Accounting
is a continuous and systematic collection, recording, and interpretation of specific information. If we analyze the issue of accounting in detail, then we are talking about a system that allows you to operate with data regarding all business transactions and obligations expressed in financial terms carried out in business.
Documentary recording of this information is carried out on the principle of permanence and continuity, that is, from the moment of registration of a new company until its complete liquidation, in accordance with current regulations.
Legislative regulation and basic definitions of accounting
Today, accounting is mandatory when conducting business and economic activities, because this provision is enshrined in the domestic legislative framework. The main provisions are set out in the Regulations “On Accounting and Financial Reporting in the Russian Federation”, as well as in the Federal Law “On Accounting” No. 402-FZ, which came into force on January 1, 2013.
All requirements are enshrined at the legislative level and must be complied with without fail throughout the country for representatives of non-banking commercial structures.
Basic Accounting Definitions
To solve the main problems of accounting, you need a whole set of techniques and methods, which together make up the accounting method. This method includes a number of important elements:
- Accounting accounts are an effective way of grouping current liabilities, assets and transactions;
- documentation - a thorough written recording of all completed business activities, which gives legal force to the data displayed in the accounting records;
- valuation is an effective way of expressing funds, as well as their sources, in monetary terms;
- inventory is a regular check of property listed on the balance sheet of an organization, which is carried out by weighing, describing, counting, mutual reconciliation, evaluation of identified funds, and further comparison of the results obtained with accounting data;
- double entry - an interconnected display of business transactions on accounting accounts, in which each operation is simultaneously entered into the debit of one account and the credit of another account for the same amount;
- The balance sheet is one of the main sources of information, as well as a method of economic grouping of various assets of an organization according to the sources of formation, composition, placement, expressed in monetary terms and issued for a certain date or period of time;
- accounting statements - a group of accounting indicators that are reflected in the form of tables and characterize the continuous movement of liabilities, property and financial position for a certain period of time;
- calculation - calculation of the cost of one unit of any product, work, service, expressed in monetary terms, in other words, cost calculation.
Classification of accounting objects
In the most common sense, accounting objects are divided into:
- enterprise property,
- sources of enterprise property
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
The accounting object “enterprise property” is an accounting of all assets of the enterprise:
- fixed assets;
- stocks;
- accounts receivable;
- cash and monetary documents;
- etc.
Accordingly, the accounting object “sources of the enterprise’s property” is an accounting of the enterprise’s liabilities:
- own capital;
- borrowed capital;
- arrived;
- accounts payable;
- etc.
For each of the objects of accounting for assets and liabilities of an enterprise, the corresponding accounting accounts, rules for reflecting operations on objects, rules for documentation, etc. are regulated.
For better accounting at an enterprise, its objects are divided by type of activity. This may be a classification of activities in a general sense, i.e. current, financial and investment activities. Or a classification of specific types of activities that are defined individually in each organization.
For example, for an enterprise of a retail chain of stores, the accounting objects are:
- each store as a separate accounting area;
- general warehouse for storing goods;
- enterprise management apparatus;
- sales and supply department of the enterprise
- transport (logistics) department
- etc.
Finished works on a similar topic
Coursework Types of accounting objects 430 ₽ Abstract Types of accounting objects 260 ₽ Test work Types of accounting objects 230 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
For a manufacturing enterprise, accounting objects can be:
- separate workshops, product manufacturing areas;
- auxiliary areas;
- energy areas;
- warehouses for storing and distributing finished products;
- etc.
For construction organizations, accounting objects are individual construction projects.
Reasons for the need for accounting
The first and most significant reason why it is necessary to keep accounting records of an enterprise according to a generally accepted procedure is that this requirement is enshrined in law. Therefore, there is no choice; if an entrepreneur wants to work, he must conduct his activities according to the letter of the law.
There is no provision in the law that would allow an organization not to keep accounting records, because they are mandatory. If accounting records were never kept, business transactions were not recorded properly, and reports were not submitted to regulatory authorities, then the entrepreneur will be held liable:
- provided that the fiscal authorities have not received information about economic activities within a clearly defined time frame, citizens will be required to pay a fine of 100-300 rubles for each identified case, as well as a 300-500 ruble fine for an official for each case of failure to provide data or delay (according to Article 15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses).
- in case of gross neglect and non-compliance with the rules for maintaining records and providing accounting documentation, as well as the procedure and deadlines for saving accounting documents, the official is obliged to pay a fine of 2000-3000 rubles in accordance with Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses.
Accounting objectives
Accounting allows you to form a complete picture of the dynamics of an organization’s activities and data on its property status. This data is necessary not only for stating facts and tax reporting, but with their help you can make forecasts for the future. Based on this, accounting helps in solving the following tasks of the business manager and owner:
- determination of reserves of all kinds of property assets of the company to maintain its stable financial condition;
- regular and up-to-date submission of objective, structured and accurate economic information to management;
- minimizing risks that can lead to a negative outcome of business activities;
- implementation of the control function (both from the state and from other external contractors).
Since the interests of interested users differ, accounting data cannot satisfy each party in full. The information generated in accounting for external users partially satisfies the needs that are common to all users. Decisions that are made by all stakeholders will require an assessment of the organization's ability to generate cash and other similar assets, as well as the volume and frequency of their receipts. The result of such a check will be a realistic assessment of the company's ability to make payments to the state, employees, investors, suppliers, lenders and contractors.
The purpose of accounting for internal users is to provide management with a complete picture to help them make sound management decisions. Also, the organization's management is fully interested in providing information to external users for control, analysis and proper planning. It is understood that information for external users is generated, including on the basis of information for internal users related to the financial results of operations, the financial position of the organization, and also changes in its financial position.
Accounting objects
The main objects of accounting are considered to be:
- the entrepreneur’s agreements are also obligations;
- property assets owned by a commercial organization;
- transactions that are carried out in the process of doing business.
Property or property assets, in turn, consist of current (for example, money in cash and accounts, inventories of raw materials, accounts receivable) and non-current assets (for example, capital investments, land, fixed assets). The organization's obligations include: wages, bills payable, taxes payable, etc.
Assets, Liabilities and Sources of Funding
Definition 1
Assets are the property or resources of an enterprise that it owns and manages to carry out its activities in order to achieve the goal of making a profit. Considering the principles of Russian accounting, we are talking only about assets that belong to the enterprise as a property.
Liabilities are the debt of an enterprise to its counterparties and creditors, which must be repaid by a certain period of time.
The main difference between these concepts is that assets imply the inflow of funds, and liabilities imply their outflow. Depending on the urgency of circulation, assets and liabilities are classified into short-term, up to 12 months, and long-term, more than a year. The dependence of obligations on ownership divides them into own and borrowed. Assets and liabilities are reflected in the balance sheet of the enterprise.
Finished works on a similar topic
Coursework Objects of accounting 460 ₽ Abstract Objects of accounting 280 ₽ Test work Objects of accounting 230 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Sources of financing the activities of an enterprise are the very first financial resources from which the formation of the enterprise itself begins; they are necessary initially for the creation, and subsequently for its existence and functioning. Subsequently, they are the subject of innovative development and investment.
There are many classifications - we list the main types of sources of financing: external, internal, attracted, borrowed, short-term and long-term. Balances in bank accounts or in the cash register of an enterprise as of a certain date are a monetary form of expression of the company’s financial resources.
Main tasks of accounting
The main and primary task of accounting is the constant formation of up-to-date and reliable information regarding the activities of the organization, as well as the full property status. This accounting information is necessary for a wide range of users: founders, owners of the organization’s property, managers, creditors, members of the organization, investors and other users of financial statements. With proper analysis, the data allows you to solve a whole range of problems:
- identification of internal reserves that are necessary to ensure the financial stability of the company;
- minimizing risks and preventing future negative indicators of the organization’s economic activity;
- control over the movement and availability of obligations, as well as property;
- control of the necessity and feasibility of business operations;
- careful control over compliance with legislation in the process of carrying out activities;
- monitoring compliance of activities with estimates, standards and approved standards;
- control over the use of financial, material and labor resources of the organization.
The concept of accounting objects
Definition 1
The objects of accounting are a set of any accounting elements that take part in the economic activities of any organization.
In the general understanding, the main general unit of accounting (object) is the enterprise itself as a separate participant in entrepreneurial activity.
At each enterprise, accounting is divided into separate objects, which may be different in composition, structure and nature of participation in the process of the organization’s activities.
Fundamental Accounting Principles
The accounting process requires scrupulousness and accuracy, therefore it is based on the following principles:
- The principle of double entry - absolutely all business transactions of an organization must be simultaneously displayed as a debit to one accounting account and a credit to another account for a similar amount.
- The principle of autonomy - each organization must exist as an independent legal entity. Therefore, accounting records the property that directly belongs to a specific enterprise or organization.
- The principle of objectivity lies in the fact that all business transactions must be reflected in accounting, as well as registered at each stage of the process and confirmed by the relevant documentation on the basis of which accounting is carried out.
- The principle of prudence implies extreme caution in making judgments used in making calculations under conditions of uncertainty. This will help avoid future understatements of expenses and liabilities, as well as overstatement of projected income and assets. Strict adherence to the principle of prudence will help prevent excessive inventories and hidden reserves, deliberate understatement of income and assets, or deliberate overstatement of expenses and liabilities.
- The principle of a functioning organization. If an operating organization plans to maintain its position in the market in the future, then it is very important to pay off its own obligations to partners on time.
- Accrual principle - transactions are carefully recorded as they occur, without waiting for payment, and then they will begin to relate to the reporting period in which the transaction was made. This principle can be divided into two components: the principle of correspondence - this is when income for the reporting period must be correlated with the expenses with the help of which these incomes were received; the principle of recording income (in other words, revenue) - according to the rules, income must be reflected in the period when it is received, and not at the time of payment.
- The periodicity principle obliges the preparation of balance sheets and statements for the following periods: month, quarter, half-year and year. Thanks to this principle, it is possible in the future to easily compare reporting data, calculate financial results and make forecasts for the future.
- The principle of confidentiality. Data from internal accounting documentation is a trade secret of the company, therefore liability before the law is provided for damage or disclosure.
- The principle of monetary measurement - the results of economic activities must be measured in monetary units, that is, in the currency of the country where the organization operates.
Division of accounting objects
Group 1 – objects that support activities, Group 2 – objects that make up activities
The first group includes economic means , the second - processes . To understand the objects, it is important to present a diagram of the enterprise’s property, from which the accounting objects are made up. Property, or “Assets,” is considered from two sides: from its composition and through what it was acquired or formed.
Figure 1. Enterprise property
Figure 2. Composition of working capital
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Subjects and objects of accounting 410 ₽ Abstract Subjects and objects of accounting 260 ₽ Examination Subjects and objects of accounting 250 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
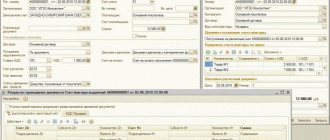
1C: Accounting 8
“1C: Accounting 8” is the most popular accounting program that can take accounting automation to a whole new level. A convenient product and services connected to it will allow you to effectively solve the problems of the accounting department of any business!
- Support of different tax systems, maintaining accounting and tax records, submitting reports;
- Inventory accounting, batch accounting, settlements with counterparties, extracting primary documents;
- Payroll calculation, accounting of cash transactions;
- Integration with other 1C programs and websites;
- Working with electronic certificates of incapacity for work (ELS).
Try 30 days free Order
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter