What are uncollectible accounts receivable
This is the amount that buyers (clients or other counterparties) have not returned and which cannot be recovered.
Conduct a reconciliation of mutual settlements with counterparties via the Internet Connect to the service
Bad debt should not be confused with doubtful debt. The definition of “doubtful” includes debt that is not repaid within the terms specified in the contract and is not secured by guarantees (clause 70 of the Accounting Regulations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n). Similar wording is given in the Tax Code.
It turns out that although the doubtful debt is overdue, there are still chances for collection. But it will most likely never be possible to collect a hopeless one.
Accounting records for writing off unrealistic (uncollectible) and doubtful debts
Write-off of unrealistic (uncollectible) and doubtful receivables (for income, sources of financing the budget deficit, granted loans, advances) relates to subarticle 173 “Extraordinary income from transactions with assets” of the KOSGU (clause 9.7.3 of the procedure, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance Russia dated November 29, 2017 No. 209n, hereinafter referred to as Procedure No. 209n).
More on the topic: Gratuitous work (services): how to take it into account in the value of an asset and reflect it in 1C:BGU 8
Unrealistic (unreliable) for collection, doubtful receivables for expenses (for advance payments made, for state and municipal guarantees for which equivalent claims do not arise on the part of the guarantor to the debtor) are written off to subarticle 273 “Extraordinary expenses for transactions with assets” of KOSGU ( clause 10.7.3 of Order No. 209n).
Transactions are reflected in accordance with paragraphs. 78, 80, 82, 84 instructions, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 6, 2010 No. 162n (for government institutions), paragraphs. 94, 98, 102, 106, 152 instructions, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n (for budgetary institutions), paragraphs. 97, 101, 105, 109, 180 instructions, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 23, 2010 No. 183n (for autonomous institutions).
Accounting entries are reflected in correspondence with accounts 040110173 “Extraordinary income from transactions with assets”, 040120273 “Extraordinary expenses on transactions with assets”. In 1 – 17 digits of accounts the same code is indicated as that of the settlement account corresponding to them.
Doubtful debts written off from the balance sheet are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 04 (clause 339 of Instruction No. 157n).
Example 1. A budgetary educational institution provides paid educational services. The accounts include doubtful accounts receivable for the education of children who graduated from school. The institution's commission decided to write off the debt from the balance sheet to the off-balance sheet to monitor the possibility of collection.
Debit KDB 2,401 10,173 Credit KDB 2,205 31,667 – doubtful debts are written off from the balance sheet;
Increase in off-balance sheet account 04 – debt accepted on off-balance sheet.
Example 2. A budgetary educational institution has accounts receivable for advance payment for materials. The counterparty is declared insolvent. The institution's commission decided to write off doubtful debts from the balance sheet to the off-balance sheet to monitor the possibility of collection.
Debit KRB 2,401 20,273 Credit KRB 2,206 34,664 – doubtful debts are written off from the balance sheet;
Increase in off-balance sheet account 04 – debt accepted on off-balance sheet.
What debts are considered bad
According to paragraph 2 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, bad debts include amounts for which:
- the statute of limitations has expired (in general, it is equal to three years; Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- the obligation is terminated due to the impossibility of its fulfillment, on the basis of an act of a government body or liquidation of the company;
- there is a decree from the bailiff to terminate enforcement proceedings in the following cases: there is no opportunity to obtain information about the debtor (about his whereabouts, his property, whether he has money); the debtor does not have property that can be recovered, and all measures taken to find it were unsuccessful;
- the debtor is an individual declared bankrupt, exempt from further fulfillment of the creditor's claim.
Check the counterparty for bankruptcy
What debt can be written off?
Not all of a company’s debts can be written off, but only those that meet the criteria for a debt that is unrealistic to collect. The concept of bad debt is given in paragraph 2 of Art. 266 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is a debt with an expired statute of limitations, as well as a debt of a liquidated company or a company that is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities as inactive. In addition, the bailiff can establish the impossibility of receiving money and issue a ruling to end enforcement proceedings.
| Note! “Closing” an individual entrepreneur does not make his debt hopeless. |
If an individual entrepreneur owes you money, you cannot carry out the procedure of writing off receivables only because of his exclusion from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs, since the individual entrepreneur is liable for debts with all his property (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 16, 2015 No. 03-03-06/53157). Write-off of a businessman's bad receivables is possible only after the completion of the bankruptcy procedure, in the event of the death of the individual entrepreneur or a judicial authority makes a decision on the impossibility of collecting money due to the fact that it was not possible to establish the whereabouts of the businessman. That is, before writing off receivables, you should make sure that the above conditions have been met.
If two companies owe each other, first of all, it is necessary to offset the debts, reducing the amount of receivables by the amount of debt to the counterparty. If the partner company still owes you, this money is considered uncollectible, and you can write off the overdue receivables.
So, you found out that the debtor company went bankrupt (or it was excluded from the register of legal entities later than September 1, 2014). In this case, you understand that you will not be able to repay the debt. How to write off receivables that are past the statute of limitations?
As a general rule, it is 3 years, but it can be interrupted or suspended.
The limitation period is interrupted if (clause 20 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2015 No. 43):
- the debtor accepted and signed the reconciliation report;
- sent a letter - an acknowledgment of the debt or a request for a deferment;
- paid interest or penalty;
- The firms drew up an additional agreement to the contract, under which the debtor acknowledged its obligation.
The company must begin counting the interrupted statute of limitations anew. However, it cannot exceed 10 years from the date of formation of the debt (clause 1 of Article 181 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The limitation period is suspended on the grounds provided for in Art. 202 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in particular, for the period when the parties carry out the procedure for resolving a dispute out of court provided for by law (mediation procedure, mediation, administrative procedure, etc.). Also, the statute of limitations does not run while judicial protection of the violated right is carried out (Article 204 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). When the relevant circumstances end, the statute of limitations continues to run (and is not counted again).
| For more information on how to write off receivables with an expired statute of limitations, read the article “How to write off bad receivables with an expired statute of limitations . |
How to write off accounts receivable
In tax accounting (TA), there are two ways: to write off a bad debtor immediately as a loss, or to create a reserve and use it to pay off debts.
There is no choice in accounting (AC): the organization must create a reserve for doubtful debts. And then use it to pay off debts that are unrealistic to collect.
IMPORTANT
There are situations when at first glance the debt seems hopeless, but it cannot be written off to the NU. For example, when a debtor company is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities at the initiative of the tax authorities due to unfiled reporting and lack of transactions on bank accounts. The Ministry of Finance believes that under such circumstances there are no grounds for writing off receivables. You have to wait until the three year statute of limitations expires. And only after that write off the debt (for more information about this and other situations, see “Seven cases when receivables cannot be considered hopeless”).
Receive a fresh extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs with the signature of the Federal Tax Service Send an application
Documents for writing off accounts receivable
In order to pay off a hopeless “receivable” in accounting, you must first conduct an inventory of it. Most often this is done at the end of the year, before drawing up the balance sheet. But it is possible at any other time (clause 2.1 of the Methodological Recommendations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated June 13, 1995 No. 49). For example, based on the results of a quarter, half a year or 9 months.
Documents required:
- Order to conduct an inventory (unified form No. INV-22).
- An act that records the status of settlements with buyers and other debtors (unified form No. INV-17).
- Information about debtors: name, amount of debt, date of its occurrence, etc. (attachment to form No. INV-17).
These forms were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49 and Resolution of the State Statistics Committee dated 08.18.98 No. 88.
REFERENCE
It is not necessary to use standardized forms.
The organization has the right to develop its own forms and reflect the inventory results in them. Based on the inventory results, the accountant will write off the required amount. To do this, you will need to issue an order from the director and an accounting statement, which shows all the calculations in detail. You will also need papers for the transaction with the debtor: contracts, invoices, bills, etc. If the statute of limitations has been interrupted, supporting documents are needed, in particular, reconciliation acts and letters.
Exchange legally significant “primary data” with counterparties via the Internet. Free inbox.
Write-off of bad receivables in tax accounting
If the LLC creates a reserve for doubtful debts
Let’s make a reservation right away: we are talking about those who pay income tax and use the accrual method. Under the cash method, the creation of a reserve is not provided for (subclause 7, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A number of actions must be taken.
First, determine which debt identified during the inventory is doubtful. These are amounts that arose in connection with the sale of goods (work, services), if they are not repaid within the terms established by the contract and are not secured by a pledge, guarantee, or bank guarantee (clause 1 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). An advance paid to the seller does not fit this definition, even if the delivery never took place. Fines for failure to meet payment deadlines are also not suitable. Prepayment and sanctions are not included in the reserve.
Secondly, doubtful debts should be divided into three groups (clause 4 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; see table).
Table
Dividing overdue debts into groups depending on the period of their occurrence
| Group | Debt period | What part of the debt can be included in the reserve? |
| First | over 90 calendar days | 100% |
| Second | from 45 to 90 calendar days inclusive | 50% |
| Third | up to 45 calendar days | 0% |
Thirdly, create a reserve. You need to take into account the entire amount of “receivables,” including VAT (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated June 11, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/21726; see “When forming a reserve for doubtful debts, the seller has the right to take into account the entire amount of the buyer’s doubtful debts, including VAT”) .
Keep records, prepare and submit income tax and VAT reports
Fourthly, check that the amount of the reserve does not exceed 10% of sales revenue. To make the calculation, you should take the revenue for the tax period, based on the results of which the reserve is created. If an accountant forms it based on the results of the reporting period, the following rule applies. The reserve must be within a limit equal to the greater of 10% of revenue for the previous tax period or 10% of revenue for the current reporting period.
Fifthly, assign the amount of the reserve to non-operating expenses.
Example 1
Luchik LLC creates a reserve for doubtful debts in tax accounting. As of June 30, 2022, an inventory was carried out, which revealed overdue accounts receivable in the amount of 600 thousand rubles.
The period for its occurrence lies in the range from 45 to 90 calendar days. This means that it belongs to the second group, and 50% can be included in the reserve. The accountant considered that it is permissible to include 300 thousand rubles as a reserve (600,000 rubles × 50%).
Sales revenue according to NU data for the first half of 2022 amounted to 2 million 800 thousand rubles. Therefore, the reserve cannot exceed 280 thousand rubles (2,800,000 rubles × 10%).
At the end of the first half of 2022, the accountant wrote off 280,000 rubles. for non-operating expenses.
Next you need to do the following. As soon as the debt turns from doubtful to bad, it must be paid off from the reserve. In this case, the amount of the reserve will decrease, and new expenses will not appear.
Example 2
As of June 30, 2022, the reserve for doubtful debts of Luchik LLC amounted to RUB 280 thousand.
In July 2022, part of the debt in the amount of 50 thousand rubles. became uncollectible because the debtor organization was liquidated. As a result, the amount of the reserve amounted to 230 thousand rubles (280,000 - 50,000). No expenses in connection with this arose in tax accounting.
An adjustment should be made on the last day of each reporting (tax) period. You need to compare two quantities. The first is the newly created reserve. The second is the unused part of the reserve formed based on the results of the previous period. If the first value is less than the second, the difference is included in non-operating income of the current period. If the first value is greater than the second, the difference is included in expenses (clause 5 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, the deduction limit of 10% must still be observed.
Example 3
As of September 30, 2022, the receivables of LLC Luchik amounted to 550 thousand rubles. (600 thousand rubles were identified as of June 30, of which 50 thousand rubles were written off in July).
By the end of the third quarter, this debt moved to the first group with a maturity period of more than 90 calendar days. This means that “Luchik” can include it in the reserve in the amount of 100%.
Sales revenue according to NU for 9 months of 2022 amounted to 5 million rubles. Therefore, the reserve cannot exceed 500 thousand rubles (5,000,000 rubles × 10%).
The accountant compared 500 thousand rubles. with the unused reserve created based on the results of the previous period (RUB 230 thousand). The first digit is greater than the second. This means that in NU “Luchika” it is necessary to show expenses of 270 thousand rubles (500,000 - 230,000).
If the LLC does not create a reserve for doubtful debts
This accounting option is very simple. If during the inventory it is revealed that a particular amount of “receivable” has become uncollectible, the organization writes it off as non-operating expenses.
Let us add that this rule does not apply to the simplified tax system. “Simplified” companies do not have the right to include doubtful receivables in expenses (see ““Simplified” cannot include the amount of doubtful receivables as expenses”).
On what basis is it legal to write off receivables?
When can accounts receivable be written off? It is legitimate to talk about three main scenarios for its write-off:
- Write-off upon repayment of debt by the debtor. Such a write-off does not imply that the creditor has any additional rights or obligations in terms of taxation - if we are talking about the principal amount of the debt. Exceptions will be observed:
- when receiving income from interest - in this case, tax on it will have to be calculated and paid;
- when the debtor is an individual not registered as an individual entrepreneur, and the interest rate on the loan is less than the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation: in this case, the creditor as a tax agent will need to calculate and pay tax on the debtor’s material output.
- Write-off upon forgiveness of the debt to the debtor. Similarly, the creditor does not have any tax rights or obligations here, with the exception of the need to calculate and pay tax on material benefits on a forgiven debt to an individual who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur. Debt forgiveness is regarded as a gratuitous transfer of property and therefore cannot be included in expenses (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 4, 2012 No. 03-03-06/2/34, clause 4 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated July 15, 2010 No. 2833/10 provides for the possibility of writing off a debt as an expense if the creditor company has a commercial interest in forgiving the debt. But in legal disputes with the Federal Tax Service, it is not always possible to defend such an expense (resolution of the Fifteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated November 14, 2013 No. 15AP-13132/13).
- Write-off upon recognition of a debt as bad. Here the situation from the point of view of tax consequences is more interesting: the written-off bad debt can be taken into account in non-operating expenses when forming the tax base for the special income tax (subclause 2, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Under the simplified tax system, such a preference is not provided (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 13, 2007 No. 03-11-04/2/274).
A debt can be recognized as bad if (clause 2 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the statute of limitations for judicial debt collection has expired;
- the debt is canceled due to the impossibility of repaying it;
- the debt is canceled by a decision of the authority;
- the debtor organization was liquidated;
- bailiffs were unable to collect the debt from the debtor’s property.
Let's consider the grounds for writing off accounts receivable in accounting due to the recognition of the debt as bad - with the prospect of including it in expenses, in more detail.
Accounting for accounts receivable
According to paragraph 70 of the Accounting Regulations, accounting cannot do without a reserve for doubtful debts. However, the order of its creation has not been established. Therefore, each company must independently develop this procedure and approve it in its accounting policies (see “Accounting policies of an organization: samples for 2022, how to draw them up, examples”). In practice, most often they choose the same method as in tax accounting.
ATTENTION
There is a difference between accounting and tax accounting standards.
In the accounting system, any overdue “debts” must be included in the reserve for doubtful debts. And in NU - only those related to the sale of goods, works, and services. Prepare, check and submit financial statements to the Federal Tax Service via the Internet Submit for free
Accounting and tax accounting
When working with irrevocable overdue payments, it is important to take into account the opinion of officials about write-offs and reserves. If the company has a reserve for doubtful debts, the amount of bad debt is written off against this reserve. If the non-refundable delay is greater than the reserve, then the difference is taken into account as part of other expenses for taxation.
We described in the article “Reserves for doubtful debts in accounting” how a debt is recognized as doubtful and what are the rules for forming a reserve fund.
After the amount of the irrecoverable overdue amount is written off from the balance sheet accounts, it must be reflected on the balance sheet. For this purpose, account 007 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss” is used. It is mandatory to keep off-balance sheet accounting of written-off amounts in case the creditor restores its solvency and is able to pay. In this case, the income tax will have to be reinstated.
Let's consider the procedure for recording the main situations of writing off bad debts.
Postings for writing off accounts receivable
The creation of the reserve is reflected in the credit of account 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts” and the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”.
Writing off the debt from the reserve is a posting to the debit of account 63 and the credit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” (or the credit of account 76 or 60).
Example 4
As of June 30, 2022, the balance sheet of Luchik LLC included doubtful debts for settlements with customers in the amount of 280 thousand rubles. The accountant created a reserve and made the following posting:
DEBIT 91 CREDIT 63
— 280,000 rub. — overdue debts are included in the reserve;
In July 2022, part of the debt in the amount of 50 thousand rubles. became hopeless. Wiring appeared:
DEBIT 63 CREDIT 62
— 50,000 rub. — bad debt is written off against the reserve.
Write-off of buyer's debt
Under the conditions of Example 1, the amount of accrued reserves in accounting and tax accounting differs.
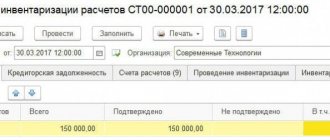
In accounting, there is a bad debt in the amount of RUB 150,000.00. We will write it off completely from the reserve. In tax accounting, only 100,000.00 rubles will be written off from the reserve, and the remaining debt in the amount of 50,000.00 rubles, not covered by the reserve, will be included in non-operating expenses.
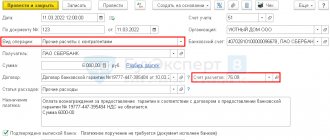
To write off bad debt using reserves, you can use the standard document of the Debt Adjustment program (Fig. 3). This document is available both from the Sales and Purchases sections.
The header of the Debt Adjustment document must be filled out by selecting the following values from the proposed lists:
table 2
| Field | Data |
| "Type of operation" | Debt write-off |
| "Write off" | Buyer's debt |
| "Buyer (debtor)" | Name of the debtor organization for which the amount of receivables recognized as bad is listed (selected from the “Counterparties” directory) |
The document is filled out automatically by clicking the Fill -> Fill in balances for mutual settlements based on accounting data. The tabular part on the Buyer's debt (accounts receivable) tab is filled in with the balances of mutual settlements as of the adjustment date as follows:
Table 3
| Field | Data |
| "Settlement amount" | Total amount of debt (RUB 150,000.00) |
| "Sum" | The amount of debt write-off in accounting. By default, this amount corresponds to the total amount owed |
| "Amount NU" | The amount of debt write-off in tax accounting. By default, this amount also corresponds to the total amount owed. Since this document will write off the debt from the reserve, it is necessary to manually correct the amount in the “Amount NU” field (RUB 100,000.00) |
| "Account" | Account on which the debt arose (62.01) |
On the Write-off account tab, you need to indicate the account where the doubtful receivables will be allocated (63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”), as well as the details of the agreement with the counterparty and the settlement document on which the doubtful receivables were generated (see Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Write-off of bad receivables using reserves
After posting the document, an accounting entry will be generated:
Debit 63 Credit 62.01 - for the amount of debt written off from the reserve created in accounting (RUB 150,000.00).
For tax accounting purposes for income tax, amounts are entered into special resources of the accounting register:
Amount NU Dt 63 and Amount NU Kt 62.01 - for the amount of debt written off at the expense of the reserve created in tax accounting (RUB 100,000.00). Amount PR Dt 63 and Amount PR Kt 62.01 - for a constant difference, the value of which is RUB 50,000.00.
For profit tax purposes, the remaining portion of the bad debt is written off as non-operating expenses using the Transaction document (section Transactions -> Accounting -> Transactions entered manually). In the document form, to create a new transaction, click the Add button and enter the amounts in the special resources of the accounting register (the Amount field must remain empty):
Amount NU Dt 91.02 and Amount NU Kt 62.01 - for the amount of written off debt not covered by the reserve (RUB 50,000.00). Amount PR Dt 91.02 and Amount PR Kt 62.01 - for a negative constant difference (-50,000.00 rub.). When performing the routine operation Calculation of income tax for March, which is included in the Closing of the month processing, this permanent difference leads to the recognition of a permanent tax asset in the amount of RUB 10,000.00.
Please note that in order to correctly fill out the income tax return, it is important to correctly select the item of other income and expenses - Write-off of accounts receivable (payable). Then, when automatically filling out the income tax return for the first quarter of 2022, losses from writing off bad debts in the amount of RUB 50,000.00. will be reflected on line 302 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02, as well as in the total amount on line 300 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02.
To make sure that bad debts are written off in accounting and tax accounting, you can generate a balance sheet for account 62 for March 2022, having previously made the appropriate settings on the Indicators tab. The balance sheet generated under account 63 for March 2022 will show the absence of reserves for doubtful debts.
To account for written-off debt in order to monitor the possibility of its collection (in accordance with paragraph 2 of clause 77 of the Regulations), we will also use the Operation document.
In the document form, to create a new transaction, you need to click the Add button and enter an entry in the amount of RUB 150,000.00. on the debit of off-balance sheet account 007 indicating the corresponding analytics (sub-account Counterparties and Agreements).