Step-by-step instruction
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
On April 03, the Organization entered into a contract with the foreign company POSexpertLLC for the provision of services for organizing an exhibition in Milan in the amount of EUR 5,900, including VAT.
The place of sale of services is the Russian Federation (clause 4, clause 1, article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore, the Organization acts as a tax agent for VAT (clause 2, article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
On June 01, the Organization made an advance payment to the counterparty in the amount of EUR 5,000, and also paid VAT to the budget as a tax agent.
On June 5, services for organizing the exhibition were provided.
Conditional courses for example design:
- June 01, rate 71.00 rub./EUR;
- June 05 exchange rate 72.00 rub./EUR.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Agreement with a foreign company for the provision of services | |||||||
| April 03 | Agreement for the provision of services, the organization acts as a tax agent (clause 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | Directory Contracts | |||||
| Transfer of an advance to a foreign supplier | |||||||
| June 01 | 60.22 | 52 | 355 000 | 355 000 | Transfer of advance payment to the supplier | Debiting from the current account - Payment to the supplier | |
| 91.02 | 52 | 160 000 | 160 000 | Revaluation of foreign currency balances on a foreign currency account | |||
| Payment of VAT to the budget by a tax agent | |||||||
| June 01 | 68.32 | 51 | 63 900 | Payment of VAT to the budget | Debiting from a current account – Tax payment | ||
| Introducing the Federation Council as a tax agent | |||||||
| February 03 | 76.NA | 68.32 | 63 900 | Issuance of SF by a tax agent | Invoice issued by tax agent | ||
| 63 900 | Reflection of VAT in the Sales Book | Sales book report | |||||
| Reflection in accounting of services for holding an exhibition | |||||||
| June 05 | 44.01 | 60.21 | 355 000 | 355 000 | 355 000 | Accounting for service costs | Receipt (act, invoice) - Services (act) |
| 60.21 | 60.22 | 355 000 | 355 000 | 355 000 | Advance offset | ||
| 19.04 | 76.NA | 63 900 | Acceptance for VAT accounting | ||||
| Acceptance of VAT paid by a tax agent | |||||||
| 30 June | 68.02 | 19.04 | 63 900 | Acceptance of VAT for deduction | Generating purchase ledger entries | ||
| 63 900 | Reflection of VAT deduction in the Purchase Book | Purchase Book report | |||||
When, when purchasing works and services, VAT is calculated by a tax agent
Recently, one can notice an increase in the demand of Russian companies and private enterprises for foreign work and services purchased, including through the Internet. There are situations when buyers are required to fulfill the duties of a tax agent for VAT and provide relevant documents to the fiscal authorities.
The tax agent must pay a tariff when transferring money to a foreign partner. Many payers are interested in the procedure for paying VAT for non-residents and paying VAT when paying for services to a non-resident. If a Russian organization buys goods from a foreign company, then the agent’s obligations to collect the added value may arise in a number of cases. For example, if the place of sale of the service is Russia, the foreign person is not registered with the tax service as a payer.
There are some exceptions, which include foreign organizations providing services to individuals within the Russian Federation. When purchasing such goods, buyers from the Russian Federation may not be considered agents if the work is performed through a division of the company located in Russia.
According to the law, from the beginning of 2022, a foreign company that provides services electronically must register with the tax service if it provides services to individuals and legal entities. We can conclude that if works are purchased from a representative office of a foreign company registered in the tax Russian Federation, the buyer does not receive the status of an agent. When purchasing goods from a non-resident company, the buyer must fulfill the obligations of the agent.
There are some rules for establishing the correct place for the sale of a service. If a person cooperates with a partner from the EAEU countries, the place of sale is determined in accordance with the Treaty on the EAEU. In other situations, the place of sale is established in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When purchasing work or services, the agent is required to pay a tariff to the budget when transferring funds to a foreign partner. The calculated and withheld tariff is transferred during the transfer of funds when working with foreign companies.
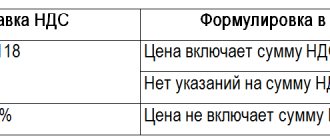
The tariff base is established as the amount of income from the sale of services taking into account the tariff. The basic rate is defined as 20/120, but there is also a preferential percentage of 10/110, which is relevant for some categories of goods.
Most often, foreign organizations do not include the collection rate in the cost of their own services. In this case, a reservation may be made that the cost does not contain indirect tariffs that must be paid in accordance with Russian laws. In such situations, in order to establish a base, it is necessary to increase the price specified in the contract by the rate.
When purchasing a service, you must fill out the SF. Line 5 of the document displays the date and number of the payment documentation for transferring the rate to the budget. Lines 2 and 2a must be filled in; they indicate the full or abbreviated name and location of the seller according to the contract. Other SF values are prescribed as usual. The agents' rate is 20/120, so column 7 shows the calculated value, and column 9 shows the cost including the tariff. In paragraph 5, the price of the service is written without the rate.
The issued SF must be registered in the sales book in the period when the fee must be paid, namely, on the day when the funds were transferred to the foreign partner.
There are some features of accounting for the calculated fee for an agent. If he is a payer and the service was purchased to carry out actions subject to a fee, it is possible to subsequently accept the tariff for deduction, however, there are some conditions for the return of funds.
A deduction can be made only after the work done has been registered and if the corresponding primary documents are available. It can be concluded that the agent cannot claim for deduction the fee withheld by him when transferring the advance payment until the service is performed. If a service is purchased for an activity specified in Article 170 of the Tax Code, that is, for tax-free procedures, payment cannot be accepted.
The agent who pays the tariff must submit declarations to the tax authorities, which include section 2. These persons, who are not payers, must also provide documentation to the relevant authorities no later than the 25th day of the month following the previous period in which the payment was made.
Agents who use special regimes, such as, for example, the simplified tax system or unified agricultural tax, fill out the title page and section 2 of the declaration. If there are no indicators for filling out section 1, a dash is added. Agency tax returns that were drawn up when transferring money to a partner from another country are reflected in section 9 of the declaration; when the fee is accepted for deduction, section 8 is filled out.
There are some features of filling out section 2 of the document for agents. If the person in question purchases work from a person in another country, the values transferred to the partner are required to be reflected in the declaration. Line 060 specifies the value of the fee that needs to be paid into the treasury. Paragraph 070 indicates the code of the operation that is performed by agents.
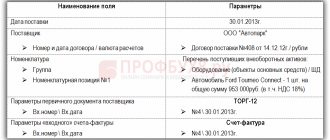
Agreement with a foreign company for the provision of services
When purchasing services (work) from a foreigner, the VAT tax agent in 1C 8.3 fills out the Agreements as follows:
In the Calculations :
- Price in EUR , i.e. the currency in which the contract was concluded;
- Payment in EUR checkbox , i.e. payment currency.
In the VAT :
- The Organization acts as a tax agent for VAT checkbox is selected ;
- Type of agency agreement - Non-resident (clause 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- The generalized name of goods for a tax agent invoice is the name indicated in column 1 “Name of goods (description of work performed, services provided), property rights” in the Invoice , selected from the Nomenclature directory. PDF
If in the Invoice document issued by the tax agent the wording is in the Nomenclature and Service Content columns, additional. information differs from each other, then column 1 of the printed form of the tax agent invoice 1s 8.3 will display information from the column Contents of the service, additional. details .
The requirements and procedure for filling out the name of the services (work) provided in the Federation Council are established in clauses 5, 5.1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 2 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 N 1137.
Selecting analytics Type of agency agreement Non-resident (clause 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) in the Contracts with supplier card affects the correct completion of the VAT return.
In Section 2 of the declaration “The amount of tax payable to the budget, according to the tax agent” on page 070 the code will be filled in 1011712.
When you are a VAT tax agent
Cases when the state assigns the duties of a tax agent for VAT to you are listed in Art. 161 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Let's translate them into a more understandable language.
You will be a VAT tax agent if:
- you buy goods, works or services from foreign persons who are not registered in Russia. In this case, the place of implementation is our state of the Russian Federation (we will consider this nuance in detail below);
- rent state property from the authorities themselves or buy it as your own.
The following are cases that are much less common:
- sell confiscated property, treasures, purchased valuables and other wealth;
- buy property of a bankrupt;
- as an intermediary you sell goods, works, services of foreign persons who are not registered in Russia;
- if you built a ship and within 46 days, after the transfer of ownership, did not register it in the International Register of Ships (suddenly there are such among our users).
Let's take a closer look at the most common operations, purchasing from foreign companies and leasing state property.
Transfer of advance payment to the supplier
The transfer of an advance to a foreign supplier is reflected in the document Write-off from the current account transaction type Payment to supplier in the Bank and cash desk section – Bank – Bank statements – Write-off button.
Let's look at the features of filling out the document Write-off from a current account using this example.
When you select an agreement in currency in the document Write-off from a current account, accounts for settlements with suppliers are automatically set in the Settlement account - 60.21 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors (in currency)” and in the Advance account - 60.22 “Settlements for advances issued (in currency) "
When transferring an advance to a non-resident, the VAT rate is set to Without VAT .
Postings according to the document
Checking the calculation of revaluation of currency balances:
date Amount, EUR Central Bank rate (EUR) Amount (rub.) January 31 Account balance 20 000 79 1 580 000 June 01 Revaluation at the time of payment 20 000 71 1 420 000 June 01 Exchange difference -160 000
Income tax return
In the income tax return, negative exchange rate differences are reflected as non-operating expenses: PDF
- Sheet 02 Appendix No. 2 page 200 “Non-operating expenses”.
Payment of VAT to the budget by a tax agent
The organization is obliged to pay VAT to the budget simultaneously with the payment of funds to the foreigner.
Payment of VAT to the budget is reflected in the document Write-off from the current account transaction type Payment of tax in the Bank and cash desk section – Bank – Bank statements – Write-off.
Let's look at the features of filling out the document Write-off from a current account using this example.
The document fields are filled in as follows:
- Tax - VAT;
- Type of obligations - Tax;
- Accounting account - 68.32 “VAT when performing the duties of a tax agent”;
- selection of the VAT amount based on payment documents to foreign suppliers in the Reflection in accounting Add , Fill out or Selection button .
For settlements with the budget in 1C, the tax agent uses account 68.32 “VAT when performing the duties of a tax agent.”
The account has three sub-accounts:
- Counterparties;
- Agreements;
- Calculation documents.
This analytics must be completely filled out by selecting it in the document Write-off from the current account when reflecting the payment of tax to the budget. Otherwise, VAT will not be automatically deducted in the future.
Be careful when completing the Payment Order , because... When issuing a payment order to pay VAT to the budget, code 02 “tax agent” is filled in field 101 “Status of originator”. PDF
Postings according to the document
Who is a tax agent and what are his responsibilities?
An organization or individual entrepreneur (even under special regimes) acts as a tax agent when it transfers mandatory taxes and contributions to the budget for another company or individual (clause 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the customer is a non-resident, the contractor is a resident, VAT is a mandatory payment that a domestic agent transfers to the budget for a foreigner. IMPORTANT!
If your counterparty is a foreigner who does not pay tax payments (including VAT) to the Russian budget, and your organization or individual entrepreneur provided him with services on the territory of the Russian Federation, then you need to act as a tax agent and transfer value added tax for your foreign partner.
Carrying out work for a non-resident on the territory of the Russian Federation is also subject to VAT. The agent pays value added tax to the territorial Federal Tax Service - at the location (clause 3 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Non-resident partners include not only foreign companies, but also foreign individual entrepreneurs (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-08/181 dated June 22, 2010).
The main duty of agents is to transfer taxes for other individuals and legal entities (clause 3 of article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the counterparty is not registered in the Russian tax system, the tax agent is obliged to withhold and remit value added tax in the same way as a regular taxpayer (Clause 4 of Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Check the registration using the company’s TIN: enter the number of the foreign payer in the special service of the Federal Tax Service.
Issuing an invoice as a tax agent
create a document Invoice issued in the Tax Agent type from the document Write-off from the current account of the transaction type Payment to supplier clicking the Create button .
In the invoice (hereinafter referred to as SF), transaction type code 06 “Tax agent, art. 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation."
In the Payment document of the Invoice issued document, the number and date of the payment order for payment of VAT to the budget are indicated, and not the details of the order for payment to the supplier.
For this reason, in 1C, the payment of VAT to the budget is first reflected, and then an invoice from the tax agent is issued in order to immediately enter data about the payment order into the invoice.
Tax agent invoice 1s 8.3
VAT tax agent: postings in 1s 8.3
Tax agent invoice 1C 8.3
An invoice issued by a tax agent is drawn up according to the general rules, but is issued in one copy (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The tax agent invoice form can be printed by clicking the Print in the document Invoice issued with the transaction type Tax Agent . PDF
The amount of VAT calculated and withheld by the tax agent is reflected in the Sales Book.
Sales Book report can be generated from the Reports - VAT - Sales Book section. PDF
Purchasing services from a foreign partner
When purchasing work or services from a foreign partner, a Russian organization, as a tax agent, must withhold tax from income paid to the foreign entity and transfer it to the budget. After this, the tax agent receives the right to deduct VAT withheld from the foreigner’s income (provided that the work or services are used in taxable activities).
The agent needs to keep in mind that the tax in this case is paid to the budget simultaneously with the amount transferred to the foreign partner. The bank will not accept a payment order for the transfer of funds to a partner without an order to pay the withheld tax (paragraph 2, 3, paragraph 4, article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Due to the fact that settlements with a foreign partner are made in foreign currency, and the obligation to pay tax is fulfilled in national currency (clause 5 of Article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), in order to transfer VAT to the budget to the tax agent - a Russian organization, it is necessary to determine the ruble exchange rate according to in relation to foreign currency, according to which the tax base is recalculated (in our case, this is the amount of the contract). The financial department believes that in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base is recalculated into rubles at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of actual expenditure (Letter dated July 3, 2007 N 03-07-08/170).
Example 1. A Russian organization purchases from a foreign partner who is not registered with the tax authorities of the Russian Federation, services related to the setup of equipment and provided on the territory of the Russian Federation. The cost of the work is estimated at 3,540 euros. The equipment, like the work itself, is intended for conducting VAT-taxable activities. For purposes of clarity, we will assume that, according to the contract, payments are made upon the provision of services. The euro exchange rate on the date of provision of services was 38.8534 rubles. per euro, on the settlement date - 39.0532 rubles. per euro.
The terms of the contract provide for the withholding of VAT from income transferred to the foreign partner. The amount of VAT to be withheld is €540 (€3,540 x 18/118).
The following entries will be made in the accounting records of a Russian organization:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| On the date of provision of services by the foreign partner | |||
| The provision of services by a foreign partner without VAT is reflected ((3540 euros - 540 euros) x 38.8534 rubles/euro) | 20 | 60 | 116 560 |
| On the date of settlements with a foreign partner and with the VAT budget | |||
| The difference when repaying the obligation is reflected (117,160 - 116,560) rubles. <*> | 91-2 | 60 | 600 |
| Payment was transferred to the partner minus the amount of VAT ((3540 euros - 540 euros) x 39.0532 rubles/euro) | 60 | 52 | 117 160 |
| The amount of VAT withheld from the cost of services (work) provided and subject to payment to the budget by the tax agent is reflected (540 euros x 39.0532 rubles/euro) | 19 | 68 | 21 088 |
| Withheld VAT is transferred to the budget <**> | 68 | 51 | 21 088 |
| Paid VAT is subject to deduction <***> | 68 | 19 | 21 088 |
<*> We remind you that costs in the form of negative exchange rate differences from the revaluation of claims (obligations) are recognized as non-operating expenses (clause 5, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore the difference that arises in accounting can be taken into account when calculating income tax.
<**> Ultimately, a debit balance is formed on account 68 (RUB 21,089) from three entries, which precisely shows that the tax amount was reduced by the tax agent by the amount of VAT paid for the foreign partner.
<***> A Russian organization has the right to deduction in the tax period in which the tax was paid to the budget (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 15, 2009 N 03-07-08/151, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus Region dated December 21, 2009 N A32- 21695/2008-46/378-2009-34/283), although tax authorities transfer the deduction to the next tax period (Letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 09/07/2009 N 3-1-10/ [email protected] , dated 09/14/2009 N 3- 1-11/730).
Reflection in accounting of services for holding an exhibition
Services for organizing an exhibition are classified as advertising expenses (non-standardized); for tax accounting purposes, these expenses are not standardized (clause 4 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Advertising expenses associated with the costs of selling products, works and services in accounting (hereinafter referred to as BU) are reflected in accordance with Dt 44.01 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities” (Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n).
The provision of services is registered with the document Receipt (act, invoice) transaction type Services (act) in the section Purchases - Purchases - Receipts (acts, invoices) - button Receipt - Services (invoice).
Let's look at the features of filling out the document Receipt (act, invoice) using this example.
In the Prices form in the document, the exchange rate is set from the Currency on the date of reflection of the document Receipt (act, invoice) .
The exchange rate on the date of service provision is used only to recalculate the unpaid portion of services. The paid cost of services is taken into account at the prepayment rate (paragraph 2, paragraph 9, PBU 3/2006, paragraph 10, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The VAT amount is calculated at the exchange rate on the date of payment of the tax (clause 5 of Article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 3 of Article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2015 N 03-07-08/1467).
In our example, to determine the amount in ruble equivalent, the exchange rate is taken:
- from the document Write-off from current account , because there was 100% prepayment. The rate that is indicated in the document Receipt (act, invoice) in the Prices form in the document from the Currencies does not participate in the calculation of the ruble valuation.
There is no VAT in the primary documents from the supplier, but in the Receipt document (act, invoice) the VAT rate is set at 18% and the tax agent independently allocates the VAT amount.
In the tabular part, prices are indicated in foreign currency, but in the postings the amounts are expressed in ruble equivalent.
This is due to the fact that accounting in the Russian Federation is carried out in rubles. Assets or liabilities in foreign currency are subject to conversion into rubles (PBU 3/2006).
Postings according to the document
Checking the generated document amount:
Cost in EUR Event Exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (EUR) Cost in rub. Paid amount 5 000 Prepaid expense 71 355 000 VAT amount 900 Issuing a tax agent to the Federation Council 71 63 900 Total sum 5 900 418 900
Income tax return
In the income tax return, advertising expenses are reflected as indirect expenses: PDF
- Sheet 02 Appendix No. 2 page 040 “Indirect costs”.
NTVP "Kedr - Consultant"
LLC "NTVP "Kedr - Consultant" » Services » Consultations on accounting and taxation » VAT » Are we a tax agent for VAT as an enterprise when paying remuneration to a non-resident agent searching for buyers in a foreign state?
Question
Are we a tax agent for VAT when paying remuneration to a non-resident agent searching for buyers in a foreign country?
Expert's answer
In accordance with subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Code), the object of taxation of value added tax is the sale of goods (work, services) in the territory of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for determining the place of sale of work (services) for the purpose of applying value added tax is established by Article 148 of the Code.
1. For the purposes of this chapter, the place of implementation of works (services) is the territory of the Russian Federation if:
(as amended by Federal Law dated December 29, 2000 N 166-FZ)
provision of consulting, legal, accounting, auditing, engineering, advertising, marketing services , information processing services, with the exception of the services specified in paragraph 1 of Article 174.2 of this Code, as well as during research and development work. Engineering services include engineering and consulting services for preparing the production process and selling products (works, services), preparing the construction and operation of industrial, infrastructure, agricultural and other facilities, pre-design and design services (preparation of feasibility studies, design developments and other similar services). Information processing services include services for collecting and summarizing, systematizing information arrays and making the results of processing this information available to the user;
(as amended by Federal Laws dated December 29, 2000 N 166-FZ, dated May 29, 2002 N 57-FZ, dated July 22, 2005 N 119-FZ, dated July 19, 2011 N 245-FZ, dated July 3, 2016 N 244-FZ )
Art. 148, “Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part Two)” dated 05.08.2000 N 117-FZ (as amended on 04.06.2018) {ConsultantPlus}
To determine whether services are classified as marketing or advertising, the Russian Ministry of Finance recommends referring to the Federal Law dated March 13, 2006 N 38-FZ “On Advertising”, as well as the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 20, 2006 N MM-6-03/ [email protected ] (Letter dated 06/03/2009 N 03-07-08/118).
Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 20, 2006 N MM-6-03/ [email protected]
The position of the department is given that marketing services include:
a) determining the size and nature of the market;
b) calculation of real and potential market capacity;
c) analysis of factors influencing market development;
d) taking into account the specific features of the analysis of product and regional markets;
e) determining the degree of market saturation, etc.;
f) market segmentation and determination of consumer types according to basic characteristics: age, gender, income, profession, social status, place of residence, objective need for the product offered, etc.;
g) research into the capacity of the trade and distribution (commodity distribution) network serving a given market;
h) the presence of retail and wholesale trade enterprises, the provision of trade warehouses and auxiliary premises, etc.;
i) analysis of external factors of market development.
Tax Guide. Encyclopedia of VAT disputes {ConsultantPlus}
If the type of activity of your non-resident agent can be classified as marketing services, then your organization will be a tax agent for VAT.
If the services provided under an agency agreement are not marketing services, then the territory of the Russian Federation is not recognized as the place of sale of such services provided by a foreign organization to a Russian principal and, accordingly, such services are not subject to value added tax in the Russian Federation.
Selection of documents:
Typical situation: How to determine the place of sale of services for VAT purposes (Glavnaya Kniga Publishing House, 2018) {ConsultantPlus}
The explanation was given by the accountant-consultant of LLC NTVP "Kedr-Consultant" Natalya Borisovna Petrova in July 2022.
When preparing the answer, SPS ConsultantPlus was used.
This clarification is not official and does not entail legal consequences; it is provided in accordance with the Regulations of the CONSULTATION LINE ().
This consultation has passed quality control:
This consultation has passed quality control:
Reviewer: Selezneva Irina Akhmatyasavievna, Associate Professor of the Department of Accounting, Finance and Auditing, Izhevsk State Agricultural Academy
Acceptance of VAT paid by a tax agent
VAT is accepted for deduction if the conditions are met (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the tax agent is a VAT taxpayer;
- VAT was paid by the tax agent to the budget;
- services purchased for activities subject to VAT;
- there is a correctly executed SF, issued by the NA itself;
- services are accepted for accounting.
Acceptance of VAT for deduction is formalized by the document Generating purchase ledger entries in the Operations section - Closing the period - Regular VAT operations - Create button.
To automatically fill out the Tax Agent , you must use the Fill .
Postings according to the document
Purchase Book report can be generated from the Reports – VAT – Purchase Book section. PDF
VAT declaration
The VAT return regarding the transactions of the tax agent will be completed as follows:
In Section 2 “The amount of tax payable to the budget, according to the tax agent”: PDF
- line 060 - the amount of calculated VAT according to the tax agent;
- page 070 - operation code "1011712".
A separate Section 2 must be completed for each foreign person.
In Section 3, page 180 “The amount of tax paid to the budget by the taxpayer as a buyer - tax agent, subject to deduction”: PDF
- the amount of VAT subject to deduction.
In Section 8 “Information from the purchase book”:
- invoice issued by the tax agent. Operation type code "".
In Section 9 “Information from the sales book”:
- invoice issued by the tax agent. Operation type code "".
How to calculate VAT
The tax base is calculated in the amount of income from the sale, including VAT, and the tax, in turn, is calculated at the calculated rate - 10/110 or 20/120 (clause 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Typically, foreign companies do not include the amount of domestic VAT in the cost of their own services under the contract. The contract may contain a separate clause defining the amount of VAT, or it may not exist at all. Therefore, to calculate the tax, it is necessary to increase the cost of work under the contract by the amount of VAT, i.e. add 20% to their cost (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-03-06/2/20797 dated 06/05/2013, No. 03-07-08/276 dated 09/08/2011).
For example, if under the contract the price of work is 1000 euros excluding VAT, then the amount of income on which the agent needs to calculate VAT will be considered 1200 euros (1000 + 1000 x 20%).
Before transferring payment under the agreement, the parties must draw up and approve documents confirming the actual fulfillment of the terms of the agreement. The moment of payment of VAT is considered to be the transfer of money under the contract, i.e. Two payment documents must be submitted to the bank - for payment of services to the counterparty and for the transfer of VAT to the budget.
A company can accept VAT as a deduction if two conditions are met:
- The delivered goods/services are accepted for accounting;
- Payment under the contract has been completed.