Quarterly property tax reporting has been cancelled.
The law made three changes to the procedure for calculating property taxes.
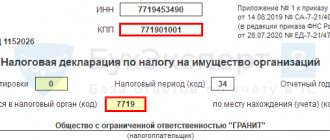
1. The obligation to submit quarterly property tax payments has been cancelled. Thus, organizations will only have to prepare an annual declaration based on the results of the tax period. The form of the declaration, as well as the procedure and format for its submission, were approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 14, 2019 No. SA-7-21/ [email protected]
2. It has become possible to submit a single tax return from 01/01/2020. Taxpayers who own real estate have the right to use it:
- taxable solely on the average annual value;
- located on the territory of one subject of the Russian Federation, but registered in different inspectorates.
The right to submit a single declaration is granted after sending a notification to the regional Federal Tax Service.
Owners of such property will be able to report on it to one tax authority of their choice. Applicants for a single tax return must submit a notification to the Federal Tax Service for the entity where the organization’s property is located before the end of the reporting campaign for the first quarter, that is, no later than 03/02/2020.
The possibility of filing a single declaration does not apply if regional legislation provides for tax deductions to local budgets.
3. The procedure for determining the tax base has been changed: from 2022, advances for the year in which the cadastral value changed are calculated at the new value. That is, from paragraphs. 1 clause 12 art. 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, effective from 01/01/2020, excluded the indication that in order to calculate the advance payment, the cadastral value must be taken exactly as of January 1 of the current year.
FEDERAL LAW No. 63-FZ dated April 15, 2019 “On amendments to part two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Article 9 of the Federal Law “On amendments to parts one and two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees”
For transport
As stated at the level of federal legislation, the rate of transport tax (TN) is regulated by regional authorities .
TN must be paid by citizens living throughout the country. All money raised from the tax ends up in the local budget.
All citizens of the Russian Federation who own cars and other vehicles must pay TN . This is stated in the three hundred and fifty-seventh article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The same applies to companies with vehicles on their balance sheets.
Organizations have to independently calculate the amount of advance payment and the tax itself. This is done for individuals by employees of territorial tax authorities based on information about the state registration of the car.
TN is calculated based on the results of a certain period, which is called the tax period. The amount consists of the established rate, the base and the number of cars owned by the citizen . Companies calculate the difference between the TN itself and the amount of advances that were made during the tax period and determine the amount of tax.
For organizations, advance amounts are calculated after the end of the reporting period. This is 1/4 of the product of the current base and the rate, as stated in the three hundred and sixty-second article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What objects are subject to TN?
The objects for which the TN is valid are mentioned in the three hundred and fifty-eighth article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, you will have to pay for:
- automobile;
- motorbike;
- buses, self-propelled, tracked vehicles;
- boats, sailboats, cutters, helicopters, towed vessels, snowmobiles, airplanes and water or air transport.
Regardless of whether a citizen owns a car or an airplane, he must register the vehicle in accordance with the procedure provided for by law.
What do you not need to pay for?
Also, by law, you can not pay for some vehicles . We are talking about an impressive list that is required to be studied. So, you do not need to pay tax for:
- A rowing boat or motor boat, the engine power of which is no more than 5 hp.
- Passenger cars converted for disabled people, passenger cars with an engine no more powerful than 100 hp, purchased with the help of social security .
- River and sea vessels intended for fishing.
- Vessels that are the property of an organization or businessman engaged in transporting people or goods by water .
- Agricultural machinery owned by farms and used to produce products. This includes a variety of machines, ranging from tractors, combines, milk and livestock tankers, poultry carriers, fertilizers, maintenance, etc.
- Cars and other vehicles that belong to government authorities, for example, military, intelligence or law enforcement agencies .
- Vehicles stolen or stolen are wanted . In this case, you need to obtain a document that confirms the theft of a car or other vehicle.
- Aviation and medical helicopters, airplanes, as well as ships included in the international register, are stated in the three hundred and fifty-eighth article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Property tax return updated
Updating the form was required due to innovations introduced by Law No. 63-FZ, in particular, in connection with the abolition of quarterly reports.
Please note: the form is subject to use from the tax period of 2022, that is, the next submission of reports must take place on a new form. There are few changes compared to the previous form:
- in section 1, four new lines appeared - 021, 023, 025 and 027. They will need to reflect the calculated amount of tax that must be paid to the budget for the tax period, and advance payments for each reporting period;
- The line with the amount of advance payments has been removed from sections 2 and 3.
In sections 2 and 3, a new line will appear: “Calculated amount of tax to be paid to the budget for the tax period (in rubles).”
ORDER of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 14, 2019 No. SA-7-21/ [email protected] “On approval of the form and format for submitting a tax return for the property tax of organizations in electronic form and the procedure for filling it out, as well as on the recognition of orders of the Federal Tax Service as invalid dated 03/31/2017 No. ММВ-7-21/ [email protected] and dated 10/04/2018 No. ММВ-7-21/ [email protected] »
Payment procedure and terms
For individuals, employees of the Federal Tax Service are responsible for calculating the tax amount. After this operation is completed, the citizen must receive a notification by mail containing information about the timing and amount of tax payment.
If the notification has not been received, the person should independently contact the nearest tax office and clarify information on this issue.
Otherwise, the citizen may receive late fees or be brought to tax liability.
A citizen can check the accuracy of the tax inspectorate’s calculations by first checking the cadastral value of the taxable object and the tax rate in force in a given region. The tax notice must arrive no later than one month before the payment deadline. Federal Tax Service employees have the right to collect tax for no more than 3 past years. If the last possible tax payment day falls on a weekend or holiday, the tax payment deadline will be the business day closest to that date.
The deadline for paying property tax for individuals is December 1 of the year, which is the tax period.
Legal entities must independently calculate the amount of tax. No later than March 1 of the year following the end of the tax period, legal entities are required to transfer funds for property tax, as well as submit reporting documentation for the year.
For this category of citizens, quarterly advance payments for property tax are also provided, which amount to 1/4 of the total tax amount.
As a rule, tax rates are determined by the regional authorities. However, they cannot exceed the maximum value established by Federal laws.
Tax payment can be made in one of the following ways:
- at the cash desk of any bank;
- through payment terminals;
- through ATMs;
- using mobile banking;
- on the tax service website through the taxpayer’s personal account.
Find out how personal property taxes are calculated. Who files a property tax return? Information here.
Are there any benefits for pensioners on the property of individuals? Details in this article.
Owners of land and vehicles will have a new obligation
Law No. 325-FZ made the most changes to the procedure for calculating property taxes.
Land tax:
- starting from 01/01/2021, companies are required to inform inspectors about taxable areas that were not taken into account by the Federal Tax Service when calculating tax. The message must be accompanied by documents confirming ownership of the land plot and the message must be sent once, before December 31 of the year following the expired tax period. If an organization does not comply with this requirement, it may be fined 20 percent of the unpaid tax amount (Article 129.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the application of a preferential rate of 0.3 percent is limited. From 01.01.2020, in relation to land plots of the housing stock, this rate cannot be applied to plots for individual housing construction used in business activities;
- the rule establishing for individuals the start date of tax calculation from the date of opening of the inheritance will also apply to legal entities from 01/01/2020;
- the possibility of establishing differentiated rates depending on the types of territorial zones within the boundaries of which the site is located is excluded;
- a procedure has been established for identifying areas not used for agricultural purposes. From 07/01/2020, the body exercising state land supervision is obliged, within 10 days from the date of issuing an order to eliminate the identified violation of the requirements of land legislation, to submit to the tax authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation information about the non-use of the site for its intended purpose. If the responsible body establishes that the said violation has been eliminated or if the order is canceled, information about this is also submitted to the tax authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation within 10 days;
- From 01/01/2021, municipalities are excluded from the procedure for establishing deadlines for payment of land tax by organizations. Thus, the representative bodies of municipalities will lose the right to set deadlines for paying land tax;
- The deadline for payment of land tax is established - no later than March 1 of the next year, and advance payments - no later than the last day of the month following the reporting period. The changes apply starting with 2022 tax payments.
Transport tax
For vehicle owners, in accordance with paragraph “a”, paragraph 3 of Art. 1 of the law, from 01/01/2021, the obligation to inform the Federal Tax Service about their availability has been established. This is the same rule that regulates notification of the availability of land plots, discussed above. It is necessary to report a vehicle if:
- they are objects of taxation;
- are not eligible for the benefit;
- The vehicle has never received a message about the calculated amount of tax.
In addition, copies of documents confirming vehicle registration must be attached to the notification.
It is enough to do this once before December 31 of the year following the expired tax period. Documents can be sent to any convenient Federal Tax Service. The reason for the innovation is the abolition of declarations. For 2022, inspectors themselves will send messages about the calculated tax. Therefore, if an organization purchases a vehicle in 2022 and does not receive a tax notice from the inspectorate in 2022, it will need to notify the tax authorities about the acquisition by December 31, 2022.
The sanctions previously provided for individuals in accordance with paragraphs. “a” clause 49 art. 1 of the law also applies to legal entities. So, starting from 01/01/2021, a company for failure to submit a report will be punished with a fine of 20 percent of the unpaid tax amount.
By analogy with land tax, paragraph 63 of Art. 2 of the law excluded, from January 1, 2021, from the powers of the regions the establishment of deadlines for payment of transport tax by organizations.
Clause 68 of Art. 2 of the law sets a deadline for paying taxes. According to the new edition of paragraph 1 of Art. 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, transport tax is payable by taxpayer organizations no later than March 1 of the year following the expired tax period. Advance tax payments must be made by taxpayer organizations no later than the last day of the month following the expired reporting period (I, II and III quarters). The innovation applies starting with the payment of transport tax for the tax period 2022.
Organizational property tax
From 01.01.2020 clause 1 art. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation classifies as objects of taxation at cadastral value not only fixed assets, but also any real estate owned by organizations under the right of ownership or right of economic management. Thus, it will not matter whether real estate is taken into account as a fixed asset or not - you will still have to charge and pay tax according to the cadastre. True, unless the region decides otherwise.
Previously, if objects were not registered as fixed assets, cadastral valuation tax was not paid on them. This follows from the explanations of the Ministry of Finance set out in letter dated June 30, 2017 No. 03-05-05-01/41582. Exception according to paragraphs. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - residential buildings. If they are a fixed asset, then the tax is paid based on the average annual value, and if they are not, based on the cadastral value. That is, from the new year, owners of such real estate will bear an increased tax burden.
The list of objects taxed at cadastral value, from 01/01/2020, includes other real estate subject to property tax for individuals, that is, residential buildings, apartments, rooms, garages and parking spaces, unified real estate complexes, unfinished construction projects and other objects. The list of taxable “other” objects was specified by Law No. 379-FZ.
FEDERAL LAW No. 325-FZ dated September 29, 2019 “On amendments to parts one and two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation”
Movable or immovable property: how to determine
From 2022, movable property is exempt from tax. Therefore, it is extremely important to understand its differences from real estate, so as not to overpay to the budget and not have disputes with the tax authorities.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, all property that is not real estate is recognized as movable. Therefore, when qualifying an object, one must act by the method of elimination. Let us name five signs that property is immovable. If none of them are characteristic of the object you are interested in, then it is movable.
1. The property is firmly connected to the land. Such objects cannot be moved without disproportionate damage to their purpose (clause 1 of Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, see also letter of the Federal Tax Service dated March 1, 2021 No. BS-4-21/2512).
Real estate includes, for example, buildings, structures, and unfinished construction projects. Exceptions are objects without a foundation that are moved without compromising their purpose (hangars, kiosks, etc.). This is movable property.
Aircraft, sea vessels and inland navigation vessels are also recognized as real estate, subject to registration in the relevant registers.
Read more about this feature of real estate in ConsultantPlus by signing up for a free trial access:
2. The object is designated as real estate by law (clause 1 of Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
There are specific objects that are considered real estate according to the law: communication lines (Law “On Communications” dated 07.07.2003 No. 126-FZ), space objects (Law of the Russian Federation “On Space Activities” dated 20.08.1993 No. 5663-I), unmanned aerial vehicles vessel (clause 1, article 33 VK).
3. Rights to real estate are subject to mandatory state registration (Article 131 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
If an object is registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate, it is most likely real estate.
In the same time:
- state registration of rights is not a prerequisite for recognizing an object as real estate (determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 30, 2015 No. 303-ES15-5520, letters of the Federal Tax Service dated March 1, 2021 No. BS-4-21/2512, dated October 1, 2018 No. BS-4- 21/ [email protected] );
- An unregistered object can also be recognized as immovable (clause 38 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated June 23, 2015 No. 25, letters of the Federal Tax Service dated February 8, 2019 No. BS-4-21/2181, No. BS-4-21/2179, dated November 20, 2018 No. BS-4-21/22488).
When conducting audits, tax authorities rely on information from the Unified State Register of Real Estate. And as you know, they are prone to formalism. Therefore, make sure that movable property is not included in the register by mistake. Otherwise, you will have to prove your right not to pay tax in court.
4. There are available for the facility (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated June 29, 2021 No. 03-05-05-01/51043, Federal Tax Service dated October 1, 2018 No. BS-4-21/19038, dated August 2, 2018 No. BS-4-21/ [ email protected] ):
- construction permit, commissioning;
- documents of technical accounting, technical inventory;
- project documentation.
In this case, the object is recognized as immovable, even if there is no registration in the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
5. The property is not capable of functioning independently.
If the property is part of a property complex and cannot be used independently or the property loses its functional qualities without it, it is taken into account and taxed as part of the real estate (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated April 23, 2018 No. BS-4-21/7770). Examples of such property are elevators, garbage chute, heating system, water supply, etc. (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 02/08/2019 No. BS-4-21/2181, No. BS-4-21/2179).
This is especially true when such equipment is being replaced. The question immediately arises: to consider it as movable and not pay tax or to accept it as part of a taxable immovable object? The second option will be correct.
If the movable and immovable object can easily do without each other, register the movable and you may not have to pay tax.
Use these signs to avoid breaking tax rules. And keep track of judicial practice regarding the classification of certain objects as movable or immovable property. The Federal Tax Service itself regularly deals with this.
Thus, by letter dated July 30, 2019 No. BS-4-21/14997, the department sent the position of the Supreme Court (ruling dated July 12, 2019 No. 307-ES19-5241) on recognizing production equipment (lines) for which a separate building was built as movable property.
A number of court decisions on the topic are given in letters from the Federal Tax Service dated April 20, 2020 No. BS-4-21/ [email protected] , dated August 28, 2019 No. BS-4-21/ [email protected] In these examples from practice, such objects are designated as movables , How:
- along-route cable communication line of the gas pipeline branch;
- paving;
- fencing;
- high-rack structures;
- evaporators, crystallizers, elevator and diffusion apparatus, etc.
The main feature of movable property here is the ability to dismantle it.
Examples of property that was recognized as real estate, from ConsultantPlus In controversial situations, the following were recognized as real estate: a transformer substation, which is located in a specific location, installed on a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation, connected by communications (cable power lines underground) with other objects (Definition of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated 03.09 .2018 N 307-KG18-13146, Appendix to the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 04/20/2020 N BS-4-21/ [email protected] with reference to the Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the North-Western District dated 05/18/2018 N F07-5328/2018 on case No. A05-1595/2017, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 28, 2019 No. BS-4-21/ [email protected] ); See K+ for more examples. Trial access to the system is free.
Also, the Federal Tax Service recognizes as real estate inseparable improvements to leased property if they are (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated April 20, 2020 No. BS-4-21 / [email protected] ):
- are of a capital nature and are taken into account by the tenant as part of the operating system;
- entail a change in the service (functional) purpose of the real estate, change its area;
- cannot be freely moved or dismantled without causing damage to the rented object.
Whether to pay property tax on unfinished construction projects, read here.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
The list of objects subject to cadastre taxation has been specified
Law No. 325-FZ brought confusion to the business environment, leaving open the list of real estate taxed by legal entities at cadastral value. But at the end of November, a law was published that clarified this list. So, from 01/01/2020, according to clause 2 of Art. 1 of the law, tax will need to be paid:
- from residential premises;
- unfinished construction projects;
- garages;
- parking spaces;
- residential buildings, garden houses, outbuildings and structures that are located on plots for personal farming, gardening, horticulture or individual housing construction.
FEDERAL LAW No. 379-FZ dated November 28, 2019 “On amendments to Articles 333.33 and 378.2 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation”
Organizations must report benefits separately
Amendments have been made to the procedure for calculating land tax, according to which not only individuals, but also legal entities are required to report available benefits from 01/01/2020.
FEDERAL LAW No. 63-FZ dated April 15, 2019 “On amendments to part two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Article 9 of the Federal Law “On amendments to parts one and two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees”
Deadline for submitting explanations for property taxes
There are no declarations, but no one has relieved the owners of vehicles, land and property of responsibility for the correctness and completeness of payment of taxes.
If there are inaccuracies in the tax payment report, the organization’s accounting department can provide explanations and documents confirming:
- correctness of calculation, completeness and timely payment of tax;
- justification for using reduced tax rates and tax benefits;
- existence of grounds for exemption from paying tax provided for by the legislation on taxes and fees.
From 2022, the deadline for submitting explanations to reports on the amounts of transport, land taxes and property taxes to the tax office will be doubled.
To prepare documents and clarify tax amounts, 20 days are given according to the new edition of Article 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In 2022, this period was half as long - 10 days.
How to claim benefits for land and transport
Starting from 01/01/2020, in order to take advantage of benefits on land and transport taxes, you must submit an application to the inspectorate.
A new form was needed due to the cancellation of filing tax returns for the specified taxes for 2022 with the Federal Tax Service. Therefore, if a company applies for benefits, then in 2022 it is necessary to submit an application to the Federal Tax Service for their provision. The fact is that the availability of benefits before the cancellation of declarations was confirmed in the declaration form itself in the special detail “Tax benefit code”.
To submit an application, a single form is used, which is called “Application of a taxpayer-organization for a tax benefit for transport tax and (or) land tax.”
The form consists of three sections: a title page and one section each for transport and land taxes.
The procedure for filling out the application indicates that if an organization claims only a land tax benefit, the blank sheet with fields for transport tax does not need to be submitted. However, this issue needs to be clarified with your inspection.
When claiming a land tax benefit, you must indicate:
- cadastral number of the plot;
- the duration of the benefit and its code;
- information about the municipal act that establishes the benefit;
- information about documents confirming the benefit.
Benefit codes are also given in the appendix to the procedure for filling out the application.
Please note that some land tax benefits are established not at the municipal level, but at the federal level - in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the fields intended for information about the local legal entity are not filled in. We are talking, for example, about benefits for areas under public roads. For transport tax benefits you must indicate:
- type of vehicle, its make (model) and license plate number;
- the period for granting the benefit;
- information about documents confirming the benefit;
- benefit code and details of regional law.
In the appendix to the procedure for filling out the application, only four codes are indicated: one for benefits under an international treaty and three for regional benefits (exemption from payment, reduced rate and reduced tax amount). Let us remind you that currently benefits for organizations are established only in the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. For example, in Moscow, SEZ residents do not pay transport tax, in the Sverdlovsk region, public organizations of disabled people pay only 35 percent of the calculated tax amount, and in Bashkiria, agricultural producers apply rates that are halved.
ORDER of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated July 25, 2019 No. ММВ-7-21/ [email protected] “On approval of the application form of a taxpayer-organization for the provision of a tax benefit for transport tax and (or) land tax, the procedure for filling it out and the format for submitting the specified application in electronic form"