- The purpose of the articles is to display information about the company’s liabilities, the amount or maturity of which has not been determined.
- Lines in the balance sheet: 1430, 1540.
- Account numbers included in the line: account credit balance. 96.
In accordance with current legislation, a provision is a debt of an organization, the amount or maturity of which cannot be reliably determined.
Possible reasons for the appearance of this type of obligation:
- norms of current legislation and other regulatory documentation, legal proceedings, business customs;
- the expectations of a circle of people that the company will fulfill the obligations assumed as a result of the activities of past years, for example, an announced restructuring.
Recognition in accounting is permissible if the following mandatory conditions simultaneously meet:
- As a result of actions in past periods, the organization has acquired debt, the repayment of which cannot be avoided.
- There is likely to be a reduction in the economic benefit required to settle the provision. A reduction is considered probable if it is more likely than not that such a reduction will occur. Determined separately for each uncertain situation.
- The extent of the company's responsibilities can be reasonably estimated. In this case, an assessment must be made of the amount of possible costs of funds that the company will spend to repay the debt. The assessment is carried out on the basis of expert opinions and experience in conducting business activities of the organization.
Note from the author! According to the accounting regulations, documentary evidence of the validity of the conclusion about the amount of liabilities is required.
Examples of estimated liabilities:
- possible costs when restructuring an organization (if there is a detailed plan that contains information about the activity, the location of its implementation, the timing of the start of the restructuring, etc.);
- likely costs of litigation;
- the fact that the transaction is likely to be unprofitable is known in advance;
- warranty obligations;
- guarantee in favor of third parties whose performance period has not yet arrived;
- reserve for payment of employee vacations;
- reserves for the upcoming expenditure of money on preparation for the season during seasonal production, etc.
In accounting on the account. 96 records information about the creation of reserves to pay off emerging obligations, the funds from which will be included in expenses evenly. Account 96 is active-passive: the loan shows the reservation of calculated amounts in correspondence with the accounts of production costs or costs of selling goods and services. The actual expenditure of funds for which the reserve was created is displayed as a debit. The correctness of the calculation of the amount of reserves must be periodically re-evaluated and adjustments made.
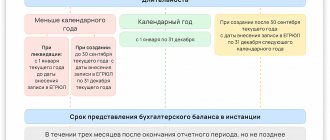
Lines 1430 and 1540 in the balance sheet reflect the amount of outstanding estimated liabilities as of December 31 of the current year, the previous year and the previous year. In this case, line 1430 displays short-term liabilities for a period of less than 12 months, and line 1540 – more than 12 months.
Calculation of the amount of the estimated liability
- The value is defined as the weighted average of a set of values.
- The value is determined by selecting from a certain range of values, calculated as the arithmetic mean of the largest and smallest values.
When making an assessment, the following are taken into account:
- consequences arising after the end of the reporting period;
- possible risks;
- future events likely to affect the amount of the estimated liability.
According to the accounting rules, if the probable repayment period is more than 12 months, then the amount of the estimated liability is calculated taking into account discounting, and the discount rate should reflect the existing market conditions and possible risks.
When do estimated liabilities arise?
Such obligations may arise as a result of court decisions, obviously unprofitable contracts, as a result of the company’s actions, when confidence is created that it will fulfill its promises. For example, the upcoming closure of a company branch may lead to an increase in the cost of paying severance benefits to staff or the termination of contracts for which a penalty will have to be paid. At the same time, in order to form a reserve for the costs of restructuring production, the following conditions must be met:
- there is an action plan that determines the approximate amount of costs;
- management began implementing this plan - for example, notices of upcoming dismissal were sent to employees, letters of termination of cooperation to contractors.
If the company becomes aware of the unprofitability of the concluded contract, and termination threatens to impose an impressive fine, then the estimated liability is recognized in the smallest amount - the loss from the execution of the contract or the fine upon its termination. A reserve is created in the month when the unprofitability of the agreement is established.
Example
The company has entered into an agreement for the supply of its products. Estimated revenue – 2000 thousand rubles. In connection with the changed market situation (increasing prices for raw materials), the company carried out an assessment, the result of which was the conclusion: the cost of manufactured products will be 2,500 thousand rubles. Execution of the terms of the agreement has not begun. The penalty for unilateral termination is indicated in the amount of 700 thousand rubles.
Such an agreement is considered obviously unprofitable, since the costs of its implementation will exceed the planned income, and for the termination of the contractual relationship the company is obliged to pay 700 thousand rubles.
Since losses in this situation are inevitable, the estimated liability will be recognized in the company’s accounting in the amount of the smaller loss - 500 thousand rubles. when fulfilling the contract (2500 - 2000), since the amount of the penalty for termination is 700 thousand rubles.
Practical examples on calculating the amount of an estimated liability
Example 1
In 2022, Company LLC was a defendant in a lawsuit against Firm LLC. At the end of the reporting year, the case was not completed, but the expert assessment is inclined to believe that the court decision will not be made in favor of the company. Possible losses of LLC "Company" depend on the court's decision: 20 thousand rubles, if a verdict is issued on compensation of the plaintiff's direct costs; 30 thousand rubles – if necessary to cover the plaintiff’s lost profits. Expert opinion on options for a court decision: 80 to 20%.
Despite the fact that it is possible that the outcome of the proceedings will be in favor of compensation of only direct costs, in the accounting of an LLC, the calculation of estimated liabilities is carried out taking into account the possibility of compensation for the plaintiff’s lost profits:
20,000 * 0.8 + 30,000 * 0.2 = 22 thousand rubles.
It is assumed that the maturity of the estimated liability is 6 months. In accounting, this obligation is reflected in the account. 96 in the amount of 22 thousand rubles.
Estimated liabilities. Line 1540
This line reflects short-term estimated liabilities recognized in accordance with the norms of PBU 8/2010.
What estimated liabilities are reflected in line 1540 “Estimated liabilities”?
Line 1540 “Estimated Liabilities” reflects the amounts of estimated liabilities recorded on account 96 “Reserves for future expenses”, the expected fulfillment period of which does not exceed 12 months after the reporting date (clauses 4, 8 of PBU 8/2010).
The estimated liability is recognized in accounting if the following conditions are simultaneously met (clause 5 of PBU 8/2010):
— the organization has an obligation resulting from past events of its economic activities, the fulfillment of which the organization cannot avoid;
— there is likely to be a decrease in the economic benefits of the organization necessary to fulfill the estimated liability;
— the amount of the estimated liability can be reasonably estimated.
An estimated liability, the expected period of fulfillment of which does not exceed 12 months after the reporting date or a shorter period established by the organization in its accounting policies, is recognized in accounting in the amount reflecting the most reliable monetary estimate of the expenses necessary for settlements on this liability (clause 15 of PBU 8 /2010).
What accounting data is used when filling out line 1540 “Estimated liabilities”?
When filling out this line of the Balance Sheet, data on the credit balance as of the reporting date for account 96 is used in terms of estimated liabilities, the expected settlement period of which does not exceed 12 months after the reporting date.
Line 1540 “Estimated liabilities” = Credit balance on account 96 in terms of estimated liabilities with a maturity date of no more than 12 months after the reporting date
In general, the indicators on line 1540 “Estimated liabilities” as of December 31 of the previous year and as of December 31 of the year preceding the previous year are transferred from the Balance Sheet for the previous year.
The “Explanations” column provides an indication of the disclosure of this indicator. If an organization draws up Explanations to the Balance Sheet and the Statement of Financial Results according to the forms contained in the Example of Explaining Explanations given in Appendix No. 3 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 66n, then in the column “Explanations” on line 1540 “Estimated liabilities” it indicates table 7 “Estimated liabilities”, which discloses the indicators of line 1540 of the Balance Sheet.
Example of filling out line 1540 “Estimated liabilities”
Indicators for account 96: rub.
| Index | As of the reporting date (December 31, 2014) |
| 1 | 2 |
| 1. The amount of credit balances on analytical accounts to account 96, which account for estimated liabilities with a maturity period of no more than 12 months after the reporting date | 800 000 |
Fragment of the Balance Sheet for 2013
| Explanations | Indicator name | Code | As of December 31, 2013 | As of December 31, 2012 | As of December 31, 2011 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 7 | Estimated liabilities | 1540 | 400 | 600 | 480 |
Solution
The amount of short-term estimated liabilities is:
as of December 31, 2014 - 800 thousand rubles;
as of December 31, 2013 - 400 thousand rubles;
as of December 31, 2012 - 600 thousand rubles.
A fragment of the Balance Sheet will look like this.
| Explanations | Indicator name | Code | As of December 31, 2014 | As of December 31, 2013 | As of December 31, 2012 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 7 | Estimated liabilities | 1540 | 800 | 400 | 600 |
Formula for calculating net assets
The key procedure for calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is determined by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and is presented in a separate order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. Please note that previously a different procedure was in effect, but it is not currently used.
This formula for net assets on the balance sheet is applicable to the following range of economic entities:
- public or non-public joint stock companies;
- state or municipal unitary enterprises;
- limited liability companies;
- production cooperatives or housing cooperatives;
- business partnerships.
Net assets formula:
NA = (AO - DU - ZA) - (OB - DBP),
Where
- JSC - the amount of non-current and current assets of an economic entity as of the reporting date;
- DE - debt of the founder incurred to the enterprise for the formation of the authorized capital;
- FOR - debt on own shares generated upon issue;
- OB - the sum of the company's short-term and long-term liabilities;
- DBP - future income in the form of state financial support or gratuitous transfer of property assets.
How to calculate net assets according to balance sheet lines?
To calculate the net asset value on the balance sheet, the calculation lines use the following:
NA = (line 1600 – DU) – (line 1400 + line 1500 – DBP).
Calculating the amount of net assets in the balance sheet (the lines indicated above) using a pencil calculator is not enough. This calculation must be documented. However, a unified form for reflecting calculated data is not provided for in Order No. 84n. Organizations are required to independently develop a form and regulate it in their accounting policies.
Note that before the approval of Order No. 84n, the old form was in force (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10 and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of Russia dated January 29, 2003 No. 03-6/pz). In the new instructions, the Russian Ministry of Finance has not prohibited the use of this form, therefore, firms can use it to prepare calculations of net assets in the balance sheet (the document lines contain all the necessary information).
Assets
Line 1150 Tangible non-current assets
- Fixed assets: Dt minus Kt 02.01 minus Kt 02.03 .
- Dt minus Kt 02.02.
- Dt + Dt 08.01 + Dt 08.02 + Dt 08.03 + Dt 08.04 + Dt 08.06 + Dt 08.07 + Dt 08.12.
Line 1120 Intangible, financial and other non-current assets
- Intangible assets: Dt 04.1 minus Kt .
- Dt 04.2 + Dt 08.08.
- Dt 08.05 + Dt 08.11.
- Dt.
- Dt 58.01.1;
- Dt 55.03.
- Dt 08.06 + Dt 08.07;
Line 1210 Inventories
- Inventories: Dt (including special equipment and special clothing) + Dt minus Kt + Dt + Dt minus Kt + Dt + Dt + Dt + Dt + Dt + Dt + Dt minus Kt + Dt;
- plus Dt + Dt 76.01.2 + Dt 76.01.9 (Type of asset – Inventories).
- Dt minus Dt 19.06 .
Line 1250 Cash and cash equivalents
- Cash and cash equivalents: Dt + Dt + Dt + Dt ( except Dt 55.03 and Dt 55.23 ) + Dt.
Line 1230 Financial and other current assets
- Financial investments: Dt 58.01.2 + Dt 58.02 + Dt 58.03 + Dt 58.04 + Dt 58.05 + Dt 55.03 + Dt 55.23 + minus Kt ;
- plus manually Dt 73.01 (short-term interest-bearing loans).
- Dt 62.01 + Dt 60.02 minus Kt 76.VA + Dt + Dt + Dt 73.02 + Dt 73.03 + Dt 76 + Dt 97 minus Kt minus Kt 79 .
Estimated liabilities in the balance sheet
In accounting, PAs are reflected in account 96 “Reserves for future expenses”: accrual on a loan, write-off (repayment) - on a debit.
Posts:
- for reserve formation D/t 20, 23, 25, 26, 44 K/t 96;
- according to its write-off D/t 96 K/t 10, 76, 70, 90.
The correspondence of accounts depends on the nature of the business transaction - the repayment of obligations to counterparties is recorded on accounts 10, 76, to personnel - in account. 70, etc.
The accrued amounts of reserves for PAs are easy to find in the financial statements. Estimated liabilities in the balance sheet are line No. 1430 in the long-term liabilities section and line No. 1540 in the short-term liabilities section.