A corporate card can be issued for making small purchases for the current needs of the enterprise or for use on business trips. Cards are available in three versions:
- Debit – this payment instrument allows you to use money that was previously credited to the account linked to the plastic card. If the user's available balance is not enough, he will not be able to borrow additional funds from the bank.
- Credit – the servicing banking institution sets a card limit within which users can pay for purchases.
- Debit cards with overdraft facility. When paying with such a card, corporate clients can use not only the resources available in the account, but also the credit limit allocated by the bank. Loans will be repaid automatically the first time funds are received on the card.
What is the procedure for obtaining a corporate card ?
Which card is better to have - debit or credit?
For corporate purposes, it is possible to issue various versions of bank cards:
- debit only (the card will be replenished with funds before they can be spent);
- credit (funds on the card are provided by the bank within the limit);
- debit with overdraft (there is the possibility of spending funds in excess of the debit balance - as a rule, also limited).
Which card to choose depends on the purposes for which it is issued, as well as on a certain degree of trust in the employee who will use it. For example, if a card is issued to a manager for use on business trips, including foreign ones, it is advisable to provide for the possibility of spending funds on a loan or overdraft (“extra” money may come in handy). If the card is issued to a business owner for regular small purchases within the budget, the best option may be a debit card with a fixed monthly replenishment.
NOTE! If a credit card has a period of interest-free use of credit funds, the economic benefit from such use for tax purposes does not need to be calculated (see letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 18, 2012 No. 03-03-10/38).
How to use a business card, do you need a power of attorney for this?
The issuance of a corporate card is regulated by the company’s internal regulations; we have already mentioned that personalized cards should not be transferred to another person; there are no such restrictions for others.
It may sound strange that a power of attorney is sometimes required to pay with a card , but this is true. For example, if you want to pay a product to a supplier, receive a delivery note, an invoice, and the product itself, you will have to confirm that you are indeed a representative of the organization for which the purchase is intended.
You can use a corporate card only for work purposes; for personal purchases, you can use your own cards. Don’t forget that purchases are actually made from the organization’s account and the company will have to be responsible for spending money, among other things. to its director.
How should card transactions be regulated?
If corporate cards are used in an organization, it is advisable to approve by local regulations the procedure for using cards and submitting reports on spent funds.
Such regulations will also help in the following cases:
- Settlement of possible claims from tax authorities regarding the procedure for reflecting spent funds on corporate cards in accounting. For example, if the internal regulations do not establish a clear procedure for an employee to report on funds withdrawn from the card through an ATM, tax authorities may consider that in this case all amounts withdrawn from the card should have been transferred through the organization’s cash desk (recorded according to the PKO and immediately issued a cash register for issuance for the report). Of course, such a claim is based on rather weak grounds, because in fact the money did not end up in the enterprise’s cash register. But in order to avoid such nuances, it is better to register all options for spending funds from the card and reporting on them in the internal regulations.
- Submitting claims to an employee in case of misuse of card funds or detection of shortages and abuses. If the internal regulations are correctly drawn up, it will be possible not only to withhold losses from the misuse of funds from the salary of the guilty employee, but also to apply disciplinary action to the employee under Art. 192 and part 1 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (for violation of the provisions on discipline in the organization).
For information on drawing up an order for discipline, read the article “Order for disciplinary punishment - sample and form.”
What are business cards?
Ruble debit cards are used for ordinary payments, for example, purchasing office supplies, paying for a hotel on a business trip, etc., while the organization’s own funds are spent, in contrast to credit cards, where the funds are provided by the bank. Currency cards are used on foreign business trips.
Personalized cards are issued to a specific employee and can only be used by him. If an employee quits, the card is blocked.
Unnamed business cards can be used by any employee of the organization who receives it. For example, if a company has several employees who sometimes go on business trips, they can transfer the card to each other.
It is better to specify the procedure for using a non-named card in the internal regulations of the organization so that there is no confusion. Each employee must account for their expenses.
Do I need to submit information about corporate cards to the tax office?
The Law “On Amendments...” dated April 2, 2014 No. 52-FZ, from May 2014, abolished the obligation of taxpayers to submit information on opening (closing) bank accounts to the tax authorities.
As noted above, the issuance of bank cards itself also refers to the operations of the issuing bank, and not the enterprise.
Thus, there is no requirement to inform the tax office that you have issued a corporate card.
How to take into account the costs of issuing corporate cards for income tax, see ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the legal system is free.
...and with company employees
A corporate card is a personal means of payment intended for employees to pay for goods or services, as well as for receiving money from ATMs and banks.
The bank debits money from the company's card account as settlements are made for holders' transactions. It is considered that the funds debited from the account are issued for reporting to an employee of the organization. In stores, hotels and other places of payment, an employee of the organization receives documents confirming expenses made using the card. Such documents are considered to be invoices for hotel accommodation, travel tickets, receipts, checks, invoices, etc. They must be accompanied by original slips, receipts from electronic terminals and ATMs. The employee of the organization submits all these documents to the accounting department of the enterprise along with the expense report. If he did not do this, and the bank statement indicates that cash was withdrawn from the card account, the organization’s accountant reflects the debt of the organization’s employee as follows:
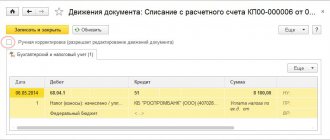
Debit 73 Credit 55
– the write-off of cash from a special card account, which is not confirmed by primary documents, is reflected.
Upon receipt of the advance report, expenses incurred (related to the production activities of the organization) are reflected in the general manner. If the expenses incurred by an employee of the organization are not related to production activities, then the latter is obliged to reimburse them.
Reimbursement by the employee of these amounts can be made in two ways: either the employee of the organization deposits cash into the organization's cash desk, or the organization deducts the amount of damage from the employee's salary. In this case, the accountant will make the following entries:
Debit 50 Credit 73
– contribution by the employee of cash to reimburse expenses;
Debit 70 Credit 73
– deduction from the employee’s salary of the amount of money spent on a corporate card for personal purposes.
How does an employee account for funds spent from the card?
The money on the card belongs to the company and is at its disposal. Consequently, the employee’s obligation to report arises only when he paid with a card or withdrew cash from an ATM.
As a general rule, funds used by an employee from a corporate card are considered as accountable amounts. Accordingly, the reporting procedure for them is similar. The employee should:
- Prepare an advance report on the amounts spent. This can be done using the standard AO-1 form, but it can also be done using a form approved within the organization (for example, internal regulations on the use of corporate cards may also contain a special report form).
All details of preparing an advance report when expenses are paid with a corporate bank card are set out in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to K+ for free.
- Attach supporting documents to the report: cash register receipts, invoices, acts, etc.
- Submit the report to the accounting department of the enterprise in the manner and within the time limits provided for by the regulations on the use of corporate cards.
NOTE ! Banks periodically (usually monthly) compile and send statements to clients on their card products. Thus, the reports of employees using cards are quite easy to check regarding non-cash payments and withdrawals through ATMs.
Features of payments using a corporate card
A corporate card issued by a financial organization remains its property, and the money on it belongs to the company for which the plastic was issued. The client receives authority only to use the card in payments, carry out operations to credit and spend funds on the card account. The plastic card issued by the bank is not accounted for by the company.
IMPORTANT! An enterprise is not required to report the opening of a corporate card (debit or credit) to the tax office. This function is assigned to banking institutions that provide services for issuing and servicing such payment products.
Employees must submit written reports to the employer about the movement on the corporate card in each case of cashing out funds from it or conducting expense transactions with its help. Monetary resources transferred to this type of card are reflected in the company’s accounting as part of accountable amounts. Responsible employees who are granted the right to dispose of a corporate card are obliged to:
- at the frequency established by the enterprise for compiling reports on the movement of funds on corporate cards, submit a final report (an organization can develop its own report template or invite employees to fill out the AO-1 form);
- keep all documents confirming each operation and attach them to the report (checks, acts, invoices).
At what point do employees receive funds against their corporate card report ?
The accounting department, after receiving reports from responsible officials on the expenditure of funds from corporate cards, verifies the data with bank statements. If shortfalls are identified due to unreasonable or inappropriate spending of funds from a corporate card, the company can withhold the amount of damage from the employee if a number of conditions are met:
- the amount of damage caused by the actions of the responsible person can be reliably determined;
- the guilt of a particular employee has been documented;
- Based on the results of an internal investigation, the head of the company issued an order to withhold the amount of the shortfall;
- from the moment of recording the fact of the occurrence of a shortage or damage to the day of issuing an order to withhold a certain amount from the salary of the perpetrator, no more than a month has passed;
- the alleged deductions are not disputed by the person at fault.
IMPORTANT! Corporate cards cannot be used to issue wages and social benefits to employees.
The number of corporate cards for one company is not limited. An organization can order several personalized or non-personalized cards from the bank, and link them to one or different accounts. For each plastic card, it is possible to limit the amount of expenses by setting an individual limit value.
How to prepare an advance report if expenses were paid with a corporate bank card ?
Using a corporate card you can carry out the following expense transactions:
- payment of expenses for employees on business trips;
- entertainment types of expenses;
- implementation of transfers in favor of public utilities;
- conducting settlements with counterparties;
- purchase of low-value assets;
- payment of bills for services directly related to the company's business activities.
Question: How are payments for purchased materials for business needs, which are paid by an employee of an organization using a corporate bank card, reflected in accounting? View answer
Is it possible to withhold damages from an employee for using funds for other purposes?
Yes, you can. Subject to a number of conditions:
- the amount of damage can be estimated;
- the employee’s guilt in the damage has been proven (for example, the purchase of goods for personal needs is confirmed by a bank statement on a personal card and copies of the seller’s payment documents);
- a decree (order) was issued from the head of the enterprise to withhold amounts of damage from the employee’s salary no later than 1 month from the moment the fact of damage and guilt was established (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- The amount of deduction made corresponds to the standards established in Art. 138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- the employee does not challenge the withholding (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
more about the terms of salary deductions here .
What are the typical transactions for transactions with corporate cards?
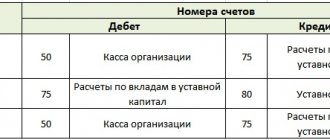
In accounting, card transactions are reflected using accounts 55 “Special accounts in banks” and 71 “Settlements with accountable persons.” Typical operations are presented in the table:
| Dt | CT | Content | Note |
| 55 | 51 | Replenishment of a corporate card | Score 55 is maintained in analytics for each card account |
| 55 | 66 | Use of bank credit funds | For credit card and overdraft |
| 91 | 55 | Payment for services or bank commission on the card has been debited | |
| 71 | 55 |
| Posting is carried out if the accounting department has means of operational control over card movements, for example, Internet banking |
| 25, 26, 44, 60, 76 | 71 | The employee's report on the amounts spent is reflected | The posting is made on the date the report is accepted |
| 71 | 57 | The fact that the employee used the card to pay expenses is reflected |
|
| 57 | 55 | The use of card funds is reflected according to the bank report and employee report | As of the date of receipt of the bank report |
| 91 | 66 | Interest accrued for using loan funds | For credit cards and overdraft |
| 66 | 55 | Repaid credit card loan | Usually in the amount of the mandatory payment on the card presented by the bank |
Read about the types of fraud associated with bank cards in the article “ Fraud using payment bank cards . ”
Accounting for settlements with the bank...
The basis for drawing up settlement and other documents to reflect the amounts of transactions performed using payment cards in accounting is the payment register issued by the bank, or an electronic journal. Debiting or crediting funds for card transactions is usually carried out no later than the business day following the day the bank receives the payment register, or an electronic journal from a single settlement center. Subsequently, these documents can be obtained by the company.
When opening or closing a bank account for servicing corporate cards, you must notify the inspectorate within seven business days from the date of its opening or closure.
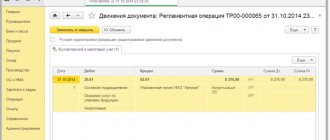
Transfers of funds to card accounts must be reflected in accounting as follows:
Debit 55 Credit 51 (52)
– funds are transferred to a bank card account from a current (currency) account.
The amount of remuneration that the bank charges for servicing a special card account is an operating expense in accounting and is accounted for as follows:
Debit 91 Credit 55
– paid for bank services.
However, the most difficult thing is to organize analytical accounting for the “Special Card Account” subaccount. After all, accounting for this sub-account must be organized in the context of specific card accounts opened in a particular bank. In addition, analytical accounting is significantly influenced by the conditions for the issuance and use of bank cards offered by a financial institution. So, for example, when concluding an agreement, the bank may impose a condition on the presence of a minimum balance on the organization’s account (a security deposit that can be used for settlements in exceptional cases to cover exceeding the payment limit). In this case, it is advisable to use second-order subaccounts, for example, “Special card account – minimum balance” and “Special card account – payment limit”.
If several cards are opened for a special card account, then any holder can carry out transactions using them within the total payment limit. In this case, analytical accounting of cardholders is not necessary until the funds are issued to the accountable person.
When each payment card corresponds to a separate account, then when funds are transferred to a special card account, a special statement is sent to the bank containing the holders’ data and card numbers, as well as the amounts to be credited to each bank card. In this case, analytical accounting is carried out in the context of holders of issued cards. When opening a bank card in foreign currency, it is necessary to keep in mind that the foreign currency located on a special card account must be revalued on the date of the transaction and on the date of preparation of the financial statements (PBU 3/2000 “Accounting for assets and liabilities, the value of which is expressed in foreign currency ").
Emerging exchange rate differences are taken into account for accounting and tax accounting purposes, and in both types of accounting, the amounts of exchange rate differences are considered non-operating income (expenses). In accounting, exchange rate differences are included in financial results and are reflected as follows:
Debit 55 Credit 91
– reflects the amount of positive exchange rate difference;
Debit 91 Credit 55
– reflects the amount of negative exchange rate difference.
If an organization has entered into an agreement to issue corporate credit cards, then the following operations will be performed in accounting:
Debit 55 Credit 66
– the loan amount was credited to a special card account on the date the funds were spent;
Debit 91- 2 Credit 66
– interest has been accrued on the loan (postings are made periodically, within the terms established by the agreement for payment of interest. – Author’s note);
Debit 66 Credit 51
– the interest on the loan is listed;
Debit 10 Credit 55
– inventory items are capitalized (in case the funds from the corporate card were spent on purchasing inventory items. – Author’s note).
Results
Accounting for corporate cards is carried out according to general rules. At the same time, for accounting purposes, card accounts opened in banks are classified as special bank accounts, and funds spent from cards by employees are classified as accountable amounts. It is recommended to approve the procedure for using cards in a separate internal document, which records all aspects of their use, paying special attention to the procedure for reporting on the expenditure of funds.
Sources:
- Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 18, 2012 N 03-03-10/38
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What types of services can be paid for with a corporate card?
It is customary to use corporate cards to pay for the services of counterparties (various types of supplies), the purchase of office supplies, office equipment, tools for business activities, and the purchase of spare parts for company cars. Corporate cards can also be used to pay for corporate communications services, copying equipment maintenance, cargo delivery, and vehicle rental. As mentioned above, corporate cards are used mainly to account for expenses associated with business trips, which include tickets, hotel accommodations, taxi services, and gasoline costs. It is better to accrue daily allowances either to the personal cards of employees, or issue them in cash, in order to avoid various kinds of incidents.