Return of goods after acceptance by the buyer for accounting
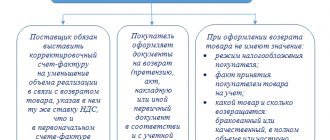
According to the position of the official authorities, if on the date of return the goods are registered, the return of the goods by the buyer is recognized as a reverse sale.
It does not matter for what reasons the goods are returned. In this case, the buyer, if he is a VAT payer, must issue an invoice to the seller (letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 29, 2013 No. 03-07-11/51923, dated August 10, 2012 No. 03-07-11/280).
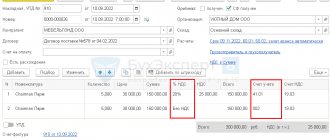
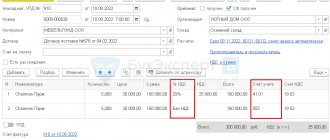
Example Promooborudovanie LLC purchases blanks for the production of parts from Omega LLC.
Products are purchased in batches of 1000 pieces. On a monthly basis, upon acceptance of MPZ, incoming quality control is carried out in order to identify defective workpieces. On April 30, 2022, the next batch of workpieces arrived, which were entered into the warehouse, and the arrival of the goods and materials was reflected in the accounting.
Before sending the workpieces to the workshop, the quality control inspector, conducting laboratory incoming quality control, discovered metal defects that were not visible during the initial visual inspection and were revealed only during ultrasonic testing. According to the terms of the contract, if a defect is detected in the control samples, the entire batch must be returned.
In this case, Promooborudovanie LLC, the buyer, issues an invoice for the returned shipment and charges VAT on the proceeds from the reverse sale.
The invoice for reverse sales of Promooborudovanie LLC (former buyer) is registered in the sales book, and the invoice received from Omega LLC is registered in the purchase book.
LLC "Omega" (former seller) registers the initial invoice in the sales book, and the one received from LLC "Promooborudovanie" - in the purchase book (clause 5 of article 171, clause 10 of article 172 of the Tax Code, letters of the Ministry of Finance dated November 29, 2013 No. 03-07-11/51923, 08/28/2012 No. 03-07-09/126).
If the buyer and seller are on OSNO, then in the seller’s purchase book and the buyer’s sales book, an invoice for the return of goods is registered using the transaction code “01” (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 20, 2016 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] ).
Returning goods before the buyer accepts them for accounting
As stated above, the issuance of an invoice for the return of goods depends on whether the returned goods are registered or not.
If the goods are accepted, you need to issue a regular invoice for return sales. In this case, the seller and buyer change places, and the goods are returned to the starting point.
If the buyer returns an item that was not accepted for registration, or only part of the item, the seller needs to issue an adjustment invoice.
Example
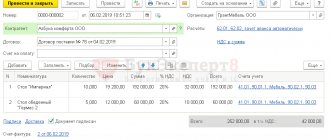
During the acceptance of workpieces received from Omega LLC, OO Promoborudovanie identified defects that arose during their improper transportation (chips, cracks, etc.). It was decided to return the entire batch of blanks. Since the buyer did not accept the goods for registration, the transfer of ownership of the blanks to Promooborudovanie LLC did not occur, so there is no reverse sale in this case and there is no need to issue an invoice to Omega LLC (Clause 1, Article 39 of the Tax Code RF, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/07/2015 No. 03-07-09/19392).
The defective batch of blanks was sent to the supplier with a TORG-12 invoice marked “Return”. The remaining documents confirming the fact of the return of the blanks (return certificate, claim, agreement to terminate the contract, etc.) were sent later.
For Promooborudovanie LLC, the return of workpieces without registering them did not entail any tax consequences; nothing needs to be reflected in the purchase book and sales book .
And Omega LLC, as the seller who reflected the sales in the sales book, must draw up an adjustment invoice and register it in the purchase book (letters of the Ministry of Finance dated 08/10/2012 No. 03-07-11/280 and 08/07/2012 No. 03-07 -09/109, Federal Tax Service dated 07/05/2012 No. AS-4-3/ [email protected] ).
Return of goods as a new sale
When the buyer records the purchased goods, he becomes its owner. Although, as we have already found out, this is not an obstacle to a return if the parties agreed on it within the framework of a valid contract.
In a letter dated August 24, 2022 No. 03-07-14/73988, the Ministry of Finance indicated a situation where a refund on an adjustment invoice is not possible.
This procedure does not apply if there are indications that the goods are essentially being resold. That is, a new deal is concluded. And in this new transaction, the former seller is the buyer, and the former buyer is the seller.
To formalize the return of goods as a new sale, the seller and buyer must necessarily enter into a new sales contract or supply agreement. Otherwise, the former seller will not be able to deduct VAT upon receipt of the returned goods.
Also, the new seller prepares a new invoice and registers it in his sales book. The former seller can deduct VAT on returned goods based on this invoice, just as a regular buyer can deduct input VAT.
A deduction for the return of goods (work, services), registered as a new sale, can be applied within 3 years after their acceptance for registration (clause 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
As you can see, this condition for deducting VAT on actually returned goods is much softer.
Partial return of goods before the buyer accepts it for accounting
Let's consider a situation where the buyer, upon acceptance of the goods, identifies a discrepancy with the specifications, but only part of the received goods is subject to return (not acceptance).
In this case, the buyer (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated May 12, 2012 No. 03-07-09/48):
- Registers in the purchase book the initial “shipping” invoice only for the cost of those goods that were accepted for accounting;
- The CSF received from the seller is not recorded either in the purchase book or in the sales book.
The seller registers his copy of the adjustment invoice in the purchase book and adjusts the VAT payable to the budget by the amount of tax on the value of the returned blanks accepted for deduction.
What other documents are needed to return goods?
It should be borne in mind that the list of documents that need to be completed when returning goods has not undergone any changes. In order to return the goods, it is not enough to simply draw up an adjustment invoice.
Most often, a product is returned if it is of inadequate quality or a mismatch is detected. In this case, a document such as a statement of discrepancies is drawn up. If it is drawn up in the presence of the supplier, then his signature is placed on the document.
A claim is also drawn up, which contains a convincing request to accept the goods back, indicating the reason for the return and the quantity of the goods. Another document that is drawn up when returning is a return invoice. It should also indicate which product and in what quantity can be returned.
The report, along with the claim and return invoice, is sent to the supplier. The supplier, in turn, must accept the returned goods and at the same time make a note on the return label. The usual TORG-12 can be used as a return invoice, on which a note is made that such an invoice is a return one.
As you can see, returning an item is not that difficult. From 2022, a new procedure for processing the return of goods will be applied. This procedure applies to returns made after April 1. The burden of creating an adjustment set - invoice - lies entirely with the seller of the goods, who accepts the return. When making a return, you should be very careful about the formation of primary documents so that the regulatory authorities do not have any complaints.
Preparation of invoices when returning goods due to mis-grading
Sometimes in practice there are situations when the supplier transfers goods to the buyer, making mistakes in the assortment.
According to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, in such a situation one should proceed as follows. If the buyer identified and accepted a re-grading, when in fact there were more of some goods and less of others, it is necessary to issue an adjustment invoice. In this case, the supplier has two options for issuing an adjustment invoice to one initial one (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 17, 2016 No. 03-07-09/67407):
- issue one adjustment invoice, increasing the quantity of some goods and decreasing the quantity of others;
- issue two adjustment invoices. In the first, increase the number of goods that were shipped more than required. In the second, reduce the quantity of those goods that the supplier brought less.
The agency explains its conclusion by saying that the rules for drawing up adjustment invoices do not contain any specifics for filling out documents for such a case.
This means that the proposed options do not contradict the law. Please note that, in our opinion, this approach is correct in the case where both names of goods were indicated on the original invoice. If the buyer, having identified the misgrading, finds goods that are not indicated in the original invoice, then the adjustment procedure will be different: the supplier in this case does not issue an adjustment invoice, but makes corrections to the original invoice.
In our opinion, this approach is correct in the case where both names of goods were indicated on the original invoice. If the buyer, having identified misgrading, finds goods that are not indicated in the original invoice, then the adjustment procedure will be different. The supplier does not issue a correction invoice, but makes corrections to the original invoice.
What are adjustment invoices used for?
It's simple.
Adjustment invoices are used when it is necessary to correct previously issued invoices. That is, it is set when the cost of goods shipped, work performed, services provided, or transferred property rights changes. Price changes are possible in the following cases:
- price (tariff) changes after shipment (for example, when providing a discount on an already shipped product);
- clarification of the quantity (volume) of shipment.
Errors identified in previously generated invoices cannot be corrected using adjustment invoices. In this case, the previously issued invoice is corrected.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
How to prepare and register adjustment invoices in different business situations
Return of goods by a VAT non-payer
If the seller and buyer use special modes (STS, UTII, etc.), invoices for sales and returns are not issued, and entries in the purchase and sales book are not made.
If the seller is located on OSNO, and the goods were sold to a company that is not a VAT payer, then when the buyer returns goods (both accepted and not accepted by him for registration), the supplier must issue an adjustment invoice for the cost of the goods returned by the buyer and register it in shopping book.
When the supplier registers an adjustment invoice drawn up when returning goods from a buyer who does not pay VAT (except for individuals), column 2 of the supplier’s purchase book reflects transaction code 16.
Thus, the seller registers the same invoice twice: the first time - in the sales book with code KVO 01 or 26, the second time - in the purchase book with code KVO 16.
Return of goods according to an adjustment invoice
Through an adjustment invoice, it is allowed to process any return of goods - both those not accepted by the buyer for registration, and those that he has already managed to put on balance. Moreover, this rule has been in effect for a long time – since April 1, 2022. It was established by Government Decree No. 15 of January 19, 2022.
The seller must adjust the shipment, that is, reduce the number of goods shipped by the number of goods returned.
The seller can deduct VAT on returned goods (work, services). If the buyer does not return all the goods, then VAT is deducted in relation to the cost of return.
Deductions can only be made on the basis of an adjustment invoice.
A deduction for the return of goods (work, services) issued with an adjustment invoice can be applied no later than one year from the date of return of the goods (clause 4 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
But before issuing it, both parties to the supply contract are required to agree on this adjustment in writing. For example, conclude an appropriate agreement or contract, or draw up another primary document confirming the consent of both parties to change the terms of a previously concluded transaction.
An adjustment invoice is used to make a downward adjustment to the price or quantity of an item only as a condition of the original transaction.
Return of goods by an individual
When selling goods, works or services to individuals for cash, the VAT payer supplier has the right not to issue invoices to them.
This is stated in paragraph 7 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, you can register a cash register tape in the sales book. If individuals pay in non-cash form, the VAT payer seller must issue a consolidated invoice for all sales and register it in the sales book (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 15, 2015 No. 03-07-14/34405. The seller should do the same in a situation where individuals receive goods by mail (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/20/14 No. 03-07-09/29630), and when goods are transferred free of charge to employees (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/08/2016 No. 03-07-09/6171 ).
Consolidated invoices and cash register tapes are registered in the sales book of the seller with code KVO 26.
If the buyer, an individual, returned the goods or refused the work (service), the seller must return the money to him. The salesperson should then record in the purchase ledger the consolidated invoice or cash register tape that was previously recorded in the sales ledger.
In this case, in the column intended for the KVO code, you should put 17 (order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] , letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2014 No. 03-07-09/37589). In the column intended for information about the document confirming the payment of tax, you must indicate the number and date of the document drawn up when returning money to the buyer.
According to officials (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 19, 2013 No. 03-07-15/8473) and tax authorities (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated May 14, 2013 No. ED-4-3 / [email protected] ), if a buyer who did not pay VAT when selling goods was a cash receipt has been issued without issuing an invoice (in retail trade using cash register), in the seller's purchase book you can register the details of the cash receipt issued when returning money to the buyer (if there are documents confirming the receipt of returned goods).