What property is classified as fixed assets when reflected on the balance sheet?
The accounting rules for this category are established by PBU 6/01. The list includes property used in the manufacture of products (carrying out work, providing services) and necessary for the purpose of managing the organization.
Signs of OS are the absence of plans to sell this asset and the possibility of extracting benefits from it.
The main criterion by which an asset in accounting is classified in this category is its useful life of more than 12 months (or another period that coincides with the operating cycle of the organization). This is logical, since these are long-term assets of the organization.
The fixed assets include:
- buildings, capital and non-capital construction projects;
- plots of land;
- production and work equipment;
- cars, motorcycles;
- computers, office equipment;
- household equipment;
- other specialized types of assets.
This type of asset also includes natural resources, capital investments in land or rental property.
The ways in which a company acquires this type of asset may be different. These include a purchase under a sales contract, a gratuitous transfer, a contribution to the company's charter, an exchange as part of barter, production within an organization or through the use of contractors, or the identification of surplus during an inventory check.
Net balance
IMPORTANT! A sample of the net balance sheet of a peasant farm from ConsultantPlus is available here
The term "net" means "pure". During the preparation of this type of balance, a number of indicators are regulated and “cleaned”. Let's consider the main ones:
- Depreciation of intangible assets. It is calculated using the formula: Balance Dt 05 minus balance Kt 04. The result is entered in line 1110 of the balance sheet.
- Depreciation of fixed assets. It is calculated using the formula: Balance Dt 01 minus balance Kt 02. The result is reflected in line 1150 of the balance sheet.
- Financial investments. The reserve for their depreciation, recorded in account 59, is not reflected in the balance sheet. Therefore, the calculation on line 1170 is done using the formula: Balance Dt 58 minus balance Kt 59.
Reserves for depreciation of inventory items are not reflected in the balance sheet (account 14). They should be distributed, reducing the cost of inventory items, which include reserves, similar to the above algorithm. In this way, the cost of accounts 43, 41, 10 is reduced. Account “Goods” 41 must also be reduced by the amount of the trade margin (account 42, credit).
Doubtful debts on credit account 63 reduce accounts receivable, in particular, on account 62, which reflects settlements with buyers (customers). Liability line 1370, reflecting retained earnings or uncovered loss, deserves close attention. There is an 84 score with the same name. However, when drawing up a balance sheet, it is subject to adjustment taking into account data from account 99 using the following formula: Balance 99 plus/minus balance 84.
Thus, depending on the financial results of the organization, there are 4 options for this formula:
- balance Kt 99 plus balance Kt 84;
- balance Dt 99 plus balance Dt 84 (the result is written in parentheses);
- balance Kt 84 minus balance Dt 99 (the result is written in parentheses if a negative value is obtained during the calculation);
- balance Kt 99 minus balance Dt 84 (same as the previous one).
If interim dividends are accrued during the reporting period, this should be taken into account and an additional balance of 84 deducted in relation to accrued interim dividends. If the organization does not have retained earnings or uncovered losses for previous years, the value of line 1370 will be equal to the value of line 2400 f. 2, disclosing data on profits and losses, namely net profit or loss for the year.
How are fixed assets reflected on the balance sheet?
Fixed assets in the balance sheet are reflected in a separate line under code 1150 (in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n).
The value of this asset is determined as the difference in the balances on the following accounts:
| Account number | Account name | Note |
| 01 | Fixed assets | — |
| 02 | Depreciation of fixed assets | Depreciation on items listed on line 1140 (Tangible Exploration Assets) should not be taken into account. |
| 07 | Equipment for installation | The balance of this account is taken in relation to the costs of construction in progress. |
| 08 | Investments in non-current assets | The balance of the invoice for costs of construction in progress is accepted when indicated in line 1150. |
It is important to note: objects that fall under the OS criteria, but are temporarily owned and used to generate income, are accounted for separately. To do this, use account 03 “Profitable investments in material assets.” In this case, depreciation for them is calculated on the credit of account 02. If the company has similar objects, then when entering data in line 1150, the debit of account 01 should be subtracted from the depreciation amount.
A promising way to switch to FSBU 6/2020
An organization with simplified accounting when switching to FAS 6/2020 may not recalculate the book value for “old” fixed assets, while further accounting of all fixed assets must be carried out according to the rules of the new standard.
Example 1
The organization (OSNO, VAT payer) is a small business entity that is not subject to mandatory audit.
From 2022, the organization will ahead of schedule switch to the application of FAS 6/2020, reflecting the consequences of changes in accounting policies prospectively.
At the end of 2022, the organization’s balance sheet includes a fixed asset - a milling and engraving machine. The initial cost of the machine is 240,000 rubles, accrued depreciation is 105,600 rubles, the useful life is 50 months, the remaining fixed income is 28 months. The depreciation elements for the machine are not revised, including the salvage value is considered equal to zero.
In July 2022, the organization acquires a new fixed asset - a server worth 240,000 rubles. (including VAT 20%). In accounting and tax accounting, the useful life of a server is set at 25 months.
The liquidation value of the server is determined to be 50,000 rubles, since the organization intends to sell the server in 25 months.
The organization uses the straight-line method of calculating depreciation for all fixed assets in accounting and tax accounting.
To make an early transition to the new standard for accounting for fixed assets, it is necessary to indicate in the accounting policy settings that FAS 6/2020 has been applied since 2022 (see Fig. 1). After the specified settings in the processing form Closing the month for December 2022, the routine operation Transition to FSBU 6 appears. If there is a future transition to FSBU 6/2020, this operation may not be performed. But even if the organization makes the transition to FSBU 6, the book value of the milling and engraving machine will not be recalculated, since for it, under the terms of Example 1, the depreciation elements do not change.
Let us recall that according to the previous rules, using the linear method, the annual amount of depreciation in accounting was calculated based on the original cost of the fixed assets and the depreciation rate. The depreciation rate is defined as the reciprocal of the useful life of an asset, expressed as a percentage. Monthly depreciation charges amount to 1/12 of the annual amount (clause 19 of PBU 6/01).
Thus, until 2022, the amount of monthly depreciation of the machine in accounting was 4,800 rubles. (RUB 240,000 / 50 months).
From January 2022, the amount of depreciation for the reporting period is determined as the ratio of the difference between the book value and liquidation value of an asset to the value of its remaining useful life. Thus, in January 2022, the amount of depreciation of the machine is 4,800 rubles: (240,000 rubles - 105,600 rubles - 0 rubles) / 28 months.
In this case, the amount of depreciation of the machine remains the same, although its calculation is performed using a different algorithm.
Under the conditions of Example 1, in July 2022, the organization takes into account a fixed asset with a non-zero liquidation value.
In the document Receipt of fixed assets, which is intended to simultaneously reflect the receipt and acceptance of fixed assets for accounting, along with other restrictions, it is not possible to indicate the liquidation value. But it can be specified in the document Change of fixed assets depreciation elements.
Let's use the classic scenario for working with fixed assets: first, we will create a Receipt document (act, invoice, UPD) with the type of operation Equipment, and then the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets.
When posting a receipt document with the type of transaction Equipment, the following accounting entries are generated:
Debit 08.04.1 Credit 60.01
— the amount of costs for purchasing a server (RUB 200,000);
Debit 19.01 Credit 60.01
— the amount of input VAT presented by the supplier when purchasing the server (RUB 40,000).
Hereinafter, for tax accounting purposes, special fields of the accounting register are simultaneously filled in (for those accounts where tax accounting is supported).
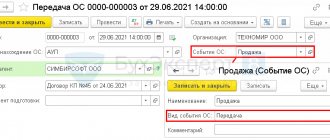
In the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets on the Accounting tab, you can now specify the liquidation value (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Indication of the liquidation value when accepting fixed assets for accounting
When posting a document, an accounting entry is generated:
Debit 01.01 Credit 08.04.1
- for the cost of the fixed asset (RUB 200,000).
The entered liquidation value is stored in the Asset Depreciation Parameters (Accounting) register. From August 2022, the server begins to be depreciated in accounting and tax accounting. When carrying out the routine operation Depreciation and depreciation of fixed assets, which is included in the Month Closing processing, entries are generated for calculating depreciation of fixed assets:
Debit 26 Credit 02.01
- for the amount of server depreciation, which in accounting is 6,000 rubles, and in tax accounting - 8,000 rubles.
Debit 20.01 Credit 02.01
- for the amount of depreciation of the milling and engraving machine, which in accounting and tax accounting is 4,800 rubles.
A detailed calculation of depreciation in accounting is given in the Help-Calculation of Depreciation (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Help calculating depreciation according to the rules of FSBU 6/2020
Let's analyze the calculation of server depreciation in August 2021:
- residual value (or book value in terms of FSBU 6/2020) - 200,000 rubles. (column 6);
- liquidation value - 50,000 rubles. (column 7);
- remaining SPI - 25 months (column 9);
- depreciation amount - (200,000 rub. - 50,000 rub.) / 25 months. = 6,000 rub. (column 10).
In tax accounting using the linear method, the amount of monthly depreciation is determined as the product of its original cost and the depreciation rate determined for a given object. The depreciation rate is the reciprocal of the useful life of an asset, expressed as a percentage (clause 2 of Article 259.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The liquidation value is not taken into account, so the amount of depreciation of the server for profit tax purposes is 8,000 rubles. (RUB 200,000 / 25 months).
At the end of 2022, the depreciation elements for all fixed assets should be checked for compliance with the conditions of use of the fixed assets and, if necessary, changed using the document Change of fixed asset depreciation elements.
An example of how fixed assets are reflected on the balance sheet
The rules for entering data for this type of asset coincide with the requirements for creating a balance sheet. It is filled in using the value “thousands”. rub.".
Let's take as an example the display of assets from the balance sheet of a company:
| № | Indicator name | Code | Data as of December 31, 2018 | Data as of 12/31/2019 | Data as of 12/31/2020 |
| 001 | 1. NON-CURRENT ASSETS Intangible assets | 1110 | 2 007 | 1 645 | 1 560 |
| Research and development results | 1120 | — | — | — | |
| Intangible search assets | 1130 | — | — | — | |
| Material prospecting assets | 1140 | — | — | — | |
| 002 | Fixed assets | 1150 | 10 718 | 11 856 | 11 947 |
| Profitable investments in material assets | 1160 | — | — | — | |
| Financial investments | 1170 | — | — | — | |
| Deferred tax assets | 1180 | 85 | 56 | 76 | |
| Other noncurrent assets | 1190 | — | — | — | |
| Total: | 1100 | 12 810 | 13 557 | 13 583 | |
| 004 | 2. CURRENT ASSETS Inventories | 1210 | 9 560 | 8 156 | 10 745 |
| VAT on purchased assets | 1220 | 945 | 3 948 | 1 564 | |
| 005 | Accounts receivable | 1230 | 5 875 | 7 046 | 5 378 |
| Financial investments (excluding cash equivalents) | 1240 | — | — | — | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 1250 | 3 450 | 2 735 | 1 837 | |
| Other current assets | 1260 | — | — | — | |
| Total: | 1200 | 19 830 | 21 885 | 19 524 | |
| BALANCE | 1600 | 32 640 | 35 442 | 33 107 |
As can be seen from the balance sheet:
- fixed assets are reflected in one line and are one of the elements of the first section “Non-current assets”;
- data is entered into the line without decryption in a single amount;
- If necessary, details can be provided in the balance sheet appendix.
In particular, changes in the value of fixed assets as a result of their reconstruction or additional equipment are included in the annexes. The same scheme is followed if the property is revalued as a result of recalculation of the actual market value. The differences are recorded as additional capital.
Receipt, acceptance and commissioning of the OS
1C software products for accounting automation allow you to register fixed assets in accounting using “Receipts of fixed assets,” which is accessible from the “Fixed assets and intangible assets” section of the main menu of the system.
Fig.1 Receipts of fixed assets
The document's header, table section and footer must be filled out.
The header of the document indicates:
- Number and date of the supplier's invoice;
- Name of the supplier counterparty;
- Agreement between the organization and the counterparty;
- Location of the OS, as a division of the organization;
- The financially responsible person, as an individual receiving a fixed asset;
- Asset accounting group – selected from the proposed predefined list.
Fig.2 Document header
Particular attention should be paid to the detail “Method of reflecting depreciation expenses”. As you fill out the header details listed above, the mentioned details are gradually automatically filled in with the data of the current document. This is what the created method usually looks like:
Fig. 3 Method of reflecting depreciation expenses
The element belongs to a specific organization, in our case, Spetsavtomatika LLC. It shows the cost account. By default, the cost account is substituted from the organization's accounting policy, configured when the accounting configuration was launched. You can go to the accounting policy through the link in the organization card.
Fig.4 Transition to UE
Fig.5 Replace cost account
Here the cost account can be replaced with any necessary value - 20, 23, 25, 29, 44, 91.
After installing the desired cost account, you will need to fill out all the analytics elements:
- For accounts 20, 23, 29 – divisions, item groups, cost items;
- For accounts 25, 26 – divisions, cost items;
- For account 44 - cost items;
- For account 91.02 - items of other expenses.
The last attribute of the method, “Coefficient,” performs a very important function. Its use makes sense if the fixed asset is involved in several categories of accounting costs during the reporting period. For example, fixed assets are used for management purposes and for trading purposes, as a sales expense. To correctly set the depreciation method, you need to determine the shares attributable to each cost category. These shares must be reflected as coefficients.
Fig.6 Reflection of shares
In the example given, the values of the coefficients are equal to ones, they mean that depreciation will be divided equally/in half and accrued between cost accounts 26 and 44.
This way you can manage the ratios of the amounts of credited depreciation for an asset.
Let's fill out the receipt table.
Using the “Add” button, a new row is created in the table section.
Fig.7 Creating a new line
In this line you must fill in the object by selecting or creating it in the directory of the same name.
Fig.8 Filling the object
For correct accrual, you need to fill in the fixed assets accounting group, the code of the All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets (OKOF)* and the depreciation group in the card.
*OKOF must be pre-loaded into the system from an external file that comes with the configuration installation package.
The tabular part is completed by indicating the cost of the fixed asset, the VAT rate, and the useful life.
The document in question provides for the registration of receipt of a non-current asset, registration and putting the fixed asset into operation. After posting the document, the following transactions will be generated:
Fig.9 Wiring
Noteworthy is the fact that the document “Receipt of fixed assets” can be used to register a fixed asset, the depreciation of which will be credited using the straight-line method. To select other methods, it is recommended to use the sequential creation of documents “Receipt (act, invoice)” and “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets”.
In the example under consideration, the OS is used for business purposes, so you can move on to the next step.
Cost of fixed assets to be reflected on the balance sheet
When accounting, fixed assets include assets whose cost usually exceeds 40 thousand rubles, and whose service period is over 12 months. They should be reflected in the balance sheet minus the amount of depreciation (at the so-called residual value).
If an asset has the characteristics of a fixed asset, but its cost is less than 40 thousand rubles, then the company can take it into account both in the column “Fixed assets” and in the column “Inventories”. The second column records the assets that the organization plans to use during the year.
The organization determines the value limits for classifying property as a certain category of assets in its accounting policy (in accordance with clause 5 of PBU 6/01).
When the value of an asset changes, the new value can be accepted for accounting only after it has been adjusted.
Simplified transition to FSBU 6/2020
Now let’s look at how “1C: Accounting 8” version 3.0 automatically recalculates the book value during a simplified transition to FAS 6/2020.
Example 2
The organization (OSNO, VAT payer) will switch from 2022 to the application of FAS 6/2020 in a simplified manner.
Fixed assets that are listed on the organization’s balance sheet at the end of 2022 exceed the cost limit established by the organization from 2022. For all fixed assets, the straight-line depreciation method is used.
Let's assume that before switching to FAS 6/2020, the organization decided to change the depreciation elements for a number of fixed assets.
To do this, you will need to create a document Change of fixed assets depreciation elements dated 12/31/2021. The program “understands” that a document has been introduced dated at the end of the year preceding 2022, that is, the year from which the new standard will be applied. Therefore, the tabular part of the document is modified. Now for accounting purposes you can change:
- method of calculating depreciation. Please note that the transition from the linear method to the method of calculating depreciation in proportion to the volume of production (work) is not supported;
- remaining useful life or scope of work. In this case, the total useful life is recalculated automatically;
- liquidation value.
By clicking the Selection button, you can go to the form for selecting fixed assets for which depreciation elements should be changed. You can select fixed assets by name, by depreciation method (in accounting), as well as by remaining useful life (in accounting). By clicking the Transfer to document button, the selected fixed assets are transferred to the tabular part of the document Change of fixed assets depreciation elements.
The previous depreciation items are automatically reflected on the line before the change. Changed depreciation elements should be entered in the line after the change (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Revision of depreciation elements
For example, for a fixed asset with inventory number “22,” before the changes were made, the useful life was set at 60 months, the expired period was 12 months, and the remaining period was 48 months. Liquidation value has not been determined.
Following the changes, the remaining useful life has been reduced to 38 months, resulting in a total life of 50 months. The liquidation value is determined in the amount of 25,000 rubles. The depreciation method does not change.
By clicking the Depreciation Elements button, a printed form of the document of the same name is available. We believe that this form can be used as a primary document when revising depreciation elements, since it contains all the mandatory details in accordance with Federal Law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011. In addition, FSBU 6/2020 does not contain requirements to draw up a separate document for each OS.
When posting the document Change of fixed assets depreciation elements, accounting entries are not generated, but entries are entered into the information registers of the asset accounting subsystem, including in the Asset Depreciation Parameters (accounting) register.
The changes made will apply:
- when performing a regulatory operation Transition to FAS 6, which appears in the processing form Closing the month for December 2021;
- when calculating depreciation starting from the month following the month of the document, that is, from January 2022.
Regulatory operation The transition to FAS 6 should be carried out only after the formation and saving of accounting (financial) statements for the reporting year (under the terms of Example 2 - for 2022). For a correct transition, we recommend that you first cancel the regulatory operations of the fourth group following the Transition to FAS 6 (Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU/18, if the organization applies PBU 18/02, and Balance Sheet Reformation). Then you should perform the Transition to FSBU 6 and all subsequent operations - each operation in turn.
The simplified procedure for switching to FAS 6/2020 consists of a one-time adjustment to the book value of fixed assets at the beginning of the reporting period, with the difference being allocated to retained earnings. In this case, the carrying value of fixed assets is considered to be their initial cost (taking into account revaluations), recognized before the application of FAS 6/2020, less accumulated depreciation. And accumulated depreciation is calculated according to the rules of FSBU 6/2020 based on the specified initial cost, liquidation value and the ratio of the expired and remaining useful life.
A detailed calculation of the adjustment amounts is given in the Help-calculation of depreciation adjustments during the transition to FAS 6 (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Help calculating depreciation adjustments when switching to FAS 6/2020
Let's analyze the calculation of the adjustment to the book value for a fixed asset with inventory number “22”:
- the initial cost of the object is 600,000 rubles. (column 4);
- liquidation value - 25,000 rubles. (column 5);
- SPI after the transition to FSBU 6/2020 - 50 months. (column 7);
- expired SPI - 12 months (column 8);
- the amount of depreciation according to FAS 6/2020 is 138,000 rubles. ((600,000 rub. - 25,000 rub.) / 50 months x 12 months) (column 10);
- accrued depreciation before the company switched to FSBU 6/2020 - 120,000 rubles. (column 9);
- adjustment of depreciation upward - 18,000 rubles. (RUB 138,000 - RUB 120,000) (column 11).
Depreciation adjustments are calculated in a similar way for other fixed assets for which depreciation elements changed before the transition to FSBU 6/2020.
When carrying out the routine operation Transition to FSBU 6, accounting entries are generated:
Debit 84.01 Credit 02.01
— by the amount of depreciation adjustment upward. For OS with inventory number “22” this amount is 18,000 rubles;
Debit 02.01 Credit 84.01
- by the amount of depreciation adjustment downward.
Starting from January 2022, depreciation of fixed assets is already calculated according to the rules of FAS 6/2020 based on the revised depreciation elements.
conclusions
The organization's fixed assets in the balance sheet are displayed on a special line in the first section of the reporting document, which is dedicated to the company's non-current assets. Assignment of property to this category is carried out in accordance with internal accounting policies when fixing a certain cost and period of use (standard thresholds are 40 thousand rubles and more than 12 months of use).
To send reports to government agencies, use Astral Report 5.0 - an online service that allows you to generate and submit electronic documents from any PC and from anywhere in the world with Internet access.