonuses;
- heating and electricity costs.
Attention!
Formula for calculating marginal profit: MP = D (revenue) – PR (variable expenses).
Variable expenses are expenses that a company would cease to make if operations were suspended. They directly depend on the volume of goods produced. The total expenses indicator consists of variable and fixed expenses. Only variables are taken into account in the calculation of MP.
Calculation example:
The enterprise for the production of plastic containers produces containers with a volume of 5 liters. The cost of plastic containers is 25 rubles. Variable costs for its production are 15 rubles. MP = 25 – 15 = 10 rub.
The higher the “margin”, the faster costs are reimbursed, which means the enterprise is more profitable.
In practice, there are other options for deciphering the definition:
- General increase in funds received from the sale of goods.
- Increase in profit from the sale of each additional unit of product.
- The difference between the purchase price and the selling price.
To increase the marginal profit, the sales volume or the markup on the product is increased.
What factors influence the indicator
The goal of every company is to make a profit. Only if it exists, the enterprise is considered profitable. Accounting for this indicator is an important task for an accountant, since the efficiency of the company depends on it. Even if the organization is a non-profit, income accounting is still required.
As an accounting value, profit is represented by the difference between income from the sale of goods and the costs associated with their production. Getting it is the main task of every enterprise. It is associated with risk, therefore, the higher the risk of a businessman, the more income he receives.
This indicator is influenced by factors:
- price of raw materials
- labor productivity
- prices set by competitors
- production efficiency
- number of similar organizations on the market
Attention! If a company is a monopolist, then it can set prices without taking into account the policies of competitors, which significantly increases profitability.
Margin analysis
Using marginal analysis, you can find out which products/services are most profitable. Which ones are profitable to promote and which ones are not.
Margin analysis functions:
- allows you to determine with the greatest accuracy how various factors influence changes in profit;
- clarify the profitability threshold;
- calculate the break-even point;
- plan the sales volume necessary to obtain the desired profit;
- evaluate the company's performance;
- justify changes in assortment, production capacity, and pricing.
MP is calculated according to the given formula separately for each type of product.
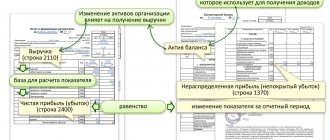
retained earnings
If, after receiving the proceeds, all expenses and necessary payments are paid, and part of the profit remains, it can be considered undistributed. Funds are not spent, but accumulated year after year. Dividends on shares or bonds of the company are paid from the profits deferred last year.
Attention!
Retained earnings are calculated using the formula: NP = NPPP (profit from previous years) + PE (net profit) - dividends, if they are provided for by the organization’s charter.
Retained earnings are spent only on the basis of a general decision of the owners.
What is book profit
Balance sheet profit (BP) is the total profit of an enterprise available on the balance sheet for a certain period of time. It includes sums of money generated through production and other activities.
To determine balance sheet profit, it is necessary to have an operating profit indicator.
Attention!
Method for calculating balance sheet profit: BP = OP - interest.
BP illustrates the effectiveness of enterprise management and production decisions.
Operating profit accounting functions
This indicator is used to assess the effectiveness of the company's core activities. It allows one to judge its investment attractiveness. The calculated operating profit indicator, which is recorded in the report, is taken into account and applied for the purposes of:
- determination of net profit, mandatory budget payments;
- optimization of future expenses and coverage of losses already incurred, as well as existing ones;
- sharing profits among the founders;
- replenishment of accumulated income and study of non-production income.
Therefore, the enterprise always has 2 key tasks in the first place: correct calculation of the indicator and ensuring its high value.
Accounting and economic types of profit
Accounting and economic types of profit are used in accounting reports and analysis of company performance. Let's look at each type of profit in more detail.
Accounting profit
Accounting profit is the positive difference between the recorded income and expenses of an enterprise or organization. To calculate, you need to know the amount of income actually confirmed by accounting documents and the amount of confirmed expenses.
Attention!
The formula required to calculate the value of BP: BP = D (income) – P (expenses).
Based on accounting profit (AP), the balance sheet of an enterprise or organization is calculated.
Formula
To determine the indicator, cost, as well as selling and administrative expenses, are subtracted from sales revenue received over a limited period of time. Therefore, a financial result is determined that reflects the efficiency of the business.
For proper calculation, a reporting period is recorded, for which different indicators are compared. Afterwards, the full amount of income received from the competent sale of goods, provision of services or performance of work is revealed. Expenses incurred are deducted from revenue, which include:
salary of hired specialists- insurance payments transferred to state funds for employees
- price of raw materials, materials or components
- depreciation deductions
- commercial expenses associated with an advertising campaign, making rent payments or paying for utilities
- other expenses
If the result reveals a positive value, then the firm receives money to be used for conservation or consumption. Otherwise, a loss appears.
Attention! When determining income and expenses, accounting nuances are taken into account, so the exact calculation depends on the qualifications of the specialist.
The value is reflected on line 2300 in the report, designed to correctly reflect financial results. This indicator is not always multiplied by the tax rate, since during the calculation of the fee, sometimes different incomes are not recognized for tax accounting. Instead of PDT, the tax base is calculated, the determination of which takes into account the provisions of Chapter. 25 NK.
The value is calculated using a simple formula:
PDN = PP + interest receivable – interest payable + other income – other expenses
All indicators are taken from accounting and payment documents.
All about profit calculations on video: