Line 1240 of the balance sheet: financial investments (except for cash equivalents)
- Purpose of the article: generalization of available information on the placement of a company's free funds for short-term investment (for example, providing short-term loans to counterparties) for a period of less than 12 months in order to extract additional profit.
- Line in the balance sheet: 1240.
- Account numbers included in the line: debit account balance 58 + debit account balance 55 – credit account balance 59.
The term short-term financial investments (with the exception of cash equivalents) includes operations for the temporary placement of the company’s own free funds, i.e., assets of an enterprise without a tangible form, but which are capable of generating additional income in the future:
- Securities: shares, bills, bonds, etc.
Debt securities are included in this category if the price and date of full repayment are agreed upon in advance, such as promissory notes. In line 1240, an enterprise must reflect only those debt securities whose maturity does not exceed 12 months.
- Borrowed funds provided by a legal entity to other companies to obtain benefits in the form of interest paid for the use of funds for a period of less than 12 months.
- availability of documentation confirming the organization’s rights to these assets and to receive additional income from the use of this right - for example, a loan agreement, etc.;
- recognition by the organization of all potential risks associated with the investment procedure (bankruptcy of counterparties, price fluctuations on the stock market, depreciation of assets, etc.);
- obtaining additional income from investments made in the future (for example, for transactions with securities, additional income may arise upon resale - the realized value may be much higher than the purchase price).
All procedures for placing free funds for a period of more than 12 months are displayed in line 1170 based on the results of the year. In this regard, it is necessary to supplement account 58 with subaccounts in advance to separate investments by maturity.
Short-term financial investments are made when there are available funds, for example, when business is seasonal. Then you can get a lot of additional income in a short period of time.
In accordance with the accounting rules, in order to include the company's placed funds in the assets of the company, it becomes necessary to comply with a number of mandatory conditions:
Line 1240 of the balance sheet refers to the section of current assets: it collects generalized information about the company’s short-term financial investments made during the reporting period for a period of less than a year, the purpose of which is to extract additional benefits (for example, interest on loans or the difference in the price of shares upon resale).
Note from the author! Line 1240 does not display cash equivalents - highly liquid financial investments with an insignificant risk of changes in value and that can be easily converted into cash (a pre-agreed amount). An example of cash equivalents is demand deposits with credit institutions.
Accounting for financial investments
The placement of investments is accounted for on account 58, based on their original cost. We list the main wiring used in typical situations:
| Operations | D/t | K/t |
| Opening a deposit, transferring money to counterparties at interest | 58 | 51,52,55 |
| Acquisition of Central Bank | 58 | 76 |
| Repayment of debt on loans provided | 51,52,55 | 58 |
| Write-off of the Central Bank | 90/2,91/2 | 58 |
| Central Bank revaluation: | ||
| revaluation | 58 | 91 |
| cost reduction | 91/2 | 58 |
| creation of a reserve for depreciation of financial investments | 91/2 | 59 |
The information on line 1240 of the balance sheet is generated at the end of the reporting period according to the algorithm: the sum of the debit balances of accounts 58, 55 and 73 (in terms of loans to personnel), reduced by the amount of the formed reserve for the depreciation of investments - the credit balance of the account. 59.
Balance sheet, line 1240: what does this include?
Since the 2nd section of the balance sheet is being considered, it means that we are talking exclusively about working capital, i.e. the amounts of such investments cannot be directed directly to the acquisition of fixed assets or intangible assets, the construction of buildings or the modernization of production. The concept of short-term investment includes only operations for placing a company's money in assets that do not have a material form, but are capable of generating income, for example, interest on loans or the difference in the price of resold shares.
Thus, in the balance sheet line 1240, its interpretation, includes financial investments, which mean the acquisition:
various securities (CS) - state, municipal or commercial;
debt securities, in particular, bills with a set value and a maturity date within 12 months;
shares in the authorized capital of third-party companies, including subsidiaries or dependent companies;
Line 1230 of the balance sheet (230, 240): decoding, principles of structure of line codes
Each line of the balance sheet has a code that allows you to identify the data contained in it. The main consumers of these codes are statistical and regulatory authorities, which can carry out analytical work on them.
Currently the codes are 4 digits long. For example, line 1230 of the balance sheet, former line 240, contains accounts receivable in the breakdown. This line shows the amount of debt that its partners, counterparties and other persons interacting with it have to the company in a certain period of time.
Line 230 also belonged to this category and reflected debts that could be repaid in no earlier than 12 months.
The balance sheet line codes contain very specific information:
- The first digit is that it belongs specifically to the balance sheet and not to another document.
- The second digit indicates belonging to a specific section of the asset.
- The third number shows the place of this asset in the liquid ranking. The higher the liquidity, the higher the number.
- The fourth digit is required for line detail. Thus, the requirements contained in PBU 4/99 are met.
Using a similar principle, we will selectively describe which codes correspond to the strings and provide a brief explanation of them. We will separately indicate in the table the new and old codes, since the balance must be drawn up for 3 years, and 2 years ago the previous code values were still in effect.
Features of filling line 1240
In this case, it is worth taking into account the actual costs that were allocated for the acquisition of financial investments in the form of assets. So, in line 1240 you need to indicate all amounts that the seller received under the main agreement, for example, for consultation or provision of any information. These amounts include rewards. At the same time, they must be transferred to the person who transferred the assets for use to the company, as well as all costs associated with them.
In line 1240, when accounting for investments such as securities, you need to take their current market value based on the date of acceptance in accounting. It is calculated in the manner established by the organizer of securities trading.
If there are financial investments that were transferred to the organization free of charge, you need to take into account their current market value, as well as the amount that can be generated from their sale in accordance with the date of their entry and determination in accounting.
You also need to disclose information such as methods for evaluating these investments when written off. To do this you need:
- Distribute them by type or other criteria;
- Then write down the consequences of differentiating these valuation methods. Write down their value even if their market value cannot be determined. If it was determined initially, then reveal the difference between the current and previous value, as well as the original and nominal;
- If there are investments that are taxed, as well as those that were transferred to other organizations, you need to disclose their value in accordance with their types.
After this, enter data on reserve financial investments for impairment. Also transfer this data in the notes to the balance sheet and reporting on the results of financial operations.
Regulatory regulation
The rules for recognizing investments as short-term financial investments in the assets of an enterprise are reflected in accounting in accordance with PBU 19/02, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 10, 2002 No. 126n.
Example 1
In 2022, Aktsiya LLC decided to temporarily withdraw a certain amount of funds from circulation and place them as a bank deposit. Terms of the deal: deposit amount – 500 thousand rubles, contract period – 3 months.
Since the bank deposit agreement stipulates a period for the return of funds and it is 3 months, at the end of the reporting year, Aktsia LLC will display the amount of invested funds in line 1240 of the balance sheet.
Example 2
Solnyshko LLC and Kod LLC entered into an agreement on the provision of borrowed funds on December 12, 2017:
- loan amount: Solnyshko LLC provides a loan in the amount of 250 thousand rubles;
- repayment period of obligations: according to the agreement, the loan must be fully repaid, including all accrued interest on it, no later than 10/12/2018;
- borrowed funds are issued at 10% per annum.
Posting in the accounting records of Solnyshko LLC: Dt58.03 Kt51.
Since the terms of the loan agreement stipulate the terms of repayment of obligations, and there is also evidence that these funds were transferred for the purpose of generating additional income, this transaction is reflected in the accounting records of Solnyshko LLC as part of financial investments. Since the contract period is 10 calendar months, the company will display information about the short-term placement of funds in line 1240 of the balance sheet at the end of 2022.
How to calculate cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year
To calculate the value of the most highly liquid assets, use data from financial statements submitted to the tax authorities annually. For small enterprises, a simplified form is used, where the indicator we need is contained in a line with the same number as in the report for medium and large organizations - 1250.
Thus, the formula for finding cash in the balance sheet is very simple: just take the value of line 1250. The only difficulty is how to fill out this line correctly. Problems sometimes arise when separating deposits and securities with a short maturity, which are taken into account as part of financial investments (account 58). For convenience, it is recommended to account for such assets in separate subaccounts with a special mark.
Examples
An example of calculating the amount reflected on line 1250, No. 1:
Let's calculate the amount of cash in the balance sheet: 51,500.00 + 658,021.22 + 630,000.00 = 1,339,521.22 rubles.
Financial investments in the amount of 630,000.00 rubles. - These are bills with a maturity of less than three months.
Accounting for cash equivalents
As already mentioned, to account for DE, account 58 is used - “Financial investments”. Since only short-term investments are recognized as equivalents, you need to use subaccount 58.1 - “Short-term deposits”. Accounting is carried out both for each type and for DE in general. For subaccount 58.1, an additional analytical subaccount is opened - 58.2.1.
Since the account is active, the increase in DE is reflected in the debit of the account. If there is a decrease in DE, for example, their implementation, then count. 58 is reflected on the loan. The balance is debit.
The formula for calculating the balance at the end of the period is as follows:
Balance at the beginning of the period + Debit turnover – Credit turnover.
There cannot be a credit balance on financial investments. At most, the enterprise can break even.
Documentation
Financial contributions are documents of the following type:
- Securities of a state and municipal nature.
- Those for which the cost of full repayment is certain.
- Loans provided to other organizations.
- Deposits in organizations that issue loans.
- Receivables purchased on the basis of a right of claim.
- Contributions in accordance with the partnership agreement.
- Investments of other types.
Accounting
On account 1260, only current assets that are not recognized as significant can be taken into account. The information is generated based on the following data:
- The cost of expenses for already completed stages of construction of an unfinished facility, which has independent significance and is calculated on the basis of the contract.
- Data on unreported revenue that was generated as a result of a construction contract agreement whose duration is more than one year, or when the start and end dates of work are set for different reporting years. It is calculated based on the cost specified under the contract or information on costs incurred during the specified period during the execution of work, if the possibility of their reimbursement was recognized.
- The cost of losses due to shortage or damage to valuables, which was not included either in production costs or accrued as a debt to the account of the guilty party.
- The amount of VAT that was accrued on advance payments and prepayments is displayed in accounts 62 and 76 in a separate form.
- Total estimate of excise taxes that will be deducted.
- The cost of VAT calculated on shipped goods is from revenue that cannot be taken into account in a given period and is accounted for separately on account 76 and 45.
- VAT and excise taxes calculated for exports, which are not confirmed and will be covered from budget funds in the future.
Therefore, the size of the cost indicator in line 1260 directly depends on:
- Estimates of the debit balance for accounts 46 and 94.
- Balances recorded in debit for analytical type accounts 62 – VAT, 68, 76 and 45 as of the date of the report.
Example: during accounting, a shortage of 32,000 rubles was identified at the Snezhinka weaving enterprise. On January 21, an advance payment for products was received in the amount of 324,000 rubles, including accrued VAT.
On January 27, products worth 462,000 rubles were shipped. with VAT in accordance with the concluded agreement. The cost of the finished goods was 212,000 rubles.
How to display in accounting:
- Write-off of the cost of shortage or missing goods - 32000. Posting: Dt. 94 K. 41.
- Prepayment received on account of future shipment - 324000. Posting: Dt. 51 K. 62 Av.
- Value added tax accrual – 49423.43. Wiring: Dt. 76 K. 68.
- Accounting for shipped goods – 212000. Posting: Dt. 45 K. 41.
- VAT accounting - 70474.58. Wiring: Dt. 76 K. 68.
Line 1260 will display:
32000 + 49423,43 + 70474,58 = 151898,01.
In cases where, after an accounting audit, an increase in the values in line 1260 “Other working capital” was revealed, we can say that the company is using the available cash resources and funds efficiently and stably.
It is recommended to conduct a specialized analysis of current assets regularly. This allows you to see the efficiency of use and monitor the dynamics of growth of the company’s funds.
Deferred expenses in current assets are presented below.
How to decrypt strings
In order to understand how the process of deciphering codes line by line is carried out, it is worth understanding that not a single code is a simple set of numbers. This is a code for a certain type of information.
- The first value confirms the fact that this line relates specifically to the main type of accounting statements, or rather, to the balance sheet, and not to another type of reporting documents.
- The second digit indicates which section of the asset the amount belongs to. For example, a unit indicates that the amount belongs to non-current assets.
- The third figure serves as a certain indicator of the liquidity of this resource.
- The fourth digit is initially equal to zero, adopted in order to provide some detailing of the items according to their materiality.
For example, deciphering line 1230 of the balance sheet is accounts receivable.
For a liability, decoding occurs according to the same principle as in the situation with an asset:
- The first digit indicates that it belongs specifically to the balance sheet for the year.
- The second figure demonstrates that this amount belongs to a separate section of the liability column.
- The third number indicates the urgency of the obligation.
- The fourth value is adopted for detailed perception of information.
Example. Filling out the balance sheet
The LLC, registered in 2015, applies a simplified taxation system. The indicators of the accounting registers as of December 31, 2015 are shown in the table:
Table
Balances (Kt - credit, Dt - debit) on the accounting accounts as of December 31, 2015 of LLC
| Balance | Amount, rub. | Balance | Amount, rub. |
| Dt | 600 000 | Dt | 150 000 |
| CT | 20 040 | CT | 150 000 |
| Dt | 100 000 | Kt (sub-account “Advances”) | 505 620 |
| CT | 3340 | ||
| Dt | 17 000 | CT | 89 000 |
| Dt | 6000 | CT | 250 000 |
| Dt | 90 000 | CT | 50 000 |
| Dt | 15 000 | CT | 10 000 |
| Dt | 250 000 | CT | 150 000 |
Based on the available data, the accountant compiled a balance sheet for 2015 in a general form:
Column 4 is the only one that requires filling out by the newly created organization. This column reflects data as of December 31 of the reporting year, that is, 2015.
Column 3 is also added to indicate line codes.
The accountant determined the indicator for line 1110 “Intangible assets” as follows: the credit balance of the account is subtracted from the debit balance of the account.
In total we get 96,660 rubles. (RUB 100,000 – RUB 3,340). All values on the balance sheet are in whole thousands, so line 1110 shows 97.
The indicator of line 1150 “Fixed assets” is defined as follows: debit account balance – account credit balance. Result – 579,960 rubles. (RUB 600,000 – RUB 20,040). 580 is recorded in the balance.
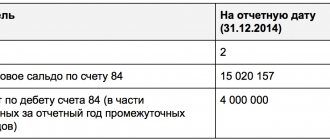
In line 1170 “Financial investments” the debit balance of the account is entered - 150 thousand rubles. (that is, it is considered that all investments are long-term).
Total for summary line 1100: 827 thousand rubles. (97 thousand rubles (line 1110) + 580 thousand rubles (line 1150) + 150 thousand rubles (line 1170)).
Now it’s the turn of current assets. The value of line 1210 “Inventories” is defined as follows: debit account balance + debit account balance. Result – 107 thousand rubles. (17 thousand rubles + 90 thousand rubles).
The indicator in line 1220 “Value added tax on acquired assets” is equal to the debit balance of the account, therefore the accountant added 6 thousand rubles to the balance sheet.
The indicator for line 1250 “Cash and cash equivalents” was found by adding the debit balance of the account and the debit balance of the account. The result is 265 thousand rubles. (15 thousand rubles + 250 thousand rubles). The line contains 265.
Total for summary line 1200: 378 thousand rubles. (107 thousand rubles (line 1210) + 6 thousand rubles (line 1220) + 265 thousand rubles (line 1250)).
The final line 1600 shows the sum of the indicators of lines 1100 and 1200. That is, 1205 thousand rubles. (827 thousand rubles + 378 thousand rubles).
The remaining lines of column 4 are filled with dashes.
Let's move on to the balance sheet liability. The indicator on line 1310 “Authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners)” is equal to the credit balance of the account, that is, the balance sheet costs 50 thousand rubles.
Line 1360 “Reserve capital” – account credit balance. In our case, this is 10 thousand rubles.
Line 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” shows the account balance. It's credit. This means that the organization has a profit at the end of the year. Its value is 150 thousand rubles. There is no need to put the indicator in brackets.
The summary line indicator 1300 is equal to 210 thousand rubles. (50 thousand rubles (line 1310) + 10 thousand rubles (line 1360) + 150 thousand rubles (line 1370)).
The indicator for line 1520 “Accounts payable” (the accountant considered that all debt is short-term) is defined as follows: account credit balance + account credit balance + account credit balance + account credit balance. The result is 995 thousand rubles. (150 thousand rubles + 506 thousand rubles + 89 thousand rubles + 250 thousand rubles).
The accountant transferred the value from line 1520 to line 1500, since the other lines of section. V balance sheets were not filled out.
The total line indicator 1700 is equal to the sum of lines 1300 and 1500. The resulting value is 1205 thousand rubles. (210 thousand rubles + 995 thousand rubles).
The remaining liability lines are crossed out due to the lack of relevant data.
The indicators for the total lines 1600 and 1700 are equal. In both lines the value is 1205 thousand rubles. The balance is correct, which means that the form can be considered compiled correctly.
What company costs are included in other expenses?
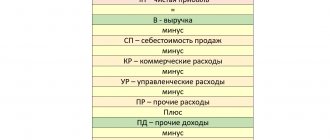
Expenses classified by the company as other are shown in the report under consideration on line 2350. Interest payable should be excluded from them.
Other costs include:
- costs incurred as a result of the company's participation in the charter of third-party business entities
- expenses caused by the write-off or sale of manufactured products, goods, fixed assets
- interest paid by an enterprise on credit and other similar obligations
- service costs in organizations lending business
- debt of counterparties with an expired statute of limitations
- expenses for issuing property for rent, including objects related to the company’s intellectual property
Formula School
Balance sheet (line 1160) Profitable investments in material assets. …More Step 1