Recovered VAT - what is it?
The question of VAT restoration arises in relation to tax previously taken into account in deductions. This needs to be done in several situations (clause 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), the most common of which are:
- changes in tax conditions;
- change in the situation with the advance payment.
The main condition for the restoration of VAT: first, the tax is accepted for deduction, and then, due to some circumstances, it turns out that all of it (or part of it) must be paid to the budget. In this case, the required amount of tax is restored (accrued for payment) and reflected in section 3 of the declaration either in 1 line (080) or in two lines (090 or 100 and in the final 080). The recovery of VAT on advances issued is recorded in two of its lines: 080 and 090.
For information on tax recovery situations not related to advances issued, read the material “The nuances of VAT recovery and what entries are used?” .
VAT recovery period
The right to a tax deduction arises upon shipment of goods, and it is necessary to restore VAT from the advance payment, which was accepted for deduction before, in this period, regardless of when the documents for the transaction were received.
It should be taken into account that the period for the restoration of VAT accepted for deduction on advance payments cannot be changed with the transition to the tax period following the quarter in which the corresponding legal obligations were actually fulfilled. If the purchasing company received an invoice after the end of the tax period in which it accepted the goods for registration, but before submitting a declaration for this period to the tax office, then it deducts the corresponding amount of tax from the period in which it actually accepted goods.
Is it necessary to restore tax on advances received?
When receiving an advance payment, in most cases the seller is obliged to calculate the tax on it for payment to the budget (clause 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and later, when making a shipment, against this advance payment, take all or part of the amount of the tax paid from the advance tax as deductions (clause 8 Article 171 and Clause 6 Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In other situations (when the advance is returned to the buyer or the overdue debt on it is written off), VAT restoration will also not be required. In the 1st case, it can be taken as a deduction on the date of return (clause 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and in the 2nd case it must be written off as expenses not taken into account in the calculation of income tax.
Thus, for advances received, the picture always turns out to be the opposite of the main condition for recovery: first, the tax is calculated for payment, and then taken as a deduction or written off. That is why there will never be a situation of VAT restoration on these payments.
ConsultantPlus experts explained how to calculate VAT on transactions related to coronavirus. If you don't have access to the system, get a free trial online.
Conditions for deducting tax on advances issued
When calculating the tax on the advance payment received, the seller issues an invoice for it and sends 1 copy of it to the buyer. Based on this document, the buyer has the right to take into account the amount of tax allocated in it as deductions (clause 12 of article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Although he may not do this, since deductions are not an obligation, but are made voluntarily (clause 1 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is better to consolidate the taxpayer’s position regarding deductions for advances issued (whether they will be applied or not) in some document (for example, in the VAT accounting policy).
However, these 2 circumstances (payment and invoice) are not enough for the buyer to deduct it. Additional conditions for carrying out such an operation follow from other provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- a condition on the possibility of transferring an advance payment must be included in the supply agreement (clause 9 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- The invoice for the advance payment must be dated within the 5-day period allotted for issuing such documents (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and have all the required details for it (clause 5.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Acceptance of deductions from the buyer will be reflected in the following posting (for each individual document):
Dt 68/2 Kt 76/VA,
Where:
68/2 - subaccount for accounting for settlements with the budget for VAT on account 68;
76/VA - subaccount for accounting for VAT on advances issued in account 76.
Application of CVO for advances
All advances issued and received are formalized by an invoice, the details of which are recorded in the books of purchases and sales under the corresponding KVO transaction type codes.
In the sales book, the seller indicates the invoice data when issuing an advance to the contractor, and the buyer recovers VAT from the advance to the seller.
The seller makes an entry in the purchase book on the invoice from the advance payment issued to him in order to accept VAT for deduction, and the buyer makes an entry on the invoice from the advance payment issued to him in order to accept VAT from the seller for deduction.
At the same time, for the advance received, the seller records an invoice in the sales book according to KVO “02”, and the buyer with the same code in the purchase book indicates an invoice for the advance payment that he issued.
When the transaction has been completed, the buyer accepts VAT deduction from the received advance payment, which is possible only after the invoice for the advance payment is recorded by the seller in his purchase book with KVO “22”.
The seller, having shipped the goods, is obliged to restore the VAT deduction from the advance payment after the buyer indicates in his sales book an invoice from the advance payment with KVO “21”.
Upon shipment, the sales invoice is recorded by the seller and the buyer in the sales and purchases book, respectively, with the KVO “01”.
To avoid confusion about which QUOs to indicate when registering invoices, use the cheat sheet below. It clearly shows how the seller and buyer should act when recording transactions in the purchase and sales books.
Procedure for recovering VAT from advances
VAT recovery on an advance payment is made in the following situations (subclause 3, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the delivery has been completed against which an advance payment has been made;
- the supply contract is terminated or its terms are changed and in connection with this the advance payment is returned to the buyer.
See also “Prepayment under a terminated contract was transferred to a new one - the buyer recovers the advance VAT .
The Russian Ministry of Finance adds one more to the list of these situations - the write-off of overdue debt on an advance payment that was not returned by the supplier under an unfulfilled contract (letter of the Russian Ministry of Finance dated August 17, 2015 No. 03-07-11/47347). The need to restore the tax in this letter is explained by the fact that the advance transfer transaction, for which the tax was taken as a deduction, ultimately turned out to be unrelated to VAT. That is, the requirements of paragraphs. 1 and 2 tbsp. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the possibility of applying deductions only to transactions subject to this tax. However, in the list of reasons for the restoration of VAT contained in paragraph 3 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there is no such basis. So, if you wish, you can try to argue with the position of the Russian Ministry of Finance.
For whichever of the listed reasons the restoration is made, it is carried out in the tax period when the corresponding event occurs (subclause 3, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the sales book reflects the data of the invoice for the advance payment for which the restoration is made, and the tax amounts and tax base related to it. The deduction on the delivery invoice is carried out in the usual manner, but this document must reflect the number of the payment document for the transfer of the advance on account of the supply.
Depending on the ratio of the advance amount and the cost of the related supply, the following situations may arise:
- The advance and delivery amounts are the same. Then the same amount that was taken as deductions is subject to restoration. The same will be true for cases of return of the advance and write-off of debt on it.
- The amount of the advance is less than the cost of delivery, and the contract does not contain additional conditions on the offset of the advance against its payment. The entire amount of the deduction made on the advance payment is restored.
- The amount of the advance payment is greater than the cost of delivery, and the contract does not contain additional conditions regarding the offset of the advance payment against its payment. VAT restoration is done for the amount of tax that is reflected in the supply document (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 1, 2010 No. 03-07-11/279).
- The amount of the advance payment may or may not coincide with the amount of delivery, but the contract contains a provision for payment of only part of the delivery from the advance payment issued. Then the tax is restored only in that part that corresponds to the amount of offset of the advance payment for the delivery (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 28, 2014 No. 03-07-11/60891). To avoid any discrepancies, it is recommended that the supplier indicate in the shipping documents exactly what amount of the advance has been credited towards this specific delivery.
For information on a document that combines a shipping document and an invoice, read the article “Universal transfer documents.”
VAT accounting for the supplier
Let's consider an example of how the 1C:Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0, reflects operations for accounting for VAT from a supplier when returning advances received to the buyer.
Please note that in accordance with Federal Law No. 303-FZ dated 08/03/2018, VAT tax rates changed from 01/01/2019: from 18% to 20%; from 18/118 to 20/120 and from 15.25% to 16.67%.
Example 1
| Trading House LLC (seller) entered into an agreement for the supply of goods with Clothes and Shoes LLC (buyer) for a total amount of RUB 180,000.00. (including VAT 20% - RUB 30,000.00) on the terms of full advance payment. After receiving the advance payment, the supply contract was terminated and the advance payment amount was returned to the buyer. The sequence of operations is given in Table 1. |
Table 1
Issuing an invoice for payment to the buyer
To perform operation 1.1 “Issuing an invoice to the buyer” (section Sales - subsection Sales), you need to use the Create button to create a new document Invoice to the buyer.
Receiving advance payment from the buyer
To perform operation 2.1 “Receiving advance payment from the buyer”, you need to create a document Receipt to the current account based on the document Invoice to buyer by clicking the Create based button.
The indicators of the document Receipt to the current account are filled in automatically based on the information in the document Invoice to the buyer.
In addition, in the document Receipt to the current account you must indicate:
- in the fields According to document No. and from - the number and date of the buyer’s payment order;
- in the Amount field - the actual amount of the prepayment received.
As a result of posting the document Receipt to the current account, the following accounting entry is generated:
Debit 51 Credit 62.02 - for the amount of money received by the seller from the buyer.
In accordance with paragraphs 1, 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the buyer of goods who has transferred the prepayment amount must be issued an invoice no later than 5 calendar days, counting from the date of receipt of the prepayment.
An invoice for the received prepayment amount (operations 2.2 “Creating an invoice for the amount of prepayment”, 2.3 “Calculation of VAT on the received prepayment”) in the program is generated on the basis of the document Receipt to the current account using the Create based button. Automatic generation of invoices for advances received from customers can also be done using the processing Registration of invoices for advance payments (section Banks and cash desk - subsection Registration of invoices).
In the new document Invoice issued
basic information will be filled in automatically according to the base document:
- in the from field - the date of preparation of the invoice, which by default is set to the same date as the date of generation of the document Receipt to the current account;
- in the Counterparty, Payment document No. and from fields - the relevant information from the basis document;
- in the Invoice type field – the value For advance;
- in the tabular part of the document - the amount of the received prepayment in the amount of 180,000.00 rubles, the VAT rate in the amount of 20/120 and the amount of VAT in the amount of 30,000.00 rubles.
In addition, the following will be automatically entered:
- in the Transaction type code field - value 02, which corresponds to payment, partial payment (received or transferred) on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (work, services), property rights (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] );
- the Compiled switch is moved to the position On paper, if there is no valid agreement on the exchange of electronic invoices, or In electronic form, if such an agreement has been concluded;
- flag Issued (transferred to the counterparty) indicating the date - if the invoice is transferred to the buyer and is subject to registration. If there is an agreement on the exchange of electronic invoices before receiving confirmation from the EDI operator, the checkbox and date of issue will be absent. If the date of transfer of a paper invoice to the buyer is different from the date of preparation, then it must be adjusted;
- The Manager and Chief Accountant fields are data from the Responsible Persons information register. If the document is signed by other responsible persons, for example, on the basis of a power of attorney, then it is necessary to enter the relevant information from the directory Individuals.
For the correct preparation of an invoice, as well as the correct reflection of the document in the accounting system, it is necessary that in the Nomenclature field of the tabular part of the document the name (or generic name) of the goods supplied is indicated in accordance with the terms of the contract with the buyer.
This information is filled in automatically indicating:
- names of specific product items from the document Invoice to the buyer, if such an invoice was previously issued;
- a generic name, if such a generic name was defined in the agreement with the buyer.
By clicking the Print document Invoice issued button, you can go to view the invoice form and then print it in two copies (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Invoice for prepayment issued to the seller
The invoice for the prepayment amount received shall indicate:
- in line 5 - details (number and date of preparation) of the payment and settlement document (clause “h” of clause 1 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Resolution No. 1137);
- in column 1 - the name of the goods supplied (description of work, services), property rights (clause “a”, clause 2 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Resolution No. 1137);
- in column 8 - the amount of tax calculated on the basis of the tax rate determined in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause “z” of paragraph 2 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Resolution No. 1137);
- in column 9 - the amount of advance payment received (clauses “and” clause 2 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Resolution No. 1137);
- in lines 3 and 4 and columns 2–6, 10–11 - dashes (clause 4 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Resolution No. 1137).
As a result of posting the document Invoice issued, an accounting entry is generated:
Debit 76.AB Credit 68.02 - for the amount of VAT calculated on the amount of advance payment received from the buyer in the amount of RUB 30,000.00. (RUB 180,000.00 x 20/120).
Based on the issued Invoice document, an entry is made in the information register of the Invoice Log.
Despite the fact that since 01/01/2015, taxpayers who are not intermediaries (forwarders, developers) do not keep a log of received and issued invoices, register entries in the Invoice Log are used to store the necessary information about the issued invoice.
Based on the document Invoice issued, a registration entry is made in the Sales VAT
.
Based on the entries in the VAT Sales register, a sales book is generated for the first quarter of 2022 (section Reports - VAT subsection), Fig. 2.
Rice. 2. Sales book for the first quarter of 2022 from the seller
The amount of VAT accrued from the prepayment received is reflected in line 070 of Section 3 of the VAT tax return for the first quarter of 2019 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] as amended by the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 28, 2014 .2018 No. CA-7-3/ [email protected] ) (section Reports - subsection 1C-Reporting - hyperlink Regulated reports).
Refund of received advance payment
To perform operation 3.1 “Return of advance payment to the buyer”, you must create a document Write-off from the current account.
You can create this document based on the document Receipt to current account by clicking the Create based on button.
The document Write-off from a current account can also be created based on downloading from other external programs (for example, “Client-Bank”). If payment orders are created in the Client-Bank program, then it is not necessary to create them in the 1C: Accounting 8 program. In this case, only the document Write-off from the current account is entered, which generates the necessary transactions.
As a result of posting the document Write-off from the current account, the following accounting entry will be generated:
Debit 62.02 Credit 51 - for the amount of advance payment returned to the buyer in connection with termination of the supply agreement.
Amounts of VAT calculated by the seller and paid to the budget from payment amounts, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (work, provision of services) sold in the Russian Federation are accepted for tax deduction in the event of a change in conditions or termination of the contract and the return of the corresponding amounts of advance payments (Clause 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Deductions of VAT amounts are made in full after the corresponding adjustment operations in connection with the return of goods or refusal of goods (work, services) are reflected in the accounting records, but no later than one year from the date of return or refusal (clause 4 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
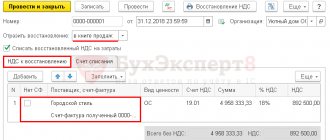
Submitting for tax deduction the amount of VAT calculated on the received advance payment (operation 3.2 “Deduction of VAT calculated on the received advance payment”) is carried out using the document Generating purchase ledger entries (section Operations - subsection Closing the period - hyperlink Regular VAT operations) using the Create command .
Data for the purchase book on tax amounts to be deducted in the current tax period are reflected on the Advances received tab.
To fill out a document using accounting system data, it is advisable to use the Fill command.
As a result of posting the document Formation of purchase ledger entries, an accounting entry is generated:
Debit 68.02 Credit 76.AB - for the amount of VAT claimed for tax deduction in connection with the termination of the supply agreement and the return of advance payment.
To create a purchase book, an entry is made in the Purchase VAT accumulation register.
Based on the entries in the VAT Purchases register, a purchase book is generated for the tax period in which the contract was terminated and the amount of advance payment was returned to the buyer, i.e. for the second quarter of 2022 (section Reports - VAT subsection), fig. 3.
Rice. 3. Purchase book for the second quarter of 2022 from the seller
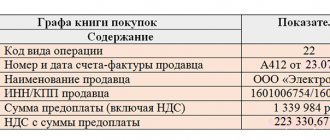
When registering the advance invoice in the purchase book, the following will be indicated:
- in column 2 - transaction type code 22, which corresponds to the operation for the return of advance payments in the cases listed in paragraph 2 of paragraph 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] );
- in column 7 - details of the document confirming the return of the advance payment to the buyer (clause “k”, clause 6 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger, approved by Resolution No. 1137);
- in column 15 - the entire amount of the invoice from column 9 on the line “Total payable” (clause “t”, paragraph 6 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger, approved by Resolution No. 1137);
- in column 16 - the amount of VAT that the seller claims for tax deduction (clause “y” of clause 6 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger, approved by Resolution No. 1137).
The amount of the tax deduction will be reflected on line 120 of Section 3 of the VAT return for the second quarter of 2022 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] as amended by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 28, 2018 No. SA-7-3/ [email protected] ) (section Reports - subsection 1C-Reporting - hyperlink Regulated reports).
Accounting entries for VAT recovery from advance payment
The VAT recovery posting will always be the same for each individual invoice:
Dt 76/VA Kt 68/2,
Where:
68/2 - subaccount for accounting for settlements with the budget for VAT on account 68;
76/VA - subaccount for accounting for VAT on advances issued in account 76.
The results of VAT recovery for specific advance invoices will vary depending on the ratio of the amount of the advance and the cost of supply associated with it:
- for the first two cases (the amounts of the advance and delivery are the same or the amount of the advance is less than the cost of delivery), with this posting the amount of tax on the advance, listed in subaccount 76/AB, will be closed completely;
- in the 3rd and 4th cases (the amount of the advance is greater than the cost of delivery or the contract contains a condition on partial offset of the advance towards payment for the supply), in subaccount 76/AB after the restoration of VAT there will be a balance of unrecovered tax.
Reflection of advance transactions in the declaration: postings, restoration
In accounting, VAT is charged on the advance received from the buyer using the following entries:
To reflect the accrual of VAT on advance payments, the chart of accounts provides a subaccount “VAT on advances received (prepayments)” to account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” and account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”. This allows:
- keep in accounting data on advances received and VAT on them (according to Kt 62, 76);
- in the balance sheet, reflect the amounts of advances received (excluding VAT, accounted for on the Dt of the relevant accounts) as accounts payable.
Please note that the previously received advance payment at the time of sale of goods (services or work) is counted towards the prepayment amount. An invoice is issued for the shipped product (service or work). On the date of offset of advances, the company accepts for deduction VAT on advances received. Please note that the deduction is made in the amount of tax calculated on goods (services or work) shipped for which advances were received. It is understood here that if VAT on advances is charged at a rate of 20/120%, and the product (service or work) is shipped at a rate of 10%, then VAT on advances received is credited at a rate of 10/110%.
In the VAT return, the advance received is reflected in section 3 on line 070 in column 3, and the amount of tax on the advance is reflected in column 5.
The deduction of VAT on advances received is reflected in section 3 of the declaration on line 170 in column 3 for the tax period in which the goods were shipped.
Reflection in accounting of VAT on the advance paid to the supplier is reflected by postings.
Account 19 is used for the purpose of separating VAT from an advance, when the issuance of an advance and the deduction of VAT are separated in time. If advance VAT on the reporting date is not accepted for deduction, then the tax reflected in account 19 is recorded in the balance sheet as a current asset separately from the “receivables” for the transferred advance payment.
To separate VAT from advances issued, you can use separate subaccounts “VAT on advances issued (prepayments)” to account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” or to account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”. Thereby:
- the accounting stores data on advances paid, including VAT (according to Dt 60, 76);
- the balance sheet shows “receivables” (minus VAT accounted for in the KT of the relevant accounts) in the form of advances issued.
VAT on advances received, accounted for under Dt 62-VAT (76-VAT), is not indicated in the balance sheet, as well as VAT on advances issued, accounted for under Kt 60-VAT (76-VAT). In the balance sheet, tax amounts are reduced by the “debtor” in the form of advances issued and the “creditor” in the form of advances received.
Reflected in account 19 from the advance VAT issued, which was not accepted for deduction by the end of the reporting period, must be included in the balance sheet. This VAT is indicated in line 1220 “VAT on acquired assets.”
Advances issued are not reflected in the VAT return, but the tax on these advances accepted for deduction is indicated in section 3 on line 130.
Please note that for the advances listed by the suppliers, the buyer acts according to the following scheme:
1) receives an invoice for the advance payment, records it in the purchase book, and accepts the advance VAT for deduction;
2) after shipment of goods (services, works), records the shipping invoice in the purchase book;
3) indicates the previously registered advance invoice in the sales book, thus recovering VAT from the advance payment issued.
Kontur.VAT+ allows you to avoid discrepancies in the quotas and reconciles invoices for transactions with advances for all quarters.
Find out more
Regarding the recovery of VAT from an advance received, the situation is as follows. The seller, having received an advance payment, charges VAT on it. Having sold the goods (service, work), he draws up an invoice for the sale and accepts VAT from the previously received advance for deduction. That is, in this case the term “restoration” is incorrect to use. The seller records an advance invoice in the sales book, and later, after shipment of the goods (service, work), an invoice for sales. At the same time, the seller registers an invoice for the advance payment in the purchase book, thereby deducting advance VAT. Oh, that is, the deduction, VAT on the advance received is not limited, the main thing is that the deduction is declared in the quarter in which all the conditions for the deduction are met.
Pros and cons of deducting VAT on advances issued
The positive aspects of the use of such deductions occur with significant amounts of advances issued and manifest themselves as follows:
- A large deduction amount can not only significantly reduce the total of the declaration drawn up for the period of its application, but also make it result in the amount of tax reimbursement from the budget.
- A deduction for an advance on account of several deliveries for it is made one-time, ahead of time and in a larger amount than deductions would be made for each of the deliveries separately. At the same time, VAT restoration occurs in parts and can be extended over several tax periods.
On the plus side, there are also conditions for payment of only part of the delivery using the transferred advance payment. In this case, deductions for the advance payment issued and for the delivery document will occur earlier and will be taken in full, and the VAT restoration will be made only in part of these amounts and will be extended over time.
The following points will be negative:
- increasing the volume of accounting operations and document flow;
- there is no point in using deductions for advances if we are talking about small amounts and the period for transferring the advance often coincides with the period of shipment for it.
Read about the rules for issuing invoices for advance payments here.
Results
The question of recovering VAT on advances paid to suppliers arises if the taxpayer takes tax deductions on invoices issued by the supplier for prepayment. The provision for advance payment must be included in the supply agreement. VAT on advances issued is recorded in a separate subaccount of account 76.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.