The economic activities of organizations are based on the use of property owned by it, which is reflected in accounting. From January 1, 2019, the movable property of an organization, according to amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 374-1), is not subject to property tax, and since accounting data is the basis for calculating NU indicators, the criteria defining movable and immovable property acquire special significance. Postings for property accounting, forming the main balance sheet indicators, are also one of the most important in accounting.
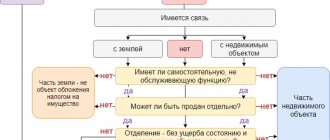
How can an organization distinguish movable property from immovable property ?
Movable and immovable property
Back in 2013, the Ministry of Finance, in letter No. 03-05-05-01/5322 dated February 25, 2013, proposed to be guided by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation when classifying property as movable (immovable).
Is a fence a piece of real estate, or is it considered movable property ?
Art. 130 defines the following property as immovable:
- land plots and subsoil;
- buildings (structures), including unfinished construction;
- residential and non-residential premises;
- garages, parking lots, parking spaces, the boundaries of which are determined in cadastral registration.
Question: Can legal entities enter into an agreement between themselves for the free use of movable or immovable property? View answer
Property is recognized as immovable because its movement without damage to subsequent use is impossible. The objects mentioned above most often become the subject of accounting for organizations and firms.
By the way! Immovable objects include vessels: sea and air vessels and space objects.
Federal Law No. 218 of 07/13/15 prescribes state registration of such objects in the Unified State Register (USRN).
Question: How does an object (equipment) qualify as movable or immovable property for the purposes of corporate property tax? View answer
The Federal Tax Service defines property as immovable if it is registered in the Unified State Register of Real Estate, or according to documents for the object, from which it is clear that it is firmly connected to the land and cannot be moved without destruction. The rest of the property of the Civil Code is defined as movable. Such property does not need to be registered in the register.
Obviously, in accounting, many objects of movable and immovable property, due to the difference in the criteria of civil and accounting legislation, will end up on the same accounts. The management of the company will have to think about how to separate property that is subject to taxation from others in accounting, and how to build an accounting policy in this area.
Draft Federal Law 02/04/02-17/00062515
Amendments to Art. are being prepared. 130 Civil Code of the Russian Federation:
- immovable things
include land plots, subsoil plots, buildings
Definitions (Article 2871 of the Civil Code as amended by Draft No. 62515):
- Building - a structure in which at least two rooms and (or) parking spaces can be formed;
- Structures - a structure in which premises or parking spaces cannot be formed;
- A room is a separate part of a building, the boundaries of which are partitions or ceilings, and has an independent economic purpose.
- Structures are real estate if they: are firmly connected to the ground,
- have independent economic significance,
- can act in civil circulation separately from other things.
The list of types of structures that do not have the characteristics of real estate is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. Objects of unfinished construction are recognized as real estate if they have characteristics approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
See also:
- [02/14/2020 entry] Annual reporting for 2022 in 1C. Property tax
- Inseparable improvements to the leased property with the consent of the tenant, but without compensation
- When do tenants not have to pay property taxes on permanent improvements?
- Million dollar consequences of rental relations
- [04/19/2019 entry] Tax reporting for the 1st quarter of 2022 - we look at the most important things in 1C
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Movable or immovable? The issue was looked into by the Federal Tax Service. The Federal Tax Service in Letter dated August 28, 2019 N BS-4-21/ [email protected] gave recommendations to employees...
- Movable or immovable? And again the Federal Tax Service clarifies. In Letter dated May 21, 2021 N BS-4-21/ [email protected] the Federal Tax Service spoke about the criteria...
- The Federal Tax Service has proposed a scheme for dividing property into movable and immovable. This division of assets is important for all property tax payers...
- Why is movable property subject to property tax based on...
Accounting for movable property
IMPORTANT! The lease agreement for movable and immovable property from ConsultantPlus is available here
From the above, it is clear that movable property, as civil law understands it, will be reflected in different accounts in accounting.
Account 01 and those corresponding to it may reflect the following movable property related to fixed assets:
- machines, equipment;
- office fixtures;
- transport;
- inventory;
- working and productive livestock;
- other types of OS.
The criteria for accounting for such movable property are defined by PBU-6:
- period of use over 12 months;
- subsequent resale is not initially planned;
- in the future the object will bring income to the company;
- its cost is from 40 thousand rubles.
BU wiring:
- Dt 08 Kt 60 (76, 10, 70) – an object of movable property (for example, a car) was acquired and the acquisition costs are reflected.
- Dt 01 Kt 08 – the initial cost (PV) of the asset is fixed.
The specified movable property is depreciated in accounting (in the following ways: reducing balance, linear, proportional to the volume of production, by the sum of the numbers of years of useful life).
There are only two methods of depreciation in NU: linear and nonlinear. As a rule, in order to bring accounting as close as possible and not make unnecessary entries, the linear method is used in both cases.
Formula for monthly depreciation: Depreciation = PS / useful life. use. Accrual posting: Dt 20 (20, 23, 26, 29, 44 and other “cost” accounts) Kt 02.
Analytical accounting for account 01 should take into account the division of property located on this account into movable and immovable. On account 10, in the context of subaccounts, another type of assets is taken into account, classified by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation as movable property: inventories, materials (raw materials, purchased semi-finished products, components, containers, spare parts, etc.) - all goods and materials that cannot be classified as main in accounting means.
Note that in NU the cost of fixed assets “starts” from 100 thousand rubles, and therefore temporary differences are formed in accounting. To account for the diversity of this group of movable property, subaccounts are widely used. For example, containers are taken into account on account 4, fuel – 3.
BU postings: Dt 10 Kt 60, 76, 20, 23, etc. - receipt of materials, depending on the source of receipt. Sometimes an interim account 15 “Procurement and receipt of inventory items” is used: Dt 10 Kt 15. Dt 08 Kt 10 – used inventory items in construction. Dt 20, 26, 28, 91, 44, 94 Kt 10 - transferred to production, for maintenance, used to correct defects, sold, written off as a shortage of goods and materials.
In addition, the civil code defines movable property as funds accounted for in active accounts 50 and 51 using standard transactions. Receipt: Dt 50, 51 Kt 60, 62, 66, 67, etc. – receipt (receipt) to the cash desk (to the current account) from various sources. 50, 51 are credited for expenses, the debit indicates where the funds went. Money can also be transferred to the current account from the cash register and back, for example: Dt 50 Kt 51.
Securities (Article 130 of the Civil Code, clause 2) are taken into account in the accounting system depending on their type and transactions. Account 58 is used as standard, and other accounting accounts are used less frequently.
VU wiring (example):
- Dt 58 Kt 51 – purchased by the Central Bank of another company.
- Dt 91 Kt 58 – sold to Central Bank.
- Dt 76 Kt 51 – bond paid.
- Dt 76 Kt 91 - income on it is recorded, etc.
Intangible assets (trademarks, software, inventions) are also classified as movable property of the company, despite the fact that they do not have a physical form. The characteristics of intangible assets are otherwise the same as those specified for operating systems; for example, they must be used for more than a year in the organization.
The postings through them, as in the previous case, are varied. Correspondence depends on the method of receipt of intangible assets, the method of its disposal.
VU wiring (example):
- Dt 08 Kt 60, 76, 66, etc. – paid to suppliers of intangible assets, duties, interest on loans, etc., were paid in connection with the acquisition of intangible assets.
- Dt 08 Kt 70, 69, 71, etc. – NMA was created in the organization.
- Dt 04 Kt 08 – registered with intangible assets.
- Dt 20, 26, etc. Kt 05 – depreciation of intangible assets.
- Dt 91 Kt 04 – asset sold, residual value reflected.
- Dt 05 Kt 04 – depreciation of retired intangible assets is written off.
Property tax for traffic lights
The material was prepared by specialists from the Center for Accounting and Taxation Methodology
The Russian organization owns a traffic light, which is located on a private public road passing through several settlements. Is it legal to exempt this traffic light from corporate property tax in accordance with paragraph 11 of Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation?
The release of a pedestrian traffic light, which is located on a private public road passing through populated areas and is on the balance sheet of a Russian organization as fixed assets, in accordance with paragraph 11 of Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is unlawful.
Rationale: Based on paragraph 1 of Article 373 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payers of the property tax of organizations are organizations that have property recognized as an object of taxation in accordance with Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
By virtue of paragraph 1 of Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the objects of taxation for Russian organizations are movable and immovable property (including property transferred for temporary possession, use, disposal, trust management, contributed to joint activities or received under a concession agreement), taken into account on the balance sheet as fixed assets in the manner established for accounting, unless otherwise provided by Articles 378 and 378.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
According to paragraph 5 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Fixed Assets” PBU 6/01, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2001 N 26n, fixed assets include buildings, structures, working and power machines and equipment, measuring and control instruments and devices, computer equipment, vehicles, tools, production and household equipment and accessories, working, productive and breeding livestock, perennial plantings, on-farm roads and other relevant objects.
Based on clause 3.9 of GOST R 52289-2004, approved by Order of Rostechregulirovanie dated December 15, 2004 N 120-st (hereinafter referred to as GOST R 52289-2004), a road traffic light is a light-signaling device for regulating traffic. Therefore, traffic lights are classified as fixed assets.
In accordance with paragraph 11 of Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, organizations are exempt from property tax, including organizations in relation to public railways, public federal highways, main pipelines, energy transmission lines, as well as structures that are an integral technological part the specified objects. At the same time, the list of property related to these objects is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
As follows from the List of property related to federal public highways, as well as structures that are an integral technological part of these objects, in respect of which organizations are exempt from taxation on the property of organizations, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 30, 2004 N 504 (hereinafter - List N 509), this List includes traffic lights and other means for regulating street traffic (code 4 3599420). List N 509 also establishes that this category includes traffic lights and means for regulating traffic on public federal highways passing through populated areas .
By virtue of Part 1 of Article 5 of the Federal Law of November 8, 2007 N 257-FZ “On highways and road activities in the Russian Federation and on amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as Law N 257-FZ), highways Depending on their significance, they are divided into: 1) federal highways; 2) highways of regional or intermunicipal importance; 3) local roads; 4) private roads.
According to part 5 of this article, public roads of federal significance are the following roads: 1) connecting the capital of the Russian Federation - the city of Moscow with the capitals of neighboring states, with the administrative centers (capitals) of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation; 2) included in the list of international highways in accordance with international agreements of the Russian Federation.
In addition, on the basis of Part 6 of Article 5 of Law No. 257-FZ, public highways of federal significance may include the following highways:
1) connecting administrative centers (capitals) of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation; 2) being access roads connecting public roads of federal significance, and the largest transport hubs of international importance (sea ports, river ports, airports, railway stations), as well as special objects of federal significance; 3) being access roads connecting the administrative centers of constituent entities of the Russian Federation that do not have public roads connecting the corresponding administrative center of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation with the capital of the Russian Federation - the city of Moscow, and the nearest seaports, river ports, airports, railway stations.
At the same time, on the basis of part 7 of the above article, the List of public roads of federal significance is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. Part 12 of Article 5 of Law N 257-FZ classifies private public roads as roads owned by individuals or legal entities that are not equipped with devices that restrict the passage of vehicles of an unlimited number of persons. Other private roads are classified as private non-public roads.
In turn, from Part 2 of Article 6 of Law N 257-FZ it follows that highways that are included in the list of public highways of federal significance are federal property.
Thus, we can conclude that private public roads cannot be classified as federal roads.
Accordingly, they do not fall under paragraph 11 of Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 15.
Sign up
Real estate accounting
Real estate is included in the OS. This:
- buildings, structures;
- perennial plantings (shrubs and trees);
- plots;
- environmental management facilities;
- other objects, according to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 130), which are real estate and require state registration.
The synthetic accounting transactions are similar to those already given for the operating system. Analytical accounting is organized in such a way as to distinguish between movable and immovable assets. Some categories of real estate are not depreciated: land, natural resources. Real estate must be registered with the state (Article 131 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law No. 218 of 07/13/15).
The state registration procedure and registration of real estate are not related to each other. Before registration is completed, you can reflect the real estate by posting Dt 01 Kt 08, opening a separate sub-account for account 01, for example, “OS with unregistered title”, and then transfer it to another sub-account using internal posting to 01.
Briefly
- Movable and immovable property, named in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is reflected in various accounts in accounting.
- Both types of property can be recorded on the account. 01 BU, in analytical accounting they need to be separated. Land and natural resources related to real estate are not depreciated.
- Other movable property (inventory, shares, money, intangible assets) is accounted for in accounting in accordance with the Chart of Accounts. Accounting accounting accounts are used by type of value.
- The moment of reflection in the accounting of real estate does not depend on the date of its state registration.