When is inventory required?
Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49 dated June 13, 1995 states what an inventory is - checking the condition of an organization’s property and comparing actual indicators with accounting information.
This is a mandatory annual procedure: it is carried out before the preparation of annual financial statements. But these are not all cases when such reconciliation is required. Federal and industry standards stipulate who must carry out an inventory in an organization without fail - an inventory commission (permanent or working) when certain situations occur (Part 3 of Article 11 402-FZ dated 12/06/2011, clause 1.5 of the Guidelines from the order Ministry of Finance No. 49). These include:
- annual reporting;
- change of MOL (financially responsible person) who is responsible for inventory items;
- detection of theft, damage, abuse of goods and materials;
- reorganization and liquidation of the enterprise;
- natural disasters, fires or other emergencies.
The regulatory procedure for conducting and recording the results of inventory of inventory items is prescribed in the Guidelines approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49. Inventory items include goods, tangible assets and finished products. During the annual reconciliation, all inventory items are checked. But when the MOL is changed or theft is carried out, a random check is carried out - for a specific area.
IMPORTANT!
The commission inventories its own inventory and materials on the balance sheet and materials on off-balance sheet accounts, the ownership rights to which belong to other organizations (goods in storage, materials in processing, leased property).
Accounting entries for inventory
Postings based on inventory results are generated differently depending on what is revealed as a result - a surplus or a shortage. The procedure for reflecting discrepancies is regulated by Order No. 34n of July 29, 1998, paragraph 28):
- Surplus - objects are accounted for at the time of inventory at the current market price with the monetary value assigned to financial results (profit) as part of other income for ordinary enterprises or as income for non-profit organizations.
- Shortage within the framework of natural loss - the amounts are attributed to expenses or distribution costs.
- Shortages in excess of natural loss - amounts are written off to identified guilty parties. If for some reason the culprits of the shortage are not identified, and it is not possible to collect the debt in court, the debt is written off against the financial results (loss) of ordinary enterprises or for expenses of non-profit organizations.
Inventory surplus: postings
| Household contents inventory operations | Account by debit | Loan account |
| Surpluses of fixed assets identified | 08 | 91.1 |
| Excess inventory items identified | 10 | 91.1 |
| Surplus goods identified | 41, 43 | 91.1 |
| Surplus detected in the cash register - posting | 50 | 91.1 |
The discovered surplus assets of the organization can be used by it in the process of future activities. When writing off production costs, accounts 20, 23, 25, 26, 29 are used. For accounting data, the cost of capitalizing surplus during inventory is taken.
Conclusion - if a surplus is detected, a posting is generated to the debit of the object’s capitalization account and the credit of the income attribution account.
The procedure and frequency of inventory
According to the rules, a planned inventory of inventory items is carried out once a year - before drawing up the final financial statements. Typically, an inspection is organized from October 1 to December 31: to confirm that the accounting data corresponds to the actual balances of materials.
IMPORTANT!
If reconciliation of inventory items was carried out after October 1, then there is no need to organize another procedure before the formation of annual accounting reports (clause 27 of Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 34n dated July 29, 1998).
The head of the institution has the right to independently order an inspection, but for this he needs to establish the number of reconciliations for the reporting year, determine their dates and specify the inventory items or obligations being checked (clause 2.1 of section 2 of the Methodology from Order No. 49). The local procedure for carrying out reconciliation should be fixed in the accounting policy of the organization (clause 3 of article 6 402-FZ).
Let's look at how an inventory is carried out for dummies - the procedure consists of several stages: preparation, the inspection itself, comparison of actual and accounting data, registration of the results and reflection of the results in accounting. Each stage should be documented using one of the existing unified forms or a register independently developed by the organization.
Step-by-step instructions on how to conduct an inventory at an enterprise, taking into account legal norms and rules:
Step 1. Preparation
Before starting the procedure, it is necessary to issue an order to conduct an inspection, form a commission and determine the timing of the event. Usually the order is drawn up on the standardized INV-22 form, but this is not necessary. Your own form of order is allowed.
There is one more important rule: financially responsible persons, before conducting an inventory of goods and materials, are required to provide the commission with receipts and expenditure documents (reports on the movement of inventory items), which they did not transfer to the accounting department, and receipts stating that all receipts and expenditure registers for the goods and materials being checked have been handed over to the accountant or members of the commission, the valuables are capitalized, and the disposed materials are written off (clause 2.4 of the Method of Instructions). In addition, each MOL provides inventory lists and acts on its own forms or standardized ones - INV-1, 3, 4 and others.
Step 2. Verification
The procedure is carried out only in the presence of all members of the commission and the MOL (clause 2.8 of the Methods). An exception is if the MOL is absent from work for a long time due to illness or avoids taking inventory. But in this case, it is important to notify the financially responsible person about the upcoming inspection with documents. But if at least one member of the commission is absent during the inventory, then its results automatically become invalid.
The check is carried out using printouts of the inventory list INV-3. Inventory items are counted, weighed, measured and their actual presence is checked (clause 2.7 of the Methods).
Step 3: Data Mapping
The commission reflects the actual state of inventory items in inventory records and acts. MOLs sign the registers, confirming that the inspection was carried out in their presence. If, when comparing actual and accounting information, discrepancies are identified, then a matching statement is drawn up using forms INV-18, 19 or a self-developed form.
Step 4. Presentation of results
After the reconciliation, a meeting of the inventory commission is held. As a result, when conducting an inventory of inventory items, not only a statement is drawn up, but also a protocol of the commission meeting. The protocol is drawn up in any form. In him:
- the results of the check are reflected;
- explanations for deviations are provided;
- the perpetrators and the procedure for bringing them to justice are indicated;
- proposals for offsetting surpluses and shortages are listed;
- general conclusions, decisions and proposals based on the results of the inventory are given.
All results are summarized in the inventory record sheet (INV-26 as an option to fill out). And the final decision is made by the manager in the order approving the inventory results.
Step 5. Reflection in accounting
The results of the annual reconciliation form the accounting indicators for the year. Based on the results of inventory procedures, all necessary entries should be made - write off shortages and inventory items that are unsuitable for use, take into account surpluses, and offset misgrading.
IMPORTANT!
All results of the inventory check must be reflected in the reporting period to which the date of its conduct refers (part 4 of article 11 402-FZ, clause 5.5 of the Methodology). It is prohibited to make changes to the approved and submitted financial statements.
Use free instructions from ConsultantPlus experts to properly conduct an inventory.
to read.
Documentation of inventory at the enterprise
The documents used in the inventory can be classified:
- For those that are prepared before inventory:
- order of the head on the formation of an inventory commission (form according to Appendix 1 to the Methodological Instructions, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49), which is registered in the Accounting Book (form according to Appendix 2 to the Methodological Instructions);
- an order to conduct an inventory (form INV-22), registered in the accounting journal (form INV-23);
- available primary documents that reflect data on inventory items (acts, invoices, PKO, RKO);
- a list of relevant primary documents as of a certain date (which must occur earlier than the date of the inventory or the start of the inventory);
- receipts from materially responsible employees stating that primary documents on inventory items have been submitted to the accounting department, the items have been capitalized or written off (again, as of the day prior to the start date of the inventory).
- For those that are recorded during the inventory process:
- inventory lists (signed by the commission and financially responsible employees);
- acts of reconciliation of inventories and accounting data;
- matching statements.
- Those that consolidate the inventory results:
- a protocol reflecting the results of the work of the inventory commission;
- a statement reflecting the results of the inventory (form INV-26);
- order from the manager to approve the inventory results.
Let's take a closer look at the specifics of documents used specifically to reflect inventory results in accounting, including those used as supporting documents when creating accounting entries.
What to do with surplus or shortage
In addition to orders, the basic documents for conducting an inventory of material assets are inventory lists, acts, matching and generalized statements. They determine the presence of surpluses and shortages.
If surpluses are identified during the reconciliation, they must be taken into account in accounting at market value, but without VAT and excise taxes. Surplus inventory items arrive on the date of the audit: they are reflected as part of other income. In tax accounting, excess income from inventory items based on inventory results is recognized as non-operating income (Clause 20, Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Surpluses are recorded at market value and for tax accounting purposes (clauses 5, 6 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Shortages, on the contrary, are subject to write-off as part of other expenses. In some cases, the shortage is written off as an accounting error. All significant shortfalls are compensated by MOL.
Sometimes during an inspection, misgrading is discovered, that is, simultaneous surpluses and shortages of one product of a different grade. In the case of misgrading, it is necessary to determine the prices of such goods and set off the financial result in accounting. Offset of shortages with surpluses due to regrading in tax accounting is not allowed.
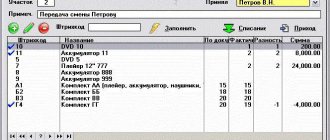
Surplus inventory items during inventory in 1C 8.3
Capitalization of surplus inventory items discovered as a result of inventory:
- In accounting, surplus inventory items are accounted for at current market value. Posting Dt accounting account – Kt account 91.1 as other income;
- In NU, surplus inventory items found during inventory are taken into account as non-operating income by virtue of clause 20 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Step 1. Creating the Goods Receipt document and filling it out
To capitalize surplus inventory items discovered as a result of inventory, use the Create based button - then Capitalize goods:
Filling out the title of the Goods Receipt document:
- In the Number field – the document number automatically generated by 1C 8.3;
- In the From field – day, month, year of the document;
- In the Organization field – filled in automatically from the Goods Inventory document;
- In the Warehouse field – the warehouse where the detected inventory items will be taken into account;
- In the Income Item field – the item of other income and expenses; income in accounting and accounting records will be attributed to it:
The tabular form of the Goods Receipt document is filled in automatically from the Goods Inventory document. All inventory items for which surpluses have been identified are transferred to a tabular form:
Step 2. Posting the document Receipt of goods
Clicking the Post button will create the following transactions:
Step 3. Printing the Goods Receipt document
We print the invoice by clicking on the Invoice for goods receipt button:
Is there liability for failure to take inventory?
Before drawing up annual financial statements, an inventory of the organization’s property and materials is carried out annually; other mandatory cases are listed in clause 1.5 of the Methods. But liability for failure to reconcile is not established by law.
The Federal Tax Service has the right to bring an organization to tax and administrative liability for unreliable accounting and reporting data (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). But only on condition that the inspector independently discovers a discrepancy between actual indicators and accounting information.
Postings when shortages are identified during inventory
The amounts of shortages identified during inventory are reflected in account 94. The amount of losses should be recorded in the debit of this account, and the losses should be written off as expenses on the credit. There should be no balance on account 94 on December 31.
If a shortage is identified, the accountant must make the following entries:
- Debit 94 Credit 10, 41, 43... - the shortage is taken into account;
- Debit 20, 44 Credit 94 - the cost of missing inventory items was written off within the limits of natural loss;
- Debit 91-2 Credit 94 - the cost of materials in excess of the norms of natural loss is written off as other expenses.
In accounting, when collecting shortfalls from employees, the following entries are made:
- Debit 94 Credit 01,10, 41, 43, 50 - the shortage is reflected;
- Debit 73 Credit 94 - the shortage is attributed to the guilty person;
- Debit Credit 41, 50, 51 Credit 73 - the shortage was compensated by the culprit;
- Debit 70 Credit 73 - the shortfall is withheld from the employee’s salary.
Is it possible to re-evaluate and in what order?
Yes, but only in cases stipulated by law (namely paragraph 12 of PBU 5/01), that is, in case of real obsolescence of assets or a significant decrease in their actual cost. In each of these two situations, they can be discounted, but their reduction in price can be reflected in the balance sheet only at the end of the reporting period. In this case, the reserve provided specifically for this purpose in clause 25 of the same Accounting Regulations should be deducted.
Please note that current standards do not require revaluation, so the value of already stored objects does not increase to the current market level.
Preparation for write-off of goods after inventory
After taking inventory, write-off of goods will be required in two cases:
- a shortage of inventory items was identified;
- the goods have lost their properties, appearance, their expiration date has expired, in a word, they have deteriorated and are not suitable for further sale.
In such cases, it is necessary to write off inventory items that are out of stock or damaged goods, for which a special act is drawn up.
But, before drawing up an act on the write-off of goods, it is necessary to reflect the damage to property, for which the Act on Damage, Damage, and Scrap of Inventory and Materials is used.
There is a unified form of document TORG-15, developed by Goskomstat in 1989.
Drawing up matching statements
- Filled out according to the INV-19 form if discrepancies are detected during the audit.
- The results of any of them at the end of the reporting period are summarized in an act corresponding to INV-26.
Each such document is accompanied by an extract from the accounting department, in which experts indicate possible options for writing off shortages: natural loss, damage during storage, natural disaster, theft, actions of criminals, and so on.
When preparing these papers, it is necessary to take into account the misgrading and the resulting difference in the cost of the goods. The amounts of shortages or surpluses should be indicated based on how they are valued in accounting.
If any objects do not belong to the company, but are temporarily on its balance sheet (rented, for processing, in storage), separate matching statements should be drawn up for them and confirmation certificates and copies of inventories should be provided to their owners.