Interesting fact: the amount of illegal VAT refunds has decreased by almost 2 times, and this is the result of the action of ASK VAT-2. This was stated by the head of the Office of Desk Control of the Federal Tax Service, Dmitry Satin.
SUR ASK VAT-2 is the latest version of the program at the moment. It is this version that distributes taxpayers into 3 risk groups, which will be discussed below. Earlier versions are not able to distribute taxpayers into groups. Let's figure out how this system works.
How does SUR ASK VAT-2 work?
It’s quite simple: when a VAT payer company submits tax reports, SUR-ASK VAT-2 compares the data from these reports with information from supplier companies and clients of the VAT payer company. The system sees the entire chain of movement of goods and services from one company to another and compares the information received from these companies. Purchases and sales are reflected from suppliers and customers of that firm. And if there is a “gap” somewhere, SUR ASK VAT-2 instantly signals this.
SUR ASK VAT-2 does in minutes what inspectors previously spent many months doing. All information is now at your fingertips.
Interesting fact: over the 11 months of 2016, the Federal Tax Service collected 2.4 trillion rubles in VAT. This is 10% more than in the same period in 2015. This is partly associated with the ASK NDS-2 RMS system.
Algorithm of operation of ASK VAT 3
Let us repeat, the ASK VAT 3 program identifies “fly-by-night companies” and those who are trying to take advantage of illegal VAT deductions. The ASK VAT 3 service verifies the VAT compiled by the payer, collects data from his sales book, and the deduction accepted by the buyer from the buyer’s purchase book. The ASK VAT 3 program records discrepancies of the following types:
- “VAT” – when both parties to the transaction have reflected VAT in their returns, but the tax amounts are reflected differently;
- “Gap” - one of the parties to the transaction did not reflect the transaction, did not submit reports at all, submitted a zero declaration, or if the counterparty is not in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities at all.
From February 1, 2022, ASK VAT 3 automatically generates reports on discrepancies in tax reporting (if they are not eliminated by the taxpayer independently within five days). The report generated by the ASK VAT 3 program is sufficient grounds for initiating a criminal case against the taxpayer for non-payment of taxes. Important! Tax inspectors may prohibit the application of a VAT tax deduction on the basis that the service provider has the characteristics of a “fly-by-night company.” The ASK VAT 3 program automatically sends letters to both the taxpayer and his counterparty with a request to clarify the fact of discrepancies and provide appropriate explanations. The taxpayer and the counterparty have five working days to provide explanations; after the expiration of the deadline for providing explanations, the tax office will begin an audit. Having received explanations from the taxpayer and the counterparty, the inspector makes a note in the program and continues to conduct a desk audit. As a result of such tax audits, both the taxpayer and his counterparty must either correct the mistakes made or pay additional tax to the budget.
If after reading this article you still have questions or need advice, you can call or write to us. We will help you sort out any difficult situation. “THEORY OF LAW” Evgenia Bulatova 89134323913 [email protected]
What are the results used for?
1. To determine which companies are claiming VAT refunds, you need to pay special attention. Previously, in order to identify “dubious” VAT refund applications, it was necessary to sift through a lot of documents, but the ASK VAT-2 RMS does everything very quickly and in an automated mode.
2. If there are discrepancies in the tax returns of the “chain” of suppliers and buyers, then the ASK VAT-2 RMS is used to determine what caused these discrepancies. Tax officials begin to look for a beneficiary in the chain - a company that somehow makes illegal tax profits. And then there will be a desk audit, and then there will be an almost 100% probability of additional tax charges.
It should also be noted that when a “gap” is discovered in some chain - that is, someone did not reflect something in the declaration, some numbers did not match, then the Federal Tax Service begins to “shake” the entire chain. And first of all, they are interested in the fact that they can be charged more taxes and actually collect them.
Application of the ASK VAT 3 program
As noted above, ASK VAT-3 is a new service of the Federal Tax Service , used in test mode since February 1, 2022 to search for illegal VAT deductions. When the ASK VAT 3 system of the Federal Tax Service of Russia was first launched, we can safely say that it reached a completely new level in the fight against “one-day companies” and other well-known methods for withdrawing (cashing out) funds. Because of this, even a conscientious taxpayer may lose the right to deduct VAT due to dishonest actions of his counterparties, since the new ASK VAT 3 system was created to search for illegal VAT deductions. Now the tax inspectorate can refuse to deduct VAT from a taxpayer only on the grounds that its counterparty has the characteristics of a “fly-by-night company.” If the taxpayer is denied a VAT deduction on this basis, then the fact that the taxpayer’s right to deduct VAT from the buyer is in no way connected with the supplier’s obligation to pay VAT, the taxpayer will have to prove in court independently. However, the taxpayer can, without waiting for the tax authorities to refuse to deduct VAT, try to reduce this probability, as well as the number of requests received from the tax inspectorate to provide explanations on VAT. To try to reduce the number of gaps in the VAT 3 ASK and try to avoid receiving requirements from the tax office, it is recommended to follow these steps:
- check the details in the electronic declaration and invoice;
- check all transaction codes;
- avoid a list of codes for one operation;
- check your counterparties according to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia using the online service egrul.nalog.ru;
- check with your counterparties using electronic programs designed for reconciliation.
Thus, thanks to ASK VAT 3, as soon as the taxpayer’s declaration is received by the tax office, the inspector will receive a fairly large amount of information without waiting for the taxpayer to provide explanations on tax gaps or VAT discrepancies in the reporting information of the seller and buyer. At the same time, the ASK VAT 3 system automatically generates a request and sends it electronically to the taxpayer. The taxpayer must also provide a response to such a request in electronic form. If we are talking about discrepancies in reporting, then it makes sense to explain yourself: call the counterparty’s accounting department, ask questions, identify the reasons and state all this in the inspection’s response. If we are talking about tax gaps, then the inspectorate will resolve the issues when submitting an updated declaration. Otherwise, there is a high probability that the company will be included in the on-site tax audit plan. ASK VAT 3 allows tax inspectors to track all transactions on the accounts of enterprises and individuals. Already, inspections have become as targeted as possible; they are carried out with information about “problem” counterparties and transactions. Now they will be able to connect the status of accounts of individuals - directors, accountants, owners and even their relatives - with these operations. The presence of a relationship between legal entities and individuals will also be recognized automatically by ASK VAT 3. Thus, new reasons will be added for ordering tax audits: declared small incomes and large savings or expenses of the manager or beneficiary. Considering that the Federal Law of November 30, 2016 No. 401-FZ introduced changes to parts one and two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as other legal acts, which tightened the legislation on bringing individuals to subsidiary liability. More attention should be paid to these changes. ASK VAT 3 analyzes the tax returns of all taxpayers and the compliance of counterparties’ data. If the information differs, the system automatically generates a request for explanations to these counterparties.
The ASK VAT 3 service tightens control over companies using the simplified taxation system (USNO). The start of testing the service showed that tax authorities began to take simplified companies and associated individuals from the chain into circulation. The ASK VAT 3 system will assign risk levels to companies based on a much larger number of factors, send out even more requirements and notifications, and even more accurately indicate to inspectors where and what to look for. Remember that each of your transactions and each transfer of funds leaves traces that are now much easier to untangle. Tax inspectors will see not only the chain of passage of goods and funds, but also the turnover of your companies without additional requests to the bank. So, we looked at the topic of the new system of the Federal Tax Service of Russia - ASK VAT 3, and how the work of this program works. It is worth noting that the tax authorities have another new mechanism for controlling taxpayers - extraterritorial audits. Now, the data provided by taxpayers will be checked by inspectors of the “foreign” district tax inspectorate, and this, first of all, excludes any possibility for the taxpayer to come to an agreement with the tax inspector.
Another innovation of the new ASK VAT 3 system is “extraterritorial inspections,” during which the business itself will be inspected by inspectors from their territorial tax inspectorate, and on-site tax inspections will be carried out by tax inspectorates from other regions. Simply put, the Federal Tax Service of Russia has set itself the task of bringing all taxpayers out of the so-called “shadow” to work legally with 100% payment of taxes. Under such severe tax pressure, business owners will now clearly need professional legal support, and most importantly, protection of their investments.
conclusions
Further more.
The Federal Tax Service is not going to stop there. There are plans to synchronize the program with the information databases of customs, the Central Bank and Rosfinmonitoring. This means that the system will be even more vigilant, corrosive and picky. 9 out of 10 tax charges are based on the fact that the company cooperates with unscrupulous contractors. Although the company's management may not know that something is wrong with partner companies.
Everyone knows that prevention is easier and cheaper than treatment. It’s the same in business - it’s better to contact an experienced tax lawyer so that he can check your counterparties and the correct operation of your own company, than to look for a defender when the Federal Tax Service already has questions.
Times have changed. The Federal Tax Service has armed itself with smart technologies. And you need to arm yourself. The experience and knowledge of a good tax lawyer is your best weapon.
How to respond to requests for detected errors
If you receive a request for clarification on control ratios or discrepancies with counterparties, you need to respond to it:
- First of all, send a tax receipt confirming receipt of the request (clause 5.1 of Article 23 of the Tax Code), otherwise the Federal Tax Service may block your accounts;
- then analyze the errors and submit an updated VAT return: in this case, you cannot change the VAT amount.
If the tax office does not charge additional VAT, it is enough to submit your explanation either in free form or in the form of a table, where you confirm the entries that you consider correct and correct the values where errors are identified. Please include copies of supporting documents with your explanations to prevent further questions.
It is convenient to send an explanation from the service in which you keep records and prepare reports. Many programs are equipped with a VAT reconciliation system, which reduces the risk of additional tax charges and helps prepare responses to tax requirements.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
Complex tax gaps for VAT and in-depth desk audit
If a gap occurs based on the results of processing the auto-requests sent by the system, the problem is not eliminated, then so-called “complex discrepancies” arise. That is, the system establishes that at the place of the gap on the part of the buyer and the seller there are transitors - otherwise “technical . Complex discrepancies established by the VAT ASK system are centrally sent by the Interregional Inspectorate for Desk Control to the inspectorate where the gap arose in order to identify beneficiary organizations/beneficiaries in the formal supply chain.
When conducting an in-depth desk audit, the tax authorities determine who, if a gap occurs in the supply chain, is the transitor and who is the beneficiary, taking into account the information:
- about the leader and founders, including the definition of the attribute “mass leader/founder”;
- about the average number of employees;
- about the upcoming exclusion of the organization from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities as an inactive legal entity;
- about the presence in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities of information about the unreliability of information about the director, founder, and registration address;
- on the availability and content of interrogation protocols of managers and founders;
- about disqualified persons;
- on the availability of current accounts and their number, information on the suspension of transactions on bank accounts;
- about the addresses of registration (registration), registration at the place of “mass registration”;
- about the assets of the organization and whether a declaration on the property tax of organizations is provided;
- about the tax burden and the share of tax deductions;
- about the date of registration (age of organizations);
- on comparison of the tax base in declarations and the turnover of funds in current accounts;
- about the presence of arrears in taxes and obligatory payments;
- about turnover on the current account of organizations and purpose, the presence of operations characteristic of real organizations;
- on methods of submitting declarations, information about digital signature;
- and so on. depending on the depth of control.
Problems of VAT refund in case of bad faith of the counterparty
Currently, the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation pays quite a lot of attention to the reality of business transactions of taxpayers with their counterparties. To ensure the purity of relationships between taxpayers and their counterparties, the Federal Tax Service of Russia has taken large-scale measures to identify so-called “unscrupulous” taxpayers in the chain with counterparties who deliberately create fictitious business transactions with the same “unscrupulous” counterparties in order to achieve a single goal - reducing the amount of taxes payable in country budget. [email protected] of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 31, 2015 cites cases of refusal by the tax authority to deduct VAT when the tax authority has proven that the taxpayer has committed actions that are obviously aimed at obtaining an unjustified tax benefit, as well as when the tax authority has evidence of the fact that the taxpayer did not exercise due diligence when choosing a counterparty.
There are often cases when, based on the results of an audit of a taxpayer’s activities, the tax authorities refuse to reimburse him for VAT, subsequently oblige the taxpayer to pay the missing amount of VAT to the budget, charge penalties, and bring him to tax liability, even if the documents submitted by the taxpayer do not contain errors or violations. Tax authorities often justify such decisions by the fact that the taxpayer’s counterparty (supplier, performer) did not actually transfer the amount of VAT paid by the taxpayer to the budget. Also, the tax authorities explain the refusal of the taxpayer to refund VAT by the fact that the taxpayer’s counterparty is not registered as a legal entity, or has been completely liquidated, that is, does not have (did not have) the civil legal capacity to enter into a transaction with the taxpayer. In such cases, the tax authorities establish the nullity of the transaction and the taxpayer’s intent to obtain an unjustified tax benefit - and this is the main reason for the tax authorities to refuse a VAT refund.
How tax authorities control the payment of VAT
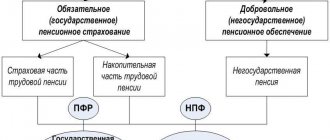
Now the tax office uses more than 20 information systems, with the help of which it checks the activities of taxpayers. Among them are AIS "Tax-3", PIK "One-Day", PIK "Invoices", "VNP-Otbor", PIK "Income", PIK "Customs", PIK "Schemes", PP "VAT Control" (formerly ASK “VAT-2”) and others, allowing inspectors to identify schemes of illegal tax evasion.
PC "VAT Control" (formerly ASK "VAT-2") monitors the chain of movement of goods subject to value added tax (VAT), from creation or crossing the Russian border to sale to the final consumer.
The system detects the following discrepancies:
1. Discrepancy of the “gap” type:
- failure to submit tax returns by organizations;
- submission by organizations of a declaration with a “zero indicator”;
- absence of transactions in the counterparty’s tax return;
- significant data distortion.
2. Discrepancy of the type “VAT”:
- the excess of the amount of VAT accepted for deduction by the taxpayer - the buyer, in comparison with the amount of VAT calculated by the counterparty - the seller from sales transactions.
If the buyer’s invoice reflected in the purchase book is not in the seller’s sales book, then a “gap” occurs, i.e. the system has established that the VAT refunded by the buyer (accepted for deduction) by the seller has not been paid to the budget (not calculated and not reflected for payment).
Thus, if the data on the same transaction (invoice) does not match, the system automatically generates claims against the seller and buyer for a gap, which indicates either an overstatement of tax deductions by the buyer or an understatement of the amount of tax payable by the seller. Requirements are set automatically by the system, and the inspector does not take any part in this.
"VNP-Selection" (AIS subsystem "Tax-3")
Using the VNP-Otbor information complex, inspectors compare data on the company’s activities (profitability, profitability) with information on the activities of companies of similar scale and localization and compare the indicators of the tax period under study with data from previous years. The VNP-Selection system assigns points to taxpayers, and if a company has many inconsistencies, it recommends it for a tax audit. At the same time, the solvency of the taxpayer (availability of property) and its owners is analyzed.
PC "VAI"
The VAI (Visual Analysis of Information) software package is used by tax authorities to present data about companies, their owners and payments made by companies in graphical form.
PIK “Income”, PIK “One-Day”, PIK “Customs”, PIK “Schemes”, etc.
These software and information systems collect data on desk audits that have already been carried out, the results of comparisons of peer companies in the region, and explanations given by company employees in past periods.
All information about taxpayers is collected in data processing centers (DPC). In May 2015, the first data center was opened in Dubna, Moscow Region. In December 2015, the Federal Tax Service launched a second Data Processing Center in Gorodets. Data centers in Dubna and Gorodets automatically generate a “single tax file” about each taxpayer in Russia. Taxable transaction data is collected and processed by robots and stored in the cloud. Human participation is minimized. All VAT reports (and therefore all invoices) are included in the all-Russian database.
In its control activities, the tax office uses technology that is based on the creation of a so-called “optimal model” of a representative of any industry or type of activity that corresponds to a kind of standard with average indicators. This is the result of a lot of analytical work.
Such indicators are determined as a result of processing information on a particular type of activity. For example, it is clearly determined that for this type of activity today the rate of return is 12 percent. Based on this, they find out what tax payments for corporate income tax should go to the budget? Or, accordingly, at what turnover of revenue for this type of activity should the budget receive the corresponding data on value added tax, based on the value added norm for the type of activity?
Again, this is somewhere close to profitability. Based on this, the corresponding standards for VAT refunds are determined, because, as is known, today almost 99 percent of audits give a result in which the tax authorities know exactly how much VAT should be refunded, and not as much as is requested in tax returns.
This is very serious work as a result of the introduction of VAT-2, and now ASK VAT-3.
Comparison with these indicators allows you to identify risky links and unwind chains of connections very deeply. That is, if earlier they talked about fly-by-night companies that hid operations behind two or three links, now it reaches 15 or more levels.
Technical gap
A “technical” discrepancy is a discrepancy that does not lead to non-payment of tax to the budget, the reason for which is a discrepancy in the number or date of the invoice, the number or date of the application for the import of goods and the payment of indirect taxes into the territory of the Russian Federation from the territory of the Customs Union, in the number DT, in the TIN of the “essential” counterparty of the Seller (or Buyer), whose declaration correctly reflects the transaction with the counterparty Buyer (or Seller) when a discrepancy is identified in his declaration and a claim is sent.
A “technical” discrepancy is eliminated by submitting a formalized explanation or an updated VAT tax return.