Photo: pixabay.com Updated: 03/27/2020
Are maternity benefits subject to taxation? No, payments related to maternity are exempt from all taxes. If the employer decides to pay the employee extra, then he will have to pay taxes, but not always. If the amount does not exceed 50,000 rubles, then the amount of the additional payment is not taxed.
- Who is paid for maternity leave?
- How long does maternity leave last?
- How to calculate the benefit amount?
- Who is granted parental leave for up to 1.5 years?
- What are personal income tax and insurance premiums, are they withheld from benefits related to maternity?
- How are personal income tax and insurance premiums withheld when maternity benefits are paid up to average earnings?
- How are maternity benefits reflected in 2-NDFL?
- Pilot project for direct payments from the Social Insurance Fund
Who is paid for maternity leave?
After issuing sick leave in connection with maternity, a woman can apply for maternity benefits. The hospital form is filled out by an obstetrician-gynecologist at the 30th week of pregnancy (clause 46 of Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 624n).
Recipient categories include:
- Officially employed
- Unemployed, if 12 months have not passed since the date of dismissal due to liquidation of the company
- Full-time students
- Military personnel under contract, and civilians in the military, outside the Russian Federation
- Adoptive mothers
Payment of benefits is made: at the place of work, service or study. Dismissed persons apply to the social protection authorities (SZN).
Maternity leave and taxes
By law, any monetary income is taxed. Is the income of individuals (abbreviated as personal income tax) paid as maternity leave taxed? Employees and their employers are certainly interested in the question: will certain tax levies be made on maternity benefits?
Of course, no one wants this money to be deducted by the authorities. Women want to receive all payments without any deductions that reduce the total amount of vacation pay. In this regard, the question arises: “If tax levies cannot be circumvented, how can they be reduced?”
Such questions are best answered by a qualified lawyer, but in this case you can delve into some of the subtleties on your own, especially since the legislative norms quite clearly state what happens to vacation pay, whether they are taxed or not. In any case, the answer to the question of whether they are taxed is clear - withholding personal income tax from maternity leave is unacceptable. Maternity benefits are not taxed because it is against the law.
Despite the fact that it is illegal to collect personal income tax from maternity leave, there are cases when taxation of cash payments received on maternity leave still occurs. If, despite all this, the accountant at the enterprise withheld a certain amount as tax, it must subsequently be returned to the employee. To return the money, an employee or employee of the organization must write a written statement addressed to the head of the company or accountant, after which the woman will be returned the money due.
The issue of tax withholding from the benefits in question is directly linked to the issue of calculating these payments accrued to a pregnant woman taking maternity leave. According to the existing law, all benefits provided by the state itself are actually exempt from personal income tax.
The only exception is taxes aimed at subsidies for temporary inability to carry out labor activities. That is, the exception is when you are on forced sick leave with a sick child. Unlike other payments, maternity benefits are not subject to any taxes also because these benefits are fully provided by the state.
How long does maternity leave last?
After receiving a certificate of incapacity for work, the woman writes an application for maternity leave. Depending on how the pregnancy proceeds, the law (Article 10 of the Federal Law-255) provides for the duration of leave:
- 140 calendar days - for normal pregnancy (70 days before and 70 days after the baby is born)
- 156 days – if there is a difficult birth or pregnancy with complications (70 and 86 days)
- 194 days – for multiple pregnancies (84 and 110 days)
If pregnancy comes with complications, two certificates are issued for temporary disability. One for 140 days - by a doctor observing the pregnancy, the second for 16 days - upon discharge from the hospital with a newborn (clause 48 of Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 624n).
Tax deduction on maternity leave
Many women on disability leave caused by maternity are concerned about whether they have the right to a tax deduction during this period. As mentioned earlier, temporary disability benefits are not the basis for income taxation, and, therefore, there is no fact of paying tax, which can be returned by applying a tax deduction. Therefore, in order to exercise her right to a refund of paid taxes, a woman must wait until she returns to work, when taxes begin to be paid on her income again.
How to calculate the benefit amount?
Maternity benefit (M&B) is calculated based on the amount of wages for the pay period. The billing period is two full years preceding the vacation.
Amount of maternity payments in 2022
After calculating the average daily income, the resulting amount must be multiplied by the number of vacation days (140, 156 or 194 days).
The law establishes the maximum amount of benefit payments under the BiR, limited by the maximum insurance base.
The size of the minimum payment cannot be less than the minimum wage. With less than 6 months of experience, the B&R benefit cannot exceed the minimum wage (Clause 3, Article 11 of Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006).
The period for calculating benefits is up to 10 calendar days from the date of presentation of the certificate of incapacity for work. The employer transfers money per day at the nearest salary (Part 1, Article 15 of Federal Law-255). If the social security authorities are involved in the calculation, the transfer of funds occurs before the 26th of the next month, after the month of presentation of the certificate of incapacity for work (clause 18 of Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia No. 1012n).
Online maternity benefits calculator
Registration of maternity leave by an individual entrepreneur
As you know, many entrepreneurs use special taxation regimes in their activities, which replace certain types of taxes, and in some cases completely exempt them from paying them. Most entrepreneurs are exempt from the fiscal burden of personal income tax, and also have certain concessions on the payment of insurance contributions to state funds.
But this does not mean at all that an entrepreneur can avoid responsibility for transferring temporary disability benefits to his employees. Of course, in fact, the money is transferred from the corresponding fund, the entrepreneur receives from the fund, as it were, compensation for the amounts that he transfers to the employee who is on maternity leave.
At the same time, the controlling function of the calculation process, payment of benefits to the employee, as well as reimbursement of maternity benefits to the organization is performed by the Social Insurance Fund. In a situation where the entrepreneur herself is going to go on maternity leave, she needs to make sure that at least a year before she regularly paid insurance premiums for herself, otherwise there is a huge chance of being left without temporary disability benefits.
If the expectant mother works part-time in several organizations, she has the right to receive maternity benefits in each of these organizations. However, the total amount of payments still cannot exceed the maximum established level.
Who is granted parental leave for up to 1.5 years?
After the end of the BiR leave and the closure of the certificate of incapacity for work, a woman has the right to take out maternity leave for up to 1.5 years.
The monthly child care benefit is 40% of average monthly earnings, and not 100% as the B&R benefit.
Amount of maternity payments in 2022
The same categories of recipients as recipients of BiR benefits can receive child care benefits. In addition to the mother of the child, the father or other relatives can take parental leave.
Parental leave is provided upon application. The start date of parental leave is the day after the end of sick leave. In addition to the application, it is necessary to provide a certificate from the second parent’s place of work stating that he did not apply for leave or benefits.
The procedure for calculating and transferring funds is the same as for the B&R benefit.
Income tax on maternity leave in 2022
There have been no changes in the rules for calculating maternity benefits or in the issue of taxation of their personal income tax in 2022. This means that in 2022, maternity leave will still not be subject to income tax. However, traditional changes have been made to the amounts depending on the size of the minimum wage and the value of the employee’s income, within the limits of which this income is subject to contributions for disability and maternity insurance.
Based on these values, from 01/01/2022 for maternity leave:
- the minimum value in connection with the next increase in the minimum wage (up to 13,890 rubles) will be 63,932.40 rubles. in case of normal birth (within 140 days);
- the minimum amount for complicated childbirth (for 156 days) will be 71,238.96 rubles;
- the minimum amount for a multiple pregnancy (for 194 days) will be 88,592.04 rubles.
How to calculate the maximum amount of maternity benefits, see the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
What are personal income tax and insurance premiums, are they withheld from benefits related to maternity?
Personal income tax (tax for individuals) or otherwise income tax is a mandatory fiscal fee in the amount of 13% of a citizen’s income, withheld monthly by the Employer in favor of the Federal budget (Article 208 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The employer pays monthly insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance (Article 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The object of taxation is income from labor activity.
All benefits received related to maternity are not subject to taxation. Articles 217, 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation list benefits that are not subject to insurance contributions, these benefits include:
- Maternity benefit (maternity benefit)
- Child care allowance
These payments are calculated from the Social Insurance Fund. Financing from an extra-budgetary fund is provided from the first day of temporary disability of the expectant mother.
Taxes paid on disability benefits
According to existing legislation, benefits for temporary disability caused by maternity are not subject to personal income tax. This is due to the fact that although assistance from the state is income, it is still formed from insurance contributions already paid to the budget.
At the same time, ordinary payments for disability due to illness, both for the individual himself and his child, are taxed. But here, too, we should not forget that once a year this paid tax can be returned as treatment expenses (within the specific amount established by the state).
How are personal income tax and insurance premiums withheld when maternity benefits are paid up to average earnings?
In a standard situation, maternity benefits are calculated taking into account the maximum insurance base.
Example: With a salary of 100,000 rubles, income for 2 years will be 2,400,000 rubles, and the average daily income will be 3,283.17 rubles. To calculate the benefit, the maximum base for the 2 previous years is taken - 966,000 rubles for 2022, and 912,000 rubles for 2022, total 1,878,000 rubles. We find that the average daily earnings cannot be higher than 2,569.08 rubles. Taking into account the size of the insurance base, for 140 days of maternity leave, the maximum benefit amount will be 359,671.20 rubles. The employer may provide for additional payment of maternity benefits up to the actual average earnings. In this case, the additional payment of the difference is calculated at the expense of the organization, and not the Social Insurance Fund.
The Ministry of Finance believes that such additional payments cannot be classified as state benefits. They are not subject to Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and are subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions in the general manner (Letter dated February 12, 2009 No. 03-03-06/1/60).
This rule can be circumvented if you issue an additional payment as financial assistance. The payment is excluded from the tax base if the amount does not exceed 50,000 rubles. In the case where the amount of the surcharge is greater, tax must be paid on the difference (clause 8, part 1, article 217, clause 3, part 1, article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Are maternity payments income?
Payment of maternity benefits relates to the income of an individual based on the general meaning of Articles 208 and 209 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. From an accounting point of view, such a payment is a type of sick leave.
When calculating maternity benefits, average daily earnings are used. Due to this, the amount of payment depends on the duration of sick leave. So, if it is less than 140 days at the initiative of the employee, then she will receive less maternity leave for sick leave (but more salary at the current rate).
How is daily earnings determined:
- Add up all the employee’s income for the last 2 calendar years. This includes payments from which insurance premiums were paid for temporary disability and in connection with maternity.
- Calculate the sum of calendar days for 2 years. The number of exception days must be subtracted from it.
- Divide the indicator from the first point by the indicator from the second.
Which days are deducted:
- regular sick leave, sick leave for BIR, child care leave;
- days of release from work while maintaining earnings without paying contributions to extra-budgetary funds.
Let's look at an example:
Svetlana Shcherbakova works in and goes on sick leave from February 1 for 140 days. In 2022, her salary was 20,000 rubles. In 2019, indexation was carried out and from January 1, the salary was 25,000 rubles. In 2020, she received a promotion and her salary increased to 35,000 in January. Over the past 2 years, Shcherbakova took sick leave 5 times - 7, 4, 10, 3 and 9 days.
Calculation:
- Total income: 20,000 × 12 + 25,000 × 12 = 540,000.
- Period: 365 × 2 – (7 + 4 + 10 + 3 + 9) = 697.
- Daily earnings: 540,000 / 697 = 775.
- Amount of payment for sick leave: 775 × 140 = 108,500 rubles.
Important! When calculating benefits under the BIR, take into account the minimum and maximum amount of payment, as well as the calculation based on the minimum wage for employees who have not had any income over the last 2 years.
Pilot project for direct payments from the Social Insurance Fund
Since 2012, a pilot project for direct payments from the Social Insurance Fund has been launched in two constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Since 2022, the number of participants has increased to 50. By July 2022, it is planned to transfer all regions of the Russian Federation to the new system.
The essence of the project is that the employer acts as an intermediary between the employee applying for maternity leave and the fund. The project helps a woman draw up an application for benefits using a special form and creates a package of documentation.
Then the employer contacts the Social Insurance Fund on behalf of the employee. The fund assigns benefits and independently transfers funds to the woman’s bank account. At the same time, the transactions are not reflected in the employer’s records, and the question of withholding personal income tax and insurance contributions does not arise.
Is personal income tax withheld from sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth?
Maternity leave on sick leave is, of course, the employee’s income, which is officially accrued and reflected in accounting. However, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has Article 217, which lists income to an individual that will not be subject to personal income tax.
Already in paragraph 1 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, all types of state aids were exempted, with some exceptions. Since maternity leave is also a benefit, personal income tax is not withheld from sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth.
Attention! All benefits related to maternity are exempt from income taxation - BIR, care, lump sum payment at birth, etc.
For workers
Personal income tax is not collected from officially employed women on maternity leave. So when choosing: to go on sick leave or continue to work, take into account this beneficial side of the maternity leave, because you give 13% of your salary to the state.
For the unemployed
Women who have not entered into a formal contract with an employer do not receive sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth and are not subject to personal income tax. The opportunity to qualify for payment to the unemployed is to have work experience for the last 2 years (then the Social Insurance Fund will pay you directly).
If the work experience is not for the full 2 years (for example, they worked for several months), then 0 income is recognized for the “empty” months. Most likely, based on the results of the calculation, the daily earnings will be less than the minimum wage, and the woman will be paid the minimum allowance.
In maternity leave
If a woman, already on maternity leave, is pregnant again, then she is again granted sick leave according to the BIR, standard payments, and they are also not subject to income tax.
Simplified
If a company does not work under OSNO, but under a special regime, for example, under the simplified tax system, this does not affect the need for sick leave payments for a pregnant employee. The benefit is not related to the regime under which the employer works, but to the insurance premiums paid for the employee in case of sick leave.
For reference! Under the simplified tax system, the employer is exempt from personal income tax: he pays a single tax on his income. But the special regime does not relieve him of the obligation to pay employees salaries, calculate and collect personal income tax and pay insurance contributions to funds.
And when an insured event occurs - temporary disability and maternity, the “simplified worker”, like other employers, pays sick leave benefits to the maternity leaver and compensates them through the Social Insurance Fund.
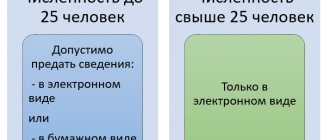
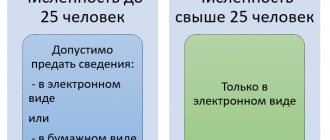
When working part-time
If a woman is employed in several companies or has had a part-time job over the last 2 years, then sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth is also not subject to personal income tax. A woman has the right to receive benefits:
- at each employer;
- at the place of last work.
Here is a diagram that will help you navigate the situation with a part-time maternity leaver:
Legislation
In fact, maternity benefits, like pregnancy benefits, are a special case of insurance. Payment is made one-time, together with receipt of the last salary before going on vacation. The employer pays the amount. However, in those regions of Russia where the FSS pilot project operates, payment is made by the social fund. The same thing happens when paying benefits to a student or unemployed person.
Accrual and payment of BiR is carried out in accordance with several legal acts:
- clause 1 art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regulates the issue of taxation of maternity and care benefits;
- Federal Law No. 81 dated May 19, 1995 lists the categories of citizens entitled to such assistance;
- Federal Law No. 255 dated December 29, 2006 indicates that social insurance for mothers is mandatory;
- Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated April 30, 2013, regulates the forms and issuance of certificates, which allows you to correctly calculate the amount;
- The order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 23, 2009 approves the procedure and lists the terms of payment.
According to paragraphs. 165.1.1 of the Tax Code of Ukraine, the total monthly (annual) taxable income of a taxpayer does not include the amount of state and social material assistance, state assistance in the form of targeted payments and the provision of social and rehabilitation services in accordance with the law, housing and other subsidies or subsidies, compensation (including monetary compensation for disabled people, disabled children during the implementation of individual rehabilitation programs for disabled people, the amount of maternity benefits), remuneration and insurance payments that the taxpayer receives from the budgets and funds of compulsory state social insurance. This is confirmed by the State Fiscal Service in subcategory 103.04 of the ZIR system.