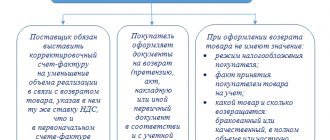
If the supplier has shipped a low-quality or incomplete product to the organization, the buyer can return it. There may also be other reasons for return, it depends on the terms of the supply agreement.
The Civil Legislation of the Russian Federation establishes several grounds on which goods can be returned. These are cases of non-compliance:
- quality;
- assortment;
- set;
- containers and packaging.
Thus, current legislation allows you to return goods to the supplier in the following cases:
- if the buyer has not received complete information about the characteristics of the product;
- The supplier did not ship the required quantity. In this case, the buyer may refuse the entire lot;
- the product is not fully completed;
- the supplier regularly violates delivery deadlines;
- the quality does not meet the terms of the contract;
- The products were shipped without packaging or containers.
In this article, we will consider what primary documents should be used to document the return of goods to the supplier.
How to arrange for a buyer to return goods to a supplier
The return of goods to the supplier is accompanied by a return invoice (for example, in form N TORG-12 with the note: “Return of goods”) or an act of returning goods to the supplier.
Documents for returning goods from the buyer to the supplier are transferred along with the returned goods.
In addition, the buyer sends a letter (claim) to the supplier demanding acceptance of the returned goods, indicating the reason for their return.
If the goods are returned to the supplier by power of attorney, then in this case, when registering it, you can use form No. M-2 (clause 2.1.4 of the Methodological Recommendations, approved by Letter of the RF Committee on Trade dated July 10, 1996 N 1-794/32-5 ).
In this case, the buyer does not need to issue an invoice for the return of goods.
Return of goods after acceptance by the buyer for accounting
According to the position of the official authorities, if on the date of return the goods are registered, the return of the goods by the buyer is recognized as a reverse sale.
It does not matter for what reasons the goods are returned. In this case, the buyer, if he is a VAT payer, must issue an invoice to the seller (letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 29, 2013 No. 03-07-11/51923, dated August 10, 2012 No. 03-07-11/280).
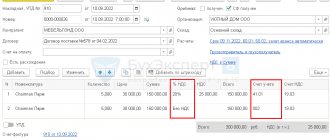
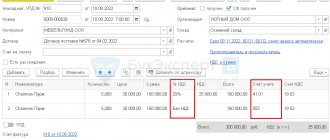
Example Promooborudovanie LLC purchases blanks for the production of parts from Omega LLC.
Products are purchased in batches of 1000 pieces. On a monthly basis, upon acceptance of MPZ, incoming quality control is carried out in order to identify defective workpieces. On April 30, 2022, the next batch of workpieces arrived, which were entered into the warehouse, and the arrival of the goods and materials was reflected in the accounting.
Before sending the workpieces to the workshop, the quality control inspector, conducting laboratory incoming quality control, discovered metal defects that were not visible during the initial visual inspection and were revealed only during ultrasonic testing. According to the terms of the contract, if a defect is detected in the control samples, the entire batch must be returned.
In this case, Promooborudovanie LLC, the buyer, issues an invoice for the returned shipment and charges VAT on the proceeds from the reverse sale.
The invoice for reverse sales of Promooborudovanie LLC (former buyer) is registered in the sales book, and the invoice received from Omega LLC is registered in the purchase book.
LLC "Omega" (former seller) registers the initial invoice in the sales book, and the one received from LLC "Promooborudovanie" - in the purchase book (clause 5 of article 171, clause 10 of article 172 of the Tax Code, letters of the Ministry of Finance dated November 29, 2013 No. 03-07-11/51923, 08/28/2012 No. 03-07-09/126).
If the buyer and seller are on OSNO, then in the seller’s purchase book and the buyer’s sales book, an invoice for the return of goods is registered using the transaction code “01” (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 20, 2016 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] ).
Letter of claim requesting the supplier to accept goods returned by the buyer
If, during the acceptance of the delivered goods or after its acceptance, it is revealed that the goods do not comply with the requirements for their quality, the buyer has the right, at his own discretion, to refuse to execute the sales contract, return the low-quality goods and demand a refund of the amount of money paid for it, or demand replacement of this product with a product of proper quality (clause 2 of Article 475 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The buyer sets out his requirements in the form of a claim, which is sent to the supplier (for example, for the return of goods). The norms of the current legislation of the Russian Federation do not provide for an established form of claim for the return of goods to the supplier.
The letter of claim is drawn up in any form.
The letter states:
- full name and details of the buyer and supplier;
- number and date of the purchase and sale (supply) agreement;
- number and date of accompanying documents for the delivered goods;
- name of the product, its quantity and cost;
- detected discrepancy (malfunction);
- links to regulations;
- requirement to satisfy the claim (request for replacement, refund, reduction of amount, etc.).
The claim is signed by the head of the organization, indicating his position and his full name, and certified by the company seal (if any).
The letter of claim is handed over to the authorized representative of the supplier against signature or sent to him by registered mail with a list of the attachments.
Return of goods by an individual
When selling goods, works or services to individuals for cash, the VAT payer supplier has the right not to issue invoices to them.
This is stated in paragraph 7 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, you can register a cash register tape in the sales book. If individuals pay in non-cash form, the VAT payer seller must issue a consolidated invoice for all sales and register it in the sales book (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 15, 2015 No. 03-07-14/34405. The seller should do the same in a situation where individuals receive goods by mail (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/20/14 No. 03-07-09/29630), and when goods are transferred free of charge to employees (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/08/2016 No. 03-07-09/6171 ).
Consolidated invoices and cash register tapes are registered in the sales book of the seller with code KVO 26.
If the buyer, an individual, returned the goods or refused the work (service), the seller must return the money to him. The salesperson should then record in the purchase ledger the consolidated invoice or cash register tape that was previously recorded in the sales ledger.
In this case, in the column intended for the KVO code, you should put 17 (order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] , letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2014 No. 03-07-09/37589). In the column intended for information about the document confirming the payment of tax, you must indicate the number and date of the document drawn up when returning money to the buyer.
According to officials (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 19, 2013 No. 03-07-15/8473) and tax authorities (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated May 14, 2013 No. ED-4-3 / [email protected] ), if a buyer who did not pay VAT when selling goods was a cash receipt has been issued without issuing an invoice (in retail trade using cash register), in the seller's purchase book you can register the details of the cash receipt issued when returning money to the buyer (if there are documents confirming the receipt of returned goods).
VAT when returning goods to the supplier
VAT when returning goods to the supplier is required to be processed according to the following rules:
- The seller prepares an adjustment invoice and records it in the purchase ledger.
- The buyer registers the seller's adjustment invoice in the sales book (if he managed to accept VAT for deduction, if not, then he accepts the deduction in the non-refundable part).
Please note that it does not matter for what reason the return occurs.
This is how the return of both defective and high-quality goods is processed if it does not comply with the contract.
We issue a return of goods using an adjustment invoice
From April 1, 2022, sellers do not process returns as reverse sales if the buyer managed to register the purchased goods. From this date, they issue an adjustment invoice to the buyer, regardless of whether the returned goods were registered before April 1, 2022 or after. That is, now any return of goods must be processed through an adjustment invoice (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 19, 2022 No. 15).
To adjust the shipment, the seller and buyer must agree on it in writing. For example, conclude an appropriate agreement or contract, or draw up a primary document confirming the consent of both parties to change the terms of the transaction.
If there is no additional agreement or agreement to change the cost of shipment, the seller will not be able to deduct VAT even if there is an adjustment invoice. Likewise, it will not be able to deduct VAT in the absence of an adjustment invoice.
But if the return is formalized as a “reverse” supply or purchase and sale agreement, the tax on the invoice of the “former” buyer (and now the seller) can be deducted on a general basis (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 10, 2022 No. 03- 07-09/25208).
No later than 5 calendar days from the date of signing the additional agreement, the seller issues an adjustment invoice to the buyer.
How to fill out an adjustment invoice
Read more…
If on the date of return of the goods the seller has already paid the VAT accrued on the shipment to the budget, he has the right to accept it for deduction while simultaneously meeting the following conditions:
- an adjustment has been made in accounting due to the return;
- less than one year has passed since the return of the goods.
The seller accepts VAT as a deduction in the amount of the difference between the tax amounts calculated before and after the return of the goods. The basis for this will be a correction invoice. He does not need to submit an updated VAT return for the period when the shipment took place.
Example.
VAT on the return of goods that are not recognized as sales In September, Aktiv JSC shipped a batch of shoes in the amount of 100 pairs at a price of 1,200 rubles to the buyer Passive LLC. per unit (including VAT - 200 rubles). In total, goods worth 120,000 rubles were shipped. (including VAT - 20,000 rubles). The cost of one pair of shoes was 800 rubles, and the cost of the shipped batch was 80,000 rubles. In October, Aktiv paid VAT on sales in the amount of RUB 6,667. (RUB 18,000: 3). Ten pairs of shoes totaling RUB 12,000. (including VAT - 2000 rubles) turned out to be defective. In October, Passive returned them to Aktiv. In the same month, the partners formalized an agreement to the contract for the return of goods, and JSC Aktiv issued an adjustment invoice to Passiv. The cost of the consignment of goods after adjustment is 108,000 rubles. (including VAT - 18,000 rubles). The difference between the updated and original VAT was: RUB 18,000. – 20,000 rub. = –2000 rubles. Thus, JSC Aktiv will apply a VAT deduction in the amount of 2000 rubles in the fourth quarter. The Aktiva accountant will make the following entries in the accounting: in September DEBIT 62 CREDIT 90-1 – 120,000 rubles. – revenue from the sale of shoes is reflected; DEBIT 90-3 CREDIT 68 SUBACCOUNT “VAT CALCULATIONS” – 20,000 rubles. – VAT payable to the budget has been accrued; DEBIT 90-2 CREDIT 41 – 80,000 rub. – the cost of shoes sold was written off. In October DEBIT 68 CREDIT 51 – 6667 rubles. – transferred to the VAT budget; DEBIT 62 CREDIT 90-1 – 12,000 rub. (RUB 1,200 × 10 pairs) – the return of goods is reflected according to the adjustment invoice (part of the revenue is reversed); DEBIT 90-2 CREDIT 41 – 8000 rub. (800 rubles × 10 pairs) – part of the cost of goods was reversed according to the adjustment invoice; DEBIT 90-3 CREDIT 68 SUBACCOUNT “VAT CALCULATIONS” – 2000 rub.
(RUB 12,000 × 20%: 120%) – VAT is reversed according to the adjustment invoice. The last entry means that “Asset” has deducted VAT in the amount of RUB 2,000. In a similar procedure, the contractor can deduct VAT paid when performing work or providing services if the customer refuses them (clause 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Return of low-quality goods to the supplier if a defect is detected immediately upon acceptance of the goods
In this case, the purchasing organization may simply not accept the damaged goods.
In this case, it is enough to correct the invoice TORG-12 - without documenting the return of low-quality goods to the supplier.
That is, if the supplier is ready to take back expired products, then from the TORG-12 consignment note issued by the supplier, the purchasing organization deletes the necessary items - those items that are defective.
Please note that corrections in the receipt document must be made in the presence of the supplier or his representative - a forwarder or driver, vested with the rights of a financially responsible person.
The specified person must sign next to the crossed out item and pick up the defective product.
In addition, the supplier must not only accept the defect back, but also adjust the invoice for the purchasing organization downward and send it to the purchasing organization within 5 business days, since less goods were actually purchased.
At the same time, in the invoice, in the adjustment lines, the supplier indicates those goods that he must accept from the buyer.
Note that in practice another option is often used, namely, additional delivery of quality goods at another time, but without paperwork. That is, the purchasing organization accepts the entire delivery, signing the invoice without adjustments. And the supplier delivers the missing quality goods a little later. This is a common case when the buyer has established a trusting relationship with the supplier.
Return of defective goods to the supplier after acceptance
There are situations when the purchasing organization cannot return the defective product to the supplier immediately, although the defect was discovered at the time of acceptance.
For example, the delivery was from another region, and the transport company - the seller's delivery contractor - does not accept anything back.
In this case, despite the defect, the purchasing organization will have to accept the products according to the TORG-12 invoice, draw up a statement of discrepancies in quantity and quality, and place the inventory items in its warehouse.
And only after this the purchasing organization can write a claim and wait for its consideration by the supplier.
Returning goods before the buyer accepts them for accounting
As stated above, the issuance of an invoice for the return of goods depends on whether the returned goods are registered or not.
If the goods are accepted, you need to issue a regular invoice for return sales. In this case, the seller and buyer change places, and the goods are returned to the starting point.
If the buyer returns an item that was not accepted for registration, or only part of the item, the seller needs to issue an adjustment invoice.
Example
During the acceptance of workpieces received from Omega LLC, OO Promoborudovanie identified defects that arose during their improper transportation (chips, cracks, etc.). It was decided to return the entire batch of blanks. Since the buyer did not accept the goods for registration, the transfer of ownership of the blanks to Promooborudovanie LLC did not occur, so there is no reverse sale in this case and there is no need to issue an invoice to Omega LLC (Clause 1, Article 39 of the Tax Code RF, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/07/2015 No. 03-07-09/19392).
The defective batch of blanks was sent to the supplier with a TORG-12 invoice marked “Return”. The remaining documents confirming the fact of the return of the blanks (return certificate, claim, agreement to terminate the contract, etc.) were sent later.
For Promooborudovanie LLC, the return of workpieces without registering them did not entail any tax consequences; nothing needs to be reflected in the purchase book and sales book .
And Omega LLC, as the seller who reflected the sales in the sales book, must draw up an adjustment invoice and register it in the purchase book (letters of the Ministry of Finance dated 08/10/2012 No. 03-07-11/280 and 08/07/2012 No. 03-07 -09/109, Federal Tax Service dated 07/05/2012 No. AS-4-3/ [email protected] ).