Do you need a document?
In the terms of the contract, the parties to the transaction can agree on the rules for issuing certificates of completed work. To this primary document, which is the basis for reflecting work in accounting, and costs - when calculating income tax. In other words, the act of completion and the invoice are considered two non-fungible documents.
This means that in order to properly process the transaction, the supplier must provide an invoice and a signed certificate of completion of work.
It is worth noting that the above two documents can be replaced by one - a unified transfer document (UDD). We present a comparison of UPD and invoice here.
Important! The contractor, for the work provided, issues an invoice no later than five days from the date of drawing up the primary document (work completion certificate) addressed to the customer.
The certificate of completion and the invoice are issued with different dates: how critical is this?
In current business practice, the package of documents accompanying the transaction includes an invoice, an invoice and a certificate of completion of work. The accounting department files this set of papers after the work has been accepted by the customer and the necessary accounting operations have been completed.
The question arises: if all three documents relate to one transaction, should they be issued on the same date or can they diverge in time? And if so, how critical is this discrepancy?
The legislation does not require that the dates in the work completion certificate and the invoice coincide. And the date of issuance of such a document as an invoice is not regulated by any regulatory act. This is explained by the fact that the invoice is not recognized as a primary document in accounting, and for tax accounting it has no significance. The contractor delivers it to the customer at his own discretion or within the time limits specified in the contract. That is, a coincidence in the dates of the invoice, invoice and certificate of completion of work is acceptable, but not necessary.
What needs to be taken into account in a situation where the act and invoice are issued on different dates?
The date in the work completion certificate is an important element that affects the reliability of the formation of information in accounting. On this date, the customer’s accounting recognizes expenses in the amount of the cost of work performed, agreed upon by the parties. In the contractor's accounting on the same date, revenue from the implementation of work is reflected and expenses associated with the fulfillment of obligations under the contract are recognized.
The date of the invoice affects the timeliness of the customer receiving the VAT deduction for the work. It is determined according to the norms of paragraph 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is selected from a segment of 5 calendar days, counted from the moment:
- performing work, providing services or shipping goods and products;
- receiving an advance;
- changes in the volume of work performed (quantity or price of goods shipped).
It turns out that the discrepancy in dates is a normal situation limited by time frames. What happens if you violate the 5-day deadline or issue a non-advance invoice before the work is completed and accepted by the customer? Such calendar leapfrog, if it occurs at the border of tax periods, can cause claims from controllers and become a reason for a fine.
We talk about the amount of fines for violating the deadline for issuing an invoice in this material.
Who is exhibiting?
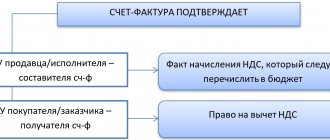
An invoice is issued by the counterparty who performs certain work under the terms of the contract, who also has obligations to pay value added tax to the state budget. The same document, for the customer, becomes the basis for accepting the work provided, indicating the amount of VAT to account for its deduction.
More information about who issues the invoice can be found here.
Registration procedure
An invoice is necessary for both the customer and the contractor , which means that it is prepared in two copies with the same content. As mentioned above, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 168 regulates the deadline for issuing this document in the following order:
- On the day of receipt of advance payment for future deliveries of goods (transfer of ownership rights).
- On the day of actual shipment of goods or transfer of ownership.
The five-day period begins on the day following the date of first shipment. An invoice for the advance payment is also provided within five days from the date of receipt of funds by the contractor on account of the future provision (provision) of work.
Filling rules
The invoice form contains lines and columns with numbering and letter designations.
Strings
| Line | Purpose | Example |
| 1 | The serial number and date of compilation are indicated. Corresponds to the current number and date of issue | No. SF 0004/01-12 dated 02/15/2018 |
| 1a | To make corrections to the serial number and date. If they are absent, a dash is placed. | – |
| 2 | A line indicating the full name of the seller. | Limited Liability Company "Print" |
| 2a | Address indication:
| 000000, Moscow, st. Novomarinskaya 18, apt. 128 |
| 3 | Shipper's name. If the name of the shipper is the same as the seller, then “he” is written in this column. | "he" |
| 4 | Name and address of the consignee (as in the constituent documents); in relation to these services, no work is indicated. | – |
| 5 | Indication of payment document details when receiving an advance payment. | PP No. 15 of 02/15/2018 |
| 6, 6a, 6b | Name of the buyer (as in the constituent documents). | Limited Liability Company "Ladya" |
| Buyer's address, as in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs. | 000000, St. Petersburg, st. Kollontai, 18, kV. 82 | |
| INN/KPP of the buyer. | 000000000000/0000000 | |
| 7 | Name and code of the currency (current currency classifier). | 643 |
| 8 | If there are government contracts, indicate the identification number of the contract for the supply of goods or the contract under which subsidies are provided to the legal entity from the federal budget. | – |
Graphs
| Count | Purpose | Example |
| 1 | Name of works. | Laying shielded twisted pair cable |
| 1a | Product type code: filled in by the taxpayer when exporting goods outside of Russia. | – |
| 2 and 2a | Code/designation of the unit of measurement (OKEI). | Linear meters |
| 3 | Quantity of goods (shipped). | 170 |
| 4 | Product price (excluding VAT). | 300,00 |
| 5 | Cost of goods (excluding VAT). | 51000,00 |
| 6 | Excise tax amount (if there is no amount, “no excise tax” is written). | Without excise tax |
| 7 | Tax rate (if excluding VAT is confirmed by the entry of clause 5 of Article 168 of the NKRF). | 18% |
| 8 | Amount of VAT (billed to the buyer). | 9180,00 |
| 9 | The total cost of the shipped goods including VAT. | 60180,00 |
| 10 and 10a | Indication of the code and name of the country of manufacture (if not in Russia). | – |
| 11 | Customs declaration number (if not in Russia). | – |
You can learn how to fill out an invoice correctly here.
Which document can be issued earlier?
Do not discount the fact that when providing work, an invoice cannot be issued before it is provided . But this does not apply to prepayment (advance payment) for work.
Arguments that enable the performing company to issue an invoice for the provision of work before the fact of presentation and in the absence of prepayment (advance payment) are considered to be those that the supplier companies do not have any fundamental values for the timing of presentation of such documentation.
Attention! The simultaneous receipt of this document by the customer becomes a mandatory condition for accepting VAT for deduction. In other words, early receipt does not affect the fulfillment of this condition.
Since the provision of an invoice does not play a role for the supplier, this document is issued by the seller at the time of signing the contract. Early receipt of a completed document does not affect the VAT deduction.
Along with the paper version, the electronic form of the invoice has legal force. This document also contains all the necessary information in compliance with all the rules, which is signed by an authorized person (read about signing an invoice here). Such a document is the basis for deducting VAT and must be stored for four years (we wrote about the rules for storing invoices in a separate article).
Forcing the supplier to issue an invoice
There is a non-standard way to force a supplier to issue an invoice. Some companies independently issue a document from the supplier with an arbitrary number, but with data on actual shipments. After this, the document is reflected in the purchase book and VAT return.
An automatic system for conducting desk audits on VAT will detect discrepancies between the data of the supplier and the buyer. The difference will be exactly the same as the self-generated document reflected by the buyer. The supervisory authority will request clarification from the parties to the transaction.
Upon receipt of the request for clarification, the supplier will have to issue an invoice. After this, the buyer will need to submit an updated declaration and make adjustments to the purchase books, since the supplier’s invoice number will be different.
For reference! Since the VAT amount will not change, and the documents will be the same for the supplier and the buyer, there will be no problems in the future.
In addition, you can force the counterparty to issue an invoice through the court. If the basis for refusal to deduct VAT is the absence of an invoice, and there is evidence of repeated requests from the buyer to provide documents, the arbitration court may side with the taxpayer. An example is the decision of the Arbitration Court of the Far Eastern District No. A51-14757/2017 dated May 31, 2022, which states that the absence of an invoice is not an obstacle to the taxpayer receiving a VAT tax benefit. The main grounds for obtaining a deduction are the real nature of the transaction and the presence of reliable information in supporting documents.
The method of forcing the generation of an invoice through the independent preparation of a document or through the court is valid if the supplier is also a bona fide taxpayer. If he is a one-day company that does not submit reports, then the buyer will simply be denied a VAT deduction on the basis that the transaction is fictitious. At the same time, the buyer will still be required to submit an updated declaration, in which the transaction with the dubious company will be absent.
Actions after invoicing
Clause 3 art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliges the taxpayer to keep a journal record of issued and received invoices, books of purchases and sales. This procedure was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
Buyers maintain a log of received original invoices from sellers. Clause 8 of the Rules obliges to register received invoices in the purchase book as the right established by Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - tax deduction.
In what cases is it necessary to issue an invoice to the buyer?
- transactions are not subject to or are exempt from VAT in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, when issuing cash loans (subclause 15, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the buyer (customer) is not a VAT payer (exempt from paying such tax) and the seller has signed an agreement with him not to issue invoices. In such a situation, invoices may not be issued, even if the transaction is subject to VAT. For example, if a seller – a VAT payer – received an advance from a buyer using a simplified method, if there is a mutual agreement, an invoice for the advance does not need to be drawn up (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 16, 2015 No. 03-07-09/13808). By the way, the seller is not obliged to demand from the buyer documents confirming that he does not pay VAT legally (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2019 No. 03-07-09/17700);
- in transactions with interdependent persons, for tax purposes, the seller increases the price of goods, works, services to the market level and adjusts the VAT tax base (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 1, 2013 No. 03-07-11/6175).
Operations involving the transfer of goods on the territory of Russia (performance of work, provision of services) for one’s own needs are not subject to VAT if the costs of such operations are taken into account when calculating income tax. This follows from the provisions of subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.