Correspondence 20 accounting accounts
Let's look at typical wiring:
- DT20 KT10 – materials written off.
- DT10 KT20 - return of raw materials to the warehouse.
- DT20 KT10-2 - semi-finished products were released into production.
- DT20 KT10-3 - fuel written off for technological purposes.
- DT20 KT60 - the cost of electricity used in production is taken into account.
- DT20 KT70 – wages accrued to production workers.
- DT20 KT69 - insurance premiums are taken into account.
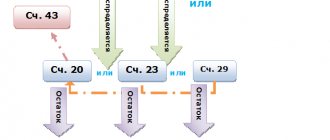
- DT20 KT23 – costs of auxiliary production are taken into account.
- DT20 KT69 - a reserve has been created to pay for private entrepreneurs and vacations.
- DT20 KT25 (26) - general production (household) expenses are written off.
- DT20 KT28 - losses from defects are displayed.
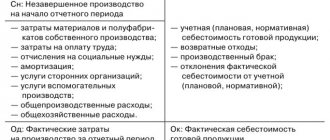
In the course of its activities, an organization can attract services (products) of its own production. In this case, accounting accounts 20 and 21 are used. Semi-finished products of own production are written off from KT21 to DT20. The ending balance shows the value of work in progress (WIP). Analytics is carried out by types of costs, products, divisions. Account 20 in accounting is reflected in the balance sheet in the second section of assets in the line “Inventories”.
Typical transactions for account 20
The debit of the account reflects the expenses that the enterprise incurs during the production of products. Simply put, expenses that form the cost of a product or service in the future. On the credit of the account, the cost of production is formed and the amount to be written off upon completion of the production process is indicated. Let's look at typical transactions for account 20 in the table:
| Debit accounts | Credit accounts | the name of the operation |
| 20 | 02, 04, 05, 10, 16, 19, 21, 23, 25, 26, 28, 40, 43, 41, 60, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76.2, 79, 80, 86, 91.1, 94, 96, 97 | Combination of all costs that arise during the production of goods or as a result of the provision of services |
| 10, 15, 21, 28, 40 (43), 45, 76.01, 76.02, 79, 90.02, 91.02, 94, 99 | 20 | Amounts that allow you to reduce the amount of expenses (defects, shortages), and then write off the balances |
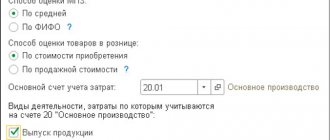
When writing off, you must use the method specified in the accounting policy of the enterprise. Before closing account 20, be sure to allocate the balance of work in progress.
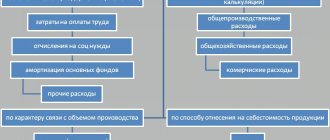
General production expenses
Indirect costs associated with servicing production are recorded on account 25. These include:
- depreciation of machinery and equipment;
- OS maintenance costs;
- remuneration of employees;
- insurance deductions;
- rent;
- utility costs for production premises;
- expenses for repairs of machines, buildings for general production purposes, etc.
During the month, actual costs are collected by DT from the credit of accounts for inventory, materials, settlements with personnel: DT25 KT02 (05, 10, 60), etc. Then they are written off to account 20 in accounting. This is reflected by the wiring of DT20 KT25. That is, the final balance on the account. 25 equals 0. Analytics is carried out by departments and expense items.
Brief description of account 20
Accounting costs in account 20 depend on the main activity of the company.
These may be expenses for the production of industrial or agricultural products, for construction and installation work, or for the provision of transport services. The purpose of accounting on this account is to form the full or reduced cost of the main production (hereinafter - OS). Account 20 - Main production - is regulated by the Chart of Accounts, Instructions for its application (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), PBU 10/99 “Organization Expenses” and other accounting standards (methodological instructions, recommendations, guidelines) for accounting for production expenses and their reflection in reporting in the context of specific economic sectors (clause 10 of PBU 10/99, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 29, 2002 No. 16-00-13/03).
Account 20 in accounting is an active calculation account that does not have a negative balance.
The following types of production costs are distinguished:
- acquisition of raw materials and materials for production, work, services;
- workers' compensation;
- depreciation and repair of fixed assets;
- modernization and introduction of new technologies;
- losses from marriage, etc.
If there is a positive balance at the end of the month, the account contains work in progress (work in progress, hereinafter referred to as WIP) - material assets that are in production or being processed, as well as finished products, but not yet shipped to storage warehouses.
Analytical accounting on the account is carried out in the context of types of products, cost items and divisions of the organization.
General running costs
Indirect costs associated with servicing the organization are displayed on account 26. These include:
- administration salary;
- social insurance contributions;
- communication costs;
- costs of maintaining security;
- administrative and management costs;
- depreciation of administrative operating systems;
- rental of office space, etc.
Expenses for the month are accumulated according to DT26. At the end of the month, these amounts are written off to account 20 in accounting or 90-2 in full.
Typical transactions for account 26 are presented in the form of a table.
| Operation | DT | CT |
| Accrued depreciation on fixed assets, intangible assets | 26 | 04, 02, 05 |
| Materials were transferred for general business needs | 10 | |
| Electricity costs included | 60 | |
| Salaries paid to workers involved in OS maintenance | 70 | |
| Insurance premiums accrued | 69 | |
| A vacation pay reserve has been created | 96 | |
| General production costs associated with auxiliary production were written off | 23 | 26 |
| General production costs associated with main production were written off | 20 | 26 |
Non-production organizations use account 26 to display information about operating expenses. Cost amounts at the end of the month are written off to DT90 “Sales”. Analytics for account 26 is carried out for each budget item, cost location, etc.
Auxiliary production
Account 23 is used to summarize information about auxiliary costs:
- service by types of energy;
- fare;
- OS repair;
- production of tools, building parts, structures.
DT23 reflects expenses directly related to the release of goods, indirect costs and losses from defects. In this case, the following transactions are generated:
- DT23KT10 – materials written off for auxiliary production.
- DT23KT70 – the wages of production workers are taken into account.
- DT23KT69 – insurance premiums have been calculated.
- DT23KT25, 26 – indirect costs are taken into account.
- DT23KT28 – losses from defects are written off.
KT23 reflects the actual cost of production. These amounts are then written off to account 20 in accounting, subaccounts “Crop production” (20-1), “Livestock production” (20-2), “Industrial production” (20-3), “Other production” (20-4). Account balance 23 reflects the cost of the work in progress. Analytics is carried out by type of production.
What is considered work in progress?
Products that have not gone through all stages of processing, as well as work not accepted by customers, are called work in progress, and the costs for them are called work in progress costs.
These assets have a common main feature - the incompleteness of the technological process. Work in progress does not include materials and purchased semi-finished products that have not begun processing.
And in quantitative terms, they are characterized by debit balances that have not been written off as of the reporting date for the following accounting accounts:
- 20 “Main production”;
- 21 “Semi-finished products of own production”;
- 23 “Auxiliary production”;
- 29 “Service industries and farms”;
- 46 “Completed stages of unfinished work.”
Work in progress also includes finished products that have not been accepted by the technical control department, incompletely completed products, as well as fully finished products that have not yet passed technical tests.
In the annual balance sheet, the value of work in progress is shown on line 1210 “Inventories”.
Accounting for losses
Products that do not meet quality standards or contracts are considered defective. If it is possible to bring the product to the required parameters, then such a defect is considered correctable. DT28 displays the cost of written-off products. According to KT28 - amounts to be withheld from the culprits, suppliers, valuation of the costs of restoring the product.
Let's look at typical transactions (for convenience, we will again present them in the form of a table).
| Operation | DT | CT |
| Materials were released to correct defective products | 28 | 10 |
| Salaries accrued to employees who corrected products | 70 | |
| Insurance premiums accrued | 69 | |
| The cost of rejected products has been written off | 20 | |
| The cost of the marriage was withheld from the salary of the guilty person | 70 | |
| Received defective parts | 10 | 28 |
| Claims filed with suppliers | 76-2 |
The cost of defective products is written off from DT28 to accounting account 20. Closing the account means that all losses from the barque are compensated. Analytics is carried out by departments, expense items, types of products, culprits and causes of defects.
Service farms
Account 29 is intended to display information on production costs not related to the manufacture of products or the provision of services:
- Housing and communal services (operation of houses, dormitories, bathhouses, etc.);
- workshops;
- buffets and canteens;
- children's institutions;
- holiday homes;
- research units.
DT29 reflects expenses associated with the performance of work, which are then written off to the account for auxiliary production. According to KT29 – the cost of work and goods.
| Operation | DT | CT |
| Materials taken into account | 10 | 29 |
| The costs of divisions-consumers of services of service industries are written off | 23, 25, 26 | |
| Products sold to third parties | 90-2 |
Account balance 29 reflects the cost of the work in progress. Analytics is carried out for each production and cost item.
How is count 20 used in accounting?
An experienced accountant knows that all costs arising during work processes must be recorded in account 20. We are talking about costs associated with the main activity of the enterprise - hence the name of the account.
The expenses collected on the balance of account 20 are called work in progress by accountants. Which is quite logical, because the invoice reflects them until the full cost of the product is formed.
The accounting policies of most enterprises indicate that expenses will be written off to the 20th account. The field of activity, with the exception of trade, does not affect this. Industrial and agricultural enterprises, construction and transport companies can use this write-off method. Closing account 20 indicates that the products have been produced, and for works and services this means that the person who has undertaken certain obligations has fulfilled them.
For small businesses, a simplified scheme is provided, according to which costs are taken into account in account 20, and other accounts (23, 25, 26) do not need to be used.
Selling expenses
Account 44 displays information about costs associated with sales. Manufacturing businesses can use this account to show costs for:
- product packaging;
- delivery, loading of products;
- commission fees;
- maintenance of warehouse premises;
- advertising;
- entertainment expenses, etc.
Trade organizations on this account display expenses for:
- transportation of products;
- wages;
- rent;
- maintenance of buildings and equipment;
- storage of goods;
- product promotion;
- entertainment expenses, etc.
Amounts of expenses are accumulated according to DT44, and then written off to account 90-2. Analytics is carried out by product and expense items. In case of partial write-off, transportation and packaging costs are subject to distribution between months (in equal amounts, regardless of actual expenses). All other items are charged to the cost of production on a monthly basis in full.
Cost formation
The final stage is determining the cost of production, taking into account the balances of work in progress.
At the end of the month, the costs accounted for DT23 are distributed between basic and general production expenses. Then, overhead costs are written off to account 20 in accounting if reduced accounting is maintained, and all costs if full cost accounting is maintained. That is, this account displays the total amount of expenses. Formula:
S/S = WIP beginning. + Costs – WIP end.
The actual cost is reflected according to CT 20. Costs are written off depending on which valuation method is chosen. If products are accounted for at standard cost, all expenses are charged to account 40 by posting DT40 KT20. If actual cost is applied, the costs are written off to account 43. This is how account 20 is used in accounting.