Internal financial control is a monitoring process through which control is exercised over the activities of an institution, as well as the rational and efficient use of budget resources, compliance with legislation in the field of accounting and reporting. The rules for implementing internal financial control must be enshrined in the accounting policies of the enterprise. The procedure for conducting and organizing internal financial control is formalized by a separate order at the enterprise.
How internal financial control is carried out at an enterprise
Internal financial control can be carried out in the following ways:
- A special structural unit is created in the institution or the position of an auditor is introduced, who reports to the head of the enterprise;
- A permanent commission is created in the institution, which will be entrusted with the implementation of this control;
- The implementation of internal financial control is entrusted to employees of the institution’s structural divisions (for example, employees of financial and personnel services). In such a situation, internal control will be carried out within the framework of preliminary and ongoing control activities.
Which method of internal financial control to choose depends directly on the amount of work at the enterprise. Is it possible for the enterprise to introduce additional rates for the implementation of this control or to assign these responsibilities to existing departments?
How is the financial audit carried out?
During audit control, officials examine the legality of business transactions and the reliability of budget reporting. They can:
- receive information about the organization and results of the financial audit;
- visit the premises and territories occupied by the facility;
- involve independent experts.
For 2022, an internal financial audit is most often carried out by a commission consisting of the heads of structural divisions of the institution that carry out budget procedures. This approach has disadvantages.
When conducting a VFA, they try to eliminate as much as possible conditions that threaten the impartiality of the auditor. Inspector:
- should not be associated with accounting;
- must not enter into a conflict of interest;
- have a relationship with the subjects of control.
It is advisable to involve external experts and prevent third parties from interfering in the financial audit of budgetary institutions.
The auditor and experts comply with legal requirements and carry out control strictly according to the approved plan. At the end, they announce the results to the site manager.
The work goes on in the background and does not interfere with the work of the institution. The audit is not punitive in nature, otherwise it would lead to “internecine wars” among the management of the institution.
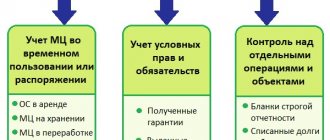
Types of internal financial control
Internal financial control includes certain types, which we will consider in table form:
| Type of control | Description |
| Preliminary control | It is carried out before the start of a business transaction in order to understand the feasibility of its implementation. |
| Current control | It consists of a daily analysis of compliance with all measures for using the budget, as well as the preparation and maintenance of financial statements. The rational and effective expenditure of funds to achieve the set goals, objectives and obtain positive indicators is also analyzed. |
| Subsequent control | Control is carried out at the final stage of a business transaction. What does it mean to analyze and verify accounting documentation and reporting, conduct an inventory and other procedures that are necessary to carry out control at the final stage. |
Preliminary and ongoing control can be carried out by the enterprise employees themselves within the framework of their job duties. But subsequent control is carried out either by the control department, namely by the auditor or by the created commission for internal control.
Requirements for the internal financial control plan
Internal financial control can also be divided into two types, namely:
- Planned financial control - this control contains a certain list of operations for the future period, which will necessarily have to be implemented in the future;
- Unscheduled financial control - this control arises according to the situation, in order to make timely adjustments for the effective implementation of the operation, as well as at the time of the operation, when the predictive results are not realized.
Both types of internal control are suitable for both budgetary organizations and private firms.
The structure of the internal control plan is not uniform; when drawn up, it differs for different statuses of a legal entity, with different types of activities, as well as with different scales. But there are general signs by which an internal financial control plan is drawn up and which are indicated in the document:
- Duration of internal financial control;
- A list of the main activities that are planned to be carried out during internal financial control is indicated;
- What objects are subject to inspection;
- Appointment of persons responsible for conducting the inspection.
In certain cases, an internal financial control card is additionally drawn up in addition to the internal financial control board.
What changed
From September 16, 2022, internal financial control bodies can conduct surveys and counter-inspections on a desk basis. That is, at your location.
They were also allowed to conduct routine surveys to ensure compliance with the terms of contracts, agreements and agreements - when the source of funding was budget funds or funds provided from it.
The Treasury also received the right to conduct scheduled inspections regarding the provision and use of budget loans for infrastructure projects (the President of the Russian Federation instructed them to issue them to the regions). Moreover, it will put these activities and the corresponding civil transactions into the draft control plan as a priority as the first priority.
And from January 1, 2022, controllers can, without assigning a counter-inspection, send requests to organizations and officials that are not the object of control. This way they can request information, documents and materials regarding controlled persons, as well as gain access to information systems.
Also Decree No. 1504:
- supplemented the list of typical topics for planned control activities (including the survey of compliance with the terms of contracts/agreements/agreements financed from the budget or through public law education);
- clarified the procedure for conducting surveys;
- clarified the frequency of appointment by the Federal Treasury of control measures in relation to one object of control and one topic of the control measure.
Internal financial control map
The internal financial control chart is mainly used in government organizations. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in paragraph 16 of section 1 of the Methodological recommendations for the implementation of internal financial control, approved. Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 09/07/2016 No. 356 establishes that this document is preparatory regarding the implementation of internal financial control measures in organizations that are the main managers of budget funds. In this document, the Ministry of Finance recommends entering complete data regarding officials who take part in financial control and are responsible for performing specific audit procedures within one enterprise.
The internal financial control map generated by the Ministry of Finance is intended only for those enterprises that participate in the use of budget funds and is included in Appendix No. 2 to the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 02-11-05/932.
There is also another approach to using the internal financial control map, namely when it is the main internal instruction of the enterprise, on the basis of which all supervisory financial audits are carried out. This conclusion can be made after studying clause 12 of the rules for the implementation by the main managers of budgetary means of internal control, introduced by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of March 17, 2014 No. 193.
The structure and details of the form of the two types of internal financial control cards are almost the same.
It can be concluded that both forms fully comply with the objectives of financial control planning. They can also be either supporting documents or fundamental documents. That is, when implementing internal financial control, a form from both the Ministry of Finance and one created within a certain department can be used.
We organize internal control in the institution
Not much attention is paid to the provisions on internal control in regulations. This material will help you correctly compose this important document.
Internal control - what is it?
One of the important conditions for ensuring the efficient use of funds, labor and material resources of an institution is to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of financial and economic control. The system of internal financial and economic control in an institution includes: – legal regulation of the rights, duties and responsibilities of officials; – subjects, that is, officials exercising control; – objects of control activities; – types, forms and methods of internal financial and economic control; – purposeful management of internal financial and economic control; – planning activities in the field of internal control. When organizing internal control in an institution, you should be guided by the following standards: – Budget Code of the Russian Federation; – Tax Code of the Russian Federation; – Labor Code of the Russian Federation; – Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting”; – local regulations. You also need to pay attention to industry and departmental instructions and analyze current practice.
Main goals
The main tasks of internal control include: – control (verification) of compliance in the institution with federal laws, regulations and orders of the Government of the Russian Federation, legal acts of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal legal acts; – execution of orders and instructions of the head of the institution; – legality of cash transactions in the institution; – organizing accounting and ensuring the safety of property in the institution; – establishing compliance of ongoing operations with regulations and the powers of employees; – identifying intra-economic reserves and taking measures to use them in the interests of ensuring the activities of the institution; – establishing the compliance of ongoing financial transactions in terms of financial and economic activities and their reflection in budget accounting; – accuracy and completeness of accounting documentation; – timely preparation of reliable financial statements; – prevention of errors and distortions in accounting; – studying the causes of shortcomings and violations in financial and economic activities, taking effective measures to eliminate them, prevent and timely compensate for material damage caused by responsible persons; – studying the experience of practical application in the institution of existing regulations, instructions and other legal acts that define the norms and procedure for financial and material support, in order to improve them.
Sections of the Regulations on Internal Control
The organization of internal control, management of control and audit work and responsibility for its condition are determined in the Regulations on internal control in the institution. The following sections may be included in this document. 1. Goals, objectives and principles of internal control. This section should indicate the regulatory documents applied within the framework of these activities, as well as their goals and objectives, respectively. 2. The procedure for organizing internal control. That is, indicate the objects of control, the schedule of activities, and the procedure for their execution. 3. Rights and obligations of controlling and controlled persons. In this section, it is necessary to determine the composition of the commission for the implementation of internal control, the division of powers, etc. 4. Responsibility of the parties for compliance with the provisions on internal control. 5. Assessment of the effectiveness of the internal control system in the institution. The assessment is carried out by subjects of internal control and is considered at special meetings held by the head of the institution. 6. Other necessary sections. Officials charged with organizing internal financial control in an institution must review the materials of audits and inspections of external regulatory bodies and take measures to timely eliminate identified violations and shortcomings, improve the quality and efficiency of control. The commission needs to consider the results of the financial and economic activities of the institution and develop proposals for its improvement. It is also necessary to take the necessary measures to strengthen cash, planning, contractual and staff discipline, compliance with the law, prevention and suppression of mismanagement, negligence, waste and abuse in the expenditure of funds and material assets. Particular attention must be paid to checking the organization of procurement for state (municipal) needs in the institution.
Checking financial activities
Let us also note this important point. Activities carried out within the framework of internal financial control must be interdependent and consistent. First, the following must be checked: – financial planning documents (drawing up estimates, staffing schedules, tariffs, etc.); – the procedure for calculating wages, assigning pensions and benefits (the presence of provisions on remuneration, orders for the hiring, transfer and dismissal of employees, orders for the creation of a commission for the Social Insurance Fund, etc.); – other local documents necessary for carrying out financial and economic activities in the institution. And later, after financial and economic transactions are completed, subsequent financial control of the documentation is carried out. For example, they check cash transactions, the accuracy of transactions carried out on budgetary and extra-budgetary personal accounts, settlements with accountable persons, suppliers and customers, the completeness of the capitalization of inventories, finished products, the correctness of accounting and disposal of fixed assets, repair work, etc. .
One of the important areas is document verification
In order to streamline the process of drawing up documents and reflecting data in them, we can advise: – create a schedule of the institution’s document flow (possibly as an appendix to the accounting policy); – sequentially number primary documents of each type during the reporting period (this is also necessary to ensure the search for documents if necessary and to identify missing documents); – cancel primary and supporting documents in specified cases (this is necessary to avoid their reuse); – bind documents into folders at the end of the reporting period; – organize an archive; – hand over folders with documents to the archive after the expiration of the period for operational storage of documents established by the organization’s document flow schedule; – prepare primary documents in a timely manner. In accordance with the requirements, primary documents in an institution must: – be drawn up at the time of business transactions or immediately after their completion, otherwise the likelihood of erroneous entries in the primary document increases. In addition, the transaction may not be recorded at all; – contain the mandatory details established by the Accounting Law; – comply with standard unified forms, if any; – comply with the forms of documents described in the accounting policies of the organization (in the case where the forms of documents are established by the accounting policies of the institution); >|Everyone who subscribes to the magazine for 2012 will have access to the “Accounting Policy 2012” service www.budgetnik.ru).|< - in addition, accounting certificates containing the rationale for corrections in cases where corrections are made to the accounting records , special calculations, must be stated simply and clearly to avoid ambiguous interpretation.
Registration of audits and inspections
Based on the results of the event, a corresponding act is drawn up. It should reflect: – the inspection program approved by order of the head of the institution; – the nature and state of accounting and reporting systems; – types, methods and techniques, methods used when conducting inspections; – analysis of compliance with legislative and regulatory acts of the Russian Federation; – conclusions about the results of internal control activities; – the extent of the material damage caused, other consequences of the violations committed, as well as the officials responsible; – a description of the measures taken and a list of measures to eliminate shortcomings and violations identified during subsequent monitoring, recommendations for avoiding possible errors in further work. When including identified deficiencies, violations and abuses in the act, it is necessary to indicate which regulations were violated, and original documents confirming the accuracy of the entries made in the act. For example, if an incoming cash order (when receiving an amount from the bank to the cash desk) indicates an amount that does not correspond to the amount on the bank statement, then the act should indicate the number, date, amount of the cash register, the number of the sheet of the cash book, the date of the bank statement, the amount written off from a personal account. Employees of the institution who have committed shortcomings, distortions and violations are required to submit written explanations to the head of the institution on issues related to the results of the control. Only on the basis of complete and reliable information can a manager take adequate measures.
The article was published in the journal “Accounting in Budgetary Institutions” No. 11, November 2011.
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
Features of the internal financial control plan in private companies
The plan is considered the main document when carrying out a business transaction. This document sets out the sequence of activities that are necessary to perform financial control. The plan is drawn up in accordance with the specifics of business processes that are relevant only to a specific enterprise.
The internal financial control plan for private companies must necessarily include the following information:
- Name of the object of financial audit;
- What is the purpose of the audit;
- Duration of financial audit;
- What period of time is subject to verification;
- What indicators need to be checked;
- Information about the employees who will be responsible for conducting the inspection.
Depending on the purpose of the internal financial control audit, the plan may be further supplemented with the necessary information.
Why is an internal audit needed?
The key role of internal financial audit in the budget process of the main manager of budget funds is to assess the reliability of the organization’s control system, the reliability of reporting, the economy and efficiency of spending budget funds. Identified risks and deviations are analyzed in all areas of activity of the audited organization. Based on the results of control, recommendations are developed for conducting financial and economic activities.
The list of inspection persons is appointed by the head of the institution. It is allowed to appoint persons from third-party organizations responsible for financial control.
IMPORTANT!
Officials entrusted with the control function are responsible for the completeness and reliability of the audit report and the quality of the recommendations developed.
According to the rules, a financial audit of budgetary institutions is carried out for 45 calendar days (clause 1 of Appendix 2 to Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 143n dated September 21, 2015).
Suspension of an audit is allowed in the following cases:
- if primary accounting documents are missing or their condition is unsatisfactory - for the period necessary to restore these documents;
- when there are circumstances that prevent the inspection - for the period of elimination of these circumstances.
Features of internal financial control board for government organizations
The most important feature of the internal control plan is that the structure of this document is determined at the level of regulations, as well as departmental orders.
The internal financial control plan for government organizations should contain the following information:
- Topics of control activities;
- Objects of control measures that are subject to inspection;
- What types of inspection will be carried out;
- For what period will the inspection be carried out?
- What are the deadlines for the inspection?
Where are the rules described?
Managers of budget funds, administrators of revenues and sources of financing the budget deficit conduct internal financial audits. The requirement is established by Article 160.2-1 of the Budget Code. By order of the Ministry of Finance No. 143n dated September 21, 2015, structural divisions of the Ministry of Finance, federal government institutions, budgetary organizations executing government contracts, financed from the federal budget, are subject to mandatory financial audit. Let's consider a simplified internal audit in a budgetary institution and the conditions under which it is carried out. Features and requirements for the implementation of financial audit are determined by the following regulations:
- BC RF (Article 157, Article 160.2-1, Article 165, etc.).
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 193.
- Orders of the Ministry of Finance No. 143n dated September 21, 2015, No. 356 dated September 7, 2016, No. 822 dated December 30, 2016.
- Federal standard (Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 237n dated December 18, 2019).
FAQ
Question No. 1 What is internal financial control?
Answer: there is no such definition of what internal financial control is. But if we analyze all his actions, we can conclude that this is a monitoring process through which control is exercised over the activities of the institution, as well as the rational and efficient use of budget resources, compliance with legislation in the field of accounting and reporting.
Question No. 2 What are the types of internal financial control?
Answer: Internal financial control can be divided into two types - planned, which is planned in advance to check certain operations, and sudden, which arises in the process of conducting a business transaction that needs to be changed or edited for the effective implementation of the operation.
BUSINESS ACTIVITIES AND INTERNAL CONTROL
The facts of economic activity are carried out in the organization constantly and continuously: goods are shipped for sale, finished products are produced, material assets are received at the warehouse, money is received in the current account and in the cash register of the organization, money is spent to pay sellers for goods (works, services) purchased from them ), issuance of wages to employees, etc.
Article 19 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ (as amended on May 23, 2016) “On Accounting” obliges internal control of the facts of economic activity . In addition to this, the company is obliged to exercise internal control over accounting and preparation of accounting (financial) statements if its statements are subject to mandatory audit (except in cases where the head of the company has assumed the responsibility for maintaining accounting records). Internal control procedures must be documented.
The main requirements for reporting and the implementation of which are verified by internal controllers:
- reliability - reporting should reflect real business transactions that can be easily verified and documented;
- completeness - reporting must contain all the necessary data for stakeholders and include relevant comments;
- neutrality - reporting should not reflect the interests of any persons;
- continuity - the sequence of application of reporting forms and their content from one reporting period to another.
The company itself decides how to organize internal control:
- create an internal control, internal audit, and audit department;
- enter into an agreement with a third party.
IT IS IMPORTANT
When choosing a control method, you need to be guided by the principle of reasonableness: labor costs in carrying out control functions must be comparable to the result obtained.