Among the variety of taxes and fees intended for mandatory calculation by business entities, VAT occupies a special place. The specificity of this tax lies in the complexity of its correct calculation, and in the ambiguity of the interpretation of the provisions of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code, which is subject to regular changes.
Over the 25 years that have passed since the introduction of the Law on Value Added Tax, many legal provisions relating to VAT have been subject to serious revision.
But over the past 10 years, the current tax rates listed in Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation have remained stable.
On a note! You can calculate the tax amount using a special VAT calculator.
When and who is required to pay VAT?
The definitions given by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation fix the indispensable participation in the formation of the budget at the expense of VAT in specific situations:
- provision of services, sale/transfer of goods or the right to use assets under any form of agreement;
- performing construction, installation or equivalent work;
- the above-mentioned works, services or transfer of valuables for personal use;
- importation of goods or products from abroad.
Subjects for mandatory payment of VAT are:
- organizations or individual entrepreneurs engaged in commerce or production using OSNO;
- non-profit companies – in case of realization of rights to property;
- banking and insurance structures;
- separate divisions and branches of organizations that sell services or products;
- customs intermediaries.
Why is VAT needed?
The very name of the tax implies that a share of the added value arising at all stages of the sale of one’s own products, goods purchased for resale, or services provided is withdrawn from the budget. This is how the main function of the VAT is implemented - fiscal .
If you trace the chain from the manufacturer of a product to its final buyer, it turns out that the process of shifting the tax will end only at the moment the product is purchased by the consumer who is the last in this scheme. The regulatory function of VAT is manifested in the formation of the consumer market, since the real payer of the tax is not an LLC or individual entrepreneur, but a living buyer.
VAT, as a regulator of the consumption market, cannot be too high, since in this case, due to extremely high prices, the demand for goods and services will fall. This factor will invariably lead to a weakening of the economic position of both individual business entities and industries as a whole.
The buyer paid off the tax debt in 2022 (before shipment)
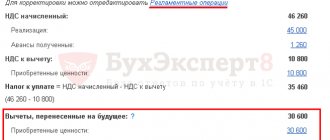
In such a situation, the amount transferred by the buyer to pay off the tax debt should be considered as additional VAT paid at a rate of 20%. Therefore, the total increase in VAT reflected in the final line of the adjustment invoice should be indicated in column 5 of line 070 of section 3 of the VAT return.
Filling out individual fields of the adjustment invoice (the buyer in 2022 repaid the debt that arose due to an increase in the VAT rate)
| Column 1a “Indicators in connection with changes in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services provided), transferred property rights” | column 7 “Tax rate” | column 8 “Tax amount” | Column 9 “Cost of goods (work, services), property rights with tax - total” |
| A (before change) | 18/118 | 18 | 22000 |
| B (after change) | 20/120 | 20 | 22375 |
| B (increase) | X | 2 | 375 |
| Total increase (sum of rows B) | X | 2 | 375 |
VAT rates
Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determined the use of several percentage tax rates - 0%, 18% and 10% . The law clearly spelled out cases of possible application of one or another tax rate. In addition, tax legislation stipulates the circumstances when the amount of VAT is calculated by calculation.
When is VAT 0%?
Taxation at a zero rate is provided for LLCs or individual entrepreneurs engaged in clearly defined types of activities:
- transfer of energy resources outside Russia;
- international transportation of goods and passengers with luggage;
- transportation of gas and oil;
- transportation of passengers and cargo in railway cars that are on the balance sheet of the organization;
- services provided by water transport;
- work related to space activities;
- air transportation of people and luggage to Crimea and Sevastopol from March to December;
- movement of goods across the Russian border.
Important: To legally use the zero VAT rate, a transport expedition agreement must be drawn up instead of a standard agreement on the transportation of goods.
to confirm their right within six months . These include:
- photocopies of contracts with foreign partners;
- goods or shipping waybills;
- register of customs declarations or individual declarations.
The six-month period for collecting supporting documents begins from the moment the cargo crosses the border and the corresponding mark is placed on the accompanying papers.
If the taxpayer does not provide the established package of documents to the tax authority, then revenue from the provision of international transport services will be taxed at the standard rate of 18%.
Features of the application of the VAT rate from 2022 by foreign organizations
Foreign companies that provide services electronically calculate and pay tax if the obligation to pay VAT on transactions related to sales is assigned to the tax agent - a foreign intermediary company that carries out business activities with buyers under agency and commission agreements , agency agreements, as well as other agreements with foreign companies. Thus, in the case of electronic services provided by foreign companies, from 2022 the responsibility for calculating and paying VAT to the budget rests with the foreign company. And this will not depend on who the buyer of these services is - an individual or a legal entity.
Options for using a reduced rate of 10%
A 10% VAT tax rate is used in cases where strictly defined product categories of a social nature and only one type of service are subject to sale - air transportation within the country.
The Tax Code allows the use of a reduced VAT tax rate for sales transactions with the following products:
- food group of goods, excluding delicatessen products;
- subcategory of children's goods, except sports shoes;
- stationery for school purposes;
- periodicals, textbooks and scientific literature;
- goods related to medicine.
It is the question of eligibility for inclusion in a preferential group with a reduced VAT rate that raises the greatest number of questions among taxpayers and fiscal authorities.
How to check the legality of the 10% VAT rate
If a product is purchased for resale, then questions about the possibility of applying a reduced VAT rate, as a rule, do not arise. All products are supplied according to accompanying documents, including invoices, which indicate the applicable tax rate.
The situation is more complicated when an LLC or individual entrepreneur independently produces commercial products, which, according to formal criteria, are subject to preferential VAT taxation. In such situations, it is advisable to adhere to regulatory documentation - lists of product codes established by the relevant Government Decrees in the latest edition.
These registers indicate codes and names of product groups from the preferential tax list. The OKP code is selected in the All-Russian Classifier and is confirmed by a certificate or declaration of conformity.
You should know: If the manufacturer cannot find the product being sold in the list of codes, then it would be more reasonable to indicate the general VAT rate - 18%. Otherwise, there is a risk of additional tax assessment during an audit by the fiscal authorities.
When the tax office may refuse to apply a preferential VAT rate
When selling packages that contain groups of goods with different VAT rates, the use of a reduced percentage may lead to justified claims from the tax authority.
Example 1
To increase sales, trading organizations often use a sales scheme for self-assembled kits, where goods are subject to VAT at different rates. For example, on the eve of the New Year holidays, a huge number of children's gifts appear on sale, containing sweets and toys. Confectionery products (sweets) are subject to VAT at the rate of 18%, and children's toys belong to a preferential group of goods.
The Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service considers the use of a 10% VAT rate on a New Year's gift set when setting the price to be an illegal action, since the list of codes of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 597 dated June 18, 2012 does not contain such a position.
A similar situation may arise, for example, when selling specialized magazines with the provision of an additional service - access to a web resource or electronic media. In this case, the 10% rate applied to printed products can only be applied directly to the magazine. The service of virtual news publication should be taxed at the standard rate of 18%.
Keep in mind ! To avoid tax claims when selling sets with different VAT percentages, it is advisable to indicate in the documents and on the price tag the individual product items included in the set.
Example 2
Sales of bakery products are carried out using a reduced VAT rate of 10%. When updating the product range, you should be careful about the names of new products. For example, the term “pizza” is not in the list of OKP , therefore, despite actual compliance with the letter of the law, for formal reasons the manufacturer must apply a rate of 18% when selling pizza.
Conclusion: It is advisable to choose a name for a new product for which it is planned to apply a preferential VAT rate, being as close as possible to the terms used in regulatory documents - lists of OKP approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Simple names will not give tax authorities grounds to refuse to use the reduced tax rate.
List of goods subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent
Basically, 10% VAT applies to food products included in the consumer basket. Let's take a closer look at which goods are subject to 10 percent VAT in accordance with tax legislation:
- Livestock and poultry supplied live for sale with subsequent slaughter and processing or for other needs;
- Meat products and meat with the exception of deli products, including various smoked meats, veal, cuts, deli-type preserves;
- Dairy products and pasteurized, sterilized milk - this category includes yoghurts, ice cream, fruit ice, etc.;
- Eggs and products based on them;
- Sunflower and other types of vegetable oil;
- Margarine is edible and food fats for use in confectionery production, fats for the production of chocolate, baked mixtures;
- Salt and sugar;
- Cereals in purified or processed form, grain waste;
- Combined feed based on grains, mixtures for animal feed;
- Flour, cereals;
- Pasta;
- Live fish except for rare and delicacy types. Among them are sturgeon, Far Eastern and Baltic salmon, and a number of other fish;
- Seafood, herring, chilled and frozen fish, except for rare species and caviar products, crabs and a number of other delicious seafood;
- All types of vegetables;
- Locally produced fruits.
Please note that if a manufacturing company operates for export, with a final delivery point outside the Russian Federation, then a zero rate is applied to it, since VAT is an internal tax. However, the exporter must still provide zero reporting, as well as the necessary permits from customs and other authorities to the tax office at the company's registered address.
Another product group that falls under the ten percent rate is products designed for children. In particular, it includes:
- Children's beds made of wood and woodworking products;
- Knitwear, clothing, sheepskin, rabbit fur, underwear;
- Summer, winter, special footwear;
- Bed dress;
- Diapers and a range of hygiene products;
- Sewing products;
- School supplies - notebooks, pens, pencils, paints, pencil cases, abacus, rulers, etc.
How to correctly apply the estimated VAT rate
The use of the estimated VAT rate - 18%/118% or 10%/110% - is stipulated in Article 164, paragraph 4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is allowed in the following situations:
- when issuing an invoice for the received advance payment;
- when calculating VAT by a tax agent;
- when using an assignment agreement (assignment of monetary claims).
The calculation assumes that the amount of the advance received or the monetary claim accepted already includes the amount of tax, which should be calculated by simple arithmetic operations.
The most common option for isolating the VAT amount is to draw up an invoice for the advance received.
Prepayment in 2022, shipment in 2019
If you prepay for goods or services in 2022, at the current rate of 18%, and ship in 2022, a tax difference arises due to the tax increase in 2019.
For example, in December 2022, MORE LLC transferred 22,000 rubles (including VAT at a rate of 18%) as an advance payment for goods to the settlement account of GRIF LLC (including VAT at a rate of 18%), incl. VAT 3356.
In January 2022, the goods are shipped against the received advance payment in the amount of 22,375 rubles.
Thus, the buyer LLC "GRIF" incurred a debt to the supplier LLC "MORE" in the amount of 375 rubles.
In the above-mentioned letter, the Federal Tax Service recommends that the seller in this situation issue an adjustment invoice. Moreover, it is possible to issue one invoice for several primary invoices.