What is meant by a contribution to the authorized capital and in what form is it paid for?
If you decide to create a business company, you will need knowledge of civil, accounting and tax legislation.
We will talk about its individual important norms in our article. The contribution to the authorized capital (VUC) refers to the following made by the founders or participants of a business company:
- money;
- non-monetary assets (shares of other business entities, intellectual rights, things, etc.)
Find out in what order the authorized capital of an LLC is paid in the Typical Situation from ConsultantPlus. Get free demo access to K+ and go to the material to find out all the details of this procedure.
VUK allows:
- ensure the activities of the company at the initial stage after creation or support its financial capabilities during operation (with an increase in the authorized capital);
- determine the amount of debt the company owes to each founder, received by him after leaving the ownership group (the actual value of the share);
- ensure the interests of the company's creditors;
- assess the necessary conditions for interaction between the company and the founders (determining the degree of participation of the founder in making management decisions based on the size of the VUC, establishing the procedure for distributing profits, etc.).
Payment of the authorized capital depends on the type of VUC:
- cash VUK are transferred to the company's current account or deposited in its cash desk.
- property VUCs are transferred to society according to a special algorithm (we will talk about this later).
Find out how a nominal share in the authorized capital differs from a real one from the article “Why is the authorized capital of an LLC needed and can it be spent?”
Contribution to a joint stock company with property
Contribution to the authorized capital by property is not provided for by law for joint stock companies. However, there is no prohibition on carrying out such a procedure. Therefore, the features of this process should be considered. If the shareholder is a legal entity and he wishes to contribute non-monetary assets to the authorized capital, some discrepancy arises.
The legislation stipulates that the gift of material assets between commercial organizations cannot exist. This even applies to parent or subsidiary companies. However, formally the Tax Code allows for the gratuitous transfer of property. However, there is no specification for which organizations this is possible.
Therefore, in some cases, for joint-stock companies, the analogy of introducing tangible and intangible assets into the authorized capital is used. There are only some restrictions on donations.
Shareholders may be interested in increasing the authorized capital of their company. At the same time, they expect net profit growth and dividend payments. However, the transfer of property in this case is considered free of charge. Moreover, the cost of these values can also be excluded from the tax base. Such property should not be transferred to third parties during the year.
If the property received by the joint-stock company to form the authorized capital is leased, pledged or in another form, the tax benefit will not apply.
Stages of contributing property to the authorized capital
The procedure for entering VUK with property includes several stages:
- stage 1 - description in the constituent documents of the company of the possibility of entering the VUK with property and the procedure for carrying out this procedure;
- stage 2 - confirmation by the founder of the rights to the transferred property VUC;
- stage 3 - independent assessment of the transferred property;
- stage 4 - approval of the results of the assessment of the VUK by the founders (drawing up minutes of the general meeting of owners or other similar document);
- stage 5 - registration of the fact of transfer of property as a VUK (signing of the transfer and acceptance certificate);
- stage 6 - implementation of VUK accounting procedures in the tax and accounting system;
- stage 7 - the founders and the appraiser bear subsidiary liability for the unreliable amount of the property valuation.
In the following sections we will dwell in more detail on the individual features of this procedure.
Concepts of movable and immovable property
The official classification of values is carried out by civil law. Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation mentions two categories:
- Real estate. This group includes objects that cannot be moved in space without causing significant harm. The list includes capital structures, land plots that have not yet been completed with the construction of a building. A separate type consists of sea, river, air and space vessels. In fact, they can be moved. However, all transactions with such objects are subject to regulation by real estate regulations. Federal legislation may include other values in the group.
- Movable things. The category includes all other assets, including money, stocks, bills, bonds, and precious metals. As a general rule, registration of rights to such items is not required. Exceptions may be provided for by regulations. A striking example is transport.
Transferability remains an important characteristic of property (Article 129 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Most valuables are allowed to be freely alienated and used in economic activities. The owner has the right to even destroy the object. Restrictions are established in strictly defined cases. Thus, in Russia the uncontrolled sale of firearms and narcotic substances is prohibited. Historical or natural monuments and nature reserves cannot become the subject of civil transactions. It will not be possible to transfer such objects as a contribution to the authorized capital. The rules for transferring rights to them are established by industry regulations, and only certain persons can be owners. Mechanisms for using such assets as contributions to an LLC have not been developed.
What norm of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation should be taken into account in the procedure for a company to receive contributions to the authorized capital with property?
If you are establishing a business company, when forming the authorized capital, you must take into account the requirements of Art. 66.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation - clause 2 of this article contains a rule on the mandatory payment in money of the minimum amount of the authorized capital.
Property contributions are permissible only in the remaining part of the authorized capital if it exceeds the minimum amount permitted by law.
Let's explain with an example:
In the constituent agreement of TSK Plus LLC, the size of the authorized capital is indicated as 100,000 rubles.
The founder of the company intended to contribute equipment as a VUK. Taking into account the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the Law “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ (hereinafter referred to as the LLC Law), he calculated the monetary and non-monetary components of the authorized capital:
VUK = DV + NDV,
100 000 = 10 000 + 90 000,
Where:
DV—minimum authorized capital for an LLC (Clause 1, Article 14 of the LLC Law);
NDV - the amount of the authorized capital minus the above minimum amount.
The founder formed the authorized capital in the following order:
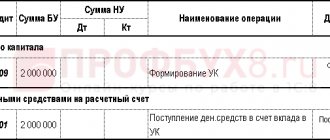
- 10,000 rub. — transferred to the bank account of TSK Plus LLC;
- 90,000 rub. - transferred equipment to the company for this amount (after receiving an independent assessment of the value of this property and approval of the assessment results).
ConsultantPlus experts explained how to determine and approve the value of property contributed to the authorized capital of an LLC. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
It is also necessary to pay special attention to the content of such a constituent document as the protocol (or decision) on the creation of the company.
As judicial practice shows (for example, the decision of the Arbitration Court of the Sverdlovsk Region dated 08/02/2016 in case No. A60-12861/2016), the absence in the decision to create a company of a description of the conditions for the formation of the authorized capital can lead to refusal of state registration of the company.
According to tax authorities and judges, such mandatory information includes the following information:
- on the size and nominal value of the founder’s share;
- the procedure and timing of payment of the authorized capital.
In such a situation, it will no longer matter in what form the VUC is contributed (property or money) - the possibility of the existence of society itself will be in question.
In what valuation is the property included in the Criminal Code reflected in the accounting records?
Any fixed asset based on clause 7 of PBU No. 6/01 is accounted for at its original cost. For assets that are received as a contribution to the management company, such value is determined as a monetary value, which is individually (!) (clause 2 of article 15 of the Law “On LLC”, clause 9 of PBU 6/01) accepted by the founders of the enterprise and recorded in the Minutes of the general meeting of founders (or in the Decision) on the creation of the Company.
Moreover , if this assessment exceeds 20 thousand rubles, then an independent appraiser is invited to confirm it . Subsequently, this assessment is further clarified (clause 12 of PBU 6/01).
It is very important to understand that the provisions of PBU 6/01 and other regulations governing accounting apply to a newly created company only after its state registration.
Therefore, it is possible to decide on the procedure for accounting for assets, if their value is equal to or does not exceed 40 thousand rubles, only after receiving documents confirming the registration of the enterprise and after approving its Accounting Policy.
Thus, initially the value of the asset is recognized as equal to the founder’s valuation and only then, if its final value, formed on the basis of PBU 6/01, is equal to or less than 40 thousand rubles, it is subject to write-off in a separate manner - as part of the inventory.
At the same time, the asset included in the Criminal Code must be entered into accounting records by the date of registration of the company. This will reflect the amount of authorized capital paid by the founders as of the date of registration of the company. The process of forming the authorized capital using fixed assets will look like this:
Debit of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” Credit of account 75 “Settlements with founders” - reflects the receipt of a contribution to the management company at a cost approved unanimously by the founders;
Debit account 75 Credit account 80 “Authorized capital” - reflects the formation of the management company at the expense of contributions from the founders;
Debit of account 01 “Fixed assets” Credit account 08 – assets recognized as fixed assets are accepted for accounting, according to the assessment formed on the basis of PBU 6/01;
or
Debit account 10 “Materials” subaccount “Low-valued fixed assets” Credit account. 08 – the value of assets recognized as fixed assets, but with a value within 40,000 rubles, is written off.
The procedure for reflecting the formation of authorized capital through the above entries is set out in paragraph 28 of the Methodological Instructions for Accounting for Fixed Assets (approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in Order No. 91n dated 10/13/2003). As for the last posting (using account 10), it is permitted by clause 5 of PBU No. 6/01 and the Instructions for the Chart of Accounts. This Instruction states that the accounting correspondence schemes proposed in it are standard and, if an enterprise needs it to reflect business transactions, then it can independently enter its own postings, observing the uniform approaches established in the Instructions.
Moreover, in favor of the last posting (correspondence between the debit of account 10 and the credit of account 08) is evidenced by PBU No. 6/01 itself in paragraph 12, which states that the value of an asset received by the management company consists of its assessment and expenses accepted by the founders, that are associated with its entry. For example, these may be the costs of installation and assembly of equipment, its delivery, etc. And all these expenses accumulate on account 08, making it possible to ultimately determine the full cost of the asset, i.e. whether it exceeds the established limit of 40 thousand rubles or not. Moreover, these expenses are already borne by the organization itself, and not by its founders, and it needs them to put the asset into operation.
On the wiring it will look like this:
Debit of account 08 Credit of account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, etc. – expenses associated with the receipt of the asset into the organization and its commissioning are reflected.
Thus, the monetary value of the property adopted by the founders may differ from the one at which this asset will be accepted for accounting. At the same time, an increase in this assessment occurs only for accounting purposes, but does not change the amount of the authorized capital and the share of the founder in it.
“Accounting” stage for property contribution
Property VUK reflect:
- in accounting - at the cost agreed by the founders (using posting Dt 75 “Settlements with founders” Kt 80 “Authorized capital”);
- in tax accounting - according to the tax accounting data of the transferring party.
A variety of property (fixed assets, inventories, goods, etc.) can act as a property asset, therefore, it is necessary to apply the appropriate accounting and tax accounting standards to the accounting of each individual type of property asset asset.
Let us consider, using an example, the features of the transfer by the founder and the receipt by the company in the form of a VUK of property that meets the criteria of a fixed asset:
LLC "X" received a used lathe from PJSC "U" as a VUK.
Initial data:
- the initial and residual cost of the machine, according to the transferring party, is 2.5 million rubles. and 1.8 million rubles. respectively;
- the size of the VUK according to the act of an independent appraiser and constituent documents - 2 million rubles;
- There are no additional expenses for the transfer of the machine as a VUK.
The following entries will be made in the accounting of the transferring party (PJSC “U”):
| Account correspondence | Amount, rub. | Content | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 58 | 76 | 2 000 000 | Reflection of debt on payment of authorized capital |
| 01 | 01 | 2 500 000 | Write-off of the initial cost of fixed assets transferred as VUK |
| 02 | 01 | 700 000 (2 500 000 – 1 800 000) | Write-off of accrued depreciation of a lathe |
| 76 | 01 | 1 800 000 | Write-off of the residual value of the machine |
| 19 | 68 | 324 000 (1 800 000 × 18%) | Recovering VAT from the residual value of the machine |
| 91 | 19 | 324 000 | Recovered VAT included in other expenses |
In the accounting of the receiving party (LLC “X”):
- debt to PJSC “U” under VUK: Dt 75 Kt 80 in the amount of 2 million rubles. (the value of the property VUK confirmed by an independent appraiser and approved by the founders).
- the cost of the machine received as a VUK is reflected by the posting: Dt 08 Kt 75 in the amount of 2 million rubles. (after putting the machine into operation: Dt 01 Kt 08).
How to show the authorized capital in the reporting, says the material “In which section is the authorized capital reflected in the balance sheet?”
Briefly about depreciation
Accountants should approach writing off the value of fixed assets with particular responsibility. The depreciation process must be reflected in documents and taken into account when preparing reports. Assets transferred as a contribution to the authorized capital are no exception. A portion of their cost should be regularly charged to business expenses. The rule does not apply only to property whose consumer and operational properties do not change over time (for example, land plots). The corresponding clause is contained in clause 17 of PBU 6/01.
The regulations recognize four methods of depreciation:
- linear method;
- reducing balance;
- write-off based on useful life;
- reduction in cost based on the volume of products produced by the enterprise.
The chosen method is fixed in the accounting policy. If an enterprise is allowed by law to maintain simplified accounting, annual depreciation can be calculated on December 31 or for individual periods in a single amount (month, quarter, half-year). Such companies have the right to write off the cost of inventory simultaneously on the day of acceptance for accounting (clause 19 of PBU 06/1).
It is necessary to start depreciating fixed assets from the first day of the month following the receipt of the asset. The process continues until the amount is completely written off. Suspension is allowed only in case of long-term shutdown of production - more than 3 months or for a period of long-term restoration repairs - more than 1 year.
Tax subtleties of accounting for property contributions
Income tax
In tax accounting, property received in the form of VUK that meets the criteria of a fixed asset (FA):
- is not recognized as income of the company (subparagraph 3, paragraph 1, article 251, subparagraph 1, paragraph 1, article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- is accounted for at historical cost (OSC), calculated using the formula:
PSOS = OSPS + DRPS,
Where:
OSPS - residual value of fixed assets according to the tax accounting data of the transferor;
DRPS - additional expenses of the transferring party associated with the transfer of property to the VUK (if these expenses are defined as the VUK - subclause 2, clause 1, article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the receiving party does not have documentary evidence of the value of the property VUC in tax accounting, it is recognized as zero (subclause 2, clause 1, article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Property tax
Property received by the company as a capital asset, accounted for on its balance sheet as a fixed asset, is subject to property tax:
- based on the cadastral value - if the property transferred as a VUK is included in the list of objects for which the tax base is determined as their cadastral value (regardless of the estimated value of the transferred property);
- average annual value according to accounting data - if the property received is not included in the specified list.
Find out about the tax rate for “cadastral” real estate from the article “Step-by-step instructions for calculating property tax from the cadastral value.”
Rules for accounting for deposits on the balance sheet of an enterprise
Since both movable and immovable property can be contributed as a contribution, it makes sense to understand the accounting rules. Things that come into the ownership of a company have different statuses. This affects postings, the procedure for calculating depreciation, and the principle of writing off costs.
Law 402-FZ dated 12/06/11 is of decisive importance when working with property. The regulation identifies several groups of material assets. The most stringent rules are established in the area of accounting for assets recognized as fixed assets. The sources of their receipt do not affect the rules for drawing up postings. Regulatory acts do not distinguish between property transferred in the form of a founding contribution and assets acquired by the company independently. Accounting principles do not change.
The condition for classifying a thing as a fixed asset is the presence of the following characteristics (PBU 6/01):
- Purpose. The object must be used in the economic activities of the company. The group is allowed to include property transferred for paid and temporary use to third parties. An example would be the provision of transport recorded on the balance sheet of a company for rent to organizations, entrepreneurs or ordinary citizens. In such situations, we are talking about means of generating income.
- Service life. The minimum useful life of the asset must be 12 months or more.
- Economic destiny. The enterprise does not have the right to classify as fixed assets the values that it plans to sell.
- Financial efficiency. Ownership of an asset must provide real economic benefits to the enterprise, including in the future.
The fourth paragraph of PBU 6/01 requires the simultaneous fulfillment of the specified conditions.
Fixed assets must be accounted for at historical cost. Accountants take as a basis the decision of the founders, the assessment conclusion (if any) and the acceptance certificate (clause 9 of PBU 6/01). As a general rule, changing the indicator is not allowed. The exception is cases of re-equipment, re-equipment, reconstruction. Revaluation also allows you to adjust the value of an asset (clause 15 of PBU 6/01). Involving an independent specialist from outside is not mandatory. There is no talk of revising the size of the contribution to the authorized capital. Articles 66.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and 15 of Law 14-FZ do not apply to such situations, and the interests of creditors are not affected. Recalculation only reflects changes in the real value of non-monetary assets over time.
Determination of accounting indicators is allowed to be carried out independently no more than once a year. In this case, you must follow methodological recommendations No. 91n dated 13.10.03. It is enough for the company’s management to establish the recalculation formula in a local regulatory document.
Note! If an asset meets the characteristics of a fixed asset when valued at up to 40 thousand rubles, it is allowed to be taken into account as part of inventories. The object will not lose its status, but will be depreciated at a time (clause 5 of PBU 06/01). It will have to be reflected in an off-balance sheet account for at least 13 months. The opening of such requires approval from the Ministry of Finance of Russia (order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000). In addition, internal control of the movement of valuables is carried out by maintaining an inventory book OS-66 or its equivalent developed by the company.
Results
Contribution of the authorized capital with property occurs in several stages - the founders provide for this possibility in the constituent documents, organize an independent assessment of the property contribution, approve its results, etc. Contribution to the authorized capital with property is possible only after payment in money of the minimum amount established by law.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Property valuation
Using a certain technology, a contribution to the authorized capital is made with property. The assessment of non-monetary values is carried out by an external specialist. This approach is established by law. The assessment (except for cash) is carried out by an expert in any case, regardless of the size of the contribution. Previously, the law was in force that if the share of the participant’s contribution to the authorized capital is less than 20 thousand rubles, the owner can determine the value independently. However, since 2014 this law has been repealed.
If the organization resorts to the help of an independent appraiser, this specialist and the participant who transfers non-monetary property bear financial liability for 3 years (from the date of registration of the organization). Moreover, it exceeds the value of the deposit. This is necessary so that the independent appraiser does not overestimate the value of the participant’s property. If the company subsequently incurs debts to creditors due to an incorrect procedure for depositing valuables, both the organization itself and the involved expert will be liable for such obligations.
The deposit is accepted at the residual value. The authorized capital with property (VAT in this case is not deducted) is replenished in accordance with the tax accounting of the participant. This takes into account additional costs associated with the transfer of property or rights. They are defined as part of the contribution to the authorized capital.