Account 98 in accounting
This account is intended to accumulate information about:
- Income received that relates to future reporting periods;
- The debt for the shortfall for previous years, which is to be collected;
- The difference in case of shortages and damage between the amount of recovery and the value of the property.
The amounts of income for future periods are reflected on the credit of account 98, and on the debit - the amount of income transferred to the corresponding accounts upon the arrival of the expected date.
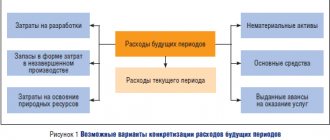
The subaccounts of account 98 “Deferred income” are presented below in the figure:
Analytical accounting of account 98 “Deferred income” is carried out for each:
- Type of income;
- Free receipt of valuables.
Correspondent accounts of subaccounts of account 98
Since shortages, subscription fees and gratuitous transfer of materials are radically different sources of finance in the accounting sense, then the correspondence of subaccounts will differ significantly.
Postings to subaccount 98.1
Subaccount 98.1 reflects the receipt of funds in the current period, but relating to future months or quarters. This is the receipt of utility bills, payment of monthly travel tickets, subscription fees for telephone services, rental payments, etc. The credit part of subaccount 98.1 corresponds with accounts reflecting the route of receipt of this income:
- – cash acceptance;
- – non-cash payment;
- – use of currency units, etc.
Accordingly, upon the arrival of the period for which income was received, posting Dt98.1 in correspondence with the account reflecting the use of these funds.
Analytical accounting for this sub-account is carried out for each type of income.
Postings to subaccount 98.2
Assets donated to the organization are reflected in subaccount 98.2. The credit part of the subaccount corresponds with accounts reflecting the purpose of the asset receipt:
- – when investing in non-current assets;
- – upon receipt of targeted funding for the implementation of the project.
The debiting of funds from this subaccount is reflected by posting Dt98.2 - Kt91 :
- when calculating depreciation on donated fixed assets;
- when writing off production costs based on donated materials.
Analytical accounting for this subaccount is carried out for each gratuitous receipt.
Postings to subaccount 98.3
Subaccount 98.3 takes into account upcoming receipts from the guilty parties to cover the shortfall. This can be either a voluntary admission of guilt and agreement to compensation, or by a court decision. The most commonly used wiring is:
- Dt94 – Kt98.3 – reflection of the amount of shortage identified in the previous reporting period;
- Dt73 – Kt94 – reflection of upcoming receipts from the guilty parties;
- Dt50 (51.52) – Kt73 – upon receipt of compensation;
- Dt98.3 - Kt91 - reflection of actual funds received to repay the previously identified shortage.
Typical transactions for account 98 “Deferred income”
Correspondence 98 accounts and main postings are presented in the table below:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description |
| 08 | 98.02 | Reflection of the market value of an asset received free of charge |
| 86 | 98.02 | Reflection of financing of expenses with budgetary funds |
| 98 | 91 | Reflection of write-off of fixed assets (depreciation) and material assets (costs) |
| 94 | 98.03 | Reflection of the amounts of shortfalls / amount to be recovered by the court for them |
| 98.03/98.04 | 91 | Reflection of debt repayment for shortfall/difference |
| 73.02 | 98.04 | Reflection of the difference between the amount of recovery and the value of the property |
Upcoming debt receipts for shortfalls identified in previous years
Subaccount 98-3 “Forthcoming debt receipts for shortfalls identified in previous years” takes into account the movement of upcoming debt receipts for shortfalls identified in the reporting period for previous years. In the credit of account 98 “Deferred income”, in correspondence with account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables”, the amounts of shortages of valuables identified in previous reporting periods (before the reporting year), found guilty of persons, or the amounts awarded for collection on them are reflected. court. At the same time, account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” is credited with these amounts in correspondence with account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” (sub-account “Settlements for compensation of material damage”). As the debt for shortfalls is repaid, account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” is credited in correspondence with the cash accounts while simultaneously reflecting the received amounts on the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses” (profits of previous years identified in the reporting year) and debit account 98 “Deferred income”. I'M IN. Sokolov woke up from his sleep” and began to pull everything possible under this category. At first these were “gifts”, then even past losses were included here.” Commenting on this component - “deferred income”, we would like to refer to the Accounting Regulations “Accounting Policy of the Organization” PBU 1/2008, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 6, 2008 N 106n, where in paragraph 5 it is established that when forming accounting policy assumes that the facts of the organization’s economic activities relate to the reporting period in which they took place, regardless of the actual time of receipt or payment of funds associated with these facts (the assumption of temporal certainty of the facts of economic activity). Recognition of income and expenses is not related to the receipt of cash and other funds. The definition of income and the criteria for their recognition are established in the Accounting Regulations “Income of the Organization” PBU 9/99, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 N 32n. Why, in this case, does the document of the third level of the regulatory system - Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts - establish a different procedure for reflecting income: only after the culprit has paid off the receivables? In this case, one of the general approaches to recording the facts of economic activity is violated. Of course, the receivables of the financially responsible person should be reflected only if he has admitted the existence of this debt, otherwise, if the financially responsible person does not admit his guilt, then there is no need to talk about income at all.
Examples of transactions with transactions on account 98
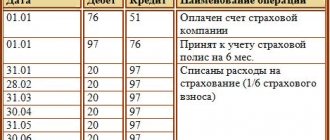
Example 1. Renting property
On February 1, 2016, a lease agreement for office space was concluded between Spide LLC and Left LLC and payment was made for 6 months in advance. On February 3, 2016, funds in the amount of RUB 354,000 were received into the account of Spide LLC, incl. VAT — 54,000 rub. According to the lease agreement, payment for the premises is made monthly, or for several months at once - the amount is reflected immediately, but is written off monthly.
Table of entries for account 98 - Accounting for future income from rental:
| Dt | CT | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 51 | 98.01 | 354 000 | Reflects the actual receipt of rent (six months) - advance | Bank statement |
| 98 | 90.01 | 59 000 | Monthly rent reflected (February) | Lease agreement, accounting certificate |
| 90.03 | 68 | 9 000 | VAT was charged on rent for February 2016. | Invoice, lease agreement |
| 76.AB | 68 | 54 000 | VAT charged on advance payment | Invoice, sales book, payment order |
| 68 | 76.AB | 9 000 | VAT deducted from rent (February) | Invoice, sales book |
Example 2. Recovery from the guilty party
Based on the results of the inventory, Knan LLC revealed a shortage (theft) by the seller of 8 kilograms of butter in the amount of 6,100 rubles, the market value of 7,100 rubles. The rate of natural loss is 500 grams. The shortfall is fully withheld after three months.
Table of entries for account 98 when recovering from the guilty party:
| Dt | CT | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 94 | 41.01 | 6 100,00 | Write-off of shortage | Inventory act and inventory |
| 44 | 94 | 381,25 | Write-off of shortages according to the natural loss rate | Accounting information |
| 73 | 94 | 5 718,75 | The shortage is transferred to the guilty party | Accounting certificate, Manager's order |
| 73 | 98.04 | 618,75 | The difference between the amount of recovery and the cost in accounting is reflected | Accounting information |
| 70 | 73 | 1 906,25 | Withholding 1/3 of the shortfall from the seller’s salary | Payroll |
| 98 | 91.01 | 206,25 | The difference after collection is taken into account | Accounting information |
Example 3. Gratuitous receipts
Kokhev LLC received equipment under a donation agreement with a useful life of 45 months, worth 400,000 rubles. Inventory and fixed assets cannot be included in gratuitously received income immediately; it is recognized as it is used.
Table of transactions for account 98 with free receipt of inventory and fixed assets:
| Dt | CT | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 08 | 98.02 | 450 000 | Receipt of equipment reflected | OS transfer act |
| 01 | 08 | 450 000 | The equipment has been accepted for registration | OS commissioning certificate |
| 20 | 02 | 10 000 | Calculation of depreciation per month | Accounting information |
| 98 | 91.01 | 10 000 | Income recognition in accounting |
Analytics for account 98
In accordance with the Chart of Accounts, the account for deferred income is supposed to be used to summarize a wide variety of information. In order to organize information, it is recommended to open the following subaccounts for account 98 (in transactions they are indicated with a “dot” or a hyphen):
- 01 - the following income is taken into account: rent paid in advance, subscription fee for service, transportation subscription, payment for utilities, etc.;
- 02—receipts received free of charge;
- 03 - expected receipt of debt for shortfalls identified earlier;
- 04 - excess of the amount collected from the perpetrators over the cost of the shortage.
For each subaccount, separate records are kept for each type of income. The list of subaccounts is open - enterprises can independently add other subaccounts according to their needs. The types of subaccounts to be opened should be indicated in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
ACCOUNTING FOR INCOME AND EXPENSES OF FUTURE PERIODS
ACCOUNTING FOR RETAINED Earnings
To summarize information about the presence and movement of amounts of retained earnings or uncovered losses of an organization, account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” . This account accumulates the amount unpaid in the form of income (dividends) or retained earnings, which remains in circulation with the organization as an internal source of financing.
The distribution of profit amounts is carried out on the basis of a decision of the competent body of the organization (general meeting of participants (shareholders)). Profit can be directed to:
for the payment of dividends (income). The following entries are made in accounting:
D 84 - K 70 - reflects the accrual of dividends to shareholders (founders) who are employees of the organization;
D 84 - K 75 - reflects the accrual of dividends to shareholders (founders - legal entities, or founders - individuals) who are not employees of the organization;
formation of the organization's reserve capital. The following entries are made in accounting: D 84 - K 82 - deductions to reserve capital are reflected;
uncovered loss from previous years. If at the end of the reporting year an organization has identified a loss, then its write-off from the balance sheet is reflected by:
D 82 “Reserve capital” - K 84 (if the loss is repaid from reserve capital);
D 80 “Authorized capital” - K 84 (if the amount of the authorized capital is brought to the value of the organization’s net assets);
D 75 “Settlements with founders” - K 84 (if the loss of a simple partnership is repaid at the expense of targeted contributions of its participants). The meeting of shareholders (participants) of the organization may decide not to distribute the profit received or leave some part of it undistributed. Analytical accounting for account 84 should be organized in such a way as to ensure the generation of information on the areas of use of funds.
To account for income received in the reporting period, but relating to future reporting periods, use passive account 98 “Deferred income ”. On the credit side, the accounts take into account income related to future periods, income arising as a result of the excess of the missing values recovered from the culprits over their book value. The debit of the account reflects the write-off of future income to the profit of the reporting year. The following sub-accounts are opened for account 98:
98-1 “Income received for future periods”;
98-2 “Gratuitous receipts”;
98-3 “Upcoming debt receipts for shortfalls identified in previous years”;
98-4 “The difference between the amount to be recovered from the guilty parties and the book value for shortages of valuables ”, etc.
To account for future income, the following entries are used:
D 51, 76 - K 98 - reflects the amount of income received (accrued) related to future income;
D 98 - K 68 - the amount of VAT on future income is taken into account;
D 98 - K 90.91 - deferred income is reflected in the reporting period to which they relate.
Subaccount 98-1 takes into account income received in the reporting period ,
but related to future reporting periods: rent and quarterly payments, utility bills, revenue for freight transportation and for passenger transportation on travel tickets, subscription fees for communications equipment, etc. Correspondence of accounts for this subaccount:
D 76 - K 98-1 - accrual of payments as part of deferred income including VAT;
D 98-1 - K 68 - VAT is charged on the amount of scheduled payments;
D 98-1 - K 90.1 - revenue related to the current period is reflected;
D 68 - K 98-1 - VAT restored on the amount of payments received;
D 90.3 - K 68 - VAT accrued for payment to the budget;
D 90.2 - K 20 - the actual cost of services provided for the transportation of goods is written off;
D 90.9 - K 99 - financial result is reflected.
Subaccount 98-2 takes into account the value of assets received by the organization free of charge, which is written off to the financial results:
1) for fixed assets received free of charge as depreciation is calculated, which is reflected in accounting with the following entries: D 08 - K 98-2 reflects the market value of the fixed asset item received free of charge;
D 01 - K 08 - the object has been accepted for accounting;
D 20 - K 02 - depreciation was accrued on the fixed asset;
D 98-2 - K 91 - the cost of the object is included in income as depreciation is calculated;
2) for other material assets received free of charge - as production costs or sales costs are written off to the accounts. The procedure for writing off assets received free of charge must be fixed in the accounting policies of the organization.
On subaccount 98-3 the following entries should be made:
D 94 - K 98-3 - reflects the amounts of shortfalls identified in previous years (found guilty by persons or sentenced to recovery by a court);
D 73-2 - K 94 - reflects the amount of damage from shortages written off to the perpetrators;
D 51 - K 73-2 - reflects the receipt of funds for damages;
D 98-3 - K 91 - income in the amount of funds received as compensation for damage is included in the financial result.
In subaccount 98-4, the difference between the amount recovered from the guilty persons for missing material and other assets and their value indicated in the organization’s accounting records is taken into account: D 73-2 - K 98-4 - the amount of missing material assets is attributed to the guilty persons ; D 50 _ K 73.2 _ as the guilty person repays the debt.
D 98-4 - K 91 - income is included in the financial results in the form of the difference between the amount to be recovered from the guilty parties and the accounting value of the missing valuables.
To account for expenses that were incurred in a given reporting period, but relate to future reporting periods, account 97 “Deferred expenses” is intended.
This account may reflect expenses for mining and preparatory work, preparatory work due to their seasonal nature, development of new production facilities, installations and units, land reclamation and implementation of other environmental measures, repairs of fixed assets, unevenly carried out throughout the year, etc. Analytical accounting for account 97 is carried out by type of expense.
Correspondence of accounts for accounting for deferred expenses:
D 97 - K 60,71,76, etc. - reflects the amounts of expenses incurred in the current period, but relating to future periods;
D 19 - K 60,71,76 , etc. - reflects the amount of VAT related to deferred expenses;
D 20, 26.44, etc. - K 97 - deferred expenses are written off in the reporting year to which they relate, in the manner established by the organization.
Account 97 also reflects the costs of acquiring licenses for certain types of activities, costs of certification of products and services, and the excess of actual repair costs over the reserved amounts.
ACCOUNTING FOR RETAINED Earnings
To summarize information about the presence and movement of amounts of retained earnings or uncovered losses of an organization, account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” . This account accumulates the amount unpaid in the form of income (dividends) or retained earnings, which remains in circulation with the organization as an internal source of financing.
The distribution of profit amounts is carried out on the basis of a decision of the competent body of the organization (general meeting of participants (shareholders)). Profit can be directed to:
for the payment of dividends (income). The following entries are made in accounting:
D 84 - K 70 - reflects the accrual of dividends to shareholders (founders) who are employees of the organization;
D 84 - K 75 - reflects the accrual of dividends to shareholders (founders - legal entities, or founders - individuals) who are not employees of the organization;
formation of the organization's reserve capital. The following entries are made in accounting: D 84 - K 82 - deductions to reserve capital are reflected;
uncovered loss from previous years. If at the end of the reporting year an organization has identified a loss, then its write-off from the balance sheet is reflected by:
D 82 “Reserve capital” - K 84 (if the loss is repaid from reserve capital);
D 80 “Authorized capital” - K 84 (if the amount of the authorized capital is brought to the value of the organization’s net assets);
D 75 “Settlements with founders” - K 84 (if the loss of a simple partnership is repaid at the expense of targeted contributions of its participants). The meeting of shareholders (participants) of the organization may decide not to distribute the profit received or leave some part of it undistributed. Analytical accounting for account 84 should be organized in such a way as to ensure the generation of information on the areas of use of funds.
To account for income received in the reporting period, but relating to future reporting periods, use passive account 98 “Deferred income ”. On the credit side, the accounts take into account income related to future periods, income arising as a result of the excess of the missing values recovered from the culprits over their book value. The debit of the account reflects the write-off of future income to the profit of the reporting year. The following sub-accounts are opened for account 98:
98-1 “Income received for future periods”;
98-2 “Gratuitous receipts”;
98-3 “Upcoming debt receipts for shortfalls identified in previous years”;
98-4 “The difference between the amount to be recovered from the guilty parties and the book value for shortages of valuables ”, etc.
To account for future income, the following entries are used:
D 51, 76 - K 98 - reflects the amount of income received (accrued) related to future income;
D 98 - K 68 - the amount of VAT on future income is taken into account;
D 98 - K 90.91 - deferred income is reflected in the reporting period to which they relate.
Subaccount 98-1 takes into account income received in the reporting period ,
but related to future reporting periods: rent and quarterly payments, utility bills, revenue for freight transportation and for passenger transportation on travel tickets, subscription fees for communications equipment, etc. Correspondence of accounts for this subaccount:
D 76 - K 98-1 - accrual of payments as part of deferred income including VAT;
D 98-1 - K 68 - VAT is charged on the amount of scheduled payments;
D 98-1 - K 90.1 - revenue related to the current period is reflected;
D 68 - K 98-1 - VAT restored on the amount of payments received;
D 90.3 - K 68 - VAT accrued for payment to the budget;
D 90.2 - K 20 - the actual cost of services provided for the transportation of goods is written off;
D 90.9 - K 99 - financial result is reflected.
Subaccount 98-2 takes into account the value of assets received by the organization free of charge, which is written off to the financial results:
1) for fixed assets received free of charge as depreciation is calculated, which is reflected in accounting with the following entries: D 08 - K 98-2 reflects the market value of the fixed asset item received free of charge;
D 01 - K 08 - the object has been accepted for accounting;
D 20 - K 02 - depreciation was accrued on the fixed asset;
D 98-2 - K 91 - the cost of the object is included in income as depreciation is calculated;
2) for other material assets received free of charge - as production costs or sales costs are written off to the accounts. The procedure for writing off assets received free of charge must be fixed in the accounting policies of the organization.
On subaccount 98-3 the following entries should be made:
D 94 - K 98-3 - reflects the amounts of shortfalls identified in previous years (found guilty by persons or sentenced to recovery by a court);
D 73-2 - K 94 - reflects the amount of damage from shortages written off to the perpetrators;
D 51 - K 73-2 - reflects the receipt of funds for damages;
D 98-3 - K 91 - income in the amount of funds received as compensation for damage is included in the financial result.
In subaccount 98-4, the difference between the amount recovered from the guilty persons for missing material and other assets and their value indicated in the organization’s accounting records is taken into account: D 73-2 - K 98-4 - the amount of missing material assets is attributed to the guilty persons ; D 50 _ K 73.2 _ as the guilty person repays the debt.
D 98-4 - K 91 - income is included in the financial results in the form of the difference between the amount to be recovered from the guilty parties and the accounting value of the missing valuables.
To account for expenses that were incurred in a given reporting period, but relate to future reporting periods, account 97 “Deferred expenses” is intended.
This account may reflect expenses for mining and preparatory work, preparatory work due to their seasonal nature, development of new production facilities, installations and units, land reclamation and implementation of other environmental measures, repairs of fixed assets, unevenly carried out throughout the year, etc. Analytical accounting for account 97 is carried out by type of expense.
Correspondence of accounts for accounting for deferred expenses:
D 97 - K 60,71,76, etc. - reflects the amounts of expenses incurred in the current period, but relating to future periods;
D 19 - K 60,71,76 , etc. - reflects the amount of VAT related to deferred expenses;
D 20, 26.44, etc. - K 97 - deferred expenses are written off in the reporting year to which they relate, in the manner established by the organization.
Account 97 also reflects the costs of acquiring licenses for certain types of activities, costs of certification of products and services, and the excess of actual repair costs over the reserved amounts.