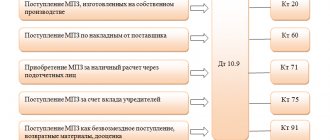
When is the method of writing off cost in proportion to the volume of products (works, services) applied?
The company has the right to choose the method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of production (SPO) at its discretion from the permitted methods of calculating depreciation.
But such an opportunity exists only in accounting. In the Tax Code of the Russian Federation everything is different. IMPORTANT! In accounting, there are 4 methods of calculating depreciation, listed in clause 18 of PBU “Accounting for fixed assets” (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n): 1 linear and 3 non-linear. There are only 2 methods in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - linear and nonlinear (Article 259).
SPO belongs to the group of “accounting” non-linear methods, however, it has significant differences with “tax” non-linear depreciation. They are related to the peculiarities of the methodology for calculating the amount of depreciation in the event of an STR:
- to calculate depreciation, it is necessary to have information about the expected volume of products (work, services) during the entire useful life of the property;
- depreciation for the billing period directly depends on the volume of products (works, services) produced using this type of property.
IMPORTANT! From 2022, PBU 6/01 will no longer be in force. It will be replaced by FSBU 6/2020. The provisions of the new FSBU can be applied earlier by enshrining such norms in the accounting policies of the enterprise.
Find out how to calculate depreciation, taking into account the provisions of FSBU 6/2020, in ConsultantPlus. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
With the “tax” non-linear method, the amount of depreciation is not calculated for a separate type of depreciable property, but depends on the total balance of the depreciation group and established by Art. 259.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depreciation standards.
When choosing a depreciation method, priority may be given to SPO in the case when:
- machines, equipment and other property are used intensively for the production of certain types of products (performance of work, provision of services);
- it is possible to definitely establish a connection between the depreciation of property and the volume of products produced (work or service performed).
In any case, the approach to choosing a depreciation method should be carried out in a balanced and justified manner, with the benefits of such a write-off of property value compared with the level of calculation and accounting costs that arise. We'll talk about this in the next section.
The material “Which method to choose for calculating depreciation in tax accounting?” will help you decide on the “tax” depreciation method.
Productive method of calculating depreciation: application features
The rational use of various methods for calculating depreciation of fixed assets allows, on the one hand, to ensure the supply of resources for the reproduction of these assets, and on the other hand, to influence the amount of depreciation charges, optimizing production costs at different stages of the organization's development.
§ The calculation of depreciation is regulated by the Instruction on the procedure for calculating depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Economy of the Republic of Belarus, the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus and the Ministry of Architecture and Construction of the Republic of Belarus dated February 27, 2009 No. 37/18/6 (as amended on December 19. 2019; hereinafter - Instruction No. 37/18/6).
PROCEDURE FOR USING THE PRODUCTIVE METHOD OF CALCULATING DEPRECIATION
The productive method of calculating depreciation is to calculate it based on the depreciable cost of the object and the ratio of natural indicators of the volume of products (work, services) produced (performed) in the current period to the resource of the object (clause 43 of Instruction No. 37/18/6).
The service life of each specific fixed asset item is established by decision of the commission based on its technical characteristics. It represents the amount of products (work, services) in physical terms, which, in accordance with technical documentation, can be produced (performed) throughout the entire life of the facility (clause 23 of Instruction No. 37/18/6).
note
A feature and advantage of the productive method of calculating depreciation is the presence of a direct dependence of the amount of depreciation charges on the intensity (quantitative parameters) of use of the fixed asset in each specific reporting period.
EXAMPLE 1
According to the technical passport, the woodworking machine is capable of processing 500,000 cubic meters of wood or working for 10,000 hours. The initial cost of the machine is 50,000 thousand rubles.
Calculation of depreciation in a productive way is carried out as follows.
One of the characteristics of using the machine is selected as an object resource - output in linear meters or hours.
Depreciation per unit of production (per 1 m.p.) will be:
1) 50,000 thousand rubles. / 500,000 m.p. = 0.1 thousand rubles. (if the resource of the object is used in linear meters of processed wood);
2) 100,000 thousand rubles. / 10,000 hours = 5 thousand rubles. (if the facility resource in operating hours is applied).
Let us assume that during the reporting month, 8800 m of wood were processed on a woodworking machine, and the operating time of the machine for the same period was 160 hours. Depreciation charges for the month will be:
1) 8800 m.p. × 0.1 thousand rubles. = 880 thousand rubles. (if the resource of the object is used in linear meters of processed wood);
2) 160 hours × 5 thousand rubles. = 800 thousand rubles. (if the facility resource in operating hours is applied).
In practice, an organization must choose one of the indicators characterizing the production capacity of a fixed asset item.
EXAMPLE 2
The organization purchased a car with a depreciable cost equal to 150 million rubles and an expected mileage of 500 thousand km. The mileage in the reporting month was 15 thousand km.
Depreciation per 1 km of run will be: 150 million rubles. / 500 thousand km = 0.3 million rubles.
Depreciation charges for the reporting month will be equal to: 15 thousand km × 0.3 million rubles. = 4.5 million rubles.
Clause 37 of Instruction No. 37/18/6 provides that the organization independently determines the methods and methods of calculating depreciation.
Restrictions on use are directly established only in relation to the non-linear method (it cannot be applied to a number of objects, including buildings and structures, with the exception of antennas and runways) (clause 41 of Instruction No. 37/18/6). There are no such restrictions regarding the productive method.
However, since when applying the productive method it is necessary to determine the resource of the object, in fact it is only possible in relation to those objects whose resource is quite accurately established by the technical documentation and has a quantitative expression, i.e. objects with the help of which the production of products directly takes place (work is performed , provision of services).
In this regard, the use of the productive method of calculating depreciation for buildings and structures in practice is very limited, since they most often do not have a specific resource of use. At the same time, the use of this method for such objects is not prohibited by law if their resource is nevertheless established.
SELECTING ACTUAL USE INDICATORS
The resource of an object and its actual use can be expressed in units intended to measure output and mileage, in hours of operation, etc.
The productive method of calculating depreciation is most appropriate in cases where the service life is determined primarily by technical indicators (for example, maximum volumes of product output, provision of services or implementation of work).
? The trade organization used the linear method of calculating depreciation, and from January 1, 2022, changed it to the productive one.
When using this method, is it possible to use the actual volume of turnover as an object resource?
The resource of each object is established based on its technical characteristics as the amount of products (work, services) in physical terms, which, in accordance with the technical documentation, can be produced (performed) throughout the entire life of the object (clause 23 of Instruction No. 37/18/6 ).
Taking into account this norm, the resource of an object can be expressed in any natural indicators characterizing the actual use of the object in each reporting period. In addition, it must be possible to reliably determine the total value of the indicator for the entire period of use of the object (useful life).
Instruction No. 37/18/6 does not establish rules by which to select indicators characterizing the resource use of objects when using the productive method. According to clause 5 of Appendix 1 to Instruction No. 37/18/6, determining the resource of each object in respect of which a decision has been made to charge depreciation in a productive way is the function of the commission for implementing the organization’s depreciation policy.
At the same time, regarding the possibility of using the indicator of the actual volume of trade turnover as a resource of an object belonging to a trade organization, it is necessary to note the following.
The volume of trade turnover is one of the final financial and economic indicators of the activities of a trade organization. This indicator:
- characterizes in value terms the result of the economic activity of the organization as a whole, and not the use of a specific object (objects) of fixed assets;
- depends on many factors (market demand, prices for goods (services), etc.) and is not directly related to the intensity of use of a particular fixed asset.
In this regard, in the author’s opinion, it is difficult to establish a connection between the volume of trade turnover and the amount of actual use of a specific fixed asset item in practice. Consequently, the use of this indicator as an object resource will be unjustified.
TRANSITION TO A PRODUCTIVE METHOD OF CALCULATING DEPRECIATION
Before the end of the useful life of depreciable objects, methods and methods for calculating depreciation are allowed to be revised:
- from the beginning of the reporting year with mandatory reflection in the accounting policy of the organization (book of fixed assets for individual entrepreneurs);
- during the reporting year in cases of completion of modernization, reconstruction of fixed assets, their additional equipment, completion, technical diagnostics and inspection with their complete stop, for fixed assets transferred during reorganization, in case of renewal or extension of the life of intangible assets, incl. h. when making investments that do not entail the creation of a new intangible asset (clause 37 of Instruction No. 37/18/6).
When revising the methods and methods of calculating depreciation, the under-depreciated cost of the object is distributed over the remaining useful life of it (in accordance with the applied methods and methods of calculation) in the manner established by paragraphs. 66–70 Instructions No. 37/18/6.
It should be remembered that when using the productive method, unlike other methods, the beginning and end of depreciation accrual coincides with the month the operation of the object began and the month of its end in connection with disposal (acceptance for accounting as an asset intended for sale, approval write-off act) respectively (clauses 34 and 36 of Instruction No. 37/18/6).
Clause 69 of Instruction No. 37/18/6 establishes the procedure for transition from linear or non-linear to productive method of calculating depreciation. According to it, when transitioning from a linear or nonlinear to a productive method of calculating depreciation, depreciation charges are calculated based on the under-depreciated cost of the object on the date of transition and the resource of the object. Calculation of depreciation charges in a productive way is carried out starting from the date of the decision to transfer.
When choosing a productive method, depreciation for an object is calculated based on its residual resource, determined by the commission taking into account the technical condition of the object as the difference between the resource of the object established in accordance with Instruction No. 37/18/6 and the used resource of the object (the actual volume of manufactured products (works, services) .
? The organizational structure of the trade organization includes shops (retail chain), public catering facilities (manufacture of products and service to visitors), and a confectionery shop (manufacture of products). The organization previously used the straight-line method of calculating depreciation.
Was it legal to change the method of calculating depreciation to productive from January 1, 2022? Is it necessary to use one method of calculating depreciation for all structural divisions?
The organization independently determines the methods and methods of calculating depreciation for fixed assets and intangible assets used in business activities, choosing a linear or non-linear method (declining balance method, direct or reverse sum of numbers of years method), productive method (clause 37 of Instruction No. 37/ 18/6).
The methods and methods of calculating depreciation used for objects of the same name may differ .
Until the end of the useful life of depreciable objects, methods and methods for calculating depreciation are allowed to be revised from the beginning of the reporting year with mandatory reflection in the accounting policies of the organization (without any additional conditions).
At the same time, there are restrictions regarding the use of the non-linear method of calculating depreciation (clause 41 of Instruction No. 37/18/6). There are no such restrictions for the productive method.
Taking into account the above, the trade organization has the right:
- from the beginning of any reporting year, review the method of calculating depreciation, changing it from linear to non-linear (for those objects for which this is allowed or to productive);
— choose your own method (method) for calculating depreciation for each fixed asset object, including for objects used in one structural unit.
? The loading and unloading equipment was put into operation in April 2022. Its useful life is 10 years. The technical data sheet establishes a resource equal to 1,500 cycles and 20,000 hours of operation. When putting loading and unloading equipment into operation, the organization decided to calculate depreciation using the straight-line method. The initial cost of the equipment is 450,000 thousand rubles, the residual value as of January 1, 2022 is 330,000 thousand rubles.
Did the organization have the right to switch to the productive method of depreciation for handling equipment from March 1, 2022? Can she do this from January 1, 2022? How to make such a transition correctly?
Taking into account paragraph 37 of Instruction No. 37/18/6, the transition to the use of the productive method in relation to loading and unloading equipment from March 1, 2022 was possible only in a very limited number of cases. Without additional conditions, such a transition can be made only from the beginning of any reporting year, including 2022. This must be reflected in the accounting policies.
In accordance with paragraph 69 of Instruction No. 37/18/6, when transitioning from a linear or non-linear to a productive method of calculating depreciation, depreciation charges are calculated based on the under-depreciated cost of the object on the date of transition and the service life of the object. Calculation of depreciation charges in a productive way is carried out starting from the date of the decision to transfer.
When choosing a productive method, depreciation for an object is calculated based on its residual resource, determined by the commission taking into account the technical condition of the object as the difference between the resource of the object and the used resource of the object (the actual volume of manufactured products (work, services) until the method is revised).
For loading and unloading equipment, the technical data sheet establishes a resource equal to 1,500 cycles and 20,000 hours of operation.
Let us assume that by January 1, 2022, the used resource of one unit of equipment will be 500 cycles and 6000 hours of operation.
When switching to a productive method, you must select one of the indicators that characterize the resource.
For example, if a resource measured in cycles is selected, at the time of transition to the productive method of calculating depreciation, the amount of depreciation per unit of residual resource, calculated by dividing the residual value by this resource, will be: 300,000 thousand rubles. / 1000 cycles = 300 thousand rubles.
In the future, monthly depreciation will need to be calculated based on the actual use of the resource (the number of cycles generated) in each month.
ACCRUAL OF DEPRECIATION WHEN CHANGING THE DEPRECIABLE COST
During operation, various capital works (reconstruction, modernization, etc.) can be carried out in relation to fixed assets.
A situation may arise when such work is carried out on a fixed asset item for which the productive method of depreciation is used. In this regard, questions may arise related to the moment of revision of the depreciable cost and its accrual in the month of such work.
? Equipment has been modernized and the productive method of depreciation is used. It lasted for 15 days: from February 1 to February 15, 2022.
How should depreciation be calculated when carrying out modernization if the productive method is used? If the modernization was carried out over several days, is it necessary to somehow adjust the amount of accrued depreciation in the month of the modernization? What cost acts as depreciation in the month of modernization - February 2021?
When calculating depreciation in a productive way in relation to equipment that is being modernized, one should be guided by both general approaches to calculating depreciation and special standards.
According to Appendix 4 to Instruction No. 37/18/6, when resuming operation of an object after modernization, reconstruction, etc., with the productive method of calculating depreciation, it is calculated based on the under-depreciated cost (taking into account its change) and the resource of the object (taking into account possible changes ) starting from the month of resumption of operation after modernization.
When carrying out reconstruction work (modernization, etc.) without stopping a fixed asset object or with its shutdown for a period of less than one month (several hours, days), depreciation accrual does not stop in the month of their implementation.
Thus, if a complete shutdown of the facility was not carried out or was carried out for a period of less than one month, when applying the productive method of calculating depreciation, the month of resumption of operation of the facility is actually the month of modernization. Accordingly, this month (February 2021) depreciation must be calculated on the cost of the object, determined taking into account the costs of modernization.
Conclusions:
1. The productive method of calculating depreciation can be applied from the date the object was accepted for accounting or switched to it during operation.
2. With this method of calculating depreciation, its amount directly depends on the volume of products (work, services) produced (performed, provided) in the current period. It is advisable to choose it when there is incomplete utilization of production capacity, fluctuations in production and sales volumes during the reporting period.
3. The productive method allows you to optimize the size of depreciation charges, taking into account the actual use of the depreciable asset.
How to evaluate the correctness of the chosen depreciation method?
To assess the correctness of the choice of depreciation method, it is necessary to calculate the amount of monthly depreciation for different methods of its calculation and compare the information obtained with the “depreciation policy” of management - its intentions regarding the write-off of property value (the need for its accelerated write-off, the need to evenly transfer the value of property to the cost of production and etc.).
SPO is not a commonly used method of calculating depreciation and is not suitable for all companies. It can be completely replaced by the simplest method to use - linear, in which:
- there is no need to regularly recalculate the amount of depreciation (it is constant from period to period, unless the property is subject to modernization, reconstruction or additional equipment that affects the increase in its value and useful life);
- there is a possibility of convergence between accounting and financial accounting in terms of depreciation charges;
- the change in residual value and accumulated depreciation occurs evenly.
The use of the linear method instead of SPO is justified if the company is expected to receive the same benefit (income) from this type of property throughout its entire service life, and its usefulness decreases gradually (as it wears out).
If we compare SPO with another accounting “depreciation” method - based on the sum of the numbers of years of useful use, then we must proceed from the following features of this method:
- the amount of depreciation is maximum in the first year of operation of the operating system and decreases gradually towards the end of its useful life;
- Depreciation is calculated over the entire useful life.
To compare this method with SPO, it is necessary to compare the calculated depreciation amounts for each period and choose the method in which you can write off the value of property faster - if such a task is provided for in the company’s development strategy.
Similarly, based on calculation, analysis and comparison, the most acceptable and rational method of calculating depreciation is selected between SPO and the reducing balance method - another “accounting” non-linear method.
Study the methods of calculating depreciation using the materials on our website:
- “Formula and example of the reducing balance method of depreciation”;
- “How to correctly apply the cumulative depreciation method?”.
Accounting for accrued depreciation
All operations of this kind must be reflected in accounting entries. The debit will be reflected in 20 (26, 44 and other cost accounts) Credit 02 - depreciation on fixed assets. Naturally, when accounting, you will definitely need to decide on the method of calculating depreciation, correctly put the asset on the balance sheet, and withdraw it after the end of its useful life. That is why it is necessary to monitor all operations from the moment the equipment and machinery, which have become fixed assets, begin to be used.
Method of writing off cost in proportion to production volume: calculation example
Let's look at an example of how to calculate depreciation using the SPO method.
Example
The company produces metal components for production equipment according to customer requests. For these purposes, in February 2022, a lathe with electronic numerical control was purchased and put into operation at an initial cost of 3,000,000 rubles.
Taking into account the technical resource and productivity of this machine, it is planned to produce 300,000 units of products over its entire useful life.
In March and April 2022, 2,500 and 3,200 units were produced on this machine. products, respectively, and in May the machine was idle due to the lack of requests from the customer for this type of product. Let us determine the amount of depreciation in the indicated months:
In March: RUB 3,000,000. / 300,000 units × 2,500 units = 25,000 rub.
In April: RUB 3,000,000. / 300,000 units × 3,200 units = 32,000 rub.
In May: RUB 3,000,000. / 300,000 units × 0 units = 0 rub.
The example shows that with the SPO method, the write-off of the value of property can be accelerated (if the property is used in an intensive, multi-shift mode) or may not be carried out at all (if there are no orders, demand for this type of product has fallen, etc.). In a situation of persistent instability of orders, it becomes unprofitable to use open source software.
Check whether you have calculated depreciation correctly in tax accounting using the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
The impact of legislative changes on the choice of depreciation method
Legislators have simplified certain aspects of calculating and calculating depreciation of property for companies that have the right to conduct accounting and prepare reports in a simplified form (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 16, 2016 No. 64n, which entered into force on June 20, 2016).
IMPORTANT! Small enterprises and non-profit companies with annual revenue of no more than 3 million rubles have the right to use simplified methods of accounting (including simplified accounting). (with the exception of certain categories of non-profit organizations), as well as companies that are residents of Skolkovo (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 27, 2013 No. 07-01-06/57795).
From June 20, 2016, these companies have the right to:
- do not include in the initial cost of fixed assets the costs associated with their acquisition (valuing the property at the price of the supplier (including installation)) - they can be immediately included in the costs of ordinary activities in full during the period of their implementation;
- Depreciation of fixed assets is calculated once a year on December 31 (or during the year at the choice of the company).
For more information about the innovations of Law No. 64n, see the material “Calculation of depreciation once a year and other innovations for those who have access to simplified accounting .
These innovations make it possible to quickly write off the cost of property (including using the SPO method), since part of the costs is included in expenses immediately, without including them in the initial cost.
The legally mandated ability to charge depreciation once a year reduces accounting calculations, although more frequent calculations may be necessary for internal financial reporting and property tax purposes.
These innovations do not have a direct impact on the efficiency of using a particular depreciation method, although they help reduce depreciation amounts and the frequency of their calculation. And to select SPO as one of the possible methods of writing off the value of property, an assessment, preliminary calculations and justification are required.
How to avoid differences in accounting and tax accounting when writing off the value of property, see the material “A way to take into account fixed assets worth from 40 to 100 thousand rubles in tax accounting, avoiding differences with accounting .