Features of the leasing agreement
Leasing is the transfer for long-term use of property related to depreciable fixed assets (FPE).
A leasing agreement can be completed either by the purchase of the leased asset or its return. The lessor company always remains the owner of the leased asset throughout the duration of the contract. However, in this case, the leased property can be taken into account both on the balance sheet of the transferring party and on the balance sheet of the receiving party. This point must be specified in the contract. The total amount of leasing payments consists of the costs of the lessor company for the purchase and lease of the subject of the contract and the cost of services. The amount of payments may include the value of the redemption value of the property, at which, upon completion of the contract, it is transferred to the recipient into ownership.
Who pays transport tax when leasing a car, read here.
What are the risks of leaseback?
It is important to note that leaseback is one of the most common tax planning schemes. In these relations, the company can be both the lessee and the seller of the property leased. A regular leasing agreement, according to Article 665 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is characterized by the presence of all three parties: the lessor, the seller and the lessee. The beginning of such a “tripartite” relationship occurs when the lessor purchases a property from the seller by signing a purchase and sale agreement. Next, this seller himself turns into a lessee of the property that once belonged to him as property. It is important to note that the sale of such property in this scheme occurs at a symbolic price, and is bought back several times more expensive.
What benefit does the seller receive in this case? The answer is simple - such a tax scheme allows the lessee to understate its obligations for income tax and VAT. That is, leased property in this case is a type of loan against fixed assets. But the advantage of such a loan is that the borrower (lessee) avoids rationing the interest that is paid to the lender (lessor).
The disadvantages of using leaseback include high tax risks, since representatives of the Federal Tax Service consider this scheme to be an unreasonable way to obtain tax benefits. However, the law (clause 1 of Article 4 of the Federal Law “On Financial Leasing”) is on the side of the lessee-seller, which states that the lessee can be the seller of the leased property within the same legal relationship.
It is important to note: In order for the tax authorities not to have “unnecessary” questions regarding leaseback, it is important that the price level when selling property to the lessor is market level and that none of the parties to the legal relationship is a “fly-by-night company.”
Accounting with the lessor using the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
A lessor company working with the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” takes into account lease payments received from the recipient of property in income (from sales or non-sales) on the date of receipt of funds (Article 346.15 and Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, advance payments must also be taken into account in income (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 25, 2014 No. 03-11-06/2/42282) and the redemption value (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 4, 2017 No. 03-11-11/49896, more about this here ).
Features of accounting for income and expenses under the simplified tax system can lead to losses under a leasing agreement. The presence of losses does not relieve the “simplified” person from the obligation to pay the minimum simplified tax (clause 6 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the leased asset is taken into account on the balance sheet of the lessor company, then it can include the cost of the property acquired for leasing according to the rules for writing off expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets (subclause 3, clause 3, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This situation may be controversial in the case of completion of the contract with the repurchase of the leased asset, which from the position of the tax inspectorate should be considered as a product. And the costs of selling goods are taken into account at the time of their sale (subclause 23, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The material “Accounting for the write-off of goods when applying the simplified tax system” is devoted to how goods are written off under the simplified tax system.
Attention! Warning from ConsultantPlus: The Russian Ministry of Finance does not have a clear opinion on the issue of accounting for expenses for the acquisition of a leased asset by a lessor using the simplified tax system. See K+ for details.
In addition, a company operating on a simplified basis and deciding to start leasing property must remember that the possibility of using the simplified tax system is limited not only by the amount of income (clause 2 of Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), but also by the amount of its residual value OS (subclause 16, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read about the income limit under the simplified tax system in the article “Income limit when applying the simplified tax system.”
If the leased asset is taken into account on the balance sheet of the lessee company, then the organization leasing the property has no reason to see it as a fixed asset in order to take into account the costs of writing off its value (Clause 4 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this situation, the costs of purchasing the leased asset by the lessor can be taken into account in full only upon completion of the leasing agreement in one of the following cases:
- upon sale at the redemption price provided for in the leasing agreement;
- when selling property returned at the end of the leasing agreement to another counterparty;
- upon further use of the property returned at the end of the leasing agreement as its own fixed assets.
If the leased asset, accounted for and written off as fixed assets, is sold before the expiration of the deadlines provided for in the last paragraph of subparagraph. 3 p. 3 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, then it may be necessary to recalculate the costs of acquiring fixed assets in accordance with the rules of Ch. 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
For information on whether the “simplified people” should rush to sell fixed assets, see the material “The simplified people have been waiting 3 years for OS sales.”
All of the above indicates that being a lessor on the simplified tax system is quite unprofitable.
If you still have questions, you can find answers to them in the Consultant.Plus system.
Employee training
Expenses for training and retraining of personnel can be written off as other production and sales expenses (clauses 1, 3 of Article 264 of the Tax Code, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 30, 2006 No. 03-03-04/2/252). The rule only works for employees who work for you under an employment contract.
You can send workers to Russian and foreign educational institutions that have the required license. If you do not have a license, the costs can be written off as consulting expenses (clause 15 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The advantages of such an event are not only in reducing the tax base, you can also deduct VAT on educational services and reduce insurance premiums for employees.
Accounting for the lessee using the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
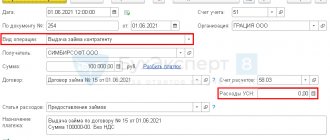
Regardless of who is the balance holder of the leased asset, the lessee company working with the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” has the right to take into account the lease payment in expenses on the date of payment (subclause 4, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, payments towards the redemption value, if it is specified separately in the contract, are advance payments and do not become expenses until the transfer of ownership of the leased asset. Leasing payments paid ahead of schedule are also considered advances.
If the leased asset is taken into account on the balance sheet of the lessee company, then its value will affect the total cost of fixed assets available to the organization. And this may entail the impossibility of applying the simplified tax system (subclause 16, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The value of the property received upon completion of the leasing agreement, equal to the redemption value, is written off as expenses in accordance with the rules of sub. 3 p. 3 art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation (as for OS) or sub. 5 p. 1 art. 346.16 (as for low-value property).
Failure to indicate the redemption value in the leasing agreement may lead to a dispute with the tax office, which in this case may consider the entire amount of lease payments under the agreement to be expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets.
With the further sale of the fixed assets received upon completion of the leasing agreement, the lessee company, as well as the lessor company, may have a situation requiring a recalculation of the costs of acquiring the fixed assets in accordance with the rules of Chapter. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (last paragraph of subparagraph 3 of clause 3 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, income from the sale will be taken into account in the usual manner for payers of the simplified tax system on the date of receipt of money (Article 346.15 and Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, obtaining property on lease for a company working with the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” is a completely acceptable option. You should pay special attention to the following points:
- the maximum value of the residual value of fixed assets available to the company in the case of accounting for the leased asset on the balance sheet of the lessee company;
- preference for highlighting the redemption value in the contract;
- the possibility of problems arising with the recalculation of expenses during the further sale of property received upon completion of the leasing agreement.
How to account for leasing transactions, see the material “Transactions for leasing a car from the lessee.”
You can find answers to all other questions in the Guide to Leasing transactions. Lessee (sublessee)" from ConsultantPlus. If you don't have access to the system, get it free for a few days.
Are there any advantages to leasing over renting?
In the table we will look at the advantages of leasing over renting for an organization / individual entrepreneur.
| Comparison criteria | Lease contract | Leasing agreement (without right of purchase) |
| Economic essence of the agreement | Identically aimed at renting property for a certain fee | |
| Opportunity to take advantage of tax advantages | No | Eat |
| Monthly payment amount | Fixed | May be uneven Comment: both parties to the transaction can change the amount of leasing payments and transfer the tax burden for VAT and income tax in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 146 and Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, from the lessee to the lessor and vice versa. |
| Opinion of representatives of the Federal Tax Service regarding the payment schedule | Unpretentious | Claims are being made by regulatory authorities, who justify them with paragraph 1 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states that expenses should be distributed over several periods in advance if the agreement provides for the receipt of leasing payments for more than one period (month). However, the possibility of uneven payments is supported by letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-03-05/131 dated October 15, 2008. and Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. 3-2-13/179 dated August 19, 2009. The courts adhere to a similar opinion, for example, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District No. F09-11634/12 dated December 7, 2012. and FAS Volga District No. A55-17520/2008 dated June 25, 2009. |
Results
When providing or receiving property on lease, the simplifier must take into account restrictions on the amount of income and the amount of residual value of fixed assets. Recognition of the value of leased fixed assets as expenses depends on whether the contract provides for the redemption value of this property, and on whose balance sheet it is located.
How leasing transactions are reflected in the accounting accounts, read the article “Leasing under the simplified tax system, income minus expenses - transactions.”
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
On the transfer of movable property into leaseback and subsequent taxation and benefits
Situation: Is the property tax exemption covered when transferring movable property into leaseback after 01/01/2013, while the property is listed on the balance sheet of the lessee-former owner (seller of this property)?
Answer: This property is not subject to tax, subject to the following conditions: the lessee and the lessor are not interdependent persons (not from the list of persons mentioned in paragraph 2 of Article 105 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If this condition is not met, tax must be paid.
Important point: When leasing back, movable property, which from 01/01/2013. is included in the operating system of the enterprise, is not subject to property tax, and it does not matter whether the property was owned by the lessee in the past.
Deferred tax recognition
When maintaining PBU 18/02 at the end of the month on the reporting date, deferred tax is generated by the regulatory operation Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU 18 .
Postings
Determination of the temporary difference in the cost of fixed assets between the used and the NU in March 2021
- Book value - 1,632,000 - 27,200 = 1,604,800 rubles.
- Tax value - 1,200,000 + 362,000 – 20,000 = 1,542,000 rubles.
- Temporary difference - 1,604,800 - 1,542,000 = 62,800 rubles. — taxable temporary difference.
- IT = 62,800 x 20% = 12,560 rubles.
The calculation of deferred tax can be checked in the help calculation Deferred income tax PDF