Chart of accounts in 1C
To get started, you need to find a chart of accounts in 1C 8.3. Accounting. To do this, the user goes to the main menu, settings/Chart of accounts section.
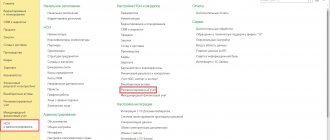
You need to double-click on the chart of accounts. In response, a standard window will open, which is adapted to the nuances of the work of a particular organization.
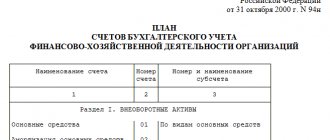
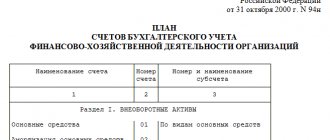
A table will open in a new window. It contains data such as account code, subaccount, name and type in sequential order. There are active, passive and active-passive types. You can add subaccounts from levels 2 and 3 using not only digital, but also letter designations.
For example, to account 10 “Materials” a subaccount 10-01 “Raw materials and materials” is opened, then a third level subaccount 10-01-I, reflecting imported production, or 10-01-K or 10-01-CH, reflecting red or black material color. It is important to remember that if there are subaccounts, only second-level subaccounts are involved in postings.
All versions of the 1C:Accounting system have a standard or basic chart of accounts. The company can additionally create its own version and adapt it to the individual terms of the organization’s functioning.
In the tab, the “Create”, “Posting Journal” buttons and the “Account Description” options are active and changes are applied. The user adds a new account to an already implemented chart of accounts using the “Create” button. It is possible to perform an identical action using the current account copy function.
In the new window, all fields are filled in, including the name and account code. When installing it, the program will ask you to select an account not in accordance with the code hierarchy. This feature in no way affects the feature of summing up the balance sheets. The user can check the separate “Balanced” checkbox to create an account of this type. The frame does not take into account the balance sheet of the enterprise itself. In the “Types of account accounting” tab, you can only click on the “Tax” section in the standard version. It allows you to take into account all available income taxes. The categories “Accounting by division” and “Quantitative” are activated only when entering accounts for which it is possible to perform accounting according to a given criterion.
Subcontos are placed on accounts depending on the degree of need in relation to certain accounts. Thus, suppliers and consumers can separately open subaccounts for consignments of goods and contracts.
It is possible to add an account to the chart of accounts if the user moves the cursor over any free space in this window. Next, you need to right-click. For ease of management, a special toolbar will open. Among the available options, the user selects the “Create”, “Copy” or “Edit” tab. Bad features are accessible by clicking on the “More” section located on the right side of the screen.
The “Journal of Postings” is a list of actions carried out by the program to create entries for all current accounts. With its help, you can quickly view the history of transactions with marked data on the document that served as the basis for the transaction, or corresponding amounts and invoices with a brief summary of the transaction
A new window opens with the option to search for a document by creation date, account or subaccount. The user can independently set a certain period of validity.
To do this, you can move the cursor over any free space and click on the “Account Description” button. After this, all existing data regarding the description will appear on the screen. Open account, subaccount (if any) and subaccounts linked to the file.
When opening a new account in the 1C: Accounting system, you must specify a description of the account. It must comply with the provisions of the law of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The “Print” button allows you to display a detailed plan with a description of the accounts on the screen, followed by transferring the data to paper. The user can draw up a Chart of Accounts as the main addition to the order.
Subaccounts and account characteristics
Many accounts have subaccounts subordinate to them. Thus, account 01 (Fixed assets) is subordinated to the following subaccounts: 01.01 (fixed assets in the organization), 01.03 (Leased property) and others. If an account has subaccounts, then it cannot be used in transactions in the program; only subaccounts subordinate to it can be used. If an account does not have subaccounts, then it is used in postings.
Accounts may have the following characteristics:
- View . The account can be active (A), passive (P) or active-passive (AP).
- Currency accounting (Val.) The attribute is set for accounts on which funds in foreign currency are recorded.
- Quantitative accounting (Qty.) The attribute is established for such accounts on which, in addition to total accounting, quantitative accounting is maintained. For example, account 10 (Materials), account 41 (Goods) and others. Standard accounting reports for these accounts display the amount and quantity.
- Accounting by divisions (Sub.) If this checkbox is checked, account postings are made by division.
- Sign of tax accounting for income tax (IT). Used when the organization applies PBU 18/02. If this attribute is set, account transactions are reflected not only in accounting, but also in tax accounting.
- Sign of off-balance sheet accounting (Zab.). Established for off-balance sheet accounts, such as “Leased fixed assets”, “Inventory and materials accepted for safekeeping” and others. Account 001, used for entering initial balances, is also off-balance sheet.
Synthetic/analytical accounting
Synthetic accounting is a set of measures for accounting for property and current liabilities. To perform standard calculations, a chart of accounts with two additional characters in the code is used, for example from 01 to 99.
Analytical accounting allows you to perform detailed accounting together with a breakdown of personal accounts (these documents affect the calculation of materials, employees and fixed assets). This option refers to the continuation of synthetic accounting, supplemented by natural and quantitative indicators. Analytics is carried out using sub-accounts linked to existing synthetic accounts. If the current account belongs to the grouping category and has ready-made subaccounts, then it is necessary to make an o.
Setting up automatic document account assignment
In order for transactions to be automatically generated when posting a document, you need to pre-set up accounts in the document itself. For example, when generating a document for the sale of goods in the item line, you can manually enter all the necessary accounting accounts in accordance with the company’s Accounting Policy.
Correctly filling out such settings greatly simplifies the posting of primary documents.
You can view and configure accounting accounts in the chart of accounts itself. To do this, on the main tab you need to go to the “Item Accounting Accounts” section and make the necessary adjustments in the window that opens.
Setting up a chart of accounts in 1C: Accounting
This process allows you to change accounts in such blocks as:
- inventory quantity accounting;
- accounting of goods in retail;
- accounting of settlements with workers.
Current accounting of DS (according to current accounts) is supplemented by an option for accounting in accordance with the articles of DDS. They include information in the context of payment cards or existing payment requests, monetary documents, and the like.
Current inventory accounting is carried out strictly according to nomenclature. When you hover the cursor over this cell, the user enters the inventory accounting editing mode, where he can safely choose analytical accounting by batch (receipt documents are taken into account here). After clicking the “Save and Close” button, you can save the changes made to the system.
To correctly display information about accounting accounts/items in current documents, you must check the boxes in the appropriate sections. Using this option, you will be able to implement instant detailing of information and immediately check the correctness of all established transactions for certain accounts. To maintain effective analytical accounting, the user checks the box “By warehouses/storage locations.” This action will help keep records in those organizations where there are not one, but several types of warehouses.
Basic chart of accounts settings
To study this function, on the main tab of the Chart of Accounts we find the section “Setting up the chart of accounts”.
In the window that opens, you can manually set up an account by counterparty, item, calculation items, or for each employee.
This tab allows you to work with analytics of the 19th account. You can adjust analytics by counterparties, invoices received, or by accounting methods. The checkboxes for counterparties and invoices are checked by default and cannot be cleared.
In this tab, you can define the procedure for analytical accounting of inventory items. Accounting can be carried out by item, batches and warehouses.
Setting the indicator “For each employee” will allow you to conduct analytics for each individual individually. This is especially recommended when working in a ZUP.
Sometimes, when working with documents, an accountant does not see the account assignment itself due to the fact that the “Show accounting accounts in documents” checkbox is not selected in the settings. You can correct the situation on the main tab of the Chart of Accounts. In the line “Document Accounts” you need to click the “Show” indicator.
Off-balance sheet accounts in 1C
With the help of off-balance sheet accounts, the property of third-party companies that are temporarily under the jurisdiction of the organization is accounted for. This same type of account is responsible for accounting for written-off expensive materials. To designate it, three-digit numeric codes from 001 to 011 or letter designations are used. All existing off-balance sheet accounts are divided into active, passive or active-passive.
To correctly account for property in balanced accounts, you need to take into account that there is no double correspondence. The debit of the account reflects only current receipts, and the credit of an identical account reflects disposals.
You can purchase services that help you work as an accountant here.
Do you want to install, configure, modify or update 1C? Leave a request!
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter
What does the account consist of?
Let’s look at what an account consists of using the example of account 10.01 “Raw materials and materials”.
- For each account, its code and name are indicated.
- Quick selection code - used to quickly add an invoice in documents. For example, we want to indicate invoice 10.01 in the document “Sales of goods and services”. In order not to waste time typing “10”, then a period and “01”, you can immediately enter “1001” - the program will understand what account you need.
- Subordination to the account - there are main accounts, there are subordinate ones - called subaccounts. They serve to decipher the main account. For example, account 10 stores information about the item as a whole. On account 10.01 you can see the nomenclature related to raw materials and supplies. Account 10.02 is purchased semi-finished products. And so on.
- Account type - active, passive or active/passive. They are defined by default and can only be changed when creating new accounts.
- Off-balance sheet—check this box for off-balance sheet accounts.
- The account is a group and is not selected in transactions - as a rule, subaccounts are used in transactions, and this check box is selected for main accounts. An exception is if the account does not have subaccounts.
- Types of account accounting - additional types of accounting are defined:
- by department;
- tax;
- currency;
- quantitative.
- The table defines additional analytics for accounts - subconto. There can be a maximum of 3 of them for a count. For some accounts, subcontos can be changed directly in the table - added, deleted. For some accounts, the composition of the analytics is determined by the program settings.