Rules for accounting for inventory items received upon write-off of fixed assets
When preparing accounting records from 2022, the company is obliged to apply FAS 5/2019 “Inventories”, regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 15, 2019 No. 180n. In addition, it can be used ahead of schedule.
The main points regarding innovations under this standard are indicated in the information of the Ministry of Finance dated April 10, 2020, No. IS-accounting-27.
For example, the new standard has changed the rules for determining the actual cost of inventories that are received upon disposal of fixed assets or during its ongoing maintenance, repair, and modernization. The costs included in the actual cost of these inventory items are considered to be the least of the following values:
- the cost at which similar inventory items acquired or created by a company are accounted for during the standard operating cycle. In other words, this is the market price;
- the amount of the book value of the written-off fixed assets and the expenses that were incurred during dismantling or disassembling the fixed assets, extracting inventory and materials and bringing them into a condition suitable for use or sale as inventories.
In accordance with the Recommendations of the Accounting Methodological Center No. R-63/2015-KpR, when extracting inventory and materials from the liquidation of a fixed asset, income does not appear in accounting, since:
- there is no new asset entering the company;
- the company has no economic benefit, since the retiring fixed asset was already its asset, and it had already incurred expenses in the previous period to obtain and operate it.
Accordingly, when liquidating a fixed asset, inventory items must be registered at the expense of the book value of the fixed asset at the time it is written off from accounting.
If inventory items remain after the liquidation of a fixed asset, and the company plans to sell them, then they are accepted as long-term assets for sale. Their accounting is regulated by PBU 16/02 “Information on discontinued activities,” which is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2002 No. 66n.
When an asset is written off, non-current assets available for sale must be valued at the lower of:
- the amount of the book value of the written-off fixed asset and the costs of retrieving inventory and materials and bringing them to a condition that is suitable for sale;
- net sales value - the estimated selling price of inventory items, reduced by the amount of planned expenses that are needed to extract them from the operating system, bring them to readiness for sale and carry it out.
For profit tax purposes, the market value of inventory items is included in non-operating income on the date of filling out the act on write-off of fixed assets (Articles 250, 271 of the Tax Code).
Since the rules for accounting for extracted inventory and materials in accounting and tax accounting differ, this point can cause temporary differences and the need to recognize deferred tax according to PBU 18/02 “Accounting for income tax calculations”, regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n .
How to take into account income and expenses when disposing of a fixed asset
Starting from accounting records for 2022, the company must use FAS 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” and FAS 26/2020 “Capital Investments”. The organization independently decides that it applies these standards before the official deadline for their use.
Detailed comments on these standards are available in the information of the Ministry of Finance dated November 3, 2020 No. IS-accounting-28, No. IS-accounting-29.
For example, standard 6/2020 clarifies the rules for displaying transactions for the disposal of fixed assets in accounting:
- when writing off fixed assets, the amount of accumulated depreciation and impairment on it is transferred to reduce its original cost;
- expenses for dismantling, disposal of fixed assets and restoration of the environment are expenses for the period in which they were (if an estimated liability was not previously recognized for them);
- the difference between the book value of the asset being written off and the costs of its disposal, on the one hand, and the proceeds from its disposal, on the other hand, is income or expense in the profit (loss) of the period in which the asset is written off. Accordingly, the financial result upon disposal of an object is indicated in a collapsed manner in the statement of financial results.
As for tax accounting, the residual value of fixed assets upon liquidation and using the linear method of calculating depreciation deductions is taken into account at a time as non-operating expenses (Article 265 of the Tax Code). Loss from the sale of fixed assets is taken into account according to the special rules specified in clause 3 of Art. 268 NK.
Differences in the accounting procedures for losses in accounting and tax accounting lead to temporary differences and the need to recognize deferred tax under PBU 18/02.
Regulatory regulation
If a fixed asset has fallen into disrepair, the organization must write it off based on the decision of the commission (clause 77, clause 78 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2003 N 91n, hereinafter referred to as Guidelines for accounting for fixed assets N 91н).
BOO. Liquidation costs and the residual value of fixed assets are included in the write-off period in other expenses (clause 86 of the Guidelines for accounting OS N 91n, clause 31 PBU 6/01, clause 11 PBU 10/99).
Materials generated as a result of the disposal of a fixed asset are accounted for at the current market value on the date of write-off of the fixed asset (clause 79 of the Methodological Guidelines for Accounting OS N 91n).
WELL. Expenses for the liquidation of fixed assets (including depreciation accrued using the straight-line method) are recognized:
- as part of non-operating expenses for fixed assets (paragraph 1, paragraph 8, paragraph 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For fixed assets depreciated by the non-linear method, depreciation continues to be accrued as part of the group, despite disposal (paragraph 2, paragraph 8, paragraph 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 13, article 259.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 3, 2015 N 03-03-06/1/70529, dated 04/27/2015 N 03-03-06/1/24095).
The generated waste at market value (confirmed by an accountant's certificate or an appraiser's report) is subject to inclusion in non-operating income (clause 13 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT. If fixed assets are written off ahead of schedule, there is no need to restore VAT (Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated April 16, 2018 N SD-4-3 / [email protected] ).
How to reflect the liquidation of a fixed asset in 1C: Accounting 8
Example
The company operates on OSNO and is a VAT payer. From 2022, it will switch to using FSBU 6/2020.
In February 2022, it writes off the OS due to ineffective use.
In accounting, the initial cost of the object is 1 million rubles, accumulated depreciation charges are 325 thousand rubles, the amount of monthly depreciation is 25 thousand rubles.
The dismantling of the OS was carried out by a third-party company, for which it was paid 120 thousand rubles. (including VAT 20%).
The estimated liability for dismantling, disposal and restoration of the environment was not previously recognized for the facility, and depreciation was not taken into account. During dismantling, inventory items were recovered, and the company decided to use them in its activities.
To reflect the costs of dismantling an object when engaging a third-party company, use the document “Receipt (act, invoice, UPD).” In this case, you need to set the type of operation to “indicate accounts for recording expenses for dismantling operations for accounting and tax accounting purposes.
In accounting, the costs of dismantling and disposal of fixed assets are included in the costs of the period of their implementation. These costs must also be taken into account when calculating:
- financial result from disposal of fixed assets;
- the cost of inventory items received upon write-off of fixed assets.
In this regard, it is recommended to display the costs of dismantling in accounting on the account. 01.09 “Disposal of fixed assets” with recording of the disposed object. When the disposal procedure is completed, the book value of the object, taking into account dismantling costs, indicated on the account. 01.09, will be written off to the account. 91 “Other income and expenses.” 1C will determine the financial result from the disposal of the object and take it into account when calculating the cost of extracted inventory and materials.
In tax accounting, the costs of liquidating a fixed asset must be included in non-operating expenses (Articles 265, 272 of the Tax Code). Accordingly, in 1C tax accounting, dismantling costs must be recorded on the account. 91.02 “Other expenses”.
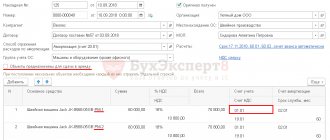
Correspondence of accounts when carrying out this document:
The write-off of an object is reflected in a document of the same name, and income and expenses from it must be taken into account in the account. 91.01 and 91.02.
However, now the document makes it possible to take into account inventory items that remain after the liquidation of a fixed asset.
In the header of the document, check the box “Materials left after decommissioning of the OS.” And then the table will have a column “Remaining materials”.
It will contain a link through which the user can go to the form of the same name. It is needed in order to indicate for each written-off fixed asset the name of the extracted inventory items (selected from the “Nomenclature” directory), quantity, market value and accounting account. For example, the market price of the remaining inventory items is 50 thousand rubles.
In the document “Write-off of fixed assets”, when you click the “Print” button, you can now use a new form of help-calculation “Cost of remaining materials when writing off fixed assets”.
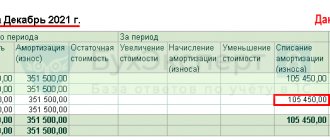
It contains the following information according to the example conditions:
- book value of the fixed asset (initial cost - accumulated depreciation and based on the results of the current month) - 650 thousand rubles;
- costs for the dismantling operation - 100 thousand rubles;
- the amount of costs for disposal of the object (book value + dismantling costs) - 750 thousand rubles;
- the market price of the remaining inventory items is 50 thousand rubles;
- the actual price of the remaining inventory items is 50 thousand rubles, because this amount does not exceed the cost of dismantling (50 thousand rubles less than 750 thousand rubles);
- the financial result from the liquidation of an object (expense) is determined by subtracting the actual (market) price of inventory items from the costs of disposal of the object - 700 thousand rubles.
Correspondence of accounts when carrying out this document:
In accounting, the benefit from the sale of such inventory items can be recognized as income upon their sale if the requirements of PBU 9/99 “Organizational Income” are met, but not upon their extraction.
What to do if the remaining inventory items have a high cost?
Let’s say, according to the conditions of the example, the market price of inventory and materials is 1 million rubles, i.e. it is more than the book value of the object and the costs of the installation operation (1 million rubles is more than 750 thousand rubles).
In such a situation, the actual cost of inventory items is equal to the book value of the object and dismantling costs, i.e. 750 thousand rubles. In this case, the 1C program will automatically determine the price of each individual material asset in proportion to the market price specified in the “Remaining Materials” document.
Expense in accounting is defined as subtracting the actual price of inventory items from disposal costs (book value and dismantling costs). In the example it would be 750 thousand rubles. — 750 thousand rubles.
Accordingly, when the document “Write-off of fixed assets” is carried out, the financial result in accounting will be equal to zero.
The program will proceed in a similar manner when business transactions are reflected in 2022.
How is the write-off of an asset reflected in cases of complete wear and tear?
When writing off an operating system in cases of wear and tear, the following operations are performed:
- Write-off of the initial price
- Write-off of depreciation
- Write-off from depreciated assets
Postings for write-off of OS:
| Dt | CT | The essence of the operation | Sum | Primary document |
| 01. | 01.01 | Starting price reflected | 450 | OS write-off act |
| 02.01 | 01. | Depreciation reflected | 120 | |
| 91.01 | 01. | The amount shown after depreciation | 330. |