An enterprise necessarily owns certain property of various types. It is necessary not only to ensure the activities of the company, but also to manage it, as well as for other purposes. A certain part of the property consists of fixed assets, they are subject to mandatory accounting.
- What are fixed assets?
- What are the principles of their accounting and reflection in financial documentation?
- Where do they come from and where do they go?
- How does their value and, accordingly, accounting change?
More details about everything.
What is the essence of fixed assets?
The concept of “fixed assets” does not include any property of an enterprise. These are material objects that a company uses for various types of its activities: production of goods, provision of services, performance of work, rental and other functions. All of the following must apply to these tangible assets:
- they do not intend to be sold or processed in the near future;
- they serve for the benefit of the entrepreneur for at least 12 months (or one operating cycle if it exceeds a year);
- potentially capable of generating income for the owner (now or in the future);
- may be subject to wear and tear and lose value (everything except land plots).
REFERENCE! In the specialized literature, the identical definition of “fixed assets” is sometimes used. But in modern business vocabulary, both domestic and international, it is considered outdated. We do not recommend using it, so as not to seem like an “economic dinosaur.”
What is included in fixed assets?
Fixed assets are classified in the All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets (OKOF). According to this register, accounting classifies the following tangible assets as main ones:
- building structures;
- land;
- mechanisms;
- instruments and devices;
- tools, equipment;
- equipment for computing and organizing activities;
- transport;
- number of livestock;
- planted perennial plants;
- natural objects in use;
- capital investments in leased inventory and land improvement;
- some other types of material objects.
These funds are not basic
If an item has served the owner for less than one year, it has not yet reached the status of a fixed asset.
There is also a limitation on cost: if a tangible asset costs less than 40 thousand rubles, it is not classified as fixed assets. This limit was established by the new edition of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 186n dated December 24, 2010. It also clarifies that the cost limit does not apply to agricultural implements, livestock, construction machinery and weapons: all of these are fixed assets, no matter how much they cost .
In addition, the list of fixed assets does not include :
- equipment intended for fishing;
- temporary buildings that are not going to be used for more than two years;
- replaceable equipment that constitutes replaceable elements of other fixed assets;
- special and uniform clothing and shoes;
- devices for working in the forest: chainsaws, loppers, alloy cables, temporary railway lines, roads, etc.;
- storage containers;
- planting material, even if it is perennial;
- young animals, bee families, birds, rabbits, fur-bearing animals, dogs.
NOTE! Any tangible asset intended for sale or rental cannot be a fixed asset.
Related Concepts
Let's analyze the key terms directly related to fixed assets.
Depending on what actions entrepreneurs perform with their fixed assets, several important concepts can be distinguished.
- Audit. The term used to account for fixed assets is "inventory object" is a single asset, part of fixed assets, considered as a separate independent value. These can be:
- a separate object with its own attributes;
- a structure designed to perform one or another separate function;
- a complex of objects that makes up a single whole, intended for a specific activity.
- Multiplication . The enterprise, in an effort to expand its activities, pays attention to the acquisition of fixed assets, their creation, modernization, improvement, etc. Costs allocated for such needs are called capital investments .
- Depreciation . Over time, any thing loses some of its useful properties, which means it loses in value. Regularly subtracting this loss, that is, taking into account depreciation, is called ascertaining the residual value . After depreciation is deducted, what remains is net fixed assets .
- Increased efficiency. If inventory items are subject to restoration and correction, they are repaired:
- current - worn parts are replaced, for which such replacement was initially provided;
- medium – the object is disassembled and restored to the extent possible;
- capital – complete replacement of all worn-out elements or their restoration.
When to apply new FSBUs
Order of the Ministry of Finance dated September 17, 2022 No. 204n, which approves FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed assets” and FSBU 26/2020 “Capital investments”, comes into force on October 27, 2022. It will be mandatory to switch to them from January 1, 2022, but it is possible earlier.
PBU 6/01 will lose force from January 1, 2022.
In addition, from the same date, the guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n, are abolished.
Funds love accounting
Fixed assets in the Russian Federation are accounted for on the basis of PBU-6/01.
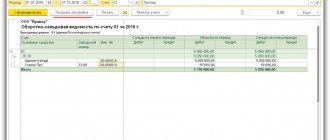
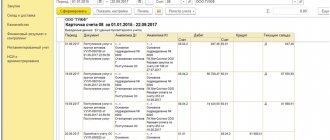
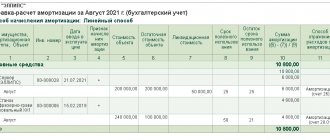
Accounting means clarifying information on the name and cost of the organization’s fixed assets. To do this, the cost of each inventory item is initially established: it depends on the way in which the asset was included in the fixed assets of the enterprise. Then this cost is reduced monthly by a certain depreciation amount, which is reflected in the balance sheet as the residual value. In this document, fixed assets appear as non-current assets .
Depreciation is an accounting of the changed value of an asset during its useful life , that is, the period when it is planned to receive income from this asset. It may be revised if capital investments were made into the facility for the purpose of its modernization, restoration, technical reconstruction, repair, etc. The amount of such investments is called replacement cost .
NOTE! The useful life often depends on the operating documents, for example, the probable service life of a tool indicated by the manufacturer is three years, which means that this will be the useful life of this item, despite the fact that theoretically the item can last longer.
Indicators for assessing property status
The property status of an enterprise is manifested in the solvency of the enterprise, in the ability to timely satisfy the payment requirements of suppliers in accordance with business contracts, repay loans, pay wages, and make payments to the budget.
The property of an enterprise is what it owns: fixed capital and working capital, expressed in monetary form and reflected in the independent balance sheet of the enterprise.
The assessment of the property status of an enterprise is made based on the analysis of the following indicators:
The amount of economic assets at the disposal of the organization
Share of fixed assets in assets
Share of the active part of fixed assets
Depreciation rate of fixed assets
Depreciation rate of the active part of fixed assets
Fixed asset renewal ratio
Fixed asset retirement ratio
The amount of economic assets at the disposal of the organization
This indicator (Rs) gives a generalized valuation of assets listed on the balance sheet of the enterprise. This is an accounting assessment that does not coincide with the total market assessment of the enterprise's assets. The growth of this indicator indicates an increase in the property potential of the enterprise:
Rs = A - U - Ak - Du
where, A - total assets on the balance sheet; U - losses; Ak - own shares in the portfolio; Du - debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital.
In a simplified way, the amount of economic assets at the disposal of an enterprise can be represented as the amount of assets of the enterprise at the end of the reporting period.
O.V. Grishchenko (Analysis and diagnostics of the financial and economic activities of an enterprise: Textbook. Taganrog: TRTU Publishing House, 2000) believes that when determining the indicator, the balance sheet total (assets) should be reduced by the amount of own shares purchased from shareholders and the amount of debt of participants ( founders) for contributions to the authorized capital.
Share of fixed assets in assets
The indicator is a generalized result of structural analysis and characterizes the degree of capitalization of assets into fixed assets of the enterprise.
Share of fixed assets in assets = Cost of fixed assets / Balance sheet total (balance sheet currency)
The higher the value of the indicator of the share of fixed assets in assets, the better the enterprise is provided with the equipment, buildings, structures and other assets necessary for the production and sale of goods and services that are used for a long period of time.
Therefore, any increase in this indicator indicates either an expansion or modernization of financial and economic activities. While the reduction in share is not always characterized as negative dynamics.
Share of the active part of fixed assets
Shows what part of the total cost of existing fixed assets is their active part (participating in the production of products). The active part of fixed assets is machinery, equipment and vehicles. The growth of this indicator in dynamics is usually regarded as a favorable trend.
Share of the active part of fixed assets = Cost of the active part of fixed assets / Cost of fixed assets
Depreciation rate of fixed assets
Characterizes the share of the cost of fixed assets written off as expenses in previous periods. Typically used in analysis as a characteristic of the state of fixed assets.
Depreciation rate of fixed assets = Depreciation of fixed assets (depreciation) / Initial cost of fixed assets
Note that the indicator is somewhat conditional. The reason for this is the dependence of the coefficient on the depreciation method used by the enterprise, i.e. the coefficient does not show the physical depreciation of fixed assets; the indicator, like the serviceability coefficient, does not provide an accurate assessment of the current state of the company's fixed assets.
A wear rate of more than 50% is undesirable. A more objective assessment of this indicator can be obtained by comparing its value for a specific enterprise with the industry average.
Depreciation rate of the active part of fixed assets
This indicator characterizes the degree of wear and tear of fixed assets directly involved in the production process.
Depreciation rate of the active part of fixed assets = Depreciation of the active part of fixed assets / Initial cost of the active part of fixed assets
Fixed asset renewal ratio
Shows what portion of the fixed assets available at the end of the reporting period consists of new assets.
Renewal coefficient = Initial cost of fixed assets received during the period / Initial cost of fixed assets at the end of the period
Using this coefficient, you can determine at what stage of the life cycle the enterprise in question is: if the value of the coefficient is less than one, then the enterprise is at the stage of industry contraction, if more than one, it is at the stage of expanded reproduction, when enterprises are interested in updating their production base.
A decrease in the renewal rate is a negative factor and indicates a tendency towards a decrease in the organization’s equipment with fixed assets
Fixed asset retirement ratio
Shows what part of the fixed assets with which the enterprise began operations in the reporting period was disposed of due to disrepair and other reasons.
Retirement ratio = Initial cost of fixed assets disposed of during the period / Initial cost of fixed assets at the beginning of the period
A decrease in the value of fixed assets can occur as a result of disposal due to dilapidation and wear and tear, sale, gratuitous transfer to the balance sheet of other enterprises, depreciation of fixed assets, or long-term lease.
If the retirement rate exceeds the renewal rate, then this is assessed negatively, since it indicates the lack of technical re-equipment of the enterprise
Formulas for calculating ratios on the balance sheet are discussed in more detail in the article: Analysis of the structure and dynamics of fixed assets.
How do fixed assets appear?
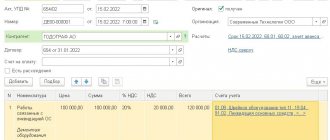
The receipt of fixed assets determines their initial cost. The material assets of an enterprise can be:
- purchased from suppliers for a certain fee, which is the original cost;
- contributed by the founders as a contribution to the authorized capital (the value will be the monetary value of the founders);
- created (built) – production costs are taken into account;
- transferred free of charge - the initial value will be the current market value;
- received under an exchange agreement - the cost is determined according to the norms of clause 11 of PBU 6/01.
Received funds are formalized by an acceptance certificate, and then by an order from the manager to put them into operation. At the same time, their initial cost is formed, which accountants will reflect on account 01 “Fixed Assets”.
OS cost limit in a new way
FSBU 6/2020 introduced a significant innovation compared to PBU 6/01. Currently in accounting there is a limit on the cost of fixed assets of 40,000 rubles. In tax accounting it is 100,000 rubles. In fact, everyone expected that the same limit would be established in accounting in order to bring the two accounts closer together.
Instead, organizations will be allowed to independently set a limit on the cost of fixed assets in accounting. Assets with a value below the accepted limit can be recognized both as fixed assets and as expenses of the period in which they are incurred, taking into account the materiality of the information.