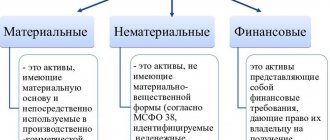
Composition and structure of non-current assets
The composition of the non-current assets of the enterprise is detailed in different ways by different documents of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation:
- by order No. 43n dated 07/06/1999, which approved PBU 4/99, dedicated to the methodology for compiling accounting reports, non-current assets included intangible assets, fixed assets (with the inclusion of non-refundable assets), profitable investments in materiel and financial investments;
- by order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000, which approved the chart of accounts, non-current assets are divided into fixed assets (with the allocation of income-generating investments), intangible assets, depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets, capital investments in them (with the allocation of equipment requiring installation) and ONA;
- By order No. 66n dated 07/02/2010, containing the latest form of balance sheet recommended for use, these assets are divided into 9 articles: intangible assets, R&D, intangible and tangible exploration assets, fixed assets, profitable investments in materiel, financial investments, non-current assets and other non-current assets .
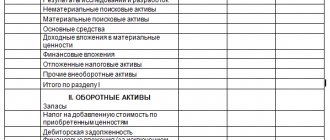
There are no contradictions between them, but the concept of non-current assets for the purposes of its reflection in the balance sheet still needs to be clarified. Non-current assets on the balance sheet are the company’s own property, which for a long time (more than a year) is used in its main activities in order to generate income. The components of non-current assets are:
- NMA;
- OS;
- unfinished investments in their creation;
- financial investments;
- SHE.
ONA (account 09), which are temporary differences in income tax that arise due to a discrepancy between accounting and tax data, is a rather random phenomenon for non-current assets . They do not correspond to the meaning of a non-current asset either in essence (this is not property, but a certain estimated amount of tax), or in terms of duration of existence (they may not be long-term). Not all organizations use them, and they, as a rule, do not play a significant role in non-current assets , so we will not dwell on them.
To learn how and when temporary differences are formed, read the article “What is deferred income tax and how to account for it?”
The concept of other current assets
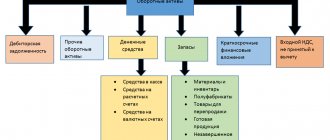
Current assets represent the organization's economic assets consumed during the year or production cycle.
During the commercial activities of the enterprise, their value is completely transferred to the manufactured products or funds received. Information about current assets is recorded in the 2nd section of the balance sheet, divided into main groups. Amounts that do not fit this group are recorded separately in line 1260 as other current assets.
IMPORTANT! According to para. 3 clause 11 PBU 4/99 information on individual types of assets can be reflected in a total amount with explanations to the balance sheet if the amount of each indicator is not significant for assessing the results of financial activities.
To detail the indicators of other current assets, a separate line 12605 “Deferred expenses” is provided in the balance sheet.
You can learn more about the balance sheet items, their meaning and content in the article “Deciphering the lines of the balance sheet (1230, etc.).”
What do intangible assets of organizations consist of?
Intangible assets, according to PBU 14/2007, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 27, 2007 No. 153n, include documented rights to unique intangible objects, for example, rights to works, designs, technologies, brands (marks), reputation.
In the balance sheet they are divided:
- on NMA;
- R&D;
- intangible exploration assets that arise only in organizations engaged in the development of natural resources and can be depreciated during the process of their creation.
The cost of operated intangible assets in accordance with clause 35 of PBU 4/99 in the balance sheet is shown minus depreciation on them. Those. data on intangible assets in non-current assets consists of balances on accounts 04 and 08 (for intangible exploration assets) reduced by depreciation amounts (account 05). If the data on intangible assets listed on account 08 does not correspond to the analytics highlighted in the balance sheet, then they may be:
- added to the balances of used intangible assets when their amount is insignificant (up to 5%) compared to the residual value of intangible assets;
- allocated to an additionally entered separate line in non-current assets ;
- shown in the line “Other non-current assets ”.
In simplified reporting (Appendix 5 to Order No. 66n), it is allowed to reflect on 1 line both the residual value of operated intangible assets and existing unfinished investments in them.
Definition
Other non-current assets 1190 are assets whose circulation period exceeds 12 months and which are not reflected in other lines of Section I of the balance sheet. These may include:
- equipment requiring installation - equipment that is put into operation only after assembling its parts and attaching them to the foundation or supports, to the floor, interfloor ceilings and other load-bearing structures of buildings and structures, and sets of spare parts for such equipment;
- Investments in non-current assets - the organization’s costs in objects that will subsequently be taken into account as intangible assets or fixed assets, and costs associated with the implementation of incomplete R&D;
- Future expenses - expenses for the development of natural resources, one-time (lump sum) payment for the right to use the results of intellectual activity and means of individualization, etc.;
- the cost of perennial plantings that have not reached operational age;
- the amount of transferred advances and advance payment for work and services related to the construction of fixed assets.
The presence of such assets increases the resource potential of the enterprise.
What applies to the enterprise OS
In accordance with PBU 6/01, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n, fixed assets represent a set of own property involved in the operation of the enterprise - from land and buildings to inventory. This also includes objects leased with the condition of being included on the balance sheet of the lessee.
In the balance sheet they are divided:
- on material exploration assets that arise only from organizations engaged in the development of natural resources and can be depreciated during the process of their creation;
- OS;
- profitable investments in materiel, which are fixed assets owned by the enterprise, but not exploited by it in its own production, but transferred for this purpose to the outside.
According to clause 35 of PBU 4/99, the cost of operating fixed assets is shown in the balance sheet minus depreciation on them. Those. fixed assets in consists of balances on accounts 01, 03 and 08 (for tangible exploration assets) reduced by depreciation amounts (account 02). If the fixed assets data listed on account 08 does not correspond to the analytics highlighted in the balance sheet, then they may be:
- attached to the balances of the fixed assets used when their amount is insignificant (up to 5%) compared to the residual value of the fixed assets;
- allocated to an additionally entered separate line in non-current assets ;
- shown in the line “Other non-current assets ”.
Together with the balances on account 08 for investments in fixed assets, the balances on account 07 are taken into account.
In simplified reporting (Appendix 5 to Order No. 66n), it is allowed to reflect on 1 line both the residual value of operating fixed assets and existing unfinished investments in them.
Other noncurrent assets. Line 1190.
This line reflects information about other assets not listed above, the circulation period of which exceeds 12 months or the duration of the operating cycle, if it is more than 12 months (clause 19 of PBU 4/99). It is necessary to take into account that the non-current assets of the organization, information about which is significant, must be reflected in section. I Balance sheet separately. Therefore, significant indicators should not form the indicator of line 1190 (paragraph 2 of clause 11 of PBU 4/99, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 24, 2011 N 07-02-18/01).
What applies to other non-current assets?
Other non-current assets of the organization may include (provided that the relevant indicators are insignificant):
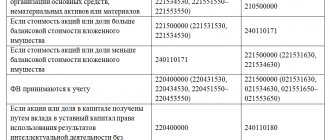
- Investments in non-current assets of the organization, accounted for in the corresponding subaccounts of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, in particular the organization’s costs in objects that will subsequently be taken into account as objects of intangible assets or fixed assets, as well as costs associated with the implementation of incomplete R&D, if the organization does not reflect these indicators in lines 1110 “Intangible assets”, 1120 “Results of research and development”, 1150 “Fixed assets” and 1160 “Income investments in tangible assets” (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, clause 41 of the Accounting Regulations and financial statements, clause 5, paragraph 4, clause 16 PBU 17/02).
- Equipment that requires installation, which is understood as equipment that is put into operation only after assembling its parts and attaching them to the foundation or supports, to the floor, interfloor ceilings and other load-bearing structures of buildings and structures, as well as sets of spare parts for such equipment, if the organization does not reflect such assets in lines 1120 “Results of research and development”, 1150 “Fixed assets” and 1160 “Profitable investments in tangible assets”. Equipment for installation is accepted for accounting as a debit to account 07 “Equipment for installation” at the actual cost of its acquisition, including delivery costs, etc. (clause 3.1.3 of the Regulations on Accounting for Long-Term Investments, Instructions for the Application of the Chart of Accounts).
The receipt of equipment for installation can be reflected using accounts 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets” and 16 “Deviations in the cost of material assets.” In this case, the balance of account 15 at the end of the month shows the cost of equipment to be installed en route (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, Guidelines for using the Chart of Accounts for enterprises and organizations of the agro-industrial complex, Guidelines for the correspondence of accounts in agricultural organizations).
- A number of expenses related to future reporting periods and accounted for in account 97 “Expenditures of future periods” (for example, a one-time (lump sum) payment for the right to use the results of intellectual activity and means of individualization). In Sect. I of the Balance Sheet, these expenses are reflected provided that the period for writing off these expenses exceeds 12 months after the reporting date or the duration of the operating cycle if it exceeds 12 months (clause 65 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting, paragraph 2 of clause 39 of PBU 14/2007, paragraph 16 PBU 2/2008, see also Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 01/27/2012 N 07-02-18/01, dated 01/12/2012 N 07-02-06/5, Appendix to the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 01/29/2014 N 07-04-18/01).
Question: What expenses can be taken into account as deferred expenses?
Answer: According to the current version of clause 65 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting, the list of amounts that can be taken into account as deferred expenses has been significantly narrowed. This type of asset, such as deferred expenses, is now mentioned only in paragraph. 2 clause 39 PBU 14/2007, clause 16 PBU 2/2008.
However, the Ministry of Finance of Russia in Letter dated January 12, 2012 N 07-02-06/5 explained that expenses incurred by the organization in the reporting period, but relating to subsequent reporting periods, are reflected in the balance sheet as deferred expenses and are subject to write-off by reasonable distribution between reporting periods in the manner established by the organization during the period to which they relate. Thus, if an organization has expenses related to the following reporting periods, it, as before, has the right to take them into account as expenses of future periods. For example, deferred expenses may include a one-time insurance premium, bank remuneration for issuing a bank guarantee, payment for the right to lease a land plot, and similar expenses.
- The cost of perennial plantings that have not reached operational age, taken into account on account 01 “Fixed assets”, subaccount 01-5 “Perennial plantings” (analytical account “Young plantings”), if the organization does not show it on line 1150 “Fixed assets” (p. 7 section 2 of Methodological recommendations for accounting of fixed assets of agricultural organizations, Methodological recommendations for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of enterprises and organizations of the agro-industrial complex, paragraph 4 of PBU 6/01, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08.14.2006 N 03- 06-01-02/33, dated 07/20/2006 N 07-05-08/279).
- The amounts of transferred advances and prepayments for work and services related to the construction of fixed assets (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 24, 2011 N 07-02-18/01).
What accounting data is used when filling out line 1190 “Other non-current assets”
From the above it follows that when filling out line 1190 “Other non-current assets”, data on the balance as of the reporting date for accounts 08, 07, 15 and 16 (in the part related to equipment for the installation), 97 (analytical expense account with a deadline) can be used write-offs over 12 months), 60 (in terms of advances and prepayments for work and services purchased for the construction of fixed assets), as well as account 01, subaccount 01-5, analytical account “Young plantings”. The balance on these accounts is formed as line indicator 1190 only if this information is unimportant. Non-current assets of the organization, information about which is significant, must be reflected in section. I of the Balance Sheet separately (paragraph 2 of clause 11 of PBU 4/99, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 24, 2011 N 07-02-18/01).
Line 1190 “Other non-current assets” = Debit balance on account 08 + Debit balance on account 07 + Debit balance on account 15, in terms of equipment for the installation +/- Balance of account 16, in terms of equipment for the installation + Debit balance on account 97 (analytical account for accounting expenses with a write-off period of more than 12 months) + Debit balance on subaccount 01/5 (analytical account “Young plantings”) + Debit balance on account 60 in terms of advances and prepayments for work, services related to construction of environmental facilities)
Provided that the amount of unfinished capital investments is not included by the organization in the indicators of lines 1110 “Intangible assets”, 1120 “Results of research and development”, 1150 “Fixed assets” and 1160 “Profitable investments in tangible assets”.
In general, the indicators in line 1190 “Other non-current assets” as of December 31 of the previous year and as of December 31 of the year preceding the previous year are transferred from the Balance Sheet for the previous year.
The “Explanations” column provides an indication of the disclosure of this indicator.
Example of filling out line 1190 “Other non-current assets”
The organization decided to separately reflect unfinished capital investments on a separate, independently entered line in section. I “Non-current assets”, and in case of insignificance of indicators - on line 1190.
Indicators for accounts 08, 07 and 97 in accounting (indicators for account 01, subaccount 01-5, analytical account “Young Plantations”, for accounts 15 and 16 in the part related to equipment for installation, as well as for account 60 in the part There are no advances or prepayments for work and services related to the construction of fixed assets): rub.
| Index | As of the reporting date (December 31, 2014) |
| 1 | 2 |
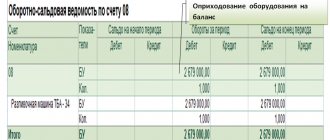
| 1. Balance on the debit of account 08, subaccounts 08-3 and 08-4 | 5 939 100 |
| 2. Balance on the debit of account 08, subaccount 08-8 | 860 900 |
| 3. Balance on the debit of account 07 (cost of equipment, subsequently subject to accounting for account 01) | 860 000 |
| 4. Balance on the debit of account 97, analytical expense accounts with a write-off period of more than 12 months (lump sum payments) | 586 806 |
Fragment of the Balance Sheet for 2013
| Explanations | Indicator name | Code | As of December 31, 2013 | As of December 31, 2012 | As of December 31, 2011 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 2.2 | Unfinished capital investments in fixed assets | 1185 | 3012 | 1604 | — |
| 1.5 | Other noncurrent assets | 1190 | 2127 | 4890 | — |
Solution
The cost of unfinished capital investments in fixed assets is:
as of December 31, 2014 - 6,799 thousand rubles. (RUB 5,939,100 + RUB 860,000);
as of December 31, 2013 - 3,012 thousand rubles;
as of December 31, 2012 - 1,604 thousand rubles.
The cost of other non-current assets is:
as of December 31, 2014 - 1,448 thousand rubles. (RUB 860,900 + RUB 586,806);
as of December 31, 2013 - 2127 thousand rubles;
as of December 31, 2012 - 4890 thousand rubles.
A fragment of the Balance Sheet in Example 1.9 will look like this.
| Explanations | Indicator name | Code | As of December 31, 2014 | As of December 31, 2013 | As of December 31, 2012 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 2.2 | Unfinished capital investments in fixed assets | 1185 | 6799 | 3012 | 1604 |
| 1.5 | Other noncurrent assets | 1190 | 1448 | 2127 | 4890 |
What is included in financial investments
The composition of financial investments is determined in PBU 19/02, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 10, 2002 No. 126n. These are securities, deposits in the management company, loans issued, deposits and receivables acquired under an assignment agreement.
Among financial investments, only those with a maturity period exceeding 1 year are classified as non-current assets Taking into account this requirement, balances on accounts 55, 58 and 73 are selected non-current assets.
Asset classification
Fixed assets have their own classification. For convenience, let’s group the data in the form of a table:
| No. | Classification feature | Name | Essence | Example |
| 1 | By AP turnover rate | Non-negotiable | The total value of an organization's property resources that repeatedly participate in the stages of the company's economic life. The period of use is more than one year. | Fixed assets (buildings, transport, machines, leasing objects). |
| Negotiable | Property assets of an enterprise that support the economic and production processes of the enterprise. The period of use is up to one year. | Inventories and raw materials, fuel and fuels and lubricants, goods, accounts receivable and money. | ||
| 2 | By degree of liquidity | Absolutely liquid | The property of an organization, which is a ready-made means for making payments and settlements. Does not require implementation. | Money cash, in foreign currency, electronic. |
| Highly liquid | Objects that can be implemented in the shortest possible time (up to one calendar month), and without significant financial losses. | Accounts receivable, short-term financial investments. | ||
| Medium liquid | Property resources of the company intended for sale within a period of one to six months without financial costs and losses. | Accounts receivable, stocks of finished goods (manufactured products) intended for sale. | ||
| Low liquidity | The assets and property of an enterprise that can be sold at a market price without significant costs (losses). The implementation period for such objects is long (from six months to 12 months). | Fixed assets, stocks of raw materials and materials, intangible assets, long-term financial investments. | ||
| Illiquid | A type of AP that cannot be implemented as independent objects, but only in a group or aggregate with other AP. | Uncollectible accounts receivable, deferred expenses. | ||
| 3 | By right of ownership | Own | Objects of property and financial resources and values that belong exclusively to an economic entity. | AP purchased using own funds. |
| Rented | Property and funds received under rental, leasing or loan agreements. | Leased or borrowed properties. | ||
| Received free of charge | Resources transferred to the ownership of an enterprise free of charge. | Deposits, donations, targeted funding free of charge. | ||
| 4 | To attract funds from borrowers | Investment | An investment asset is property assets acquired using funds received under credit, loan and loan agreements. | For example, equipment purchased on credit. |
| 5 | On the use of financial instruments | Basic | The underlying asset is the entity on which the derivative is based. The price of such an agreement is the basis for calculations for the execution of a fixed-term contract. | Securities, goods, currency. |
| By importance | Basic | Objects without which the company’s business activities are difficult or impossible. | Buildings, transport, equipment, raw materials. | |
| Others | Other assets are property resources that do not play a key role in the activities of the enterprise. | Future expenses, mothballed equipment, machines ready for installation, etc. |
Other non-current assets - what are they?
The line “Other non-current assets ” is intended to reflect data in one of 2 cases:
- For some reason, they cannot be included in any of the lines highlighted in non-current assets in the recommended form of the balance sheet.
- They are essential to be combined with one of the highlighted lines in the balance sheet. Most often it shows non-current assets formed by large balances in account 08 (for example, work in progress).
To learn how the section dedicated to non-current assets in the balance sheet will look like, read the article “Balance Sheet (Assets and Liabilities, Sections, Types).”
More complete information on the topic can be found in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.