Direct and indirect expenses in tax accounting
The Tax Code does not clearly define the terms “direct” expenses and “indirect” expenses.
However, from the wording of Articles 318 and 320 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, we can conclude that direct costs are those that have a clear connection with the process of production of goods (performance of work, provision of services). Indirect costs do not have such a direct connection. The composition of direct and indirect costs in each organization will be individual. It is necessary to determine a comprehensive list of direct expenses and consolidate it in the accounting policy. For information on how to draw up and approve it, see “Accounting policies of the organization: samples for 2021, how to draw up, examples.”
Get a free sample accounting policy and do accounting in a web service for small LLCs and individual entrepreneurs
Expenses that are not specified in the accounting policy as direct will be considered indirect (Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, there is no need to divide non-operating costs into direct and indirect (clause 1 of Article 318, paragraph 3 of Article 320 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Important
Only those organizations that operate on the accrual basis should distribute expenses into direct and indirect ones. Taxpayers who determine income and expenses using the cash method do not make such divisions.
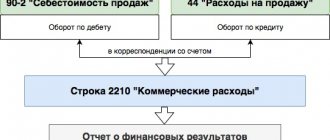
Algorithm for distribution of indirect costs
When closing the month, account 25 is distributed to account 20:
Step 1.
Distribution of indirect costs by Nomenclature groups within
one Division.
Base in UP:
direct costs Dt 20
- straight-straight +
- direct-indirect
Step 2.
Distribution of indirect costs of the general division among
all Divisions
and Nomenclature groups.
Base in UP:
direct costs Dt 20
- straight-straight +
- direct-indirect
Direct Costs base approved in the Accounting Policy
for the distribution of indirect production costs accounted for in account 25?
The selected base is the main basis for allocating costs:
- if there is no data on it, 1C automatically selects another base, for example, the number of released GP;
- if there is no data for distribution (there are no costs, revenue, production of GP and the planned cost is not used): manually distribute Dt 20 Kt 25 and generate a work in progress;
- register a technical sales document for 0.01 rubles.
What settings are needed in 1C so that account 25 is closed on 90.02 or 90.08? Account 25 should not have a balance, what to do during the months of inactivity?
The procedure for closing account 25 depends on the settings of the UE:
- if it is indicated that no accounting is kept on account 20,
account 25 will be automatically closed on Dt 90.02;
- if at least one checkbox is checked, i.e. it is indicated that accounting is kept on account 20,
then it will not be possible to set up automatic closure of account 25 to debit 90.02 in 1C - only by posting manually entered
.
During months of downtime, you can change the UE settings - remove all checkboxes from production and work, services for accounting for direct costs on account 20,
then account 25 will be closed on Dt 90.02. After the downtime is over, return the flags to how
they were .
If it is necessary for expenses to be closed in Dt 90.08, then take them into account according to Dt 26.
How in 1C to distribute electricity, rent, salaries of the laboratory and warehouse workers between production departments (shops) and a very large range of products?
Take into account indirect production costs under Dt 25 for the Laboratory and Warehouse division. At the end of the month, indirect costs for these “general” departments will be distributed in proportion to the distribution base established in the UE between all production departments and product groups.
Construction organization, hazardous production, workers are issued PPE SPI <12 months. (masks, respirators, gloves). If we indicate in the UP that we classify them as non-essential assets (account 10.21), then difficulties arise:
- accounting is kept by department (assembly, lining production, etc. (account 20, 23) and by MOL);
- It is difficult to track how many gloves were written off to the accounting department for a department during capitalization and write off the same amount using the document Consumption of materials in the accounting department for the same department.
Possible options:
Option 1.
Leave it as it was.
Do not recognize PPE in the UE as assets whose value is insignificant and continue to account for them in account 10.01 “Raw materials and materials” - there will be no confusion with the Divisions in NU and BU.
Option
2. Account for account 10.21.
Recognize PPE in the UP as assets whose value is insignificant, but when recording them, indicate in the accounting account the expenses account Dt 90.02 (without breaking them down into 20 and 23), because As a result, the costs will be included in the financial reporting period in the period of incurrence.
Option 3.
Include in indirect production costs (Dt 25).
Reflect the BU costs for Dt 25 for the general Division.
Then, during the Month Closing , they will be distributed in proportion to the distribution base in Dt 20.
To access the section, log in to the website.
See also:
- Clarifications on the mandatory application of FSB 5/2019 “Inventories” from 2021
- Closing cost accounts from 2022 taking into account FSBU 5/2019 (PROF)
- Closing cost accounts from 2022 taking into account FSBU 5/2019 (KORP)
- Example of accounting policies for production, trade, works, services (simplified methods) (OSN)
- [06/08/2021 entry] Practice of application of FSB 5/2019 Inventories in 1C - Part 3
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Direct production costs (account 20) from 2022 ...
- Are the costs of equipment repairs direct or indirect? The Supreme Court did not approve the allocation of costs for the repair of equipment involved...
- Sheet 02 Appendix 2. Direct and indirect expenses in the income tax return 2022 ...
- Management costs (account 26) from 2022 ...
What are direct costs
Direct costs are those costs that can be attributed to specific goods, work or services. For example, in production these are usually the cost of raw materials and supplies, workers' wages, as well as depreciation of production equipment (machines, machines, workshops). In trade, direct costs can be considered the cost of goods and their delivery, insurance costs, customs duties and other transportation and procurement costs.
Check the financial condition of your organization and its counterparties
What are indirect costs?
All costs that are not fixed in the accounting policy as direct and are not non-operating (clause 1 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) can be considered indirect.
Attention
The decision about the impossibility of classifying a particular expense as direct (and, accordingly, recognizing it as indirect) must be made in each specific case, taking into account economically sound indicators and features of the technological process. This has been repeatedly explained by the regulatory authorities (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated 09.05.18 No. 03-03-06/1/63428, dated 03.13.17 No. 03-03-06/1/13785, dated 05.19.14 No. 03-03-RZ/23603 and letter of the Federal Tax Service dated February 24, 2011 No. KE-4-3 / [email protected] ). The courts adhere to a similar position (decision of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated April 25, 2019 No. 876-O).
List of indirect expenses for income tax
The Tax Code does not contain a clear list of indirect costs. The only expense that is directly named in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as indirect is the depreciation bonus. This is recognized as part of the cost of a fixed asset, which is written off at a time during the period of putting the object into operation (clause 9 of Article 258, paragraph 2 of clause 3 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In practice, indirect costs are usually considered to be the salaries of management personnel and employees of departments not directly involved in production. This category of expenses also includes expenses for repairs and rental of non-production facilities, expenses for business trips or advertising. Depreciation on fixed assets that are not used to produce products (for example, office equipment, computers, furniture, vehicles intended for management personnel) is also an indirect expense.
Maintain tax and accounting records of fixed assets according to current rules Try for free
Examples of direct and indirect costs (table)
Here are examples of the most common direct and indirect costs
| Direct | Indirect |
|
|
Fill out, check and submit your income tax return online for free
What are indirect costs
According to FSBU 5/2019, indirect costs are costs that cannot be attributed to specific goods, work, or services. The company itself establishes the classification of direct and indirect costs and the mechanism for dividing indirect costs between types of goods, works, and services (clauses 23-25 of FSBU 5/2019).
Accordingly, the practice remains the same, but according to clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019 it is established that the following cannot be included in the actual cost of work in progress and finished products:
- costs that arise as a result of improper organization of the production process. For example, these include excess costs of goods and materials, electricity, labor, costs from defects, etc.;
- storage costs, with an exception if it is part of a technological process, for example, wood drying;
- administrative expenses, and an exception is if the costs are incurred for the manufacture of products, implementation of works and services.
According to the updated rules introduced on the basis of FSB 5/2019 in 1C: Accounting 8, starting from version 3.0.89, the settings for dividing indirect costs and closing cost accounts have changed (20, 23, 25, 26, 28).
Indirect costs included in the cost of finished products, work or services are reflected in the account. 20.01, 23 or 25. Count. 26 from the current year in the program is intended only for accounting for administrative expenses, for example, expenses for office supplies, communications, consulting services, audit, etc., that is, they are not included in the cost of work in progress and finished products. If earlier on the account. 26 took into account general business expenses associated with the production process as a whole, then accounting for such costs now needs to be kept on the account. 20, 23 or 25. And on the count. 28 takes into account defects in production.
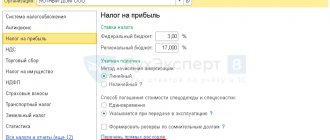
To calculate income tax, all costs are divided into direct and indirect based on the list of direct expenses that the company sets in the income tax settings. To set up the list, you need to go to the “Main” menu, select “Taxes and reports”, go to the “Income Tax” tab and then “List of direct expenses”.
In this regard, the cost of production in accounting and tax accounting may not be the same, which leads to the appearance of temporary differences and deferred tax based on PBU 18/02, regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n.
Why is it necessary to separate direct and indirect costs?
You can recognize direct expenses that fall on goods, works, and services sold in the same period as expenses of the current period. This means that in most cases, direct expenses incurred in a quarter will not be fully taken into account when assessing profits for that period. The costs attributable to work in progress, balances of finished products in the warehouse, as well as to shipped but not sold products will remain unaccounted for (Clause 2 of Article 318, Article 319 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Important
Direct expenses are written off gradually - as products, works, and services are sold. Indirect costs can be taken into account in full during the period of their implementation. There is no need to wait for implementation (clause 2 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Direct costs
Direct costs form the cost of only one type of product. In your accounting policy, you must independently determine the costs classified as direct.
Examples of direct costs:
- inventories, components and semi-finished products;
- wages of primary production workers and social benefits;
- depreciation of main production equipment.
The list of direct costs is presented in Art. 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is open and may include other expenses at your discretion. However, before including costs in the list of direct costs, please note: they must be directly related to the production and sale of goods, works and services.
For trade organizations there is a separate list of direct expenses, which is strictly regulated and cannot be changed. These include the cost of goods purchased and transportation costs.
What is more profitable for the organization?
Obviously, it is more profitable for taxpayers to recognize as many expenses as possible as indirect. This will allow you to write off related expenses faster and reduce your current tax liability. However, as already noted, costs must be divided reasonably, taking into account production technology. It is permissible to recognize one or another type of cost as indirect only if it really cannot be classified as direct. If an organization violates this requirement, it faces additional tax charges (rulings of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 24, 2017 No. 303-KG17-17016 and dated September 19, 2018 No. 306-KG18-13685).
The exception is organizations engaged in the provision of services. They are allowed to completely write off both indirect and direct expenses during the implementation period (Clause 2 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that, although such taxpayers must divide expenses into direct and indirect, they will not face any negative consequences of incorrectly classifying expenses as indirect.
Advice
Organizations providing services can use the general principle of writing off direct expenses only in the period when services are sold, the cost of which includes these expenses.
It is advisable to consolidate the chosen option for recognizing direct expenses when providing services in the accounting policy. In conclusion, let us remind you that the correct division of expenses into direct and indirect will allow taxpayers not only to avoid claims from the tax authorities, but also to optimize current tax obligations.
Direct costs in the estimate
More detailed information about what is included in the direct costs in the estimate can be obtained from the methodological document in construction MDS81-35.2004. In addition, this document also contains a brief description of other estimated costs.
The definition of what direct costs are in the estimate was given in a simplified form above in the text. It should be noted that this definition is typical for all estimate forms: be it an estimate according to Form No. 4, a local resource estimate or another form of estimate documentation.
Figure 1 shows a diagram of direct costs, on the basis of which it becomes clear that direct costs include the following items in the estimate: wage fund (WF), operation of machines and mechanisms (EMM) and materials (MAT).
Figure 1. Composition of direct costs in the estimate
The wage fund is the total cost of wages of workers (ZPR) and machinists (ZPM). That is, in this case, this element of direct costs includes two items in the estimate.
It should also be noted that although the wages of drivers are part of the payroll, their cost in the estimate is taken into account as part of the cost of operating the machines. But in any case, this does not in any way affect the fact that this indicator is included in the direct costs in the estimate.
Remuneration for both workers and machinists is determined based on labor intensity. Labor intensity is the number of hours required to perform a particular type of construction and installation work. Labor intensity is measured in man-hours (man-hours).
In addition, this item of direct costs in the estimate has a characteristic feature, which is the distribution of costs depending on the category of worker. The fact is that in any price estimate form, in terms of the wage indicator, the category that a worker must have in order to carry out one or another type of construction and installation work in compliance with all construction standards and requirements is also indicated. The higher the worker's rank, the higher the wage rate.
The machine operating index (OMI) is calculated based on the time of use of machines, mechanisms and tools. Direct costs in the estimate in this article are determined on the basis of an indicator such as machine hours (or machine hours).
As a rule, the cost of operating machines is part of the norm from the collections of estimate standards GESN or FER. However, the methodological document MDS81-35.2004 mentioned above allows for the possibility of calculating this indicator as part of direct costs in the estimate using the calculation method or the method of resource-technological models. Of course, such calculations must be justified and justified by the relevant permitting documents.
The cost of materials is also an important item, which is included in the direct costs in the estimate. It is important to note that the cost of material resources must be included in the local estimate, estimate in Form No. 4, local estimate, act of work performed in Form KS-2 and in other estimate forms, regardless of who purchased these resources .
The need for materials is determined, as a rule, on the basis of the project for the facility. Also, the amount of materials for each type of work can be taken into account in the estimate based on the defective list, list of materials, etc.
The volume of materials required for the production of each individual type of work is measured in physical units, that is, in meters, kilograms, cubes, etc. Direct costs in the estimate include the total cost of all material resources from all prices in the estimate form.
Figure 2 shows an example of a price, based on which it is demonstrated what is included in the direct costs in the estimate. Most of the norms from the collections of estimated normative bases of GESN and FER have a similar structure.
Figure 2. Example of a quote with direct costs
In addition, it should be noted that direct costs in the estimate may include indicators of energy consumption when using electrical mechanisms during construction and installation work.