Start of inventory
Any inventory begins with the issuance of an order to conduct an inventory and the approval of the inventory commission. This commission should include representatives of the organization’s management (director or deputy), an accountant and a financially responsible person. For example, salesperson, cashier, warehouse manager, etc. Other employees may also be involved in the inventory.
After the composition of the commission is approved, it receives the latest incoming and outgoing documents/reports on the movement of material assets. These documents, in order to determine product balances at the beginning of the inventory, are endorsed by the chairman with the note “before inventory on “_” (date).”
Financially responsible persons confirm that all expenditure and receipt documents for product balances were submitted to the accounting department or transferred to the commission by the beginning of the inventory.
Cheat sheet on the article from the editors of BUKH.1S for those who do not have time
1. Inventory begins with the issuance of an order to conduct an inventory and approval of the inventory commission.
2. At the time of the inventory, the remaining products are prohibited from being moved, removed from the warehouse or released to customers.
3. During the inventory, the commission, through recalculation, checks the actual availability of product balances in the warehouse/store. This procedure must be carried out in the presence of financially responsible persons.
4. Recalculation can be carried out either manually or using technical means. After the actual recalculation of product balances, the obtained data is allowed to be entered into the inventory. It is impossible to indicate anything in the inventory from the words of the inventory participants.
5. If the inventory of property is carried out over several days, then the premises where the goods are stored must be sealed when the inventory commission leaves.
6. If during the inventory the organization receives new products, it is accepted by financially responsible persons in the presence of members of the inventory commission.
7. After recalculating the balances and compiling inventories, the latter are signed by members of the inventory commission. If the inventory does not contain the signature of at least one member of the commission, the inventory results are considered invalid.
8. If, based on the results of the inventory, discrepancies are revealed between the information in the inventory act and the accounting data, the organization will have to draw up matching statements. They record the amounts of surpluses and shortages.
9. The results of the inventory are reflected in the records of the month in which it was completed. For annual inventory – in the annual report.
At the time of the inventory, the remaining products are prohibited from being moved, removed from the warehouse or released to customers.
The sale of inventory during inventory is permitted only in exceptional cases and only with the written permission of the head and chief accountant of the organization. Products in such cases are sold by financially responsible persons in the presence of members of the inventory commission.
Shortage of property written off the balance sheet
Situation: how to reflect in accounting a shortage of property that is not listed on balance sheet accounts (for example, materials written off as expenses)? The property for which the shortage was discovered belonged to the organization.
If a shortage of property is identified that is not listed on the balance sheet, the reduction of available property does not occur. However, for the organization such a shortage is recognized as damage. The procedure for reflecting such a shortage in accounting depends on the reasons for its occurrence.
A shortage of property can occur:
- due to natural loss;
- as a result of force majeure (flood, fire, etc.);
- through the fault of the financially responsible person (other guilty persons);
- for unknown reasons (the culprits were not found).
If the shortage of property not listed on balance sheet accounts occurred due to natural loss or as a result of force majeure, there is no need to reflect this with additional entries. The missing property must be written off from off-balance sheet accounting (if it was listed on off-balance sheet accounts). Apply the same procedure in cases where those responsible for the shortage have not been identified. This is explained as follows. If the shortage arose for these reasons, the organization’s accounting has no reason to take into account either expenses (the property was already previously included in expenses) or income (receipts for compensation of damage are not expected). This conclusion follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (account 91).
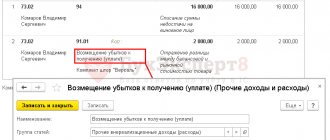
If the shortage occurred due to the fault of an employee or another guilty person, the organization has the right to recover material damages from him (Clause 1 of Article 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Articles 243, 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Since the value of the property has already been written off from the balance sheet accounts, the correspondence of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” with the organization’s property accounts is impossible. This conclusion follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (account 94). In accounting, compensation for material damage resulting from a shortage can be reflected in two ways: using account 94 and without it. The organization has the right to choose any of the above options.
When using the first method (using account 94), the wiring diagram will be as follows:
Debit 94 Credit 98
– the amount of the identified shortage is reflected;
Debit 73 (76) Credit 94
– reflects the amount of damage to be compensated by the financially responsible person (other guilty person);
Debit 70 (76) Credit 73 (76)
– the cost of the damage caused is withheld from the salary (remuneration) of the guilty person;
Debit 50 (51) Credit 73 (76)
– the amount of damage is repaid to the cash desk (to the current account) of the organization;
Debit 98 Credit 91-1
– the amount of repaid damage is reflected in income.
When choosing the second method (without using account 94), make the following entries:
Debit 73 (76) Credit 98
– reflects the amount of damage to be compensated by the financially responsible person (other guilty person);
Debit 70 (76) Credit 73 (76)
– the cost of the damage caused is withheld from the salary (remuneration) of the guilty person;
Debit 50 (51) Credit 73 (76)
– the amount of damage is repaid to the cash desk (to the current account) of the organization;
Debit 98 Credit 91-1
– the amount of repaid damage is reflected in income.
If the property for which a shortage was discovered was listed in off-balance sheet accounting, write it off from the off-balance sheet account (Instructions for the chart of accounts).
An example of reflecting in accounting a shortage of protective clothing written off from balance sheet accounts as expenses. The amount of the shortfall was withheld from the salary of the guilty employee
In March, OJSC “Proizvodstvennaya”, in accordance with industry standards, purchased workwear (wearing period 12 months) worth 1,180 rubles for an employee of the main production. (including VAT - 180 rubles). In the same month, the organization issued special clothing to the employee.
The accounting policy of “Master” states that workwear costing less than 20,000 rubles. taken into account in the composition of materials. At the same time, workwear, the cost of which is less than 20,000 rubles. and the period of use of which is no more than 12 months is written off as expenses at a time (accounting for such workwear is kept in special statements).
In May, one of the employees quit and did not return his work clothes upon dismissal. The manager decided to recover the shortage of protective clothing from the employee’s salary. To pay off the material damage, the cost of special clothing in the amount of 1,000 rubles was collected from the employee’s last salary.
The accountant reflected the amount of the shortfall in accounting using account 94.
In March, the accountant made the following entries:
Debit 10-11 Credit 10-10 – 1000 rub. – special clothing was issued to the employee for use;
Debit 20 Credit 10-11 – 1000 rub. – the cost of workwear is written off as expenses.
In May, the accountant made the following entries:
Debit 94 Credit 98 – 1000 rub. – the amount of the identified shortage is reflected.
Debit 73 Credit 94 – 1000 rub. – reflects the amount of the employee’s debt for compensation for damage caused.
Debit 70 Credit 73 – 1000 rub. – the cost of lost work clothes is deducted from the employee’s salary;
Debit 98 Credit 91-1 – 1000 rub. – the amount of repaid damage is reflected in non-operating income.
Checking product balances during inventory
At the next stage, the commission, through recalculation, checks the actual availability of product balances in the warehouse/store. This procedure must be carried out in the presence of financially responsible persons.
When conducting an inventory, it is necessary to follow the methodological recommendations approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49. The appendices to this order also contain standard forms of documents drawn up during the process and based on the results of the inventory.
Before recalculating balances, an inventory list is compiled (form No. inv-3 according to OKUD 0309003). The inventory is compiled in two copies, one of which is subsequently transferred to the accounting department for reconciliation with accounting data, and the second is transferred to the financially responsible person.
After this, it will be necessary to obtain receipts from financially responsible persons stating that all expenditure and receipt documents have been transferred to the organization’s accounting department. This receipt is given on the inventory form itself. They also sign that all inventory balances were capitalized at the time the inventory began, and those that were disposed of were written off as expenses.
Recalculation can be carried out either manually or using technical means. For example, data collection terminals that, by scanning, read codes of finished products and, based on the results of reading information from all boxes of products, automatically create inventory lists.
After the actual recalculation of product balances, the obtained data is allowed to be entered into the inventory. It is impossible to indicate anything in the inventory from the words of the inventory participants. Finished products and their remains are reflected in the inventory for each individual item. The inventory indicates the type, group, quantity, article and other characteristics of the product accepted in the organization’s accounting.
Inventory is carried out sequentially at storage locations in the order in which the products are located in the premises. After the products in the room have been completely checked and included in the inventory, the room is closed and, if necessary, sealed, and the inspectors move on to checking the next room.
If the inventory of property is carried out over several days, then the premises where the goods are stored must be sealed when the inventory commission leaves (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 3, 2018 No. 07-01-10/71098).
Moreover, during breaks in the work of the inventory commission (during lunch breaks, at night, for other reasons), the inventories must be stored in a closet/safe in a closed room where the inventory is carried out.
Accounting: compensation for damage by the guilty party
Attribute the shortage of goods in excess of the norms of natural loss, as well as the shortage of other property, to the perpetrators. In this case, the employee must compensate the organization for the entire amount of damage caused (Article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Determine the amount of damage based on the market price of the missing property, but not lower than its value according to accounting data (Article 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If the employee reimburses only the book value of the property, make the following entries:
Debit 73 Credit 94
– the shortage of property is attributed to the employee at book value;
Debit 50 (51, 70) Credit 73
– the employee’s shortfall debt has been repaid.
If an employee compensates for damage based on the market price of the missing property, make the following entries:
Debit 73 Credit 94
– the shortage of property is attributed to the employee at book value;
Debit 73 Credit 98
– reflects the difference between the market and book value of the missing property;
Debit 50 (51, 70) Credit 73
– the employee’s shortfall debt has been repaid.
As the employee repays the amount of debt due from him, write off the difference in proportion to the share of the repaid debt:
Debit 98 Credit 91-1
– the difference between the market and book value of the missing property is included in income.
This procedure follows from paragraph 5.1 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49, and the Instructions for the chart of accounts.
If a shortage is identified in the reporting year, but it relates to previous reporting periods, and the culprit is identified, take it into account as part of future income. At the same time, assign the amount of the shortfall to the guilty person. In this case, make the following entries:
Debit 94 Credit 98
– reflects the shortage identified in the reporting year, but relating to previous reporting periods;
Debit 73 Credit 94
– the shortage of property is attributed to the employee.
As the employee repays the debt, make the following entries:
Debit 98 Credit 91-1
– the shortfall repaid by the employee is included in income.
Such rules follow from the Instructions for the chart of accounts.
Situation: is it possible to recover the shortfall from a dismissed employee? Was an agreement on collective financial responsibility concluded with the employee? The inventory was carried out after dismissal.
Answer: no, you can't.
Article 232 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that termination of an employment contract does not exempt an employee from compensation for damage. But in order to prove that the shortage of property arose through the fault of the employee, it was necessary to conduct an inventory upon his dismissal. After the passage of time, it is impossible to prove the guilt of the dismissed employee. This means that it is also impossible to recover the shortage.
Inventory of new and missing products
If during the inventory the organization receives new products, it is accepted by financially responsible persons in the presence of members of the inventory commission.
Such products are reflected in a separate inventory - “Inventory assets received during inventory.” The date of receipt, the name of the supplier, the date and number of the receipt document, the name of the product, its quantity, price and amount are reflected here. After inventory, new products are received according to the goods report.
Also, separate inventories are compiled for products in transit, for products shipped but not paid for on time by buyers, as well as for products located in the warehouses of other organizations.
The inventory of products in transit for each individual shipment contains the name, quantity, cost, date of shipment, as well as a list and numbers of primary documents.
In the inventories of shipped but not paid for products for each individual shipment, the name of the buyer, the name of the product, the amount, the date of shipment, the date of issue and the number of the payment document are given.
Products in the warehouses of third parties are included in the inventory on the basis of documents confirming the delivery of these valuables for safekeeping. The inventory indicates the name of the product, quantity, grade, cost, storage location, numbers and dates of documents.
Registration of inventory results
After recalculating the balances and compiling inventories, the latter are signed by members of the inventory commission. If the inventory does not contain the signature of at least one member of the commission, the inventory results are considered invalid. In addition, at the end of the inventory, financially responsible persons give a receipt stating that the inspection took place in their presence and they have no claims against the members of the commission.
Next, the signed inventories are transferred to the accounting department, where they are verified with accounting data.
If, based on the results of the inventory, discrepancies are revealed between the information in the inventory act and the accounting data, the organization will have to draw up matching statements (form No. inv-19 according to OKUD 0309018). They record the amounts of surpluses and shortages.
Separate statements are compiled for inventory balances that do not belong to the organization, but are in its storage. The matching statements are signed by the chief accountant and the financially responsible person. After compiling the statements, the head of the organization signs an order approving the inventory results.
Identified surplus product balances are accounted for at market value. The corresponding amount is credited to financial results or increased income. The shortage within the limits of natural loss norms is attributed to production or distribution costs.
The shortage of products in excess of the norms of natural loss is compensated at the expense of the guilty persons. If the perpetrators are not identified, all losses from the shortage are written off against financial results or an increase in expenses (clause 28 of Order No. 34n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998).
The documents documenting the write-off of shortages in excess of the norms must contain decisions of investigative or judicial authorities confirming the absence of the guilty persons, or a refusal to recover damages from the guilty persons. The results of the inventory are reflected in the accounting records of the month in which it was completed. For annual inventory – in the annual report.
Let's pay attention to regulatory documents
Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial liabilities were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49 (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines), Order No. 34n dated July 29, 1998 “On approval of the Regulations on maintaining accounting records and financial statements in the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as Regulations on Accounting) and Federal Law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as the Law on Accounting).
In accordance with the Accounting Law, it is in the accounting policy that it is necessary to reflect the cases, timing and procedure for conducting an inventory, as well as the list of objects subject to inventory (determined by the economic entity independently).
In order for inventory to be carried out effectively, it must be planned. We suggest using the following inventory algorithm.
Reflection of inventory results in 1C: Accounting 8
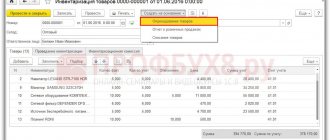
In the 1C: Accounting 8 program, the document “Inventory of Goods” is used to reflect inventory results. The document is available in the “Warehouse” section (Fig. 1).
The document can reflect the deviation of the actual quantity of inventory items (TMV) from the accounting quantity (Fig. 2) and generate printed forms: an order to carry out an inventory (INV-22), an inventory list of inventory items (INV-3), a matching sheet (INV-19).
The document “Inventory of goods” does not generate transactions, but on its basis you can create documents:
- “Receipt of goods” - if the results of the inventory reveal surpluses - if the results of the inventory reveal a shortage of goods and materials.