What is OS
The concept of fixed assets is disclosed by PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets” and the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. OS is the property of an enterprise, repeatedly used in production and economic activity, meeting the conditions:
- intended for long-term use (more than a year);
- not for sale;
- not processed during the production process (like raw materials);
- it is expected to make a profit.
In other words, OS are buildings, equipment, machines, machines, computers, office equipment, household supplies, etc. OS also include animals, fruit-bearing perennial plants, capital communication and transport facilities (communication centers, roads, power grids).
The criteria for fixed assets also include the initial cost, but it is different for accounting and tax accounting. In accounting (BU) (clause 5 of PBU 6/01), the maximum cost of classifying property as MPZ is 40,000 rubles. (accounting policy may establish a smaller amount). Such property is written off as expenses as soon as it is put into production. Anything that exceeds this limit, but meets the above criteria, is taken into account as OS.
From 2022, the new FSB 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” and FSB 26/2020 “Capital Investments” are mandatory. The provisions of these standards can be applied earlier by prescribing such a decision in the accounting policies of the enterprise.
In tax accounting (TA) objects worth up to 100,000 rubles. inclusive, fixed assets are not considered (Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The assignment of an asset to fixed assets affects the procedure for accounting for its value as part of expenses (fixed assets are subject to depreciation, i.e., they are written off gradually according to the accounting policy of the enterprise, and inventories are written off at a time), as well as the procedure for document flow, inventory and write-off.
Putting the OS into operation
03/11/2016 – The fixed asset was accepted for accounting.
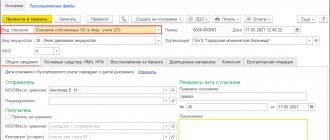
Commissioning is documented in the system with the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets (menu OS and intangible assets – Receipt of fixed assets – Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets):
Fill in the fields:
- Type of operation – in this case Equipment. The document will also be used to accept construction projects for accounting and reflect acceptance for accounting based on inventory results
- Method of receipt - in this case, the equipment was purchased for a fee
- OS event - indicate the event Acceptance for accounting with commissioning
- Equipment - the purchased fixed asset is indicated
- Account – the account to which the fixed asset was capitalized
Next, go to the Fixed Assets tab.
Here you need to indicate the fixed asset that will be listed on account 01 (fixed assets directory):
The procedure for accepting a fixed asset in accounting is described on the Accounting tab:
Here you need to indicate:
- Fixed asset account - we have 01.01
- Accounting procedure - in this case we indicate Accrue depreciation;
- Depreciation account - depreciation will be accumulated on account 02.01. It is important not to forget to check the Calculate depreciation checkbox!
- The method of calculating depreciation is in this case the Linear method. Possible options:
- Useful life of equipment – useful life of equipment in months
- Method of reflecting depreciation expenses. To be filled out as follows:
We indicate the cost account to which depreciation expenses and analytics will be assigned to the cost account.
The procedure for accepting a fixed asset for tax accounting is described on the Tax Accounting tab:
Fill in as follows:
- The procedure for including cost in expenses - in this case, depreciation. It is also important not to forget to check the Accrue depreciation checkbox so that depreciation expenses are calculated in tax accounting
- Useful life - useful life for tax accounting purposes in months
- A special coefficient is a decreasing or increasing depreciation coefficient for NU. In this case, the special coefficient is not applied
The document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets generated the following transactions:
Thus, the initial cost of the fixed asset in accounting and tax accounting was completely transferred to the organization’s fixed asset account.
Postings upon receipt of fixed assets
Fixed assets are taken into account at their original cost. It is understood as the sum of the cost of purchasing the OS and other expenses associated with this purchase (installation, delivery, customs duties, intermediary commission, etc.).
The initial cost of an asset does not include VAT if this tax is refundable for the company (clause 8 of PBU 6/01). Non-payers of VAT (for example, simplifiers) take this tax into account in the initial cost of property (subclause 3, clause 2, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The OS is accepted for accounting on the date when it is fully formed, and for NU - when the OS is put into operation.
When an asset is received, accounting records are generated:
- Dt 08 Kt 60 (10, 70, 69) - expenses for the acquisition or creation of fixed assets are taken into account;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 - input VAT is allocated;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - PS OS was formed.
If the OS requires installation, then account 07 “Equipment for installation” will be included in the postings. As a rule, it is used by construction organizations. The account accumulates information about equipment that requires technological installation, connection to networks and communications and is intended for installation in premises under construction. After the costs are fully collected on the account, the amount of the installed OS is written off to Dt account 08 (Dt 08 Kt 07). Next, the same algorithm is applied: amounts from account 08 are written off to account 01, thus forming the initial cost of the asset.
Goods received from the supplier: transactions and documents
In March, the founders made contributions to the authorized capital:
1. Cash in the amount of 30,000 rubles;
2. A machine that requires installation, the market price of which is 80,000 rubles, and the valuation agreed upon by the founders is 75,000 rubles.
The delivery of the machine, installation and connection were carried out by the company’s repair shop. Costs amounted to 4,860 rubles.
The main facility was put into operation in April of this year.
Reflect in the accounting of the enterprise the operations of accounting for contributions to the authorized capital and putting fixed assets into operation.
Solution
Journal of business transactions
| Contents of a business transaction | Amount RUR | Wiring | |
| D | TO | ||
| 1. Authorized capital announced | 200 000 | 75.1 | 80.1 |
| 1. Funds contributed by the founders as a contribution to the authorized capital | 30 000 | 51 | 75-2 |
| 2. A fixed asset requiring installation as a contribution to the authorized capital has been accepted | 75 000 | 07 | 75-2 |
| 3. The main asset has been transferred for installation | 75 000 | 08 | 07 |
| 4. Costs associated with installation are reflected | 4860 | 23 | 70 |
| 5. Installation costs were written off to increase the initial cost | 4860 | 08 | 23 |
| 6. The fixed asset has been put into operation | 79 860 | 01 | 08 |
Problem 10
An inventory was carried out in December of this year
fixed assets, as a result of which previously unaccounted for equipment was discovered in the warehouse. Its market price on the day of discovery was 24,000 rubles. This property was accepted for accounting.
Reflect this situation in the company's accounting.
Solution
Journal of business transactions
| Contents of a business transaction | Amount RUR | Wiring | |
| D | TO | ||
| The market value of the fixed assets identified during the inventory is reflected | 24 000 | 08.4 | 91.1 |
| OS accepted for accounting | 24 000 | 01 | 08.4 |
| Profit is reflected when registering fixed assets identified during inventory | 24000 | 91.9 | 99 |
Accounting for depreciation of fixed assets: postings
Unlike materials and inventories consumed in production, fixed assets transfer their cost to company expenses gradually. This process is called depreciation. However, it is not accrued for certain types of fixed assets. Such objects include assets that do not change production qualities during the operation of the enterprise: land plots, cultural heritage sites, art collections, etc.
In accounting, four methods of calculating depreciation are used (linear, reducing balance method, by the sum of the numbers of years of useful life, in proportion to the volume of production), however, for the purposes of accounting, only linear and non-linear methods are used.
As a rule, an organization uses one method of calculating depreciation for accounting and financial accounting, since different methods create tax differences that require additional attention of an accountant. Therefore, the linear calculation method is usually used.
Linear depreciation is calculated using the formula:
A = PS / SPS,
Where:
A is the monthly depreciation amount;
PS - initial cost of fixed assets (account balance 01);
SPS is the useful life of the OS.
To calculate it, you need to know the useful life of the asset, established by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups” dated January 1, 2012 No. 1. In accounting, fixed assets can be written off faster than in tax accounting, using other calculation methods and a shorter period of use, but then tax differences are formed, since accounting and tax amounts will differ.
To account for depreciation, records are kept in account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets.” Its amounts are debited from the accounts of production and commercial costs (20, 23, 25, 26, 29, 44), forming a credit balance on account 02.
The accountant creates monthly records:
- Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44) Kt 02 - depreciation has been accrued for fixed assets.
Accounting entries for the restoration of fixed assets
The initial cost may increase if work is carried out to restore the OS (modernization, reconstruction and retrofitting). The accounting procedure for such operations differs depending on whose forces this modernization is carried out: a third-party organization or independently. If the modernization is carried out by a third-party contractor, then the costs of such work are reflected in Dt account 08 in correspondence with account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”. In this case, the postings are generated:
- Dt 08 Kt 60 - reflects the cost of the contractor’s work;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 - VAT allocated.
If the work is carried out independently, then the costs of additional equipment are taken into account on account 08 in correspondence with the cost accounts (10, 70, 69, etc.). This creates the following records:
- Dt 08 Kt 10 (70, 69, etc.) - reflects the costs of upgrading the OS.
Upon completion of the work, the amounts accumulated on account 08 are written off to account 01 Dt, thus increasing the initial cost of the asset.
Materials received - no documents
In this case, a special procedure applies for accepting materials for accounting, which are now called uninvoiced deliveries.
For the purpose of acceptance of materials, an act is drawn up in form M-7, for acceptance of containers - an act in form TORG-5.
Acts should be created in 3 copies. One of them is given to the supplier. For the act to have legal force, it is necessary to create a commission, which must include a representative of the supplier company or an independent expert.
Next, the received inventories must be taken into account at a certain cost, in other words, assessed. If the actual cost is accepted as the accounting price in the organization, then inventories are taken into account at market prices.
Further, after the documents are received, different situations may arise. Either the value indicated in the documents coincides with the value at which the inventories were accepted for accounting, or it does not coincide. In the latter case, the accounting records need to be corrected.
Thus, there are quite a lot of different nuances in the “receipt of materials from supplier” transaction, but understanding them is not difficult.
The receipt of goods and services in 1C is presented in this video.
OS sales
In the case when an organization sells fixed assets, it is obliged to record the cost of sale of the asset and the original cost minus depreciation (residual value). Records are generated:
- Dt 62 Kt 91 - income from sale is recognized;
- Dt 91 Kt 68 - VAT reflected;
- Dt 02 Kt 01 - depreciation written off;
- Dt 91 Kt 01—residual value written off.
Ownership of the asset is transferred on the basis of a deed (Form No. OS-1). If the object of sale is real estate, then the date of transfer of rights is the date of state registration.