2020-11-20 7310
Internal financial control is the key to the financial health of the company. It allows you to timely detect theft, fraud with financial statements and misuse of company money. The organization of internal financial control is especially necessary for owners who have transferred their business into the hands of hired managers. And they want to track not only financial flows, but also prevent any risks, including bankruptcy.
What is internal financial control, why is it needed and how is it built in organizations - read the material below.
Stages of organizing financial control at an enterprise
Let's study what is the algorithm for implementing financial control at an enterprise, what are its main stages.
The specifics of individual stages of corporate financial control are determined by its specific form. Control measures can be:
- preliminary (carried out before the management of the company makes significant decisions in the field of corporate capital management, as well as at the stage of their preparation);
- current (accompanying the adoption and implementation of relevant decisions);
- subsequent ones (analyzing the consequences of decisions made in the field of capital management of the company).
If we are talking about preliminary financial control, then the main stages of its organization will be:
- training of responsible specialists who are competent in studying the structure of documents that consolidate the decisions made on managing the finances of an enterprise, drawing up a range of tasks for them;
- training responsible specialists competent in studying areas of the business process - technological or, for example, presented at the level of the economic-theoretical concept of corporate capital management;
- preparation of a documentary base for recording the results of preliminary control, the structure of which is optimal for recording deficiencies in the preparation of decisions on the management of the enterprise’s capital;
- development of a preliminary financial control plan;
- implementation of the preliminary financial control algorithm, carried out by competent specialists in accordance with the plan and using the prepared documentary base.
Current financial control at the enterprise will consist of the following stages:
- training of specialists competent in determining quality criteria for the implementation of capital management decisions, as well as in implementing practical procedures for its assessment;
- preparation of a documentary base to display the current results of implementing capital management decisions, the structure of which is optimal for recording areas of capital turnover that are significant for business, as well as for identifying the correlation between the indicators characterizing them and those that are set as targets;
- development of a plan for current financial control;
- implementation of the control algorithm - according to the plan using trained employees and using the appropriate documentary base.
In turn, subsequent financial control also involves the training of competent specialists in assessing the results of decision-making on capital management, the development of the necessary documentary base, plan, as well as the implementation of the corresponding algorithm.
The main problems of organizing financial control are described in detail in an article by a financial law expert, which you can view in ConsultantPlus. It's free. You just need to get trial access to the system.
Conditions for organizing financial control at an enterprise
Regardless of the specific type of financial control in an enterprise, there are a number of key conditions necessary for its successful implementation. Namely:
- availability of the necessary documentary and legal framework (local regulations);
See a sample of the Regulations on the internal control service of an enterprise in ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the legal system is free.
- availability of infrastructure (software, communications, documentation of control procedures);
- availability of required competencies among employees involved in control.
The significance of the elements related to the first of the three positions we have listed is important from the point of view of the internal corporate legitimization of financial control. Subjects of financial control must solve their problems based on the current local regulations. He can, firstly, certify the authority of a particular specialist or their group so that other employees of the company do not have questions regarding their actions, and secondly, include regulations, following which the subject of financial control must perform his work.
Financial control in an enterprise is, first of all, working with information that must be recorded somewhere, transmitted somewhere, studied and interpreted by someone. For these purposes, a special infrastructure is needed to record, transmit and interpret data obtained during financial control.
Financial control at an enterprise is a set of procedures that require sufficiently high qualifications of employees. Those specialists who perform the functions of auditors must have a competent understanding of those areas of the business process that correlate with capital management decisions and are therefore examined during the audit process.
Let us further study the structure in which corporate financial control can be represented.
Audit commission (auditor) of the company
The basic requirements of the law concerning the audit commission (auditor) of the company are established in Articles 32, 33, 47 of the Federal Law “On Limited Liability Companies” and determine that:
- in companies with more than fifteen participants, the formation of an audit commission (election of an auditor) is mandatory;
- the election and early termination of the powers of the audit commission (auditor) falls within the competence of the general meeting of participants;
- The audit commission (auditor) of the company has the right at any time to conduct inspections of the financial and economic activities of the company and have access to all documentation relating to the work of the company. During the audit, company employees, managers, members of the board of directors, and company members are required to provide the necessary explanations to the audit commission (auditor);
- The audit commission (auditor) must review the company's annual reports and balance sheets before they are approved by the general meeting. Without the auditors' opinion, annual reports and balance sheets cannot be approved at the meeting.
All other issues of the procedure for the creation and activities of the audit commission (auditor) of the company are determined by its charter. It is also recommended to adopt a separate internal document, for example a regulation on the audit commission.
Election of the audit commission (auditor)
An audit commission (auditor) can be elected only at a general meeting of participants.
Candidates for the audit commission can be proposed by the same persons who have the right to include issues on the agenda.
The audit commission cannot include:
- members of the board of directors (supervisory board) of the company;
- director of company;
- members of the board (directorate).
A member of the audit committee must have special knowledge in the field of accounting, economics, finance or taxation.
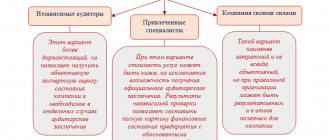
It is not recommended to include company employees in the audit commission. They are unlikely to be able to freely and impartially control the work of executive bodies, since they are subordinate to them. On the other hand, commission members who do not work in the community may also experience serious difficulties in fulfilling their duties. Perhaps it would be most correct to attract a third-party (not working in the company) auditor and pay him a certain remuneration. Or refuse to form an audit commission and schedule audits of the company’s activities as necessary.
As a rule, at least three people are elected to the audit commission with a term of office from one to five years. Decisions on the election of the audit commission (auditor) of the company are made by the general meeting of participants by a simple majority of votes.
The charter may contain other requirements. The reasons and procedure for early termination of powers of members of the audit commission (auditor) must be provided for in the charter. Members of the Audit Commission may be re-elected for a new term an unlimited number of times if they fulfill their duties in good faith.
Powers of the audit commission (auditor) of the company
The powers of the audit commission (auditor) of the company include:
- conducting scheduled inspections of the activities of the board of directors (supervisory board), sole executive body, collegial executive body;
- carrying out scheduled and unscheduled inspections (audits) of the financial and economic activities of the company for the year (on its own initiative, by decision of the general meeting of participants, by decision of the board of directors (supervisory board), at the written request of any participant of the company);
- drawing up opinions on annual reports and balance sheets, etc.
The Audit Commission (auditor) has the right to receive and use in its work all documents of the company, as well as to receive the necessary explanations from all employees of the company. The Charter or Regulations on the Audit Commission must establish:
- the procedure for access of commission members (auditor) to company documents;
- the procedure for seeking clarification from employees and management bodies of the company;
- the time frame within which the commission can receive the necessary documents and clarifications.
To ensure the safety and security of documents, auditors must work with documentation at the place where it is stored. It is mandatory to check the company's annual reports and balance sheets. The conclusion based on the results of this audit must be presented to the company's participants, among other materials, in preparation for the annual general meeting of participants. Based on the results of the audit, the audit commission has the right to demand an extraordinary meeting. If the meeting is not held within the established time frame or is refused, the auditors have the right to convene the meeting themselves. In this case, the meeting will be opened by the chairman of the audit commission (auditor).
The procedure for the activities of the audit commission (auditor) of the company
The work procedure of the audit commission must be enshrined in the charter or Regulations on the audit commission. The work of the commission is led by its chairman, elected by a simple majority of votes from among the members of the commission. The chairman of the audit commission may delegate his powers to another member of the commission for a certain period. He must notify the company about this.
The Audit Commission may be given the right to involve specialists and independent auditors. Their work is paid for by society. Estimates for paying for the services of specialists and audit firms, and the terms of contracts concluded with them are approved by the general meeting.
Based on the results of checking the annual reports and balance sheets of the company, the audit commission (auditor) draws up a conclusion in which:
- the reliability of reports and other financial documents of the company is confirmed;
- contains information about facts of violation of the established procedure for maintaining accounting records and financial and economic activities.
At the end of the inspection, a protocol must be drawn up. The deadline for the final preparation and signing of this document must be indicated in the charter or Regulations on the Audit Commission. The chairman of the commission is responsible for the accuracy of the minutes of the meeting.
The conclusions of the audit commission (auditor), protocols and other materials must be kept in the company by management. Society participants must be provided with access to these documents. This is stated in Article 50 of the Federal Law “On Limited Liability Companies”.
Structure of financial control at the enterprise
Modern researchers identify the following main elements of the structure of corporate financial control:
- work with the documentary base;
- working with various areas of the business process;
- working with employees.
The first element of financial control involves:
- examination of documents for correctness of completion, relevance of the forms used, presence of logic in reflecting the facts about the management of the enterprise’s capital;
- examination of documents for their authenticity and completeness;
- comparative analysis of documents, comparison with reference samples of sources.
As for work at the level of individual sections of business processes, the structure of financial control may include:
- analysis of the efficiency of investing in the corporation's finances - in terms of capital productivity, correlation of investments with profitability, turnover and other indicators;
- analysis of productivity of fixed assets and labor;
- analysis of the company’s financial stability, its solvency for loans and other obligations.
Financial control in terms of working with employees may include:
- checking the qualification level of specialists responsible for capital management at the enterprise;
- identifying facts of dishonest attitude of employees towards solving problems related to corporate finance management;
- development of measures aimed at stimulating advanced training of specialists involved in capital management at the enterprise, as well as increasing the level of personal responsibility of company employees for the performance of their work duties.
Let's study the specifics of the subjects of corporate financial control.
Audit as a type of financial control
Audit (independent control) is a type of activity that evaluates the functioning of an organization and expresses an opinion on the correctness of its accounting (financial) statements.
Independent control refers to the following types of audits:
- Financial;
- Price;
- Tax;
- Audit of economic activities;
- Management.
In addition, it is worth highlighting this type of independent control as a special (special) audit, which is aimed at analyzing the activities of the organization.
Attention! An audit is a non-governmental type of financial inspection, the key goals of which are to verify the reliability of the reporting of economic entities.
Subjects of financial control at the enterprise
These could be:
- individual employees of the company;
- internal corporate structures formed by hired employees (managers, specialists);
- intra-corporate or freelance structures formed by the business owner or acting as partners or outsourcers.
As for subjects of the first type, here we are talking mainly about self-control. Its use is typical for small enterprises, individual entrepreneurs, who themselves perform a significant amount of business-related work.
Internal corporate structures responsible for financial control at the enterprise can be special departments - for quality control of corporate capital management, various accounting or analytical departments of the company. A similar approach to the organization of financial control - when the main role is given to internal corporate entities that are formed by hired employees - is typical for medium-sized organizations.
In turn, ensuring effective financial control in a large enterprise may require the participation of legally independent entities or those that are formed within the company’s staff, but not with the participation of hired employees, but in accordance with the orders of the owner.
Objects of corporate financial control
The main object of financial control at an enterprise is the decision-making system for managing corporate capital. It consists of the following key elements:
- the regulatory framework that establishes the algorithms of the corresponding system;
- technological infrastructure that allows you to implement these algorithms;
- decision-making concepts followed by company employees responsible for managing the enterprise’s capital.
The regulatory framework can be represented by legal acts adopted at various levels - federal, regional, municipal, as well as local sources of law, instructions, explanatory notes.
The technological infrastructure used within the framework of capital management in a corporation is, first of all, accounting software, programs for remote interaction with banks and payment systems, software for sending reports and document flow within the organization and with other subjects of legal relations in various fields.
Objects of financial control at an enterprise can also be:
- cost and natural production indicators;
- statistical data reflecting, for example, sales rates;
- characteristics of key clients, social groups of buyers, suppliers, partners.
In principle, the objects of financial control can include any components of a business process that can characterize the effectiveness of corporate capital management.
But why do the management of the company or specialists responsible for financial issues of the business need to exercise financial control? Let's study its main goals.
Methods of financial control within an organization
There are several traditional methods of conducting financial control within an organization . Methods of financial control include:
- Analysis;
- Checks;
- Survey;
- Observation.
The “Analysis” method implies a detailed analysis of accounting and financial statements in order to evaluate the results of the organization’s activities, the organization’s provision of assets and the efficiency of their use.
The “Check” method involves checking reporting and expenditure documentation. It is carried out to detect shortcomings and shortcomings in the company’s activities.
The “Survey” method consists of a large coverage of financial, economic, and accounting indicators. With this method, the overall financial condition of the organization, its potential and reserves for its growth are assessed.
The Observation method is used to evaluate the current analysis of the financial situation in the company. It is carried out to detect discrepancies between actual and planned indicators of the financial plan (budget). The Observation method may consist of:
- Analysis of the current activities of the organization;
- Identification of the main conditions for growth, conditions for financial stability, as well as unfavorable indicators that could lead to bankruptcy or liquidation of the company;
- Finding out the reasons for the discrepancy between current and planned indicators;
- Analysis of the organization's operational financial statements.
Objectives of corporate financial control
They can be distinguished in the following spectrum:
- assessment of the quality of accounting - accounting, tax, management;
- identifying deficiencies in the performance of work duties by enterprise employees;
- identifying deficiencies in the enterprise capital management infrastructure;
- optimization of conceptual approaches to capital management;
- identification of factors influencing the efficiency of financial management of an enterprise.
The first of the goals of financial control at an enterprise, noted in the list, is important from the point of view of legitimizing business processes - in terms of the availability of documented licenses, permits, patents, correct generation of reporting (required by law, compiled due to the wishes of the company’s owners or intended for investors , banks and company partners).
The second of the above-mentioned goals of financial control is significant for an enterprise from the point of view of ensuring the stability of business processes - when their implementation directly depends on the level of competence, responsibility and experience of employees.
The third of the goals we have noted is important, first of all, for increasing the technological competitiveness of the enterprise. The quality of the infrastructure used in the implementation of financial management solutions for a company determines the amount of costs for the corresponding implementation in terms of time, compensation for personnel, and costs for maintaining the functionality of the software and hardware components of this infrastructure.
Financial control also allows us to identify the potential for improving the conceptual approaches of the company's management to managing the enterprise's capital. As a rule, the factors influencing the success of the implementation of the adopted concept are also determined. The management of a corporation's financial resources and their investment in certain funds is most often based on methods and approaches that form a certain concept, which can be adjusted from time to time - depending on the results of using the appropriate methods and approaches. And financial control at the enterprise helps to identify these results.
Successful achievement of the above goals predetermines the formation of another one. We are talking about such a goal as identifying measures aimed at:
- increasing accounting efficiency;
- increasing employee competencies;
- optimization of corporate capital management infrastructure;
- adjustment of the conceptual principles of working with finances at the enterprise;
- development of concepts to enhance the use of positive factors of capital management and reduce the dependence of business processes on negative factors.
Let's consider the key methods of corporate financial control.
Purpose of the audit and its main tasks
During the audit, it is established how financial resources are used and where cash flows are directed. An audit of financial and economic activities determines the absence of violations of money laundering obtained by criminal means. Thus, not only outgoing, but also incoming cash flows are analyzed. It is also important to ensure that money and material assets are not lost.
The audit involves checking actual transactions and documenting:
- confirmation of financial transactions with relevant agreements and documents;
- targeted use of loans received from banks and ongoing payments;
- conducting transactions with securities, discount and interest-bearing bills, shares, bonds;
- timely settlements with the budget and extra-budgetary funds and their implementation in full;
- all items of income and expenses, the formation of profits or losses from business activities are checked;
- compliance with legal requirements and accounting rules;
- accruals and calculations of wages, settlement transactions with individuals;
- costs of the company's current activities;
- how intangible assets are accounted for;
- channeling funds into investments with the formation of a diversified investment portfolio;
- receipt and distribution of profits.
Based on in-depth analysis and financial and economic control, the level of company management and compliance with legal requirements becomes clear. This control also concerns ensuring the safety of the owners' property. The efficiency of business activities, profitability, self-sufficiency and reaching the break-even point of the new enterprise are determined.