All organizations without exception are required to calculate depreciation of fixed assets. To correctly determine the amount of deductions, you must:
- form the initial cost of the accounting object, including all the organization’s expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets;
- establish a useful life (SPI).
The procedure for determining SPI has changed due to the approval of a new all-Russian classifier of fixed assets. We will tell you how to properly organize accounting for depreciation of fixed assets in view of the latest innovations.
Determining the depreciation group
The useful life of any property is established depending on which depreciation group the property belongs to. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 01.01.2002 No. 1 approved a new classification of fixed assets by terms of use.
We have compiled a table of depreciation groups of fixed assets for 2020: according to the new OKOF.
| Group | Minimum SPI, in years | Maximum SPI, in years | An example of such fixed assets |
| First | 1 | 2 | General purpose machinery and equipment |
| Second | 2 | 3 | Liquid pumps |
| Third | 3 | 5 | Radio-electronic communications |
| Fourth | 5 | 7 | Reinforced concrete fences and barriers |
| Fifth | 7 | 10 | Forest industry buildings |
| Sixth | 10 | 15 | Water intake well |
| Seventh | 15 | 20 | Sewerage |
| Eighth | 20 | 25 | Main condensate and product pipelines |
| Ninth | 25 | 30 | Any buildings and structures, except residential |
| Tenth | 30 | Not limited | Residential buildings and structures |
Types of fixed assets
Since OS objects are diverse, they are most easily classified into different groups. This division is important because, according to established standards, there are some features of accounting and transferring the price of an object to the final product of the company’s activities.
The following operating systems are distinguished:
- Building.
- Structures (temporary buildings, bridges, etc.).
- Transfer devices.
- Cars and equipment.
- Vehicles.
- Tools.
- Inventory and accessories.
- Other (not included in any of the above groups)
In addition, operating systems can be divided into production and non-production objects, based on their purpose. According to their ownership, they can be owned or rented.
Attention! Other divisions of OS may be applied - according to the degree of action during the production process, according to the time of application, according to the transfer of the price to the final product, etc.
Let us remind you how to use the classifier
The accounting property (fixed asset) should have been transferred to the new OKOF at the beginning of 2022. To reduce errors in accounting, officials approved a transition key for depreciation groups of fixed assets 2022, the table is presented in Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated April 21, 2016 No. 458.
The useful life of property purchased after the transition period should be taken into account in accordance with Order of Rosstandart dated December 12, 2014 No. 2020-st.
For example, an organization purchased a passenger car (OKOF code 310.29.10.2). According to Decree No. 1 of 01/01/2002, a passenger car belongs to the second depreciation group - from 2 to 3 years. Typically, an object has a maximum group limit. The institution has the right to establish any SPI that falls within the established interval, for example 2 years and 9 months. Such a decision should be enshrined in the official order of the manager.
Accrual methods
The current accounting instructions provide for only three accrual methods:
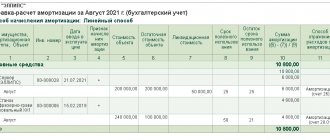
- linear - assumes an even distribution of the cost of the object throughout the entire period of the investment project. That is, the amounts of monthly depreciation deductions are a constant value, moreover, they are equal to each other throughout the entire SPI period;
- reducing balance method - this method involves calculation based on the residual value of the object. That is, the amount of annual depreciation is calculated in relation to the residual price. The calculation is made taking into account the SPI. It is also permissible to use a special coefficient - the depreciation acceleration coefficient;
- calculation of depreciation in proportion to the volume of goods or products produced - involves the calculation of amounts depending on the expected productivity of the object or on the expected indicators of use. The method is effective for seasonal operation of fixed assets. When the facility is at maximum capacity, the amount of deductions is maximum, and during months of downtime (production stoppage) it is reduced to zero.
But in tax accounting, only two methods of depreciation of fixed assets are recognized as valid - the linear accrual method and the non-linear one.
Features of reflecting depreciation in accounting
The current accounting instructions provide separate rules for calculating depreciation. Please take into account the following features established by Russian legislation:
- In accounting, accrual should begin on the 1st day of the month following the month in which the fixed asset was accepted for accounting. Moreover, depreciation calculations are made during the entire useful life of the property.
- For objects accepted into the treasury, depreciation is not accrued, except for the amount of depreciation already accrued by the previous copyright holder. For example, depreciation accrued before the transfer of property to the municipal treasury. Such amounts should be reflected in the relevant budget accounting accounts (clause 94 of Instruction 157n).
- For some objects, a special depreciation method is used: accelerated depreciation of fixed assets. A multiplying factor is set. Moreover, this method of calculation cannot be used for the first, second and third depreciation groups.
- Part of the costs of acquiring property is written off at the same time. This method is called: depreciation bonus for fixed assets 2020. The benefit can be applied only once - before the fixed asset is put into operation.
- Accrual should be stopped after the object is written off from accounting or after the expiration of the SPI. For fixed assets worth up to 100,000.00 rubles, a one-time write-off of the initial cost to the financial result is provided.
IMPORTANT!
The specifics of reflecting depreciation in accounting must be fixed in the organization’s accounting policies. Take into account the latest changes in legislation. First of all, follow the new accounting standards for fixed assets. Read more about the latest changes in legislation: “Understanding the new accounting standards.”
What documents are used to account for fixed assets
When documenting, a company can use either standard documents offered by Goskomstat or those developed independently. Whatever forms are used, they must be specified in the accounting policy.
Standard forms are divided into several groups:
| Form number | Name | What is it needed for |
| Admission and departure | ||
| OS-1 | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (except for buildings, structures) | To record the inflow and outflow of individual fixed assets, it is not filled in for buildings and structures. |
| OS-1a | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of a building (structure) | To record the arrival and disposal of buildings and structures |
| OS-1b | Act on acceptance and transfer of groups of fixed assets (except buildings, structures) | If the recording of the arrival and departure of fixed assets (does not apply to buildings, structures) is performed immediately for the group |
| OS-14 | Certificate of acceptance (receipt) of equipment | Accounting for equipment in storage that will be used in the future |
| OS-4 | Act on write-off of fixed assets (except for vehicles) | Write-off of certain OS objects that have become unusable. Not to be filled out for vehicles. |
| OS-4a | Act on write-off of motor vehicles | Write-off of a vehicle that has become unusable |
| OS-4b | Act on the write-off of groups of fixed assets (except for vehicles) | Write off the OS group immediately, not filled in for vehicles |
| Availability and movement | ||
| OS-6 | Inventory card for recording a fixed asset item | Accounting for certain fixed assets and their movement within the company |
| OS-6a | Inventory card for group accounting of fixed assets | Accounting for several similar operating systems |
| OS-6b | Inventory book for accounting of fixed assets | In small enterprises it replaces filling OS-6 and OS-6a |
| OS-15 | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of equipment for installation | Transferring the OS stored in the warehouse for installation |
| OS-16 | Report on identified equipment defects | Recording of defects that were identified during installation, testing, etc. |
| OS-2 | Invoice for internal movement of fixed assets | Recording the movement of assets between departments within the company |
| OS-3 | Certificate of acceptance and delivery of repaired, reconstructed, modernized fixed assets | Registration of OS upon completion of repairs and modernization |
Accelerated depreciation: conditions of use
Tax and accounting standards allow the cost of fixed assets to be attributed to operating results in an accelerated manner. For this purpose special coefficients are used. The maximum value is 3. Moreover, the conditions of application must be fixed in the accounting policies of the institution.
Fix the size of the special depreciation coefficient in the accounting policy. Otherwise, the accelerated depreciation method cannot be used. Tax authorities will punish the institution in this case.
Officials have identified a number of conditions under which the use of accelerated depreciation is permissible:
- A coefficient of no more than 2 is applied to an object purchased before 01/01/2014, or to property operated in an aggressive environment, for example, in multi-shift conditions. If an organization accrues using a non-linear method, then accelerated rates cannot be applied to the first or third depreciation groups of fixed assets.
- A coefficient of no more than 3 is applied to fixed assets used in carrying out research activities and to fixed assets received under a leasing agreement. But in relation to the first and third groups of property, accelerated depreciation cannot be applied.
It should be borne in mind that the management of the organization has the right to provide not only an increasing factor that accelerates depreciation. Also, current standards for maintaining accounting and tax records allow the use of a reducing depreciation rate, which is provided to slow down the monetary depreciation of property.
What are fixed assets
Fixed assets are property owned by the company or attracted by it from the outside, which is used in its production activities for more than one year and has a value above the limit established by regulations.
There are criteria by which the distinction is made between fixed assets and other property.
How OS can take objects into account:
- Use time over 12 months.
- Such property is used by the company during its activities for production, provision of services, performance of work, or for enterprise management purposes.
- It was purchased for use, not for subsequent sale.
- Its use will allow the organization to generate income.
It follows that buildings, structures, vehicles, equipment, etc. are taken into account as OS.
The leading regulatory act governing the accounting of fixed assets in Russia is PBU No. 6/01. This document defines the indicators for classification as fixed assets, as well as the accounting methodology.
Attention! Among the above-mentioned features of an OS, another important criterion is not indicated - its price. According to PBU, fixed assets must include property whose purchase price is set at 40,000 rubles. For tax accounting, as specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the price of an object that will be used as fixed assets must be from 100,000 rubles.
How is bonus depreciation calculated?
The use of bonus depreciation is a one-time allocation of costs to capital investments:
- part of the original cost of the property, but there are exceptions: a depreciation bonus cannot be applied to fixed assets received free of charge;
- part of the costs of completion, additional equipment, reconstruction, technical re-equipment, modernization or partial liquidation of the facility.
If an organization has applied an investment tax deduction for fixed assets, then it is impossible to charge a premium for depreciation on the same objects.
Budgetary institutions have the right to apply bonus deductions only in relation to fixed assets that are acquired using funds received from income-generating activities. Moreover, only in tax accounting, in accounting, such a privilege is not provided. This position was expressed by the Ministry of Finance in Letters dated April 17, 2014 No. 03-03-06/4/17800, dated May 25, 2011 No. 03-03-06/4/52.
IMPORTANT!
The rules and conditions for applying bonus depreciation will have to be fixed in the accounting policies. Otherwise, tax breaks cannot be applied. This is a violation of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which provide for administrative liability.
The amounts of bonus payments are fixed at the legislative level. So, use:
- Up to 10% - in relation to objects of the first-second and eighth-tenth depreciation groups.
- Up to 30% - in relation to operating systems that are included in the third to seventh groups.
Attribute premium depreciation deductions to indirect expenses. The premium should be recognized in the reporting period in which the start date of depreciation or the date of change in the original cost occurred.