An entrepreneur purchased real estate for work, and then lost his individual entrepreneur status
If an entrepreneur bought real estate to use in his business (namely, in transactions subject to VAT), there is every reason to accept input tax as a deduction.
This directly follows from subparagraph 1 of paragraph 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But what to do if you lose your individual entrepreneur status? The Ministry of Finance believes that before terminating business activities, the deduction must be restored. After all, the property will remain the property of the former businessman. He will continue to operate it, but outside the scope of operations subject to VAT. This means that you will have to transfer the money to the budget (letter dated October 22, 2018 No. 03-07-11/75751; see “A former entrepreneur must restore VAT on “working” real estate”).
Generate a new waybill in the web service for individual entrepreneurs
VAT bankrupts from 2022
The consequence of the exemption from taxation of the assets of debtor companies being sold is that bankrupt companies do not have the right to deduct VAT paid to suppliers of raw materials and services . If the amounts of input VAT on materials purchased before 2022 by a bankrupt manufacturer were accepted for deduction, and these raw materials were used in the production of products sold in 2022, then he is obliged to restore these amounts (clause 2, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
Let us recall how the restoration of VAT by bankrupts is reflected in accounting using the example:
Example
An enterprise whose insolvency has been registered and bankruptcy proceedings have been ordered continues its normal activities - it produces and sells its products. In the 1st quarter of 2022, the company produced and sold products worth RUB 2,000,000 to the buyer. According to the law, VAT is taken into account by the seller in the price of the goods and does not appear in the supply agreement. An invoice is not issued for shipment.
However, since raw materials purchased in November 2022 were used for the production of products (its cost including VAT was 600,000 rubles), and the VAT paid to the supplier of these raw materials was reimbursed from the budget, the bankrupt must restore the amount of tax (600,000 * 20 / 120 = 100,000 rub.). Since the company carried out non-taxable transactions in the 1st quarter of 2022, it will restore VAT in the amount of 100,000 rubles. (D/t 19 K/t 68) it follows in the same period.
VAT restoration upon sale of bankrupt property is carried out in accordance with clause 3 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: the seller registers in the sales book invoices, on the basis of which VAT was previously accepted for deduction, reflecting the amount of tax to be restored. In the VAT return, the amount of the restored tax is recorded in line 080 of section 3. The tax is paid in the usual manner - in equal installments over the three months following the end of the quarter.
The company in liquidation transferred its property to the founder
The LLC is in the process of liquidation, after which its property will pass to the founders. In this situation, according to officials of the Ministry of Finance, the deduction previously accepted for such objects should be restored.
Financial department specialists refer to subparagraph 2 of paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code.
It says that the VAT deduction on goods will be restored if the taxpayer began to use these goods for non-taxable transactions. There are a number of exceptions. But among them there is no transfer of property to the founders during the liquidation of the LLC (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 16, 2019 No. 03-07-11/52674). Important
The judges of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation came to a similar conclusion. From the decision of the Supreme Court dated December 21, 2018 No. 306-KG18-13567, it follows that if an object cannot be used for transactions subject to VAT due to the termination of a business, then the tax must be restored.
Submit reports free of charge to all regulatory authorities through the EDF operator
How to recover VAT on fixed assets
VAT accepted for deduction on fixed assets that the company began to use in non-taxable transactions must be restored and paid to the budget. This is a direct norm of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This rule does not provide for any exceptions.
When is VAT reinstated?
VAT is restored when tax conditions change - either the entire activity of the company or part of it.
Thus, on the basis of subparagraph 2 of paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, this occurs in cases of transition from the main taxation regime to special regimes (except for the Unified Agricultural Tax), or before the start of using the VAT exemption under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (based on the amount of revenue).
A very common case of VAT restoration is a situation when certain inventory items, fixed assets, intangible assets and property rights, which were previously purchased for VAT-taxable transactions, begin to be used in tax-free transactions:
- listed in Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- which are not sales according to paragraph 2 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- carried out outside the territory of Russia.
What does VAT restoration mean?
Technically, the restoration of VAT is a reflection of the tax that was once accepted for deduction in the sales book. This operation leads to the formation of the amount of tax to be paid to the budget. An entry in the sales book can be made on the basis of an invoice for which a deduction was received, or an adjustment invoice, or an accounting reference-calculation, for example, if the storage period for the invoice has already expired.
It is necessary to restore VAT only in the cases listed in paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, for the case of VAT recovery on fixed assets, there is a specific procedure.
How to recover VAT on OS
The letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 29, 2018 No. 03-07-11/77559 provides an explanation for the case when, in non-VAT-taxable transactions, a company intends to use fixed assets, previously acquired for conducting taxable activities, for several periods.
That is, the situation is such that in the future the company is going to return to activities subject to VAT and use the same OS in it.
In its response, the Ministry of Finance made it clear that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for any exceptions to the rules for the restoration of VAT. That is, in the quarter of the start of work under the new conditions, VAT must be restored and paid to the budget.
The amount of tax related to fixed assets is calculated in proportion to their residual value (subclause 2, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT accepted for deduction × Book (residual) value of fixed assets: Initial cost of fixed assets = VAT to be restored
Accounting and tax accounting when restoring VAT
When restoring VAT on fixed assets that begin to be used in non-VAT taxable activities, the accountant will make the following entries:
Debit 19 Credit 68.2
– the VAT previously accepted for deduction was restored;
Debit 91.2 Credit 19
– the amount of restored VAT is written off.
In tax accounting, amounts of recovered VAT are reflected in other expenses associated with production and sales, based on Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Example. Calculation of the amount of VAT to be restored
The VAT payer company purchased equipment (fixed assets) in January 2022 at a price of RUB 118,000. (including VAT – 18,000 rubles). Input VAT on purchased equipment was accepted for deduction. There was no revaluation of the value of the fixed asset.
From June 2022, the company began to carry out VAT-free operations using the specified equipment. Therefore, this month the accountant calculated the amount of VAT to be restored.
As of June 30, 2019, the residual value of equipment according to accounting data is RUB 83,332. The amount of VAT to be recovered was:
18,000 rub. × RUB 83,332 : (118,000 rub. – 18,000 rub.) = 14,999.76 rub.
In accounting, the accountant made the following entries:
Debit 19 Credit 68.2
– 14,999.76 rub. – VAT on equipment previously accepted for deduction was restored;
Debit 91.2 Credit 19
– 14,999.75 rub. – the amount of restored VAT is written off.
The amount of the recovered tax can be taken into account in income tax expenses.
The customer made an advance payment, but the contractor became bankrupt without completing the work
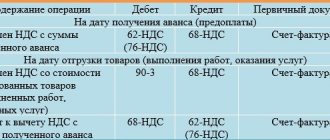
As a general rule, a customer who has made an advance payment has the right to deduct value added tax (Clause 12, Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Next, when the work is completed, you need to restore the deduction from the advance payment. And then accept a new deduction for work completed.
But it happens that the contractor receives an advance, but does not fulfill his obligations under the contract. If he is subsequently declared bankrupt, the chances of completing the work are reduced to zero. In such circumstances, the customer must restore the deduction from the prepayment. This point of view was expressed by specialists from the Ministry of Finance in letter dated 06/05/18 No. 03-07-11/38251 (see “The contractor did not pay off the advance payment: is it necessary to restore VAT from the written off prepayment?”).
However, in arbitration practice there are examples when judges decided otherwise. The Arbitration Court of the Volga District considered a case in which the contracting organization was reorganized, and the successor was in the process of liquidation. The inspectors demanded that the customer cancel the deduction for the “unprocessed” prepayment. But the court referred to subparagraph 3 of paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It names cases of VAT recovery from an advance payment: delivery, change in the terms of the contract, or its termination. None of the above events occurred. This means that the customer is not obliged to transfer the tax to the budget (Resolution No. F06-51971/2019 dated October 1, 2019; see “Arbitration practice in October 2022: checking “clarifications” on VAT, corrections in sick leave, individual entrepreneurs’ contributions to the Unified Agricultural Tax”).
Fill out the waybill with all the required details in a special service Try it for free
Other cases of VAT recovery
Despite the fact that all cases of VAT restoration are directly named in Articles 170 and 171.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, regulatory authorities in their explanations constantly find new reasons for VAT restoration. Each taxpayer has to decide for himself whether to follow such clarifications or not.
After all, if you do not follow, there may be claims on their part, and you will probably have to defend your position in court.
Some cases are shown in Table 1.
Table 1
| No. | An operation for which it is necessary to restore VAT, according to the regulatory authorities | Explanatory document |
| 1 | There was a write-off of illiquid or obsolete goods | Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2016 No. 03-03-06/1/1997 |
| 2 | The property was disposed of due to damage | Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 19, 2015 No. 03-07-11/15015 |
| 3 | Not fully depreciated property was liquidated (except for liquidation as a result of an accident) | Letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 04/14/2016 No. 03-07-11/21297, dated 02/17/2016 No. 03-07-11/8736 |
| 4 | Theft of property was recorded | Letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation from 04.07.2011 3 03-03-06/1/387, dated 05/19/2010 No. 03-07-11/186 |
| 5 | During the inventory, a shortage of property was recorded | Letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation from 04.07.2011 3 03-03-06/1/387, dated 05/19/2010 No. 03-07-11/186 |
At the same time, we must not forget that if there is arbitration practice in which the opposite point of view is expressed, supervisory authorities should be guided in their work by arbitration practice.
An example of arbitration decisions containing conclusions that there is no need to restore VAT in cases of loss of property as a result of theft, damage, etc. or impossibility of further use due to moral or physical wear and tear, the following solutions may serve:
- Decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2011 N 3943/11
- Decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of October 23, 2006 N 10652/06.
Accounting entries when restoring VAT
table 2
| Operation | Posting by debit | Loan posting |
| When transferring property as a contribution to the management company | ||
| VAT on property transferred to the authorized capital has been restored | D 19 | K 68.02 |
| The amount of restored VAT is included in the initial cost of the share in the authorized capital (posting is possible - the amount of restored VAT is included in the calculations for payment of the share in the authorized capital) | D 58.01 (D 76) | To 19 (to 10) |
| When switching to simplified tax system | ||
| Recovered VAT on materials in stock | D 19 | K 68.02 |
| The amount of recovered VAT is included in other expenses | D 20 (26) | K 19 |
The buyer returned low-quality imported goods to a foreign supplier
The importer pays VAT at customs when importing goods into Russia. If the products are used in transactions subject to VAT, the tax can be deducted (subclause 1, clause 2, article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
But what if the products turn out to be of poor quality and they have to be returned to the foreign seller? The letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 11, 2019 No. 03-07-08/86241 made an unambiguous conclusion: if the goods cannot be used in activities subject to VAT, the deduction must be restored (see “Ministry of Finance: when returning goods to a foreign supplier, VAT must be restored”).
Reference
The deduction for products imported from the EAEU countries and returned (in whole or in part) due to inadequate quality must be restored during the return period. The importer must submit to the tax authorities a “clarification” on VAT and an updated statement on the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes (without data on the returned goods). Such recommendations are given in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated June 14, 2019 No. 03-07-08/43429 (see “When returning goods imported from the EAEU, the VAT accepted for deduction must be restored”).
Receive an enhanced qualified electronic signature certificate in an hour
New responsibility
As a result, the new sub. 2 clause 3 and clause 3.1 art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliged the legal successor (there may be several of them) to restore the amount of value added tax on goods (work, services), including fixed assets, intangible assets and property rights received during the reorganization, which were previously accepted for deduction by the reorganized company.
The condition for the existence of the obligation to restore VAT: the continued use by the successor of the accepted values in transactions not subject to value added tax in connection with the transition to special tax regimes. But that's not all.
So these are the situations where:
- transition to OSN;
- the use of goods/works/services in activities not subject to VAT has begun;
- transition to the simplified tax system or UTII;
- combining the general system of taxation and imputation;
- goods/work/services were received from the seller as an advance payment, from which the reorganized company accepted VAT for deduction (when the legal predecessor, as a buyer, transferred the advance payment and claimed VAT deduction from it, and the shipment of the goods (or the return of the advance upon termination or change of the contract) has already been made successor, who also claims a deduction);
- the seller retroactively reduced the cost of goods/work/services that were supplied to the reorganized company.
The company imported OS and transferred it as a contribution to the authorized capital of another organization
Subparagraph 1 of paragraph 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states: the deduction for property transferred as a contribution to the authorized capital of another organization is subject to restoration. You need to transfer to the budget an amount proportional to the residual (book) value of the fixed assets without taking into account revaluation.
This norm fully applies to fixed assets imported into the Russian Federation from abroad. If the organization that purchased imported equipment transferred it to the authorized capital of another Russian company, the deduction must be restored. The Ministry of Finance provided the corresponding explanations in letter No. 03-07-08/83198 dated November 19, 2018 (see “VAT on imported property transferred to the authorized capital must be restored”).
How to reflect the recovery of VAT from the residual value of fixed assets when switching to the simplified tax system?
When switching to the simplified tax system, how to correctly reflect the restoration of VAT from the residual value of fixed assets so that the operation is correctly reflected in the VAT return?
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
VAT subject to restoration is calculated from the residual (book) value of the fixed asset, if VAT on it was previously accepted for deduction (clause 2, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 10, 2009 N 03-11-06 /2/99).
In 1C, VAT restoration on fixed assets is carried out using the document VAT Restoration , generated by the Assistant for the transition to the simplified tax system through the section Operations - Change of taxation regime - Assistant for the transition to the simplified tax system.
The amount to be restored, calculated by the Assistant for the transition to the simplified tax system, should be checked, since the program does not analyze fixed assets from the point of view of the Fixed Assets Accounting Group and the fact of filing VAT when purchasing property.
For assets on which VAT was previously accepted for deduction, you should fill out the VAT Restoration .
In the header:
- field Reflect recovery - in the sales book ;
- checkbox Write off recovered VAT to expenses .
In the tabular section on the VAT for recovery , the columns:
- No SF – clear the checkbox;
- Supplier, invoice – the supplier who sold the OS, Invoice received, select from the Invoices received .
Recovered VAT is taken into account in income tax expenses in accordance with Art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (paragraph 3, paragraph 2, paragraph 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
On the Write-off account :
- Write-off account – 91.02;
- Other income and expenses - Write-off of VAT on other expenses is accepted in NU .
As a result, the amount of recovered VAT will be reflected in the VAT return in Section 3 page 080 and Section 9.
If you are a subscriber to the BukhExpert8 system, then read additional material on the topic:
- Transition from OSNO to simplified tax system
- Assistant for the transition to the simplified tax system
If you haven't subscribed yet:
Activate demo access for free →
or
Subscribe to Rubricator →
After subscribing, you will have access to all materials on 1C Accounting, recordings of supporting broadcasts, and you will be able to ask any questions about 1C.
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- How to depreciate an “updated” OS that has no residual value: the opinion of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation The Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows, after modernization of a fully depreciated OS, again...
- The procedure for calculating the residual value of intangible assets in NU was prescribed “officially”...
- Restoration of VAT upon transition to UTII...
- Reinstatement of VAT during reorganization...