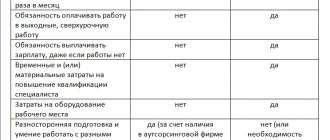
Conditions under which an enterprise can switch to piecework wages
An enterprise can switch to piecework wages if there are necessary prerequisites for this, namely:
- Well-established accounting of manufactured products or services provided;
- Developed tariff systems and local standards;
- The ability to take into account quantitative data on the performance of each employee separately;
- Effective quality tracking;
- Uninterrupted supply of materials and everything necessary for work;
- The current need to increase production levels manifold.
Scope of application
The piecework-bonus system is used:
- in sales and network marketing;
- in the manufacture of finished products at the factory;
- in the construction industry;
- in financial services.
You can stimulate active sales by rewarding them with a bonus in addition to the percentage of each transaction.
When selling financial ]insurance[/anchor], credit cards, etc.), bonuses depending on the percentage of production are most suitable, as it will encourage employees to achieve maximum performance in a short time. In the production sector, a mixed type of piecework-bonus system is suitable, since in a work team not only production indicators are important, but also labor discipline.
For example, this type of remuneration is used in settlements with masons: the main part is charged for the cubic meters of brick laid, and the bonus is for the early completion of the project and the quality of the masonry.
Piece rate
When applying piecework wages, piecework prices are used.
Piece rates are the amount of wages per unit of work performed or product manufactured.
Piece rates are determined based on established categories of work, tariff rates and production standards (time standards) and are calculated by dividing the hourly (daily, monthly) tariff rate corresponding to the category of work performed by the hourly (daily, monthly) production rate.
In practice, the following types of piece rates are distinguished:
- straight,
- indirect,
- progressive,
- chords.
Example 1. The standard does not determine the number of products
The daily rate of processing parts on a milling machine for a milling machine operator is 150 pieces.
The daily rate for the tariff is 1,500 rubles.
In a month, the employee processed 2,500 parts.
The piece rate is calculated by dividing the daily tariff rate by the daily rate for parts:
Wed = 1500/150 = 10 rubles/piece.
Then the employee’s monthly salary will be:
Salary = 10*2,500 = 25,000 rubles.
Example 2. The norm determines the time period
The time limit for using the machine is set at 40 minutes per operation.
The hourly rate is 120 rubles.
During the month, the employee performed 500 operations.
The piece rate is equal to:
Wed = 120*40/60 = 80 rubles/operation
Then the employee’s monthly salary will be:
Salary = 80*500=40,000 rubles.
Directory of types of work
Let's calculate the amount of piecework payment, taking into account the cost of the work performed, in “Settings - Types of work”.
Fig. 10 Directory of types of work performed
Here you can combine views into groups - arrange them into folders, for which you click the corresponding button and indicate the name of our group. For example, let’s create groups for work performed by a car service center – “Repair (domestic cars)” and “Repair (foreign cars)”.
Fig. 11 Creating groups by type of work
Fill out the directory with types of work via “Create”. For each element, indicate the name, price, and from what date it is entered. Set accounting settings if different from the preset settings.
Fig. 12 Element card
We are grouping.
Fig. 13 Completed reference book
On our website you can also find information about hourly wages in 1C 8.3 ZUP.
Types of piecework wages
The existence of several types of this payment is explained by the diverse specifics of existing work where piecework payment is used.
In practice, the following types of piecework wages are distinguished:
- Piece-bonus wages;
- Direct piecework wages;
- Piece-progressive wages
- Accordal payment;
- Mixed (time-piece) wages.
Piece-bonus wages
The piece-rate wage system, along with payment at direct piece rates, provides for bonuses for exceeding production standards and for achieving quantitative and qualitative indicators determined by the current bonus conditions.
In production, bonus indicators can be increased labor productivity, improved product quality, absence of defects, and cost reduction.
Direct piecework wages
Under the direct piecework system, wages are calculated based on the volume of work performed using fixed piecework rates established taking into account the employee’s qualifications.
Example:
The piece rate for a seamstress of the highest category is 60 rubles per shirt.
In a month she sewed 500 shirts.
Her piecework earnings for the month will be 30,000 rubles.
Piece-progressive wages
Remuneration for labor under the progressive piece-rate system within the established norms is made at direct piece rates, and in excess of these norms - at increased prices.
As a rule, the increased price exceeds the unchanged price by no more than twice.
Example:
A turner turned 300 parts in a month at a rate of 250. According to the piece rate, he receives 80 rubles per part. If the plan is exceeded, each detail is paid in the amount of 100 rubles.
The basic salary of a turner: 250 * 80 = 20,000 rubles.
Taking into account exceeding the norm: 50*100=5000 rub. Total salary of a turner: 20000+5000=25000 rub.
Chord payment
With a lump sum wage system, earnings are set for the entire volume of work, and not for a separate operation.
This sets a deadline for completing the work.
Payments to employees are usually made after all work has been completed.
If the work is planned to be completed over a long period of time, an advance may be paid.
Bonuses are offered for reducing the deadlines for completing tasks.
This system is used in cases where labor cannot be regulated: during construction, repair work, etc.
Example:
A contract is concluded with a team of builders to renovate a house. All work is divided into stages (carrying out electrical wiring, plastering walls, laying floors, etc.). Each stage of work is accepted by a responsible person, who determines whether the work meets quality standards, after which a settlement is made with the team
Mixed (time-piece) wages
Mixed wages are a synthesis of piecework and time-based wages.
A mixture of piecework and time-based wages is used when the employer is interested in the constant presence of an employee at the workplace, while his activity largely determines his work efficiency.
Example:
A makeup artist at a beauty salon has a fixed salary for being in the salon at certain hours. He will receive this money even if not a single client comes to him all day. In this case, the employee will receive a percentage of the amount paid by the client for each work performed.
Time-based wage system
Employees are paid for the actual time worked based on the established monthly salary (hourly or daily rate). In practice, this is how employees who do not participate in the production process (for example, economists, accountants) or participate but constantly perform the same amount of work are paid (for example, assembly line workers).
If an employee who has a monthly salary has worked all working days of the month, then he should be paid the salary in full. Moreover, the number of working days in a month does not matter. Depending on the number of working days in a particular month, only the “cost” of the day changes. So, the most “expensive” days are in January with its record low number of working days.
A situation may arise when an employee whose salary is set has worked for less than a full month. For example, an employee did not get a job at the beginning of the month, got sick or went on vacation during that month. In this case, the salary for a month not fully worked must be calculated by dividing the employee’s monthly salary by the number of working days in this month and multiplying by the number of days he worked. In formula form it looks like this:
Salary = Monthly salary: Number of working days in a given month x number of days worked by the employee
An employee who is assigned an hourly rate must calculate his salary by multiplying the number of hours he worked by the hourly rate set for him.
An employee for whom a daily rate is established has his salary calculated by multiplying the number of days he worked by the daily rate.
A special case of a time-based wage system is a time-based bonus system. With this remuneration system, in addition to the salary, the employee may be paid a bonus (provided that he has fulfilled the conditions for receiving it).
How are salaries set taking into account the bonus system?
Labor law provisions permitted for independent development are enshrined by the employer in internal regulatory documents (Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To establish a remuneration system and bonus rules, the employer can create:
- a single document containing a description of the remuneration system and bonus rules (remuneration regulations or collective agreement);
- separate documents (provisions), devoting one of them to the characteristics of the remuneration system, and the other to the bonus rules;
- the corresponding clauses are directly in the text of the employment agreement with the employee, if individual bonus conditions are provided for this employee or the employer (who has such a right under Article 309.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) does not adopt internal labor regulations.
If the text of the employment agreement does not contain a detailed description of the rules for remuneration for labor functions performed by the employee (including the procedure for bonuses), then it must make a reference to the corresponding internal regulatory document developed by the employer.
Establishing bonus rules requires determining:
- list of types of bonuses accrued;
- frequency of their payment;
- the circle of those persons who may qualify for a bonus of one type or another;
- indicators, the fulfillment of which makes the calculation of incentive payments mandatory for the employer;
- procedures for assessing the right of each employee to receive bonuses;
- a system that allows you to evaluate the amount of remuneration for each type of bonus and determine the amount due to a specific employee;
- a list of grounds on which an employee can be deprived of bonuses or the amount of remuneration due to him can be reduced;
- the procedure for establishing the amount of reduction in the amount of bonuses;
- a procedure that gives the employee the opportunity to challenge the results of the distribution of bonuses, including deprivation of his bonus or reduction in the amount of remuneration.
Read more about the procedure for establishing bonus rules in the material “The procedure for paying bonuses under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.”
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to calculate an employee’s earnings under a piecework-bonus labor system. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Formula for calculating wages for the piecework-bonus form of remuneration
In order to automate the payroll process at an enterprise, unified calculation methods are used. Thus, for the piecework-bonus system, the salary (ZSsp) will be determined by the following formula:
ZPsp = Zsd + Pkp,
Where:
Zsd - earnings at the piece price for labor;
PKP is a premium surcharge for quality indicators.
For December 2022, workshop worker S. L. Avgustovich received a salary of 25,000 rubles. He had to produce 500 products per month for 50 rubles. for a unit. According to the bonus document, if 470 products (94%) are delivered the first time (without defects), then a bonus of 6% is awarded on the piecework portion of earnings. For each percentage above the established norm of 94%, the employee is also given a bonus of 2%. In fact, in December, shop worker S. L. Avgustovich handed over 500 products, and 490 of them were handed over immediately, which amounted to 98%.
Based on the available data, you can calculate the wages of shop worker S. L. Avgustovich for December 2022:
- We determine the amount of the bonus for delivering products within the plan: 25,000 × 0.06 (i.e. 6%) = 1,500 rubles.
- Premium for exceeding the plan: 25,000 × (98% - 94%) / 100% × 0.02 (i.e. 2%) = 2,000 rubles.
- The total premium surcharge will be: 1,500 + 2,000 = 3,500 rubles.
- The salary for December 2022 will be: 25,000 + 3,500 = 28,500 rubles.
If an employee exceeds the planned norm and, in addition, receives a bonus for exceeding the production norm, the calculation is complicated by the fact that the piecework part of the salary is also calculated separately:
Calculation example:
The daily production rate of seamstress P. R. Ukhova in October 2022 was 10 products. Ukhova P.R. worked 21 working days this month. At the end of the month, it was estimated that she sewed 245 items. For each product you pay 100 rubles. For exceeding the plan for the number of products manufactured per month, a bonus of 2% is awarded for every 5% exceeding the established norm.
Let's calculate the earnings of seamstress Ukhova for October 2017:
- Amount of piecework part of wages: 245 ed. × 100 rub. = 24,500 rub.
- Let us determine the standard for the piecework part of earnings: 21 days × 10 ed. = 210 ed.
- What is the percentage of exceeding the plan for Ukhova P.R.: 245 / 210 × 100 – 100 = 16.67%
- The bonus surcharge coefficient for exceeding the plan will be: 16.67 / 5 × 2 = 6.67%
- Bonus for exceeding the plan: 24,500 × 6.67% / 100% = 1,634.15 rubles.
- The salary for October 2016 will be: 24,500 + 1,634.15 = 26,134.15 rubles.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the piecework-bonus system include:
- higher level of employee responsibility than with a simple piecework system;
- no need to control the entire work process;
- flexible system of spending the wage fund;
- ample opportunities for optimizing business processes.
A flexible payment system allows you to save money during production downtime or a decline in sales, and when performance improves, it allows you to reward conscientious employees.
In addition, the personal interest of employees in increasing the company’s profits will allow them not to spend the budget on building a system for monitoring the activities of employees during a shift.
The disadvantages of the system include difficulties in determining individual indicators that affect the size of the premium , for example, if previously a good premium was given for 100 units of goods sold, then with a stable market growth in demand for these products, the premium will have to be paid constantly or the terms of the contract will have to be changed, which cannot be done without employee consent.
Also, employees can artificially inflate individual indicators that affect the bonus through collective agreement, for example, sharing products or completed orders with each other if the pre-bonus threshold is a small percentage.