What does it mean to have a salary not lower than the minimum wage?
The minimum wage is the minimum monthly salary of an employee under an employment contract.
If the employee has worked full time and fulfilled all duties, the accrued salary for the month cannot be less. And for an employee on a probationary period too - Art. 133 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. When working with the self-employed, there is no minimum wage limit.
The minimum wage depends on the subsistence level - this is the amount on which, according to the state, a person will survive one hundred percent. The minimum wage is set by law for each year. For 2022, the minimum wage is 12,792 rubles. In 2022 it will increase to 13,890 ₽.
But more often the region has its own increased minimum wage. Then the employer must pay no less than him. For example, in Moscow for 2021 the minimum wage is 20,589 ₽ - which means the federal one does not apply to Muscovites. Purely theoretically, an employer may refuse to pay wages at the increased regional minimum wage. But in reality it is difficult: no later than a month after its introduction, you must submit a reasoned refusal to increase to the regional authorities. But even then they will be allowed to pay the federal minimum wage only temporarily.
The minimum wage is also taken for the region where the employee performs his duties, and not where the employer is registered.
Article: federal minimum wage + table with regional ones for 2022 and 2022
Salary composition
An employee’s salary may be lower than the minimum wage, but the salary for a fully worked month should not be lower than the “minimum wage” in force in the region (Article 133, 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). What is included in the payments (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- remuneration for performing labor duties (according to salary, tariff rate);
- compensation for special working conditions (in hazardous or difficult work, in an unfavorable climate);
- incentive additional payments (allowances, for example, for length of service, bonuses).
Not all of the listed components should be taken into account when comparing the accrued salary with the minimum possible.
What is subtracted and what goes on top
The salary consists of salary, bonuses and various additional payments according to the Labor Code.
Salary and bonuses
The salary itself may be less than the minimum wage if it is matched by a monthly bonus. But it is impossible to compensate for wages below the minimum wage for previous months with a quarterly or annual bonus. This bonus will be counted only in the month of payment. And in the remaining months, the employer will violate the law - as explained by the Ministry of Labor in letter No. 14-0/10/B-4085.
Personal income tax
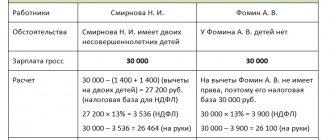
The accrued salary must definitely not be lower than the minimum wage. But the employer deducts 13% of personal income tax from the salary and transfers it to the tax office. And after deducting personal income tax, the salary in hand may be less than the minimum wage. Because paying income tax is the employee’s responsibility; simply, according to the law, it was performed by the employer as a tax agent, but not with his own money, but with the employee’s money. The Federal Tax Service confirmed this in letter No. 03-04-05/101639.
Additional payments above the minimum wage
- For overtime work, night time and weekends and holidays. Because any processing must be added - Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation No. 17-P;
- For part-time work and temporary substitution for another employee - Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation No. 40-P;
- Climate surcharges: regional coefficient and northern surcharges. The worse the climate in the city, the higher the salary should be. Until 2022, the authorities could include climate surcharges into the increased regional minimum wage. Now it’s no longer possible, you have to pay extra from above - Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation No. 38-P.
Article: where to find and how to calculate the regional coefficient and northern allowances
If the minimum wage has been increased, the salary must also be increased from the date the minimum wage was increased. And this is not counting the indexation of wages to the level of consumer prices, which the employer must also do under Art. 134 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
What cannot be deducted from your salary
You definitely cannot deduct a fine from your salary for violating duties and being late. Even if they do not go beyond the minimum wage. Because there is no fine as a punishment for an employee in the law. And for a fine to an employee there will be a fine to the employer from labor inspectors - Art. 192 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The minimum wage has been increased since 2022: what should you pay attention to?
21.01.2022
The minimum wage has increased since 2022. What will change in the work of the institution in this regard? Let's consider the questions that arise in practice.
Question:
How much is the minimum wage from 2022?
Answer:
In 2022, the minimum wage was 12,792 rubles. per month ( Federal Law No. 473-FZ dated December 29, 2020 “On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation”
).
From January 1, 2022, at the federal level, the minimum wage is 13,890 rubles. per month on the basis of the Federal Law of December 6, 2021 No. 406-FZ “On Amendments to Article 1 of the Federal Law “On the Minimum Wage”
.
Question:
What is the minimum wage used for today?
Answer:
According to Art. 3 of Federal Law No. 82-FZ of June 19, 2000 “On the minimum wage”
The minimum wage applies:
– to regulate wages; – to determine the amount of benefits for temporary disability, pregnancy and childbirth; – for other purposes of compulsory social insurance.
The use of minimum wages for other purposes is not permitted.
Today, the economic content of the minimum wage has changed: it is gradually being equated to the real subsistence level of the working population. The concept of “minimum wage” is gradually being excluded from a number of existing laws, for example the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Question:
What parameters affect the minimum wage?
Answer:
In accordance with Art. 1 of Federal Law No. 82-FZ
The minimum wage for the next year is established by federal law in the current year and is calculated based on the median wage calculated by Rosstat for the previous year.
From 2022, the ratio of the minimum wage to the median wage is set at 42%. The ratio of the minimum wage and median wage is reviewed at least once every five years based on the conditions of socio-economic development of the Russian Federation.
The minimum wage for the next year is set at an amount not lower than the subsistence level of the working-age population as a whole in the Russian Federation for the next year and not lower than the minimum wage established for the current year.
The median salary is calculated based on the methodology developed by Rosstat.
Question:
Through what means should an organization ensure wages not lower than the minimum wage?
Answer:
Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
it is determined that the minimum wage is established simultaneously throughout the entire territory of the Russian Federation by federal law and cannot be lower than the subsistence level of the working population.
The minimum wage established by federal law is ensured by:
- organizations financed from the federal budget - at the expense of the federal budget, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from business and other income-generating activities; – organizations financed from the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, – at the expense of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from entrepreneurial and other income-generating activities; - organizations financed from local budgets - at the expense of local budgets, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from business and other income-generating activities; – other employers – at their own expense.
Similar norms are prescribed in Art. 2 of Federal Law No. 82-FZ
.
The monthly salary of an employee who has fully worked the standard working hours during this period and fulfilled the labor standards (job duties) cannot be lower than the minimum wage.
Question:
There are federal and regional minimum wages. Should a regional minimum wage be established in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation? What is the minimum wage to focus on when paying wages?
Answer:
According to Art. 133.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a regional agreement on the minimum wage
may establish
the amount of the minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
The size of the regional minimum wage can be established for persons working in the territory of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation, with the exception of employees of organizations financed from the federal budget.
At the same time, the regional minimum wage cannot be lower than the federal minimum wage.
The minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation is ensured by:
– organizations financed from the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, – at the expense of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from entrepreneurial and other income-generating activities; - organizations financed from local budgets - at the expense of local budgets, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from business and other income-generating activities; – other employers – at their own expense.
After concluding a regional agreement on the minimum wage, the head of the authorized executive body of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation invites employers operating in the territory of this constituent entity of the Russian Federation and who did not participate in the conclusion of this agreement to join it. If employers operating in the territory of the relevant constituent entity of the Russian Federation, within 30 calendar days from the date of official publication of the proposal to join the regional agreement on the minimum wage, have not submitted to the authorized executive body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation a reasoned written refusal to join it, then the specified agreement is considered extended to these employers from the date of official publication of the proposal and is subject to mandatory execution by them.
Not all regions of the Russian Federation have established a regional minimum wage, therefore if:
– a regional minimum wage has not been established in the region; the institution is guided by the federal minimum wage; – a regional minimum wage has been established in the region, institutions financed from the budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets must pay wages based on the size of the regional minimum wage, and institutions financed from the federal budget - based on the size of the federal minimum wage, since according to paragraph. 2 tbsp. 133.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
the amount of the minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation can be established for persons working in the territory of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation, with the exception of employees of organizations financed from the federal budget (
Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated October 11, 2016 No. 14-1/ОOG-9076
).
Question:
Which payments should be taken into account and which should not be taken into account when determining the amount of wages for the purposes of its compliance with the minimum wage in 2022?
Answer:
For the purposes of comparison with the current minimum wage, the composition of wages includes salary, bonuses, allowances and additional payments provided for by the remuneration system (for example, for the traveling nature of work).
Labor legislation allows the establishment of salaries (tariff rates) as components of workers' wages in an amount less than the minimum wage, provided that wages, including incentive and compensation payments, which, within the meaning of Art. 129 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
are elements of wages (its component part), cannot be lower than the minimum wage established by federal law (
Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 09/04/2018 No. 14-1/OOG-7353
).
At the same time, as stated in the resolutions of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated April 11, 2019 No. 17-P
,
dated December 16, 2019 No. 40-P
, the salary (part of the salary) of an employee not exceeding the minimum wage does not include:
– increased pay for overtime work; – increased pay for work at night, weekends and non-working holidays; – additional payment for work (additional payment for work) performed as a combination of professions (positions).
Also, for the purposes of comparing it with the minimum wage, one-time payments, such as an anniversary bonus or financial assistance, are not included in the wages.
Accordingly, if, according to the employment contract or staffing table, the employee’s salary consists only of a fixed payment equal to the minimum wage, then it should be increased to the new minimum wage. To do this, you need to make changes to the staffing table or other local regulations that establish the wage system.
Question:
When calculating wages for the purpose of comparing them with the minimum wage, are regional coefficients and percentage bonuses (if they are established) for work in the Far North and equivalent areas, and in other areas with special climatic conditions taken into account?
Answer:
According to Art. 130 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The system of basic state guarantees for remuneration of workers includes the minimum wage in the Russian Federation.
In accordance with Art. 133 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
the monthly salary of an employee who has worked the full working hours during this period and fulfilled the labor standards (job duties) cannot be lower than the minimum wage.
Accordingly, when concluding an employment contract with an employee, he must set a salary not lower than the minimum wage.
As we remember, regional coefficients and percentage allowances in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas are calculated in excess of the minimum wage ( Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated December 7, 2017 No. 38-P
).
If an employee works part-time (less than the standard monthly working time established in his employment contract), for example, in connection with annual leave, business trip, temporary disability, then his work is paid in proportion to the time he worked. The work of employees hired, for example, on a part-time basis, is paid in proportion to the established wage rate for full-time work. At the same time, not lower than the minimum wage in full-time equivalent ( Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated November 10, 2021 No. 14-1/OOG-10634
).
Question:
If an employee works part-time or is an internal part-time worker, can he have a salary below the minimum wage?
Answer:
Yes, when working part-time with a time-based (time-based bonus) wage system, wages are accrued to the employee in proportion to the time worked, not lower than the minimum wage in terms of the full monthly rate.
As for part-time work, employment contracts for the main place of work and for part-time work, including internal work, are concluded separately. Accordingly, the minimum wage is also achieved separately. If an employee is employed part-time, then his salary must not be lower than the minimum wage in terms of full-time work ( Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 06/05/2018 No. 14-0/10/B-4085
).
Question:
What other payments, besides wages, need to be reviewed when the minimum wage increases from 2022?
Answer:
As mentioned above, today the minimum wage is used to regulate wages, as well as to determine the amount of benefits for temporary disability, pregnancy and childbirth, and for other purposes of compulsory social insurance.
In connection with the increase in the minimum wage from 2022, in addition to the amount of wages, it is necessary to track sick leave payments, as well as vacation and travel payments to employees.
Despite the fact that in 2022 all constituent entities of the Russian Federation switched to direct payments for sick leave, employers pay benefits for the first three days of an employee’s illness. In this regard, the employer must take into account that, in accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 7
and
paragraph 2 of Art.
8 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity,” the insured person is paid a benefit for a full calendar month at the minimum wage if:
– his insurance period is less than six months; – there are one or more grounds for reducing temporary disability benefits.
In these cases, temporary disability benefits in January 2022 are calculated from the average daily earnings equal to 448.06 rubles. (RUB 13,890 / 31 days).
As for vacation and travel payments, when increasing the minimum wage from 2022, you need to remember that according to clause 18 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007 No. 922 “On the specifics of the procedure for calculating average wages”
in all cases, the average monthly earnings of an employee who has worked the full working hours during the billing period and fulfilled labor standards (job duties) cannot be less than the minimum wage established by federal law. Accordingly, it is necessary to recalculate vacation and business trip pay if the employee’s actual average earnings for the billing period are less than RUB 13,890, and the vacation or business trip began before January 1, 2022.
Question:
If an employee receives a salary equal to the minimum wage, is it necessary to withhold personal income tax from such income?
Answer:
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 3 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Every person must pay legally established taxes and fees.
This norm develops that enshrined in Art.
57 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the constitutional and legal obligation of everyone to pay legally established taxes and fees.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 210 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
When determining the tax base for personal income tax, all income of the taxpayer received by him, both in cash and in kind, or the right to dispose of which he has acquired, is taken into account, as well as income in the form of material benefits, determined in accordance with
Art.
212 Tax Code of the Russian Federation .
Currently, for the taxation of most types of income of individuals, a single rate of 13% is established.
The current personal income tax system is focused on reducing the tax burden through the use of standard, social, property and professional tax deductions, each of which is aimed at supporting a certain category of citizens.
In addition, Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
a list of income not subject to personal income tax has been established (
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/07/2019 No. 03-04-05/41713
).
Accordingly, the tax agent for personal income tax - a healthcare institution that pays income to its employee - must withhold personal income tax, including from wages equal to the minimum wage.
Ryabinin V., expert of the information and reference system “Ayudar Info”
Send to a friend
What will happen for a salary below the minimum wage?
The tax office monitors the salary amount. It is seen in the quarterly 6-NDFL reports and calculations of insurance premiums submitted by the employer.
The tax office will send a request for clarification
For each report, inspectors conduct a desk audit. You have three months for this. If they see a salary below the minimum monthly wage, they will ask for a written explanation of why this is so. The tax authorities must respond to the request within five days and attach copies of documents that show why the salary is less. The legitimate reasons for the decline will be discussed below.
If the explanations are ignored, the tax office will suspect a scheme to evade payroll taxes and will include it in the on-site inspection plan. If it finds violations at the exit, it will charge additional taxes and fine you. They will also transfer the information to the labor inspectorate, and there they will fine you for a gray salary.
Article: tax risk criteria for on-site audit
Fine from the labor inspectorate
For a salary less than the minimum wage, you can receive a fine under clause 6 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. For individual entrepreneurs this is from 1000 to 5000 rubles, for companies from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles, and separately for a director from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles.
The employee will recover wages up to the minimum wage through the court
The employee will receive an additional payment up to the minimum wage through the court. This often happens when the minimum wage salary already includes additional payments for overtime and climate allowances.
When the monthly salary is legally lower than the minimum wage
Here are cases when the salary will be less than the minimum wage. This must be confirmed by documents for the tax authorities.
Salary in hand after deductions
From the accrued salary, the employer can withhold alimony, debts under writs of execution and his own material damage - if he has issued it. Then the salary in hand may be less than the minimum wage. But deductions have a limit: you can deduct no more than 70% of alimony, and even less for other debts; details are in Art. 138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Part-time
Full salary is due for full working time. For regular workers, this is 40 hours a week. For teenagers - 24, for disabled people - 35, for workers with hazardous working conditions - 36 - Art. 91, 92 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
An employee may work part-time or part-time. Then the salary will be proportionally lower. For example, if a salesperson works half a day at 0.5 rate, then his Moscow salary will be 10,294.5 rubles: 20,589 × 0.5.
Part-time pay will be visible from employment contracts with employees and time sheets.
The salary for a part-time employee, when converted to a full-time rate, must still be no lower than the minimum wage. And if it turns out that the employer has only formally reduced working hours, but in reality he forces a full shift to work, this will be overtime, for which overtime must be paid - letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 14-0/10/B-4085.
Article: how to apply for a part-time job and not break the law
Failure to meet the quota for piecework payment and few shifts
An employee may have piecework wages - when he is paid per unit of work done. But then the employer must have a monthly quota for this output. And the employee must have it written down in the employment contract. Alternatively, the employer may have a Regulation on Remuneration, which the employee is familiar with when applying for a job.
Payment for the monthly norm of work done must not be lower than the minimum wage. Plus, the employer must ensure that this standard can be met: provide premises, working equipment, suitable materials and ensure safe working conditions - Art. 163 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
And if the employee does not pass the standard, the salary can be cut.
It's the same with time-based payment. Only there, instead of a unit of work done, there will be an hour or a work shift.
Article: how to create a sliding schedule
Marriage and simple
Complete defects caused by the employee are not paid. Partial payments are paid at reduced rates depending on the degree of suitability. The marriage must be registered - Art. 156 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Downtime, for which no one is to blame, in the amount of no less than ⅔ of the salary. Downtime due to the employee's fault is not paid. The employer issues an order regarding idle time - Art. 157 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Article in Kontur.Journal: how to design a simple
Non-monetary form of salary
20% of the employee's monthly accrued salary can be given in products or things that were produced in the employer's company. But you cannot pay with coupons, promissory notes, alcohol, drugs, poisons and weapons - 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Non-monetary salary will be legal if the conditions from clause 54 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court No. 2 are met:
- The employee has a written statement that he agrees to receive a specific part of the salary not in money. If an employee has written a statement several months in advance, he can withdraw it at any time and demand the entire salary in cash.
- They gave no more than 20% of the accrued salary in kind.
- Issued products or goods are common in the industry. For example, a farm worker was given part of his salary in potatoes.
- The worker can eat the food himself or put things into the household. This means that the employee does not need to resell wages in kind.
- Goods or food are recalculated in proportion to the salary at the market price, and are not inflated.
Leave without pay
An employee has the right to go on leave without pay for family reasons - Art. 128 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
No salary will be paid during this time. There must be a statement from the employee, plus the employer issues a leave order with specific dates.