Salaries must be paid strictly on the established days; delays are unacceptable. Otherwise, workers' compensation and a fine. And in some situations they may be brought to criminal liability if payments are delayed for a very long time, to a large number of employees and in large amounts.
But there are not quite standard situations, for example, the salary deadline fell on a weekend. Should I pay the salary the day before or can I still pay it on the day off, will there be a violation? Let's try to turn to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and figure it out.
Is it possible to pay wages ahead of schedule?
Yes, it is possible to pay wages ahead of schedule. But only in certain cases :
- the payday falls on a weekend or holiday;
- wages are paid for time actually worked at least every half month (advance).
If you violate the half-month deadline, you will have to prove to the labor inspectorate that the employer did not violate the rights of workers.
But in the first case there will be nothing to fear, since payment of wages on the last working day before the weekend is a norm of the Labor Code.
What is said in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation about days off and wages
In 2022, wages must be paid at least every half month on the day established by the internal labor regulations, collective agreement, and employment contract (Part 6 of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the salary payment date coincides with a weekend or non-working holiday, the money must be issued on the eve of this day (Part 8 of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 1
The day of final payment of wages in the organization is the 5th day of the month following the settlement month.
In this case, wages for September 2022 must be paid on 10/03/2021 on Friday, since 10/05/2021 falls on a Sunday (Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
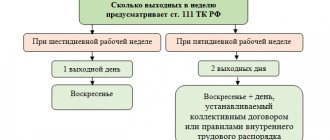
Is it possible to pay wages on Saturday during a six-day work week?
If the payday falls on the weekend, it must be paid on the last working day. Generally accepted weekends are Saturday and Sunday .
But for companies that operate a six-day work week, Saturday is a working day. How to be in this case?
There is no official answer to this question. But experts believe that we must adhere to the following position.
If the salary is paid through the cash register, the payday falls on a Saturday, which is a working day for everyone, then the money can be issued on Saturday. But if the six-day workday is not for all workers, but only for production workers, and the accountant or cashier does not work, then the salary must be paid on Friday, the day before the day off.
When transferring your salary to a card , you need to find out the payment schedule from the bank. If the bank does not process payments on Saturday and Sunday, the salary must be transferred on Friday. And it doesn’t matter that the company is on a six-day break.
However, if the bank is open and makes payments on Saturday, then you can transfer your salary on that day.
Salary entry rules
Service help: the exact terms of payment between the employer and the employee are specified in the employment contract - this is a legal requirement. The employer must ensure that the employee receives his salary no later than the day specified in the agreement.
The law does not establish specific payment dates: they are determined by the collective labor agreement. Consequently, these can be any working days of the month, the maximum period between which should not exceed 15 calendar days. The minimum frequency of calculations is at least twice a month. In practice, the salary is divided into an advance part, which is paid in the middle of the month, and the main part, which is transferred at the end of the current month or at the beginning of the next.
The employer cannot, at its discretion, change the procedure and amount of payments. This is prohibited by labor law. If the payday falls on a holiday or weekend, the money is transferred to employees in advance, otherwise a delay of 1 or more days will be classified as a salary delay.
How long does it take for banks to transfer wages?
Payment terms depend on the specific bank. A credit institution is the middle link in the chain between employer and employee. The salary project works as follows:
- The employer (accountant or other responsible person) creates a register of payments and writes in it the amounts that must be transferred to each employee monthly.
- After reconciling the data, the credit institution generates payment orders.
- The employer pays the final amount.
In most cases, reconciliation of information takes one business day at the bank. Therefore, the employer must create and send to the bank a register of payments and other documents 1-2 days before the due date of wages. If everything is done according to the rules, then salaries are credited to employees’ accounts without delay. Any delays on the part of the bank are practically excluded, so failure to receive wages on time is the reason on the employer’s side.
Responsibility for late payment of wages
If wages are not paid, the employer is obliged to pay compensation to employees, and may also be subject to administrative and criminal liability. In addition, by a court decision, he may be required to pay compensation for moral damage.
Compensation for non-payment of wages
If wages are delayed, the employer is obliged to pay compensation to employees (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The amount of compensation is 1/150 of the current key rate of the amount of unpaid wages for each day of delay.
But if the employment or collective agreement specifies an increased amount of compensation, then you need to focus on it. For example, an employment contract may indicate that the amount of compensation is 1% of the salary. Which is more than 1/150 of the refinancing rate.
Example: the date of payment of wages for the second part of the month at Romashka LLC is the 10th day of the next month. The employer paid wages only on the 20th. Sidorov was supposed to receive 60,000 rubles. The current key rate is 7.5%. The compensation amount is standard.
In addition to the salary, the employer must pay the employee an additional 300 rubles (60,000 rubles * 0.05% (1/150 * 7.5%) * 10 days).
To pay compensation, the employer must draw up an order . It indicates the amount of compensation and the period of salary delay. A list of employees whose salaries were not paid on time and were entitled to monetary compensation is compiled with the order.
Administrative responsibility
In addition, an employer who violates the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation may be held liable under Part 6 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the form of a fine in the amount of:
- from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles for officials;
- from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles for individual entrepreneurs;
- from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles for companies.
In case of repeated non-payment of wages, the employer’s responsibility:
- a fine in the amount of 20,000 to 30,000 rubles or disqualification for a period of one to three years for officials;
- a fine of 10,000 to 30,000 rubles for individual entrepreneurs;
- a fine of 50,000 to 100,000 rubles for companies.
An employer can be held administratively liable only if it is his fault.
If there is no fault, for example, the bank’s license was revoked, then there will be no administrative liability.
Criminal liability
The general director of the company or the head of a branch or division may be brought to criminal liability. But only if the salary delay is 2 months or more.
According to Part 1 of Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, for partial non-payment of wages for more than 3 months in a row, managers can:
- fined up to 120,000 rubles or in the amount of the salary or other income of the convicted person for a period of 1 year;
- deprive the right to hold certain positions or conduct certain activities for a period of up to 1 year;
- subject to forced labor for a period of up to 2 years;
- imprisoned for up to 1 year.
Partial non-payment of wages - payment of wages in the amount of less than half of the accrued amount.
If the employer did not pay wages to employees at all for more than 2 months in a row, or paid, but in an amount less than the minimum wage, then he will be held accountable under Part 2 of Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation:
- a fine in the amount of 100,000 to 500,000 rubles. or in the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of up to three years;
- forced labor for a term of up to 3 years with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for a term of up to three years;
- imprisonment for up to 3 years and, by court decision, may be prohibited from holding certain positions or conducting specific activities for up to 3 years.
If non-payment or partial payment of wages has resulted in negative consequences , then a case will be opened against the employer under Part 3 of Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation:
- a fine in the amount of 200,000 to 500,000 rubles or in the amount of salary or other income for a period of 1 to 3 years;
- imprisonment for a term of 2 to 5 years.
In addition, the manager may be prohibited from holding a certain position or conducting a specific activity for up to 5 years.
If the salary was issued on December 30
The above means that for the purposes of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a salary that is paid (transferred) on December 30, 2022 has the same status as an advance paid on the 20th of the month. According to the rules of Art. 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the date of payment, income is not yet considered actually received. This means that strictly according to the Tax Code, personal income tax is not required to be calculated and withheld from this payment.
The employer will calculate personal income tax on payments as of December 31 and withhold tax from the advance payment for January or other amounts paid before that in January (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated May 5, 2017 No. 03-04-06/28037).
In practice, not all employers can issue wages without withholding personal income tax. They deduct tax even if the payment is not made on the last day of the month. In this case, the company must transfer the tax to the budget no later than the next working day (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
As for 6-personal income tax, regardless of the date of payment and withholding of personal income tax, the corresponding operation is fully reflected in the annual calculation (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 08/09/2021 No. SD-19-11 / [email protected] ).
Calendar cheat sheets
If the salary was issued on December 29 and earlier
In some companies, by decision of management, salaries for December are issued ahead of schedule - on December 29 or even earlier. From a tax point of view, such a payment is no different from the one that will be made on December 30 due to the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In the same way, personal income tax does not have to be calculated or withheld when issuing money. However, if this is done, then the tax must go to the budget no later than the next working day, i.e. back in December.
The operation will be included in the annual calculation of 6-NDFL, regardless of the date of withholding and transfer of tax.
But there is one “labor” nuance here. Remember that salaries must be paid out at least every half month, that is, once every 14–15 days, depending on the length of the month (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
This means that if the salary for December is paid ahead of schedule, for example on December 29, then in January it is necessary to pay not only the “standard” advance on the 20th or 25th, but also the “interim” advance - no later than the 13th. Otherwise, the organization and the manager may be brought to administrative responsibility for violating the frequency of payment of wages (Part 6, Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). Companies that have a standard payday of January 10 will have to do the same if they issue salaries in December, including on the 30th.
Example . At Zvezda LLC, the accountant paid all employees salaries for December on December 29. To comply with the rules for issuing salaries, the accountant issues an advance for January 10-12 on the 13th, an advance for January 13-24 on the 25th, and balances for January 25-31 on February 10.