Why are tax registers needed?
Tax accounting registers serve to summarize the information necessary to calculate certain taxes.
They, firstly, help tax authorities monitor the completeness of tax payments by taxpayers, and secondly, allow taxpayers themselves to check the correctness of their calculations for a particular type of tax liability and simplify the generation of tax reports. IMPORTANT! Despite the fact that tax legislation obliges taxpayers to create and maintain such registers, their forms are not approved by law, and therefore each enterprise (or individual entrepreneur) is obliged to independently develop the structures of the applicable tax registers, and it is very desirable to approve them with accounting policies.
Tax registers must meet the following general requirements:
- continuous generation of tax accounting data in chronological order;
- implementation of full disclosure of the procedure for forming the tax base;
- ease of perception of information reflected in the register and ease of filling it out;
- maintenance in paper or electronic form.
For more information on how to maintain tax registers, see the article “Maintaining analytical tax accounting registers (forms)” .
As for tax registers for personal income tax, Art. 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes its own specific criteria for them. Such a register should include:
- information that allows you to uniquely identify the taxpayer;
- his status;
- types of income paid to him and their amounts;
- types and amounts of deductions provided;
- amounts that reduce the tax base;
- dates of income payment, withholding and payment of personal income tax.
For information on the requirements for personal income tax registers, read the article “How is the personal income tax register maintained?” .
Responsibility for the formation of tax registers lies with the employees who compile and sign them. They are also responsible for the safety of these documents and for ensuring that unauthorized persons cannot access them. Only a responsible employee can make corrective entries in the register. At the same time, he is obliged to certify the adjusting entry with his signature, indicate the date the adjustment was made and provide appropriate explanations.
For an example of a tax register for 6-NDFL, see the typical situation from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Formation of the register
The company has the right to decide for itself how it will account for income and the personal income tax calculated from it, and what accounting forms will be used for this. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines what needs to be reflected in tax registers. The necessary information to be included in the register is set out in paragraph 1 of Article 230:
- Identification data for each individual;
- Types of paid income;
- Provided personal income tax benefits that reduce the base for calculating the tax;
- Amounts of amounts paid;
- Dates for issuing amounts to staff;
- The amount of calculated tax;
- Dates of its retention and transfer;
- Information about payment documentation confirming payment.
This information is provided for each employee.
The tax register form for personal income tax is developed in order to ensure convenient work with information and clarity of its presentation. In this case, the form includes the necessary information required by the tax authorities.
Qualities that the developed register form must have:
- Simplicity – there should be no confusion in presenting employee data;
- Visualization - the data should be easy to read, the form should allow you to quickly transfer the necessary information to 2-NDFL;
- Brevity - unnecessary information is not needed, it does not carry any significance and creates difficulty in perceiving the information.
The register form must take into account the specifics of the organization’s activities and the types of income paid, therefore a universal register form has not been approved. Each enterprise draws up a document that will include the necessary information and have the above properties.
For convenience, a company can create several tax registers to fully reflect the necessary data for personal income tax accounting purposes. Tax legislation does not limit employers in this matter. You can use a separate register for each type of income or each individual.
Companies often take the previously valid 1-NDFL certificate form as a basis, using an example of which to prepare a suitable register.
What is form 6-NDFL
From 01/01/2016, tax agents are required to fill out a reporting form - 6-NDFL. Since 2022, this form has been radically updated by order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 15, 2020 No. ED-7-11/ (in the same document you can find the procedure for filling it out).
ConsultantPlus experts in their review spoke in detail about the main changes in the 6-NDFL report from 2022. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial demo access for free.
6-NDFL current form can be found here.
What are the features of this report:
- 6-NDFL is filled out not in the context of data for each taxpayer, but for all individual taxpayers to whom income was paid by the tax agent as a whole (clause 1 of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Data on income withheld and paid to individuals is recorded on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year (clause 1 of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Delivery frequency is quarterly.
- The basis for filling out the form is tax accounting data contained in the registers (Clause 1, Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For information on where and how to fill out this form online, read the article “Is it possible to fill out form 6-NDFL online?” .
Basic settings for personal income tax accounting
Set up payroll options
On the 1C 8.3 platform there is a specialized program for salary accounting - 1C Salary and HR Management (ZUP). It can take into account complex payroll schemes and automatically calculate sick leave and other benefits. In a word, 1C 8.3 ZUP has everything for accounting wages and personnel in medium and large enterprises. If you have a small organization and the number of employees is less than 60, then the 1C 8.3 Accounting program is quite suitable for you to track salaries.
Before you start calculating salaries in 1C 8.3 Accounting, you must specify in the general settings which program you will use to calculate salaries. To do this, go to the “Administration” section (1) and click on the “Accounting Settings” link (2). The options window will open.
In the window that opens, click on the “Salary Settings” link (3). The settings window will open.
In the settings window, check the “In this program” button (4) if you will keep records in 1C 8.3 Accounting. If you plan to keep track of salaries in 1C 8.3 ZUP, then check the “In an external program” checkbox (5).
Set up accrual accounting
If you chose the “In this program” accounting method, you must specify additional settings. To do this, in the salary settings window, click on the “Salary calculation” link (1) and configure the following parameters:
- Keep records of sick leave, vacations and executive documents
(2). Check the box if you will have these charges; - Salary calculation for separate divisions
(3). Check this box if you have separate units; - Automatically recalculate the “Payroll” document
(4). Check the box if you want taxes to be recalculated in the “Payroll” document immediately when changes are made.
Set up payroll accounting methods
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with another salary setting and, if necessary, make changes to it. We are talking about the procedure for reflecting wages in accounting accounts.
As you know, organizations with different specific activities accrue salaries to different accounting accounts. Trade organizations use account 44 “Sales Expenses”; in manufacturing companies, salary calculations are reflected in the following accounts:
- 20 “Main production”;
- 23 “Auxiliary production”;
- 25 “General production expenses”;
- 26 “General business expenses”.
Within the same enterprise, different accounting methods can be used simultaneously for different groups of employees, divisions and product groups.
To set up accounting methods, click in the salary settings window on the link “Reflection in accounting” (1) and then on “Salary accounting methods” (2). A directory of accounting methods will open.
The default directory contains several methods of accounting for salaries; add new ones if necessary. To do this, click the “Create” button (3). A window will open to create a new method.
- Name of the new method (4);
- Accounting account (5);
- Nomenclature group (6);
- Cost item (7);
- To take into account consumption under the simplified tax system or not (8);
- Cost item for UTII (9).
To save the new method, click the “Save and close” button (10). A new method has been created, now it can be used when calculating salaries, we’ll tell you how later.
What data is needed to generate 6-NDFL
In order to understand how to create a tax register for generating this report, let’s consider what information the 6-NDFL form contains and analyze its composition.
6-NDFL includes:
- title page;
- Section 1 entitled “Data on Tax Agent Obligations”;
- Section 2, called “Calculation of calculated, withheld and transferred amounts of personal income tax.”
To fill out the title form you will need:
- Details of the tax agent (his name, INN, KPP).
- Details of the reorganized organization and forms of its reorganization (for legal successors).
- The period for which the report is prepared.
- Code of the tax office to which the calculation must be sent (for organizations - to the Federal Tax Service at their location, for individual entrepreneurs - at the place of residence or at the place of activity (for impostors and those individual entrepreneurs who work on a patent)).
- OKTMO code in accordance with the All-Russian Classifier of Municipal Territories OK 033-2013 (Order of Rosstandart dated June 14, 2013 No. 159-st). Organizations put down the code of the territory in which they are located, and individual entrepreneurs - the one in which they live or carry out activities.
To complete section 1 we will need:
- deadline for payment of personal income tax (clause 6 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the amount of withheld tax from individuals to be transferred on the date indicated above.
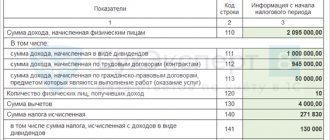
To complete section 2 we need:
- the amount of personal income tax rates at which the tax is calculated;
- the amount of income accrued to all individuals;
- amounts of personal income tax deductions;
- the amount of tax calculated and withheld;
- the number of individuals who received income from the tax agent.
Having dealt with the list of information that we will need to generate the 6-NDFL report, we will move on to developing a tax register form for it.
“Practical problems on personal income tax with solutions” will help you better understand the procedure for calculating personal income tax .
An example of filling out a report on Form 6-NDFL for the year can be found here.
If the basis is form No. 1-NDFL
Let’s say right away: some mandatory details do not appear in Form No. 1-NDFL (see Table 1). Therefore, they must be provided for in the new register.
Among such mandatory disclosures are the date of transfer of personal income tax and the details of the payment order. Please note: from the new year, the amount of tax transferred to the budget must be the sum of the total amount of tax paid indicated in the new tax registers for that date. Therefore, it is better to provide for all facts that could affect the amount of personal income tax in the “payment” in the new form of the tax register.
Attention
Since January 2011, the amount of personal income tax transferred to the budget must be the sum of the total amount of tax indicated in the new tax registers as of that date. Therefore, it is better to provide for all facts that could affect the amount of personal income tax in the “payment” in the new form of the tax register.
In addition, in Form No. 1-NDFL there was no place to reflect property and social deductions provided by the employer. Let us clarify: an employee can take advantage of a property deduction at his place of work only after confirming his right to it with the tax office. Meanwhile, its amount, as well as the amount of social deduction provided by the employer in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 219 of the Tax Code, may affect the payment of tax to the budget of both the personal income tax payer himself and other payers working in the company. After all, since the new year, such “offset” has been enshrined in the Tax Code (Clause 1, Article 231 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Form No. 1-NDFL also does not provide lines for reflecting income taxed at a rate of 15 percent (dividends received by non-residents). The line to reflect income previously taxed at a rate of 6 percent will have to be amended: replace the rate with the current rate of 9 percent (dividends received by residents).
And on the contrary, some information from Form No. 1-NDFL for the new tax register will be useless (see Table 2). We are talking about section 7 “Information on income, taxation of which is carried out by tax authorities,” which indicates information on income paid to individuals when purchasing property from them, to entrepreneurs or notaries. Let us remind you: these persons independently calculate and pay personal income tax, in this case the company is not a tax agent (clauses 1, 2 of Article 227, subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the new register, it is not necessary to note the numbers and dates of certificates issued in Form No. 2-NDFL, as well as the amount of debt transferred for collection to the tax office (Section 9 “Information on the submission of certificates” of Form No. 1-NDFL).
It makes sense to shorten section 8 “Results of tax recalculation for previous tax periods.” In essence, you can limit yourself to a couple of lines, for example, “Debt owed by the taxpayer at the beginning of the tax period” and “Excessive amount of personal income tax withheld by the tax agent at the beginning of the tax period.”
Pay attention to the codes and sizes of standard tax deductions in form No. 1-NDFL! Some of them are no longer valid:
deduction code 101 in the amount of 600 rubles now corresponds to deduction code 108 in the amount of 1000 rubles;
deduction code 102 in the amount of 1200 rubles was replaced by deduction codes 110 (111) in the amount of 2000 rubles;
instead of the previous deduction code 106 in the amount of 1200 rubles, deduction code 109 is used in the amount of 2000 rubles;
finally, deduction code 107 in the amount of 2400 rubles was replaced by deduction code 112 (113) in the amount of 4000 rubles.
How to create a tax register for personal income tax accounting
If the taxpayer already has and uses registers for filling out 2-NDFL, no one is stopping him from using them to generate the 6-NDFL calculation.
The register for filling out 2-NDFL has the following structure:
| Accounting register information | Comments on filling |
| Taxpayer identification information | Here is a list of information about current employees:
|
| List of income | Each type of income must have its own field in which a special digital code corresponding to the type of income must be entered. The codes are taken from the Federal Tax Service order dated September 10, 2015 No. MMB-7-11/ It is not necessary to report data on non-taxable personal income tax. Income subject to personal income tax, which has tax-free limits, is recorded in the register on a general basis, since it can accumulate throughout the year. |
| List of deductions | Deductions are recorded in the register with the corresponding codes. For the list of codes, see the order of the Federal Tax Service dated September 10, 2015 No. MMB-7-11/387 |
| Amounts of income | We indicate the amounts accrued before tax and reduction for deductions |
| Income payment dates | This field indicates the date of payment of income in accordance with the provisions of Art. 223 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Taxpayer status | This field indicates what type of person the taxpayer belongs to based on his residence in the Russian Federation |
| Personal income tax withholding date | We indicate the day of actual tax deduction |
| Date of personal income tax transfer | Fill out in accordance with payment documents |
| Payment document details | We indicate the number, date and amount of the payment slip for personal income tax payment |
| Personal income tax amount | We fix the amount of calculated and withheld tax |
You can download the register form formed in the structure discussed above from the link below:
Frequency of preparation of the tax accounting register for personal income tax
A special place in the form of the tax accounting register for personal income tax is occupied by data on income on which tax is calculated. They are formed in the document by types and deductions with the assignment of the corresponding code.
When assigning a code, you must refer to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia “On approval of codes for types of income and deductions” dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] , where each type of income is assigned a corresponding code. For example, when indicating a salary, code 2,000 is used, and if a deduction is provided for the first child under 18 years of age, code 126 is indicated.
A separate register is maintained for each employee. It indicates all payments made, even if the tax percentage rate differs (from 13 to 35%). But they are all reflected separately, for example in different sections of the document. A similar system is used in 2-NDFL certificates, in which each rate has its own section.
IMPORTANT! From 2022, information from the 2-NDFL certificate is submitted to the Federal Tax Service quarterly as part of the updated 6-NDFL calculation. See details here.
The frequency of registration of a new personal income tax register is established by the taxpayer. As a rule, a personal income tax register for an employee is opened every year so that income to which a 13% rate is applied, as well as tax deductions, are reflected in it both monthly and on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year. Income to which other rates apply is sufficient to indicate only monthly.
Income that is not subject to personal income tax may not be included (for example, maternity benefits).
Income, the amount of which is limited when calculating personal income tax, must be indicated in the register to monitor compliance with such a limit. One of such income is material assistance, which will not be subject to personal income tax until its amount reaches RUB 4,000.00. per year (clause 28 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
We compile a tax register for the 6-NDFL report
Due to the features of the 6-NDFL form (we reviewed them earlier), the register created above is not always convenient to use for filling it out. But it’s very simple to create a “personal” register based on it specifically for 6-personal income tax.
We present to you a completed sample tax register for form 6-NDFL. If necessary, you can download it:
EXPLANATIONS from ConsultantPlus: The main thing when filling out the 6-NDFL calculation is to carefully transfer data from the tax registers for personal income tax. Therefore, if tax accounting is in order, then filling out the 6-NDFL calculation will not be difficult... ConsultantPlus experts told us how to fill out the calculation correctly. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Enter tax deduction data for the employee
To correctly calculate personal income tax, it is necessary to enter deductions for children, as well as property and social deductions for each employee in 1C 8.3. To enter deductions, go to the “Salaries and Personnel” section (1) and click on the “Employees” link (2). The employee directory will open.
In the window that opens, click on the desired employee (3). The employee card will open.
In the employee card, click on the link opposite the inscription “Income Tax” (4). A window for setting up deductions will open.
In the window that opens, click on the link “Enter a new application for standard deductions” (5). A window will open for entering a new deduction application.
In the window that opens, click the “Add” button (6), select the desired deduction (7) and click “Post and close” (8). Now, when calculating personal income tax for this employee, the tax deduction will be taken into account.
Results
Requirements for the list of information that must be reflected in the tax register for filling out 6-NDFL are listed in Art. 230 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. A taxpayer can be held liable for failure to maintain a personal income tax register only if the register does not contain the required details, or if the register provided for by the accounting policy is not compiled.
You will find all the nuances of filling out form 6-NDFL in our section “Calculation of 6-NDFL” .
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Create a tax return
To generate a tax return on the income of individuals according to tax registers, go to the “Salaries and Personnel” section (1) and click on the link “2-NDFL for transfer to the Federal Tax Service” (2). A window for generating a declaration will open.
In the window that opens, indicate your organization (3) and click the “Create” button (4). The declaration form will open.
In the declaration form, indicate the year (5) for which you want to generate reports and click the “Fill” button (6). The tabular part will be filled with data from tax accounting registers for personal income tax:
- Employee (7);
- Rate (8);
- Income (9);
- Taxable income (10);
- Tax (11);
- Held(12);
- Listed (13).
To adjust data for an employee, double-click on the desired employee and the 2-NFDL window will open.
In the window that opens, make the necessary changes, for example, fill in the fields “Retained” (14) and “Transferred” (15) and click the “OK” button (16).
To save the declaration, click the “Record” (17) and “Post” (18) buttons. To upload a file for sending to the tax office, click “Upload” (19). Next, print the declaration by clicking the “Print” button (20).
When paying individuals many types of income, the organization must calculate, withhold, and pay personal income tax to the budget. Let's look at how personal income tax accounting is organized in 1C 8.3 Accounting.