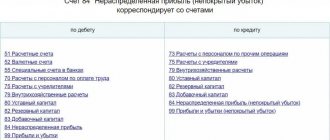
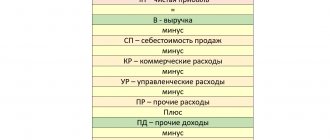
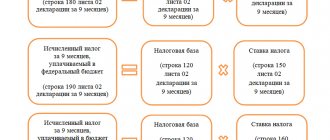
What is retained earnings of an enterprise
A company's retained earnings are its net profit (after tax) that has not yet been divided among the participants (shareholders) of the organization. How such profits will ultimately be distributed depends on the decision of shareholders at the annual meeting. Typically, funds are spent on the following purposes:
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
- payment of dividends to shareholders (participants) of the organization;
- formation or increase of reserve capital;
- fulfillment of remaining obligations;
- other goals chosen by the owners of the enterprise.
Retained earnings are a liability because they are effectively an unfulfilled obligation to the owners of the business. Ideally, the money should be paid as dividends to the owners and used to develop the business. In the same way, a liability is an uncovered loss, which is indicated in parentheses due to its negative value.
| Business valuation | Financial analysis according to IFRS | Financial analysis according to RAS |
| Calculation of NPV, IRR in Excel | Valuation of stocks and bonds |
Is retained earnings an asset or a liability?
Retained earnings on the balance sheet are, of course, a liability. The value of this indicator indicates the company’s actual debt to its owners, since ideally this profit should be distributed among the participants and invested in the further development of the business.
In fact, the company cannot dispose of retained earnings without the owners making a decision. The loss reflected in line 1370 is also on the passive side of the balance sheet, only this is a negative value, so the number is placed in parentheses.
Example of retained earnings and uncovered losses
Let's look at an example of what constitutes retained earnings and uncovered losses:
| Index | Definition | Example |
| retained earnings | The final income that was received by the enterprise as a result of business activities remained after taxation and has not yet been divided by the owners or spent on the needs of the business. | Pobeda LLC in 2022 received a profit in the amount of 755 thousand rubles. Income tax amounted to 125 thousand rubles. The accountant calculates retained earnings: RUB 755,000 — 125,000 rub. = 630 tr. This amount will be reflected in line 1370 of the balance sheet. |
| Uncovered loss | The excess of an enterprise's expenses over its income at the end of the year. | In 2022, Dela Super LLC receives income from production and other non-operating income, in total - 367 thousand rubles. The cost of producing goods is 335 thousand rubles. Other expenses that are not taken into account when calculating income tax - 46 thousand rubles. Income tax - 7600 rubles. There is no reserve capital. Uncovered losses: RUB 367,000 — 335,000 rub. — 7600 rub. — 46,000 rub. = -21,600 rub. The value will be entered in line 1370: (21,600). |
The most common causes of uncovered losses are described in the diagram below:
How is retained earnings calculated on the balance sheet?
Retained earnings increase the liabilities of the balance sheet, and, consequently, the equity capital of the enterprise. Let's look at how to calculate retained earnings (RP) using an example:
Stroika LLC operated in 2022 with a profit of 1 million rubles, income tax (PIT) amounted to 200 thousand rubles. After paying the income tax, the profit amounted to 800 thousand rubles. It is this amount, as retained earnings, that is reflected in line 1370 of the balance sheet for 2017. If at the beginning of the year the NP value already appeared in the balance sheet, then at the end of the year it will be increased by 800 thousand rubles.
The indicator on page 1370 of the balance sheet will correspond to the value on page 2400 of report No. 2 “On financial results” if the company did not have an NP at the beginning of the year, and subsequently did not pay interim (for example, quarterly) dividends.
Factors that can influence retained earnings (uncovered loss)
The amount of retained earnings may increase or decrease during the reporting period depending on what actions the managers and employees of the organization perform:
| Increase in uncovered loss | Reducing uncovered losses |
| Due to the reduction in the volume of authorized capital while bringing its value to the amount of net assets | In connection with the direction of retained earnings to the reserve fund |
| For the amount of additional capital arising during the revaluation of disposed non-current assets during the reporting period | Due to an increase in the size of the authorized capital due to retained earnings |
| For the amount of declared and unclaimed dividends for which the statute of limitations has expired | For the amount of accrued dividends (including interim) |
| On the amount of net profit of the reporting period | By the amount of net loss of the reporting period |
Example of line 1370 in the balance sheet
As of December 31, 2017, the credit balance of account 84 is 365,000 rubles. At the same time, interim dividends in the amount of 29,000 rubles were paid during the year, which corresponded to the accounting entry of the form: Debit account 84 – Credit account 75 “Settlements with founders” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). Therefore, in the balance sheet at the end of 2022, profit and its use for the payment of interim dividends will be reflected as follows:
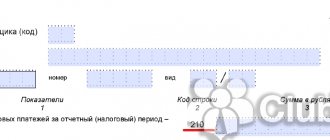
- Line 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”: 365,000
- Line 1371 “incl. interim dividends": (29,000)
Line 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”: how to fill out
First of all, it is necessary to understand several points that are directly related to entering information in line 1370:
- The amount of the enterprise's net profit for the reporting period should be reflected according to the CT account. 99 “Profits and losses” in accounting, and the amount of net loss - according to Dt account. 99.
- If, after approval of the financial statements for the current period, significant errors from the previous period were identified, they must be corrected. Corrections are made by making entries in the relevant accounting accounts in the current reporting period. Account 84 is corresponding. That is, if the company corrected significant flaws in 2014 or earlier periods by making entries in the financial statements in 2015, despite the fact that the 2014 financial statements had already been approved, the indicator on line 1370 of the balance sheet for the reporting period of 2015 containing corrective entries should be formed taking into account the correctional entry.
- The accountant must reflect the accrual of dividends according to Dt account. 84 in correspondence with account. 70 and count. 75, sub-account 75-2. This applies to both interim dividends and year-end dividends. If dividends are declared but not claimed, and their statute of limitations has expired, a reverse entry is made for their amount.
- By the final turnover of December, the amount of retained earnings should be taken into account according to the CT account. 84, the amount of uncovered loss - according to Dt account. 84. The amount of net profit or loss of the reporting period should be written off to the account. 84.
Important! The distribution of profit at the end of the period is an event after the reporting date, which indicates that after the reporting date conditions have arisen in which the enterprise carries out its business activities. In the reporting period for which profit should be distributed, no entries are made in accounting (neither in analytical nor in synthetic accounting). But in the next period, the accountant will already make an entry to properly reflect the event. This means that information on the account. 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” in the reporting period will be formed taking into account the decision made in the reporting year on the distribution of profits identified based on the results of the previous year.
Using the resulting retained earnings to modernize and improve the company's production will not lead to either a change in the indicator of line 1370 or changes in the balance of account 84. Let's find out why. The fact is that the formation in accounting of information about the purposes for which funds of retained earnings will be directed is carried out through the organization of analytical accounting for accounts. 84. In it, money from retained earnings that has not yet been used, and which it was decided to use to subsidize the modernization of production and any other events for the purchase or creation of new assets, can be divided. Costs incurred by an enterprise must be recognized in the reporting period in which they occurred, regardless of:
- time of their formation;
- presence/absence of a source of funds (various funds).
When preparing interim reporting, information from accounts 84 and 99 is used to fill out line 1370 for the reporting period. If the value that needs to be entered on line 1370 appears with a minus sign, it should be placed in parentheses to avoid confusion.
Retained earnings of the reporting year
The credit balance at the end of the year according to accounting account 99 is net profit. But in addition to the financial result, this account also reflects some other indicators. You can learn which ones and how not to make mistakes when making transactions from the Typical Situation from K+, having received trial access to the system.
When reforming the balance sheet, it is written off to accounting account 84 (Dt 99 Kt 84) and constitutes retained earnings at the end of the reporting year.
Read about the reformation procedure in the material “How and when to reform the balance sheet?”.
In order to separate the indicators of retained earnings of the current (reporting) year from last year’s, some accountants allocate separate lines 1372 and 1372 in the balance sheet, which respectively reflect the retained earnings of the reporting period and previous years.
The use of retained earnings is the prerogative of the company's owners. And highlighting this financial indicator for different years in the balance sheet is primarily convenient for them. But it is worth keeping in mind that the retained earnings of the past year cannot be fully distributed without taking into account the company’s previous operating results.
IMPORTANT! It must not be allowed that the value of the company’s net assets, after transferring retained earnings of the reporting year for the payment of dividends, becomes less than the size of the company’s authorized capital even if there is a reserve fund. The caution applies to cases where uncovered losses were recorded in previous years. The decision to cover last year's losses from retained earnings of the reporting year is made exclusively by the owners of the company.
But retained earnings for previous years can be distributed by the participants/shareholders of the company not only at the end of the year, but at any time. The main thing is to hold a thematic meeting of all company owners and approve the appropriate decision.
Does an LLC have the right to make incentive payments to employees from retained earnings and how to formalize this, and are they taken into account when calculating the average salary? The answer to this question was prepared by labor inspector in the Nizhny Novgorod region V.I. Neklyudov. Get free trial access to the ConsultantPlus system and get acquainted with the official’s point of view.
Line 1370, annual and interim reporting (balance sheet formula)
On page 1370, enterprise accountants reflect the amount of retained earnings or uncovered losses. The formulas by which the values to be entered in the line can be found differ depending on whether we are talking about interim or annual reporting.
Balance sheet formula for filling out line 1370 for annual reporting:
Balance sheet formula for calculating the value of line 1370 for interim reporting:
To fill in line 1370, you can use the formula
if the following statements are true for the enterprise under study:
- at the beginning of the reporting period there is no retained profit (uncovered loss) from previous periods;
- During the current period, there were no disposals of previously overvalued fixed assets;
- There have been no distributions of interim dividends during the current year.
This is explained by the fact that the amount of retained earnings of the reporting period is equal to the amount of net profit of the reporting period (profit after deduction of tax payments). And the amount of the uncovered loss of the reporting period is the same as the amount of the net loss of the reporting period (loss after taxes). So, if the company does not have retained earnings or uncovered losses from previous periods, and no distribution of interim dividends was made during the reporting period, the indicator on line 1370 will be the same as the value on line 2400 (form No. 2).
Retained earnings: calculation formula
According to general accounting data, retained earnings are a company's net profit after taxes that can be distributed to the company's owners.
Based on global financial practice, retained earnings (hereinafter referred to as RR) are calculated using the following formula:
NPk = NPn + PE – Div,
Where:
NPk - NP at the end of the reporting year;
NPn - NP at the beginning of the reporting period;
PE - net profit remaining after accrual of income tax;
Div - dividends paid in the reporting year based on the NP of previous years.
If you do not have the NP value, then to calculate the NP you can use the following scheme:
- first calculate profit before tax (to determine it, calculate operating profit, which is defined as the difference between operating income and operating expenses);
- then subtract depreciation and interest costs from operating profit;
- Subtract tax from the resulting profit value.
To find out whether it is possible to see the amount of operating profit in the accounting statements, read the article “Which line is operating profit reflected in the balance sheet?”
Clarifications on filling out line 1370
In order to correctly reflect retained earnings and uncovered losses, the following rules must be observed:
- Indicators on line 1370 as of December 31 of the previous and previous periods must, in general, be transferred from the balance sheet for the previous year.
- The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation recommends that interim dividends that were paid during the year for which reporting is prepared be reflected separately in section 3 of the annual balance sheet in parentheses - for this purpose, a separate line 1371 “Including interim dividends” should be entered in the mentioned section.
- The order in which interim dividends are reflected should be the same for the current, previous and previous periods (if you decide to enter line 1371, it should be everywhere).
- The accountant is obliged to ensure comparability of information on the amount of retained earnings as of the reporting date and as of December 31 of the previous and previous periods. If the enterprise's accounting policies changed in year n+1, the consequences of the changes must be reflected retrospectively. Those. comparative indicators from the columns “as of 31.12 n-1 year” and “as of 31.12 n-1 year” on page 1370 and for related items must be adjusted as if the new accounting policy was taken into account from the time facts of activity of this type appeared.
- If the enterprise was correcting significant errors of the previous year in the reporting period, and the reporting of the previous year had already been approved, a retrospective recalculation is carried out. This means that the indicator of uncovered loss or retained earnings for 31.12 years n and n-1 are subject to recalculation as if the error had never occurred.
- If the company was correcting errors of those years that preceded the previous period, it will also be necessary to recalculate the uncovered loss or retained earnings for 31.12 years n-1. But not when it is impossible to understand what the impact of the found error is cumulatively in relation to all previous years, or what is the connection between the error made and a specific period of activity.
What is line 1370: calculations
It is very easy to calculate this indicator - you need to take the account balance. 84 NU or NP for the selected period of time (year or some other time period). For calculations, you need to calculate how much profit or, conversely, losses that remained with the company when all taxes were paid.
The information obtained will be useful to fill in the required fields. But remember that the exact amount can only be obtained after deducting taxes.
Video with guidance on submitting a balance sheet:
So, as you probably already understood, filling out line 1370 is not that difficult. The main thing is to determine what exactly happened to the company’s budget during the reporting period. Did it bring profit, or, conversely, did the company report only a loss?
Accordingly, if the company had a profit, then you need to decide what it will do. If, on the contrary, there is a loss, then you need to decide how the company will compensate for it.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Adjustments to balance sheets during the inter-reporting period
In some situations, an enterprise is obliged to make adjustments to balance sheet indicators during the inter-reporting period as of 01.01 of the reporting period. Such cases are described in the table below:
| The essence of adjusting balance sheet indicators | Details |
| Assignment of the results of restatement of deferred tax assets and liabilities to retained earnings or uncovered loss | The recalculation is caused by a change in tax rates for income tax in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation. |
| Adjustment of the amount of retained earnings or uncovered loss when there is a change in accounting policy (not required when the financial implications of the change in accounting policy for earlier periods cannot be estimated with reasonable accuracy) | — When the accounting policies of an enterprise are subject to changes due to legal or regulatory requirements. accounting acts; — in any other cases of revision of accounting policies. |
| Attribution of the results of revaluation of fixed assets to retained earnings or uncovered loss | — When a previously undervalued fixed asset item is discounted; - if the amount of depreciation of a fixed asset turns out to be greater than the amount of its revaluation, credited to the additional capital of the enterprise due to revaluation, which took place in earlier periods; - when an additional valuation of a fixed asset that was previously discounted is made (in this case, the amount of the write-down for earlier years was attributed to retained earnings or uncovered losses in earlier periods). |
| Adjustment of the amount of retained earnings (uncovered loss) when the estimated values of intangible assets (their residual value) change | — If the method of calculating depreciation for intangible assets has been clarified; — when the useful life of intangible assets was clarified. |
| Attribution of the results of revaluation of intangible assets to retained earnings or uncovered loss | — If an intangible asset that was previously discounted is revalued (and the amount of the writedown for earlier years was allocated to retained earnings in earlier periods); — when it is decided to discount an intangible asset that was not previously undervalued; - if the amount of write-down of intangible assets turns out to be greater than the amount of its revaluation, credited to the company’s additional capital due to revaluation carried out in earlier years. |
Uncovered loss: definition and reasons for its occurrence
If there is a loss for the current year, the calculation formula will look like this:
- NPk = NPn – U – D, where U is the loss of the current year.
The NPK indicator may be negative if the resulting current loss exceeds the NP value at the beginning of the year. It is in this case that the loss becomes uncovered. Those. uncovered means a loss that occurs when the enterprise receives an actual loss and is unable to cover it with reserve funds (including when funding reserves were not created). The main causes of PE are considered to be:
- Excess of company costs over income due to various reasons;
- Radical changes in accounting policies that significantly affected the financial position of the company;
- Errors discovered in the reporting period from previous years, etc.
If there is a loss, the company carefully analyzes the causes of the phenomenon, since it may be a consequence of a drop in the competitiveness of the products being manufactured, which will require a change in the sales strategy or re-profiling of production, or may be a temporary phenomenon with the infusion of impressive, but slowly recouping investments into production.
Let's look at it with an example.
Let’s say that income from the company’s core activities amounted to 500 thousand rubles, non-operating income – 60 thousand rubles. Production costs – 490 thousand rubles, other non-taxable costs – 85 thousand rubles. NNP – 14 thousand rubles. The company did not create a reserve fund.
After calculating the NU, the amount of loss of 29 thousand rubles will appear in the balance sheet. ((500 + 60) – 490 – 85 – 14).
If a positive amount of NP appears on page 1370 at the beginning of the year, then the resulting loss will reduce it. If there is an existing negative result, the amount of the loss will increase the NL.
An example of filling out line 1370 when preparing annual reports
Let's imagine a hypothetical Do-It-Yourself limited liability company whose accountant prepares annual reports. The company does not keep records of special funds on the account. 84.
Indicators for account 84:
Fragment of the Balance Sheet for 2013:
Solution:
Fragment of the Balance Sheet of Do It Yourself LLC:
Answers to frequently asked questions on the topic “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”
Question: How to reflect retained earnings from previous years?
Answer: It is accumulated on account 84. Balance on Kt account. 84 should be transferred to line 1370 of the balance sheet. Since the distribution of profits is usually made at the end of the year at a meeting of owners, there is no movement in account 84 during the year.
Question: What situation with retained earnings at the enterprise will suit potential investors?
Answer: The ideal option for investors is a company that pays dividends to participants and then invests the remaining funds in business development. Investors may also be interested in the option of waiving dividends in favor of improving and modernizing production.
| Business valuation | Financial analysis according to IFRS | Financial analysis according to RAS |
| Calculation of NPV, IRR in Excel | Valuation of stocks and bonds |