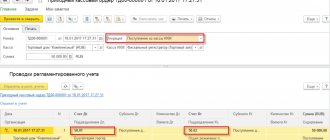
In accordance with the requirements of Federal Law dated December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting,” all facts of economic activity must pass through the internal control system of the organization. Article 19 of the Law “On Accounting” indicates the need for internal control, but it does not contain strict requirements and rules. Practical recommendations on this topic are contained in Information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 26, 2013 N PZ-11/2013 “Organization and implementation by an economic entity of internal control of the facts of economic life, accounting and preparation of accounting (financial) statements.”
Get documents on the topic for free
Stages of organizing financial control at an enterprise
Let's study what is the algorithm for implementing financial control at an enterprise, what are its main stages.
The specifics of individual stages of corporate financial control are determined by its specific form. Control measures can be:
- preliminary (carried out before the management of the company makes significant decisions in the field of corporate capital management, as well as at the stage of their preparation);
- current (accompanying the adoption and implementation of relevant decisions);
- subsequent ones (analyzing the consequences of decisions made in the field of capital management of the company).
If we are talking about preliminary financial control, then the main stages of its organization will be:
- training of responsible specialists who are competent in studying the structure of documents that consolidate the decisions made on managing the finances of an enterprise, drawing up a range of tasks for them;
- training responsible specialists competent in studying areas of the business process - technological or, for example, presented at the level of the economic-theoretical concept of corporate capital management;
- preparation of a documentary base for recording the results of preliminary control, the structure of which is optimal for recording deficiencies in the preparation of decisions on the management of the enterprise’s capital;
- development of a preliminary financial control plan;
- implementation of the preliminary financial control algorithm, carried out by competent specialists in accordance with the plan and using the prepared documentary base.
Current financial control at the enterprise will consist of the following stages:
- training of specialists competent in determining quality criteria for the implementation of capital management decisions, as well as in implementing practical procedures for its assessment;
- preparation of a documentary base to display the current results of implementing capital management decisions, the structure of which is optimal for recording areas of capital turnover that are significant for business, as well as for identifying the correlation between the indicators characterizing them and those that are set as targets;
- development of a plan for current financial control;
- implementation of the control algorithm - according to the plan using trained employees and using the appropriate documentary base.
In turn, subsequent financial control also involves the training of competent specialists in assessing the results of decision-making on capital management, the development of the necessary documentary base, plan, as well as the implementation of the corresponding algorithm.
The main problems of organizing financial control are described in detail in an article by a financial law expert, which you can view in ConsultantPlus. It's free. You just need to get trial access to the system.
Conditions for organizing financial control at an enterprise
Regardless of the specific type of financial control in an enterprise, there are a number of key conditions necessary for its successful implementation. Namely:
- availability of the necessary documentary and legal framework (local regulations);
See a sample of the Regulations on the internal control service of an enterprise in ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the legal system is free.
- availability of infrastructure (software, communications, documentation of control procedures);
- availability of required competencies among employees involved in control.
The significance of the elements related to the first of the three positions we have listed is important from the point of view of the internal corporate legitimization of financial control. Subjects of financial control must solve their problems based on the current local regulations. He can, firstly, certify the authority of a particular specialist or their group so that other employees of the company do not have questions regarding their actions, and secondly, include regulations, following which the subject of financial control must perform his work.
Financial control in an enterprise is, first of all, working with information that must be recorded somewhere, transmitted somewhere, studied and interpreted by someone. For these purposes, a special infrastructure is needed to record, transmit and interpret data obtained during financial control.
Financial control at an enterprise is a set of procedures that require sufficiently high qualifications of employees. Those specialists who perform the functions of auditors must have a competent understanding of those areas of the business process that correlate with capital management decisions and are therefore examined during the audit process.
Let us further study the structure in which corporate financial control can be represented.
Result of mandatory audit
After the study, the head of the company or the responsible person by proxy receives an audit report. It should contain:
- information about the audit company or individual entrepreneur, full name of the auditor, INN, OGRN;
- name, INN, OGRN of your business;
- a list of financial statements with dates of preparation, which were studied by the auditor;
- the auditor's opinion on the reliability of the statements;
- circumstances that may affect the reliability of reporting.
Please note: if the auditor identifies violations, he must report them to the company's management and receive in response an agreement on the timing of eliminating these problems.
If the auditor suspects a company of money laundering or other illegal schemes, he must report this to the tax office. The Federal Tax Service has the right to demand from the auditor information that he received during the audit.
Structure of financial control at the enterprise
Modern researchers identify the following main elements of the structure of corporate financial control:
- work with the documentary base;
- working with various areas of the business process;
- working with employees.
The first element of financial control involves:
- examination of documents for correctness of completion, relevance of the forms used, presence of logic in reflecting the facts about the management of the enterprise’s capital;
- examination of documents for their authenticity and completeness;
- comparative analysis of documents, comparison with reference samples of sources.
As for work at the level of individual sections of business processes, the structure of financial control may include:
- analysis of the efficiency of investing in the corporation's finances - in terms of capital productivity, correlation of investments with profitability, turnover and other indicators;
- analysis of productivity of fixed assets and labor;
- analysis of the company’s financial stability, its solvency for loans and other obligations.
Financial control in terms of working with employees may include:
- checking the qualification level of specialists responsible for capital management at the enterprise;
- identifying facts of dishonest attitude of employees towards solving problems related to corporate finance management;
- development of measures aimed at stimulating advanced training of specialists involved in capital management at the enterprise, as well as increasing the level of personal responsibility of company employees for the performance of their work duties.
Let's study the specifics of the subjects of corporate financial control.
Primary requirements
According to the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 402-FZ), an organization is obliged to organize and carry out internal control of the facts of economic life, and if its accounting (financial) statements are subject to mandatory audit, then it is obliged to organize and exercise internal control over accounting and preparation of accounting (financial) statements (except for cases where its director has assumed the responsibility for maintaining accounting records).
Law No. 402-FZ does not describe how and to what extent internal control should be carried out. However, it is clear that it must be sufficient to ensure the reliability of the facts of economic life and the accounting (financial) statements of the organization.
...law No. 402-FZ does not describe how and to what extent internal control should be carried out. However, it is clear that it should be sufficient to ensure the reliability of the facts of economic life...
For example, issues of internal control in economic entities are regulated by rules establishing the creation of audit commissions for the financial and economic activities of the company:
- Article 85 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies”;
- Article 47 of the Federal Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies”.
The requirements stipulated by these federal laws must be observed.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation has developed general recommendations for business entities on the organization and implementation of internal control over accounting and the preparation of financial statements (information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. PZ-11/2013).
This document defines internal control as a process aimed at obtaining reasonable assurance that the organization provides:
- a) efficiency and effectiveness of its activities, including the achievement of financial and operational indicators, safety of assets;
- b) reliability and timeliness of accounting (financial) and other reporting;
- c) compliance with applicable laws, including when carrying out business activities and maintaining accounting records.
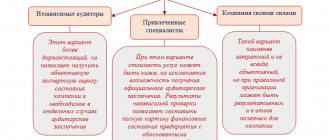
Subjects of financial control at the enterprise
These could be:
- individual employees of the company;
- internal corporate structures formed by hired employees (managers, specialists);
- intra-corporate or freelance structures formed by the business owner or acting as partners or outsourcers.
As for subjects of the first type, here we are talking mainly about self-control. Its use is typical for small enterprises, individual entrepreneurs, who themselves perform a significant amount of business-related work.
Internal corporate structures responsible for financial control at the enterprise can be special departments - for quality control of corporate capital management, various accounting or analytical departments of the company. A similar approach to the organization of financial control - when the main role is given to internal corporate entities that are formed by hired employees - is typical for medium-sized organizations.
In turn, ensuring effective financial control in a large enterprise may require the participation of legally independent entities or those that are formed within the company’s staff, but not with the participation of hired employees, but in accordance with the orders of the owner.
Who can conduct a statutory audit
Mandatory audit is regulated by the state - it can only be carried out by audit organizations or private auditors who have qualification certificates. Another requirement is membership in an SRO of auditors.
An organization can choose an auditor independently, as well as negotiate the cost of services and other nuances of the work.
There are exceptions - companies whose securities are admitted to organized trading, insurance organizations, non-state pension funds and businesses in whose authorized capital the share of state property exceeds 25%. They can involve only audit organizations in mandatory audits. You cannot use the services of private specialists.
Objects of corporate financial control
The main object of financial control at an enterprise is the decision-making system for managing corporate capital. It consists of the following key elements:
- the regulatory framework that establishes the algorithms of the corresponding system;
- technological infrastructure that allows you to implement these algorithms;
- decision-making concepts followed by company employees responsible for managing the enterprise’s capital.
The regulatory framework can be represented by legal acts adopted at various levels - federal, regional, municipal, as well as local sources of law, instructions, explanatory notes.
The technological infrastructure used within the framework of capital management in a corporation is, first of all, accounting software, programs for remote interaction with banks and payment systems, software for sending reports and document flow within the organization and with other subjects of legal relations in various fields.
Objects of financial control at an enterprise can also be:
- cost and natural production indicators;
- statistical data reflecting, for example, sales rates;
- characteristics of key clients, social groups of buyers, suppliers, partners.
In principle, the objects of financial control can include any components of a business process that can characterize the effectiveness of corporate capital management.
But why do the management of the company or specialists responsible for financial issues of the business need to exercise financial control? Let's study its main goals.
Table 1. Internal control system maturity levels
| ICS maturity level | a brief description of |
| Elementary | Control procedures are absent or partially implemented but not formalized. |
| Informal | ICS processes are partially formalized, and separate control procedures are performed. |
| Formalized | Control activities are formalized and properly documented, but not standardized. Deviations may not be detected in a timely manner. |
| Managed | Both unified control procedures and a procedure for their periodic testing have been introduced. Automation tools may be used to perform, test, or monitor the effectiveness of control procedures. |
| Improveable | ICS processes comply with best practices and are periodically optimized using new approaches. The execution, testing and monitoring of the effectiveness of control procedures can be automated. |
According to PWC, 34% of companies assess the maturity level of their internal control system as formalized, 26% as managed. And only 2% of companies have achieved an improved level of internal control system.
The company can also take another gradation of internal control system maturity levels for assessment, in particular, those defined in the recommendations of various regulators or in regulations. To successfully create an effective internal control system, it is necessary first of all to evaluate and record its initial state, and then determine the target vision of the internal control system.
Objectives of corporate financial control
They can be distinguished in the following spectrum:
- assessment of the quality of accounting - accounting, tax, management;
- identifying deficiencies in the performance of work duties by enterprise employees;
- identifying deficiencies in the enterprise capital management infrastructure;
- optimization of conceptual approaches to capital management;
- identification of factors influencing the efficiency of financial management of an enterprise.
The first of the goals of financial control at an enterprise, noted in the list, is important from the point of view of legitimizing business processes - in terms of the availability of documented licenses, permits, patents, correct generation of reporting (required by law, compiled due to the wishes of the company’s owners or intended for investors , banks and company partners).
The second of the above-mentioned goals of financial control is significant for an enterprise from the point of view of ensuring the stability of business processes - when their implementation directly depends on the level of competence, responsibility and experience of employees.
The third of the goals we have noted is important, first of all, for increasing the technological competitiveness of the enterprise. The quality of the infrastructure used in the implementation of financial management solutions for a company determines the amount of costs for the corresponding implementation in terms of time, compensation for personnel, and costs for maintaining the functionality of the software and hardware components of this infrastructure.
Financial control also allows us to identify the potential for improving the conceptual approaches of the company's management to managing the enterprise's capital. As a rule, the factors influencing the success of the implementation of the adopted concept are also determined. The management of a corporation's financial resources and their investment in certain funds is most often based on methods and approaches that form a certain concept, which can be adjusted from time to time - depending on the results of using the appropriate methods and approaches. And financial control at the enterprise helps to identify these results.
Successful achievement of the above goals predetermines the formation of another one. We are talking about such a goal as identifying measures aimed at:
- increasing accounting efficiency;
- increasing employee competencies;
- optimization of corporate capital management infrastructure;
- adjustment of the conceptual principles of working with finances at the enterprise;
- development of concepts to enhance the use of positive factors of capital management and reduce the dependence of business processes on negative factors.
Let's consider the key methods of corporate financial control.