Who and how can become self-employed
Who is self-employed and what is the essence of this status?
Self-employed are individuals registered with the Federal Tax Service and independently carrying out activities for the sale of goods, works and services.
Registration as a self-employed person allows you to significantly save on taxes, since with income-generating activities an individual does not pay personal income tax at a rate of 13%, but a tax on professional income at reduced rates - 4% or 6%.
Self-employed status does not exclude the possibility of working under an employment contract. At the same time, a citizen’s income received from work is subject to personal income tax in accordance with the general procedure.
In addition, self-employed people are prohibited from hiring employees. They must carry out all income-generating activities independently.
Who can register as self-employed
Individuals who carry out income-generating activities in the territory where the relevant experiment is being conducted have the right to register as self-employed. Currently, self-employed people can work in Moscow, the Moscow and Kaluga regions, as well as in the Republic of Tatarstan. From the beginning of 2022, the regime is planned to be extended to another 13 regions. These regions have already been identified.
Citizens of member states of the Eurasian Economic Union can also become self-employed (Part 3 of Article 5 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018). In addition, this opportunity is also provided to individual entrepreneurs. But individual entrepreneurs under special regimes (USN, Unified Agricultural Tax, UTII), if they want to become self-employed, must abandon their use and switch to the tax regime for the self-employed (Part 4, Article 15 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ).
How to register as self-employed
To become self-employed, you need to submit an application. The date of registration is the date the application is sent to the Federal Tax Service. The application must be accompanied by information from the passport and a photograph of the individual. All these documents are generated using the “My Tax” mobile application (in the latest version it became possible to register through the State Services portal), which sends them for registration to the tax office.
You can also submit an application through the taxpayer’s personal account on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia. In this case, submission of information from the passport and photograph is not required (Article 5 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ dated November 27, 2018).
Self-employed on NAP: how companies can work with them
Who cannot register as self-employed
The list of entities that cannot be payers of professional income tax is established in Art. 4 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ. These include:
- persons engaged in the resale of goods or property rights;
- persons selling excisable goods and goods subject to mandatory labeling;
- Individual entrepreneurs who apply other special tax regimes or conduct business activities, the income from which is subject to personal income tax;
- persons engaged in the extraction and sale of minerals;
- persons who have employees with whom they have an employment relationship;
- persons acting in the interests of another entity under an agency agreement, commission agreement or commission agreement.
What does this give?
Creating a self-employed regime has many advantages:
- Specialists will be able to legally provide services to the public and companies without fear. Now they will not be afraid that the tax office will audit them and impose many fines.
- The activity will become legal, you can officially work with companies and legal entities. There will be no problems with paperwork when working with legal entities.
- Entrepreneurs will be able to reduce their tax burden and pay less without closing their individual entrepreneurs. They will be able to work in the same mode, but with significantly lower mandatory payments.
In addition, many companies are more willing to work with self-employed people, because in this case their tax burden is reduced. It is more profitable and easier for them to work with the self-employed.
A self-employed person does not need a current account, does not have to provide a tax return, does not require a cash register, and can be combined with his main job.
What can self-employed people do?
What types of activities can self-employed people engage in?
Self-employed people can sell goods and property rights (for example, renting out residential premises), as well as perform work and provide services.
An important condition is that services and work must be performed by the self-employed independently, without hiring employees or concluding employment contracts with anyone.
Self-employed people also cannot have an employer for the types of activities they carry out (Part 7, Article 2 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
What types of activities can the self-employed not engage in?
The list of types of activities that are not subject to tax on professional income is established in Part 2 of Art. 6 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ. These include:
- work activity;
- sale of real estate and vehicles;
- transfer of property rights to real estate, except for the rental of housing;
- activities within the framework of a simple partnership agreement;
- assignment (assignment) of rights of claim;
- arbitration management, activities of a mediator, notary, lawyer, as well as appraisal activities.
Income from the above types of activities is not subject to income tax and is subject to personal income tax on a general basis.
Can a foreigner work in Russia as self-employment?
Maybe, but not everyone. This opportunity is provided only to foreign citizens of EAEU member states.
Such foreigners are registered as self-employed on the basis of an application using access to the taxpayer’s personal account on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia. At the same time, they have the right to authorize the credit organization to submit to the tax authority an application for registration and deregistration (Part 5, Article 5 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Can self-employed people provide services to legal entities and individual entrepreneurs?
Self-employed people have the right to sell goods (work/services) both to other individuals and to organizations/individual entrepreneurs. At the same time, with regard to income received from organizations and individual entrepreneurs, self-employed people pay tax on professional income at an increased rate (Article 10 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
If an individual receives payment for his goods via the Internet from all over the world, is he entitled to apply the tax regime for self-employed people?
Yes, such an individual has the right to apply this special tax regime. The regime for the self-employed can be applied to all income that is subject to NPA taxation, including income from sources outside the Russian Federation.
And if an individual, when providing remote services, is located in a subject included in the experiment, he has the right to apply NAP on a general basis (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 29, 2019 No. 03-11-11/38994).
Can a self-employed person receive income in foreign currency?
The legislation does not contain any restrictions on the self-employed receiving income in foreign currency.
However, if payment is received by a self-employed person in foreign currency, the amount received must be converted into rubles. The currency received by the self-employed is converted into rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the day of receipt.
The self-employed person must also indicate the amount in Russian rubles on the check. If a self-employed person does not indicate the payment amount in Russian rubles on the check, he may be fined in the amount of 1,500 to 3,000 rubles (Part 4 of Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Is it possible to be self-employed and at the same time officially work for hire?
Can. The law does not restrict self-employed people from concluding employment contracts with employers. Theoretically, a self-employed person can work under employment contracts even for several employers.
However, income from employment is not subject to professional income tax. Personal income tax is paid on such income at a rate of 13%.
NPT is paid only from income from activities that were carried out by the citizen himself, and not on behalf and in the interests of his employer (Part 7, Article 2 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
What happens if the company transfers workers to self-employment
Can self-employed people sell excisable goods?
No, they can't.
The legislation directly establishes that persons selling excisable goods and goods subject to mandatory labeling do not have the right to pay professional income tax (Article 4 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Can a self-employed person sell rights to computer programs?
Maybe, but only if the computer program was created by him. A self-employed person does not have the right to sell other people’s licenses.
Persons who resell property rights cannot be payers of professional income tax (Part 2, Article 4 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Can a self-employed person sell not his own product, but resell products produced by other entrepreneurs?
No, he can not.
The law directly prohibits self-employed people from reselling goods and property rights (Part 2, Article 4 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Types of self-employment
At the moment, there is no clear list of permitted activities that a self-employed person can engage in. But there is a list of professions that are prohibited from switching to self-employment. These include:
- Sale of gasoline, alcoholic beverages, excisable goods, as well as goods subject to mandatory labeling.
- Activities related to the resale of rights to property, cars and other goods.
- Conducting business activities in the interests of another person (assignment, agent, commission).
- Entrepreneurial activity with hiring employees.
There are also income restrictions. Self-employed people cannot receive more than 2.4 million rubles per year.
Professions that are already officially recognized as possible for obtaining self-employed status:
- Taxi
- Freelancers, which include designers, copywriters and internet marketers.
- Masters such as plumber, electrician, builder.
- General workers (primarily loaders and couriers).
- Handmade masters.
- Photographers and videographers
- Landlords (yes, those who rent out apartment space).
At the moment, everyone who is engaged in tutoring performs the functions of a nanny or cleaner; for now, there is no need to register as self-employed. This provision is valid until December 31, 2019. New changes may come into force later.
Self-employed taxes
What taxes and how much should self-employed people pay?
Self-employed people pay professional income tax (PIT) on their income. Tax rates (4% and 6%) depend on who is the consumer of goods (works, services) of the self-employed.
If a self-employed person sells goods (work, services) to other individuals, then he pays tax at a rate of 4% on the income received. If consumers are organizations or individual entrepreneurs, then a tax rate of 6% is applied to the income received from them (Article 10 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
How do self-employed people pay taxes?
Self-employed people are required to pay monthly income tax on their income.
The Federal Tax Service informs the taxpayer about the amount of tax through the “My Tax” mobile application no later than the 12th day of the next month. The payment deadline is no later than the 25th day of the next month.
The tax is paid either by the self-employed person or by a person authorized by him (the bank). If a self-employed person authorizes the bank to pay the tax, the notification is sent to the bank. The bank pays tax without charging a fee for such actions.
Is it necessary to pay tax in those months when the self-employed had no cash income?
As a general rule, NAP is paid every month. But if the amount of tax calculated by the Federal Tax Service is less than 100 rubles, the specified amount will be added to the tax payable at the end of the next month (Part 2 of Article 11 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Accordingly, if a self-employed person had no income in any month, no tax is paid for that month.
Are self-employed people entitled to a tax deduction?
The law guarantees the self-employed the right to a deduction of no more than 10,000 rubles. The deduction is 1% for income taxed at a rate of 4%, and 2% for income taxed at a rate of 6% (Article 12 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Taxpayers reduce the NAP by the amount of the deduction every month. The deduction amount is calculated on an accrual basis. Once the deduction has reached 10,000 rubles, it ceases to apply.
The deduction will not be given again after it has been used.
Should a self-employed person pay personal income tax on income from the sale of personal property (for example, a car), with the help of which he conducts professional activities?
Yes, I should. The fact is that income from the sale of real estate, as well as vehicles, is not recognized as an object of taxation of NAP (Part 2 of Article 6 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018). Such income requires payment of personal income tax.
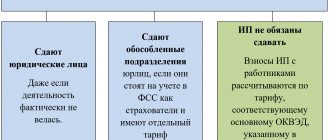
Should a self-employed person pay insurance premiums?
No, you shouldn't. Self-employed people pay only tax on professional income for the types of activities they carry out.
Individual entrepreneurs who have received self-employed status are not recognized as payers of insurance premiums for the period of application of this special tax regime (Part 11, Article 2 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Is it possible for a self-employed person to live and work in one region, but register and pay taxes in another?
The law allows for this possibility. The special NAP regime is allowed to be used by individuals whose place of business is the territory of any of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation included in the experiment (Moscow, Moscow and Kaluga regions, Tatarstan).
If an individual lives in a region not included in the experiment, but provides services on the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, which is included in this experiment, such an individual has the right to apply NAP.
Moreover, in fact, a self-employed person can work in another region and provide services remotely (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 29, 2019 No. 03-11-11/38994).
Plus 19 regions
When Federal Law No. 422-FZ came into force in 2022, there were only four subjects of the Russian Federation in which a new special tax regime was introduced on an experimental basis - Moscow, the Moscow and Kaluga regions, as well as the Republic of Tatarstan.
On what basis these regions were chosen, history is silent. But almost immediately, as soon as the new rules came into effect in practice, potential taxpayers began to ask questions about the extension of Federal Law No. 422-FZ to other regions. To this, representatives of the Ministry of Finance responded that the decision to expand the list of constituent entities of the Russian Federation - participants in the experiment to establish a special regime in the form of NAPs starting in 2022 will be made based on the results of an analysis of the interim results of the experiment (Letter dated June 27, 2019 No. 03-11-11/47162) . What are its results? Results of the experiment on the use of a special regime in the form of NPD
Let's start with the numbers. According to the Federal Tax Service, as of October 31, 2019, the number of registered NPD payers amounted to 260 thousand people, including by region:
— Moscow — 151.7 thousand individuals;
— Moscow region — 55.7 thousand individuals;
— Kaluga region — 5.9 thousand individuals;
— Republic of Tatarstan — 46.6 thousand individuals.
At the same time, the total income received from the implementation of activities by NAP payers as of this date is about 30 billion rubles.
Based on these data, the Federal Tax Service concluded that the features of this regime (simplified registration procedure without the need to visit the tax authority, exemption from the use of cash registers, absence of any reporting to government bodies, comfortable tax rates) were in demand by taxpayers who had not previously paid taxes.
In addition, monitoring of NAP payment also showed that about 50?% of taxpayers (of registered NPA payers) did not declare their income in 2022. Based on this, the Federal Tax Service considered that they did not pay any taxes and other obligatory payments, working entirely in the shadow sector of the economy. But one can argue with this: at least some of the designated persons only began their activities in 2022.
The first results of the experiment, according to supporters of expanding the scope of application of the special regime in the form of NAPs, allow us to assert that today this tax regime provides a solution to the main task of its introduction - creating incentives for people to come out of the shadows.
Self-employed bank accounts
Can a self-employed person open a bank account?
A self-employed person has the right to open a bank account. There are no legal restrictions for this.
Why can a bank block a self-employed person’s account and card?
The bank has the right to block the bank account/card of a self-employed person on the basis of “dubiousness” of the transactions being carried out (Clause 11, Article 7 of the Federal Law of 07.08.2001 No. 115-FZ “On combating the legalization (laundering) of proceeds from crime and the financing of terrorism”) .
In this regard, the Federal Tax Service recommended that self-employed people inform the banks in which they have accounts about their activities.
How self-employed people interact with the Federal Tax Service
How to report to the tax authorities for income received and taxes paid
Self-employed people do not submit any tax returns or calculations to the Federal Tax Service (Article 13 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
As for taxes, tax authorities independently calculate the tax payable based on the information received from the “My Tax” mobile application.
How does the tax office find out how much a self-employed person has earned?
Information about each settlement related to the receipt of income from the sale of goods (work, services, property rights) is transmitted to the Federal Tax Service through the “My Tax” mobile application. This is where the self-employed person’s obligation to submit reports to the inspectorate ends.
The composition of the transmitted information about calculations and the procedure for their transmission are established by the procedure for using the “My Tax” mobile application (Part 1, Article 14 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ).
Self-employed and online cash registers
Should self-employed people use online cash registers?
Self-employed people are not required to use online cash registers when making payments to buyers/requesters of services (work).
Self-employed people generate and transmit all cash receipts and payment information using the “My Tax” mobile application (Part 1, Article 14 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
How self-employed people give checks to customers
Receipts are generated by self-employed people using the “My Tax” mobile application and sent to customers. The check can be submitted electronically or on paper. In the second case, the receipt is simply printed from the mobile application and given to the buyer.
An electronic check can be sent to the buyer in two ways: either to a subscriber number or email address, or by providing the buyer with the ability to read the QR code contained in the check (Part 5, Article 14 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ).
Individual entrepreneurs (self-employed), who are payers of professional income tax, can account for income and generate checks for transmission to the inspectorate directly in the 1C program (in the cloud “1C: Enterprise via the Internet” and “1C: BusinessStart”).
1C for self-employed: accounting for tax obligations and current activities
At what point must a self-employed person give the check to the buyer?
As a general rule, the self-employed person is obliged to hand over the check to the buyer at the time of settlement. This applies to cash payments, as well as payments using electronic means of payment.
For other forms of non-cash payments (for example, by means of a payment order), the check can be transferred to the buyer no later than the 9th day of the month following the month of payment (Part 3 of Article 14 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ).
Should a self-employed person hand over receipts when selling goods through commission agents?
When selling goods (work, services) in the interests of a self-employed person on the basis of agency or commission agreements, the self-employed person does not have the obligation to hand over a check.
The responsibility for using the cash register and transferring checks in such cases lies with the intermediary - the commission agent or agent (Part 2 of Article 14 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ).
Prospects for the self-employed
Will taxes for the self-employed be raised or new taxes introduced in the next few years?
There are no plans to increase taxes for self-employed people in the coming years.
The experiment with self-employment will last until December 31, 2028 inclusive. During these 10 years, a ban is established on increasing tax rates and reducing the income limit for the self-employed (Article 1 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
Is it possible for an entrepreneur to switch from individual entrepreneur mode to self-employment?
The law allows individual entrepreneurs to switch to paying tax on professional income. At the same time, the status of an entrepreneur does not cease.
At the same time, if the individual entrepreneur was previously on the simplified tax system, UTII or unified agricultural tax, he is obliged to refuse the applied special regime. To do this, the individual entrepreneur must send a corresponding notification to the Federal Tax Service. The notification must be sent within one month from the date of registration as self-employed.
Otherwise, registration of an individual entrepreneur as a self-employed person is canceled (Part 5, Article 15 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018). At the same time, if the individual entrepreneur used OSNO, there is no need to submit a notice of termination of the application of the special regime to the Federal Tax Service.
Can an individual entrepreneur simultaneously apply the simplified tax system and be self-employed (for example, if he has several types of activities)
The tax on professional income cannot be combined with the use of other special tax regimes (STS, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax). Moreover, even in cases where an individual plans to conduct different types of activities under different special regimes.
An individual entrepreneur can pay income tax under the simplified tax system/UTII or switch to paying professional income tax on all income. You cannot combine special modes (Part 5, Article 15 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
What is the annual income limit after which it is unprofitable to work in self-employment format?
There is no such border. An individual independently decides whether to remain self-employed or switch to another special tax regime.
However, the legislation establishes a maximum annual income (2.4 million rubles), if exceeded, the right to use the special regime is lost (Part 2, Article 4 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
A self-employed person is prohibited from having employees under an employment contract. But can he formalize them under a GPA agreement or in some other way?
According to the law, persons who have employees with whom they have an employment relationship cannot be registered as self-employed. That is, formally the law deals specifically with employment contracts (Part 2 of Article 4 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ).
The law says nothing about hiring employees under contract or paid services.
However, this will not prevent tax authorities, if necessary, from recharacterizing the GPA agreement into an employment contract and assessing additional taxes to the self-employed. So it is still better for the self-employed to refrain from hiring employees.
What should a self-employed person do if his income exceeds the limit of 2.4 million rubles per year?
If this year an individual’s income exceeds 2.4 million rubles, he is automatically deregistered as self-employed.
It will be possible to re-register only next year. To do this, you will need to submit an application to the Federal Tax Service. An individual has the right to re-register only if he has no arrears in taxes and fines (Article 5 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
How to live as a self-employed citizen
How can a self-employed person confirm his income to obtain a loan or a Schengen visa?
In order for self-employed people to obtain information about the amount of income subject to personal income tax, the Federal Tax Service has developed a special certificate on the status of calculations (income) for professional income tax (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 5, 2019 No. SD-4-3/10848).
The specified certificate can be generated in electronic form in the “My Tax” mobile application and in the “My Tax” web account. The generated certificates are signed with an electronic signature of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
How do self-employed people pay child support?
The legislation does not establish any special rules for the self-employed regarding the payment of alimony. Self-employed people pay alimony on a general basis.
In this case, information about the income received by the self-employed is taken based on data from the “My Tax” mobile application.
Can a self-employed person receive sick leave benefits?
Self-employed people are not recognized as payers of insurance premiums for the period of their application of the special tax regime of the NAP (Part 11, Article 2 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ).
Thus, as a general rule, the self-employed cannot receive temporary disability benefits.
However, an NPA taxpayer can enter into a voluntary health insurance agreement and receive an insurance payment in case of disability.
How is seniority and pension calculated for the self-employed?
As part of the tax regime for self-employed people, there is no mandatory deduction of contributions to the Pension Fund. In this case, the pension can only be social, which is paid in the minimum amount. At the same time, a self-employed person can voluntarily enter into legal relations with pension insurance and contribute funds to the Pension Fund.
In this case, the pension amount will be higher than the social pension. To obtain a year of insurance experience, you must be registered with the Pension Fund for the entire year and pay insurance premiums.
For 2022, this minimum contribution amount is 29,354 rubles.
In order to voluntarily join the compulsory pension insurance system, a self-employed person must send an application to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in the form approved. by order of the Ministry of Labor dated May 31, 2017 No. 462n.
Expanding the types of activities for paying NAP
Another important amendment was made to Federal Law No. 422-FZ: from 2020, paragraphs.
9 paragraph 2 art. 6 is declared invalid. This norm stated that for the purposes of paying NAP, income from the activities specified in paragraph 70 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, received by persons registered with the tax authority in accordance with clause 7.3 of Art. 83 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is income in the form of payments (rewards) received by individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs from individuals for the provision of the following services to them for personal, household and (or) other similar needs: - for the supervision and care of children, sick persons, persons who have reached the age of 80 years, as well as other persons in need of constant outside care according to the conclusion of a medical organization;
- tutoring;
- Cleaning residential premises and housekeeping.
Note that from 2022, paragraph 70 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation actually loses its effect, since this norm was in force only from 2022 to 2022.
The innovation under consideration will allow taxpayers who have previously sent notifications about the implementation of activities to provide services to an individual for personal, household and (or) other similar needs, from 2022 onwards, to pay NIT on income received from such activities.
The practice of applying a special regime in the form of payment of NAP
Since the territory of application of the special regime has been significantly expanded since 2022, the issues that arise during the implementation of the provisions of Federal Law No. 422-FZ become even more relevant. Let's look at some of them.