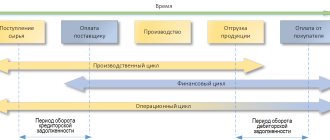
Current assets are assets of an organization that are regularly renewed. Necessary to ensure the activities of the company. They are one of the indicators of liquidity and management efficiency. The basic feature of mobile assets is their single or multiple turnover during the year or production cycle. They are distinguished by an increased turnover rate.
Question: How to reflect in accounting the costs of purchasing special equipment and putting it into operation if in accounting, special equipment is taken into account in the manner prescribed for accounting for current assets, and in tax accounting it is recognized as depreciable property? The special equipment was purchased for RUB 240,000. (including VAT 40,000 rubles) and put into operation in the month of purchase. The useful life of special equipment belonging to the second depreciation group in accounting and tax accounting is set equal to 25 months. According to the accounting policy, for accounting purposes, repayment of the cost of special equipment accounted for as part of current assets is carried out in a straight-line manner, starting from the month of transfer to operation. Interim financial statements are prepared as of the last day of each calendar month. For tax accounting purposes, income and expenses are accounted for on an accrual basis; depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method. View answer
Composition of current assets
Knowledge about mobile assets meets the management goals of the enterprise. The manager must have information about the company's performance indicators and ratios. The source of obtaining this information is financial statements. Most of its accounts are devoted to operations related to working capital. Let's look at the composition of mobile assets:
- Various supplies: raw materials for production, products.
- VAT charged on purchased items.
- Accounts receivable.
- Financial contributions.
- Cash and cash equivalents.
Mobile assets are reflected in the second section of the balance sheet.
How to fill out line 1260 “Other current assets” ?
The concept and meaning of working capital on the balance sheet
Any enterprise draws up a balance sheet, which reflects data on its economic assets (assets) and their sources (liabilities).
This is a system of tabulated indicators that describe the property and financial position of the enterprise at the reporting date. Note 1
The essence of the balance sheet is the equality of its two main parts: assets and liabilities. This equality is guaranteed by the fact that the same objects are evaluated from the input and source sides. For this purpose, the double entry method is used, in which each transaction in an asset and liability of one account is reflected in the balance of another account.
Equality is ensured by the fact that the same objects are described from the side of their sources and from the side of attachments. This equality is ensured by the double entry method - the reflection of each transaction on the asset of one account and the liability of another account.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
Definition 1
Assets are economic resources that an organization needs to conduct and develop its activities. These are assets and liabilities, i.e. what the company owns. And liabilities are the totality of all sources of formation of the enterprise’s funds.
In the balance sheet, working capital is the amount advanced into the totality of the company's material assets, which are necessary to service the business process. Unlike fixed assets, working capital is fully used during one production cycle, transfers its value to finished products and is restored in physical and monetary terms. At the same time, they are in a state of constant movement.
Working capital on the balance sheet plays a key production role. Their significance lies in the systematic formation and use of production assets in a minimum volume. They allow the enterprise to carry out the program in a specific period. In addition, working capital participates in the formation of the planned and predicted economic result of the company’s activities.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Working capital on the balance sheet 460 ₽ Abstract Working capital on the balance sheet 280 ₽ Test work Working capital on the balance sheet 210 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Why is mobile asset analysis required?
OA indicators are used to calculate some of the most important indicators:
- Profitability.
- Enterprise stability.
- Liquidity.
Question: How to calculate the amount of own working capital and the supply ratio based on the balance sheet? View answer
Mobile tools provide insight into a company's business activity. The analysis uses dynamic indicators. You can get them from the reporting. Financial stability is determined based on ratios. Verification of mobile assets is carried out using a reporting audit.
Indicators of current assets play an important role in the following circumstances:
- The need for credit . Working capital is one of the determining factors in lending. The bank, especially before issuing large funds, checks all financial indicators of the enterprise. Mobile assets can be used to secure loan obligations.
- Tax audits . Having records of current assets facilitates interaction with tax authorities. These indicators will help justify the occurrence of seasonal losses. Mobile devices often cause discrepancies between VAT deductions and VAT accruals.
Current assets are required by the enterprise manager. Indicators are the basis for drawing up a company development plan. They allow you to timely track all financial problems in the organization.
Current assets ratio
The coefficient allows you to determine the number of transfers of mobile assets into cash and vice versa. It looks like this:
Cob = B / CCOA
The following values appear in the formula:
- Cob is the coefficient that you want to find out;
- B – revenue received during the year or other period;
- CCOA is the average cost of mobile devices for the analyzed time.
It is also advisable to calculate the average cost to obtain accurate results. The calculation is carried out using the following formula:
SSOA = (SOA0 / 2 + SOA1 + SOA / 2) / (N – 1)
The formula includes the following indicators:
- SOA0 is the working balance at the beginning of the time being analyzed;
- SOA1, SOA – balance at the end of similar periods of time under consideration;
- N – number of similar intervals;
- SSOA is the average price of mobile assets that needs to be calculated.
This method takes into account seasonal changes in balances, as well as the impact of external and internal circumstances.
ATTENTION! The resulting coefficient reflects only the general condition of the enterprise. More accurate values can only be obtained by having additional data: dynamics of coefficients, comparison with standard indicators.
Calculation example
The company received revenue for the year in the amount of 1,500,000 rubles. The average cost of mobile assets is 100,000 rubles. To calculate, you need to divide revenue by average cost. As a result, we get a coefficient of 15.
Calculation of turnover in days
Turnover in days provides more information. To calculate, you can use the following formula:
Ob = K_dn / Kob
The formula uses the following values:
- About – turnover expressed in days;
- K_day – number of days in the analyzed period;
- Cob is the turnover ratio, the formula for calculating it is given above.
The obtained indicators should be compared with standard values. The latter can be installed by the enterprise independently. They are determined based on the following factors: contractual terms with partners, features of the field in which the company operates, territorial location.
Example
Let's look at the data from the example given earlier. The analyzed period is 300 days. The number of days is divided by a factor of 15. As a result, we get a turnover ratio of 20.
What to do with the obtained coefficients?
The profitability of an enterprise is indicated by a coefficient exceeding one. The higher this value is, the greater the profitability of the company. You can increase the coefficients using the following measures:
- Increasing the competitiveness of products (improving quality, attractive design, expanding the sales market).
- Reducing product production time.
- Sales optimization.
To improve performance, it is important to carry out work at all stages of the enterprise’s activities. The manager's task is to increase the coefficient to the maximum. It is important to determine the value annually and compare it with last year’s indicators. Tracking dynamics provides objective data on the development of the company. Ratios can also be compared to industry averages of interest.
Types of balance sheets
Let's look at all types of balance sheets with a brief description of the document:
- Balance of income and expenses. It is a document of a financial nature that is created for a year or quarter. The purpose of its formation is the consistency of the movement of funds, the ability to make a forecast about the development of the company. Using this document, you can track the financial relationship of the company with its creditors. It includes the calculation of income and expenses, tax payments, and the creation of funds.
- Gross balance. This document is distinguished by the presence of regulatory articles. It is needed to conduct scientific research and improve balance functions.
- Net. There are no regulatory clauses in this document. Such a balance is needed to establish the real value of the company's property.
- Introductory BB. This balance is formed immediately after the company is registered. The document contains a minimum of information, since the company is just starting to operate. Assets indicate the composition of available property. The liability serves to reflect the sources of capital and property formation. As a rule, before creating such a BB, you need to perform an inventory.
- Final BB. It is a reporting paper on the financial performance of the company for a specific period. It is drawn up on the basis of accounting information that has been previously verified.
- Consolidated BB. Represents consolidated reporting on the work and financial results of parent and subsidiary entities. This is common reporting for several interconnected organizations. A BB of this type does not include mutual turnover of subsidiary entities.
- Liquidation BB. This is a reporting BB from which you can obtain information about the property status of the company as of the date of completion of its activities. Displays the amount and sources of funds, the status of settlements after the end of the liquidation period.
- Reverse BB. This document sets out information about the movement of property over a certain time. It contains information on turnover for the reporting period and fund balances. Such a BB is an intermediate paper used in the formation of the initial, liquidation and closing balance sheet.
- Preliminary BB. The document is drawn up in advance for the end of the reporting period, taking into account predicted corrections. The compilation involves already existing and forecast information about operations.
- Trial BB. Needed to check the accuracy of money accounting.
- Intermediate. Formed before the end of the year.
- Interim liquidation. The paper includes data on the structure of the property of the legal entity that is being liquidated. It indicates the requirements from creditors and the results of their satisfaction. Issued by a commission.
- Dividing. Based on this paper, the legal entity is divided. The balance records the fact that the rights of one legal entity are distributed among several entities. The document contains information about the succession of obligations of the reorganized legal entity.
- Baldovy. The document records the company's property and the sources of its appearance on a given date. It is formed based on the calculation of account balances.
- Consolidated. It is issued through the association of BB of persons who are connected. Such documents are usually created by holding companies.
- Consolidated. Formalized through the combination of different closing balances. Such balances are compiled by ministries and statements.
At the moment, commercial firms use mainly net balance sheets.
Mobile asset structure
The structure of current assets is the ratio between the amount of current assets and fixed assets. Its formation depends on the following factors:
- Product liquidity.
- Taking into account existing risks.
- Type of activity of the enterprise.
Let's look at an example. The company is engaged in specifying legal services. Their execution does not require equipment or other material objects. Therefore, mobile assets will consist mainly of accounts receivable.
IMPORTANT! Standards for accounts receivable are determined depending on the size of accounts payable.
What's the result? Mobile assets are constantly changing. These are dynamic indicators that require regular calculations. Ratios respond immediately to external and internal changes. They allow you to track the efficiency of the enterprise at the moment of interest. The formulas for calculating them are quite simple. Current assets have different structures determined by the policies and activities of the enterprise. In one company the majority will be debt, in another it will be equipment. They are of interest not only to the manager, but also to banks and tax authorities.
Balance Sheet Classification
BBs are classified according to characteristics. Let's look at these features and the type of document:
- According to the formation method. This is a balance BB, which is formed based on account balances. This is also a balance sheet balance sheet, which includes information about the movement of money during the reporting period.
- By frequency of creation. BB can be created at different intervals: once a year, a month, a quarter. The introductory document is drawn up after the registration of the company, the final document is a report for a specific period of time. The annual BB is the basis for creating accounts in the new year. The interim document is a condensed form of the annual BB. A sanitized balance sheet is needed if there is a threat of bankruptcy. A liquidation BB is needed upon completion of the activities of a legal entity.
- According to the degree of readiness. The preliminary document is prepared in advance. In this case, predicted adjustments are taken into account. The final BB is formed based on real information.
- According to the degree of consolidation. An individual BB records the results of the economic activities of one company. The consolidated document combines the values that arise through the summation of balance sheet items of several institutions. A consolidated BB is needed to combine the balance sheets of independent companies that are interconnected. A separating BB is created when one organization is divided into several legal entities.
- According to sources. BBs are divided into types depending on the sources on which they are compiled. There are inventory balances drawn up on the basis of information about the inventory of property. There are also book BBs drawn up on the basis of accounting.
- By including regulatory articles in the document. The gross balance sheet includes items that regulate the values of other items. For example, this is depreciation of intangible assets. This is also a net balance created on the basis of gross balance information. Its main difference is the absence of regulatory articles.
BB is a fairly broad concept. A balance sheet can mean a variety of documents.