Cash control discipline in 2022
Cash control (or cash) discipline is compliance by legal entities and individual entrepreneurs with the rules for making cash payments legally established in the Russian Federation.
Cash payments include all types of income and expense transactions carried out by a company or individual entrepreneur with cash. The broadest concept for cash payments is the concept of a cash desk (operating cash desk), through which a company or individual entrepreneur makes cash payments. Most often, these are operations such as payment of salaries, receipt and delivery of money to the bank, settlements with accountable persons, issuance and repayment of loans. The cash register may also receive cash proceeds.
Receipt of cash proceeds obliges the use of cash register equipment (Clause 1, Article 1.2 of the Law “On Cash Register…” dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ). Although in a number of cases its non-use is permitted, in particular:
- Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs when carrying out certain types of activities (clause 2 of article 2 of law No. 54-FZ).
- Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs when carrying out activities in conditions that impede the use of cash register systems (Clause 3, Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
For a complete list of cases when it is allowed to work without a cash register, with explanations of ambiguous points, see ConsultantPlus. Trial full access to the system is provided free of charge.
The number of cash registers or other points for receiving money in ways that allow the non-use of cash registers is not limited. But at the end of the working day, the received revenue must be credited to the cash desk of the company or individual entrepreneur.
Thus, compliance with cash discipline in 2022 presupposes compliance with the rules for conducting incoming and outgoing transactions carried out at the cash register of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur, and the rules for working with cash registers or documents that are drawn up when cash registers are not used.
Cash discipline is mandatory for everyone.
Accounting for restrictions on cash payments
An individual entrepreneur participating in settlements with a legal entity or other individual entrepreneur must comply with the maximum limit on the amount.
| Constraint condition | Features of application | Add-ons |
| The size of the established limit | 100 thousand rubles (the amount established earlier in 2014 continues to apply in 2022) | The restriction does not apply to payments to individuals |
| Documentation of the limit by concluding an agreement. In the absence of an agreement, the limit is determined by shipping invoices | The limit applies within one contract. When using contracts of the same type, the risk of fines remains | When concluding additional agreements, the size of the limitation applies to all agreements |
| Duration of the contract to determine the limit | Not limited by calendar boundaries | The extension of the contract must be indicated |
When making a non-cash payment under an agreement for an amount of more than 100 thousand rubles, further payments in cash are considered a violation of the maximum limit.
What is cash discipline?
Compliance with cash discipline comes down to compliance with the rules established by the following documents:
- Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U, which defines the rules for conducting cash transactions for legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. The latest version of the instruction, which came into force on November 30, 2020, introduced a number of changes.
Read more about this document in the article “Nuances of the regulations on the procedure for conducting cash transactions” .
- Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated December 9, 2019 No. 5348-U, which contains the conditions for cash payments.
- Law of the Russian Federation dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ, establishing the rules for the use of cash register systems.
- Law of the Russian Federation dated July 3, 2016 No. 290-FZ or the law on online cash registers, which introduced significant changes to the rules of Law No. 54-FZ.
Regarding the operating cash desk, the basic rules are as follows:
- A person is appointed to perform the functions of a cashier, with whom an agreement on full financial responsibility must be concluded. An exception would be situations when the cash register is run by the head of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur, working alone.
- Money and cash documents are stored in conditions that ensure their safety.
- Operations carried out at the cash desk are documented in the prescribed form in compliance with a certain procedure for filling them out. Documents are completed directly upon completion of the transaction, and for the posting of cash proceeds received outside the operating cash desk - daily at the end of the working day. Cash discipline in 2022 for individual entrepreneurs who keep simplified records of their transactions allows for the possibility of not completing cash register documents.
Read more about the types of cash transactions in the article “The concept and types of cash transactions (legal regulation)” .
- If cash proceeds are received at the operating cash desk, then a cash register must be present. The issuance of a cash receipt upon receipt of cash proceeds is mandatory (Article 5 of Law No. 54-FZ).
- Money accepted by the cashier is checked for authenticity. A certain procedure for checking their quantity and quality during acceptance and issuance is observed, named in the instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated October 5, 2020 No. 5587-U, valid from November 30, 2020:
- Cash proceeds received by the operating cash desk should be spent only for certain purposes: payment of wages, settlements with suppliers and customers, issuance on account. Individual entrepreneurs can take money for personal needs.
Is it possible to spend from the cash register (bypassing the current account) the balance of the advance unused by the accountable, see here.
- The maximum amount of cash payments between legal entities, between individual entrepreneurs, between legal entities and individual entrepreneurs is limited to 100,000 rubles. under one contract. At the same time, settlements with individuals are not limited, and individual entrepreneurs have the right to take any amounts from the cash register for personal needs.
Read more about the limit on payments between legal entities here .
- Issuance on account is carried out by order of the manager or on the application of the accountable person endorsed by him. To report on amounts issued, the number of working days specified in the employer’s local regulations is provided from the expiration date for which the money was issued (including travel allowances). Unspent amounts must be returned to the cashier or will be withheld from the salary of the accountable person (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- A limit is set on the balance of money in the cash register at the end of the working day. The procedure for calculating it is chosen by the company or individual entrepreneur independently from two methods proposed by the Bank of the Russian Federation Directive No. 3210-U. The excess must be deposited in the bank. An excess balance is allowed only on paydays (no more than 5 working days). Cash discipline in 2022 for LLCs related to small-scale enterprises and individual entrepreneurs assumes that these individuals may not set this limit. For separate divisions, it is established either by the head office (if the division does not have its own current account) or independently (if the division has its own current account).
Read about determining the cash balance limit in this material.
Examples of calculating the cash balance limit at the cash register from ConsultantPlus 5.1. An example of calculating the cash register limit taking into account the volume of receipts. Cash revenue of Rassvet LLC from the sale of goods for the billing period from 03/01/2022 to 05/31/2022 (61 working days) amounted to RUB 2,385,648. Proceeds are surrendered daily (once a day). To calculate the cash balance limit in the cash register, taking into account the volume of receipts, use the formula. For all examples of calculating the cash limit and samples of documents drawn up for this, see K+. Trial access is available for free.
- Transactions with cash currency can be carried out through the cash desk. Most often they are associated with the issuance of money for foreign business trips and the delivery and receipt of currency at the bank. In some cases, settlements with residents may occur (Article 9 of the Law of the Russian Federation of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ).
Read more about currency transactions in the article “Currency transactions: concept, types, classifications” .
Report deadlines
As stated in clause 6.3 of the instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U, the employee is obliged to provide a report on the amounts received no later than three working days after the expiration of the period for which these amounts were issued.
But the new requirements for the preparation of accountable amounts do not establish a specific period during which an employee must submit a report on the money spent. It is indicated in the employer's order. If the return period is not established, the employee submits the report on the same day on which he received them. This is indicated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated January 24, 2005 No. 04-1-02/704.
But for travel expenses there are special conditions for the advance report. According to clause 26 of the regulations, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749, the employee is obliged to report on them within 3 working days from the date of return.
What you need to know about working with CCP
The requirements for the CCP used in 2022 are determined by the updated law No. 54-FZ.
From 02/01/2017, only new-style cash registers (online cash registers) began to be registered with the Federal Tax Service. From July 1, 2019, this type of cash register became mandatory for use by almost all business entities.
Online cash registers are fundamentally different from previously used cash registers with a fiscal drive. Accordingly, the requirements for them are completely different.
For general requirements that online cash registers must meet, read the article “Where and at what price can you buy an online cash register?” .
The problems that arise during their work also became different.
You will find answers to many questions related to the use of online cash registers in our section “Online cash registers KKT KKM”.
Individual entrepreneur on the simplified tax system using online cash desks
The use of individual entrepreneurs online cash desks in 2022 is also mandatory for entrepreneurs who have a deferment due to the use of special regimes, including the simplified tax system. Starting from July 1, 2022, the deferment has also ended for individual entrepreneurs who do not have hired employees. Terms of use of KKT:
- An individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system must use equipment that complies with the register and is registered with the Federal Tax Service.
- The equipment must have a serial number and a fiscal drive.
- The equipment allows you to transmit OFD data and print a two-dimensional code on a receipt.
- The equipment must have a timer, functions for generating current reports, document search and other important settings.
Fiscal data allows you to obtain information about cash receipts, including documents with corrections, reporting, data on opening and closing shifts and other forms.
Individual entrepreneurs operating in hard-to-reach areas are allowed not to use the new type of cash register equipment. In conditions of unstable Internet operation or in its absence, the functioning of online cash registers is impossible. At the request of buyers, individual entrepreneurs are required to issue a document containing mandatory details. The list of remote regions is determined by regional acts.
What is the basis for knowing the procedure for preparing cash documents?
The changes made to Law No. 54-FZ by Law No. 290-FZ not only affected the requirements for the cash register equipment used, but also led to updated requirements for the documents generated by this equipment: cash receipts and BSO. At the same time, the BSO has become a document in the execution of which devices similar to online cash registers must be used. Accordingly, the list of details for documents generated by the new cash desks turned out to be the same (Article 4.7 of Law No. 54-FZ).
Read about what has changed for BSO with the advent of online cash registers in the article “Law on online cash registers - how to apply BSO (nuances)” .
There are 2 types of actions recorded at the operating cash desk:
- Receipts using a cash receipt order (PKO) form KO-1, to which, if possible, documents are attached confirming the amount of the incoming amount. The detachable part of the PKO (receipt), containing the signatures of authorized persons and a seal, is transferred to the depositor.
- Expenses using the cash expense order (RKO) form KO-2, to which, as a rule, documents are attached confirming the amount of the amount issued (pay slips, memos, copies of orders, checks, receipts). The RKO reflects the details of the recipient’s identity document. If receipt is carried out by power of attorney, then its original (if the power of attorney is one-time) or a copy (if the power of attorney is not one-time) is attached to the RKO.
The PKO and RKO forms are established by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88 and are mandatory for use in the Russian Federation when registering income and expense transactions. Each operation requires its own separate document.
All PKOs and RKOs issued during the day are recorded in the cash book of the KO-4 form, which sums up the work for the day (receipt and expense turnover) and displays the balance at the end of the day.
PKO, RKO and cash book contain a reference to accounting accounts, the indication of which is mandatory for companies and optional for individual entrepreneurs who do not have to keep accounting (subclause 1, clause 2 of the law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
Additionally, such forms of cash documents can also be filled out as a journal for registering incoming and outgoing cash documents of form KO-3 and a book of accounting for funds accepted and issued to other cashiers of form KO-5.
The procedure for filling out cash documents is given in Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 88 and instructions of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U.
Read about the rules for filling out cash orders in the following materials:
- “How is a cash receipt order (PKO) filled out?”;
- “How is an expense cash order (RKO) filled out?”.
Innovations for 2022 on accountable transactions of individual entrepreneurs
Starting from July 2022, mainly electronic cash receipts are used in circulation. Accountable persons purchasing goods or services for cash in the interests of the enterprise must attach printed electronic cash documents to the report. The authenticity of checks is verified. If in doubt, the official website of the Federal Tax Service allows you to use the “Check Check” service.
The procedure for maintaining electronic and other document flow is determined by the enterprise. Features of the design of reporting forms are provided.
| Condition | Description of application | Add-ons |
| Details required when issuing an electronic receipt for the purchase of goods | The seller of goods is obliged to indicate in the receipt the buyer’s details (name and tax identification number), country of origin of the goods, customs declaration number, excise tax amount | Details are provided if the buyer has a power of attorney from the company confirming the competence to represent interests |
| Confirmation of completeness of product information | Some individual entrepreneurs working in a special mode provide checks without deciphering the nomenclature and quantity of goods | When receiving a check without highlighting the name of the product, you must provide an additional document with a breakdown of the data |
| Possibility of receiving a check from self-employed persons | Self-employed citizens must also provide information about the services provided | When receiving services from self-employed persons, a check is printed from the “My Tax” mobile application. |
| Receiving services with registration of BSO (for example, when receiving hotel accommodation while on a business trip) | The BSO indicating the services received must meet the requirements in terms of form and set of details. The new form of BSO practically corresponds to an electronic cash receipt | The accountable person as part of the supporting documents after 07/01/2022 does not have the right to provide the BSO in the typographic form adopted earlier |
The remaining requirements for registration of accountable transactions have not changed. The issuance of funds is carried out by order of the manager. If the accountable amount is used by the entrepreneur himself, orders and an expense cash order are not required. To provide a report on the funds spent, the employee is given the period allotted by the accounting policy.
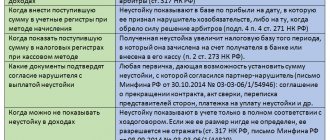
Who monitors compliance with cash discipline?
All employees associated with their implementation must control the correctness of actions for carrying out cash transactions. If the organization has a chief accountant, then he is responsible for monitoring the work of the accounting department and the operating cash desk that is part of it. The general responsibility for the activities of the company lies with its director, and the individual entrepreneur himself is responsible for the activities of the individual entrepreneur.
Checking cash discipline in 2022, which may result in an administrative fine or subsequent on-site inspection for the person being inspected, is carried out by the tax authorities (Clause 1 of Article 7 of the Law of the Russian Federation of March 21, 1991 No. 943-I).
The objectives of this audit are to identify the facts:
- incompleteness and untimeliness of receipt of revenue;
- exceeding the cash payment limit;
- exceeding the cash balance limit;
- use of prohibited, faulty or non-compliant cash register equipment;
- failure to issue cash receipts or BSO;
- discrepancies between actual cash balances in the cash register and the amounts indicated in the documents;
- issuing large sums of money on account for unreasonably long periods.
Features of cash transactions for individual entrepreneurs, accounting documentation
Individual entrepreneurs have a simplified procedure for cash transactions. The entrepreneur independently determines the timing of the deposit of funds to the bank and does not approve the limit of the cash balance at the cash desk (clause 2 of Directive No. 3210-U).
Entrepreneurs are given the right not to draw up cash orders for expenses (RKO) and receipts (PKO) and, as a result, not to maintain a cash book (subclauses 4.1 and 4.6, clause 4 of Directive No. 3210-U).
Legislation allows for undocumented cash movements.
Attention! Refusal to draw up RKO and PKO increases the risk of possible abuse of official position by officials.
Refusal to maintain cash documents is justified in the absence of hired employees or business partners.
Documents that serve as confirmation of the amount of revenue in non-documentary accounting are:
- Z-reports (in case of using CCP);
- strict reporting forms.
The issuance of wages is documented in payroll form No. T-53 (OKUD code 0301011) or payroll form No. T-49 (OKUD code 0301009).
Cash discipline in 2022 for individual entrepreneurs in all other cases, except for those discussed above, is mandatory. What it consists of, read below.
How is cash discipline checked?
Checking cash discipline in 2022 is carried out by decision of the head of the Federal Tax Service in the manner established by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 17, 2011 No. 133n. During the verification process, the following are studied:
- All documents that are related to the execution of cash transactions.
- Fiscal memory reports.
- Documents for the purchase, registration and maintenance of cash registers.
- Documents related to the acquisition, accounting and destruction of BSO.
- Accounting registers of accounting or business transactions.
- Order for cash balance limit.
- Expense reports.
At the same time, inspectors are given unlimited access to the cash register, including its passwords and cash.
During the inspection, any other documents related to the subject of the inspection, as well as explanations, may be requested.
Find out how a bank checks cash discipline in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you do not already have access to this legal system, a full access trial is available for free.
What do tax authorities pay attention to during an audit?
Previously, banks were authorized to verify compliance with cash discipline rules. However, since 2012, this competence has been transferred to representatives of the Federal Tax Service, who, during an on-site inspection, can control:
- correct accounting of cash in the cash register;
- information recorded on the fiscal memory of the cash register by printing reports;
- any documents related to the execution of cash transactions (receipt and expense orders, cash register reports, cash book);
- timely issuance of cash receipts to customers.
Responsibility for conducting cash transactions with violations
Responsibility for violation of cash discipline is administrative. Terms of involvement in it (Article 4.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- 2 months - for offenses not related to CCP;
- 1 year - for violations in working with cash register systems.
Important! ConsultantPlus warns This period begins to be calculated from the day the offense was committed, and in the case of a continuing offense - from the day it was discovered by the inspector (Parts 1, 2 of Article 4.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). A continuing offense should be understood... Read more about the nuances of the limitation period for fines for cash register transactions in K+. This can be done for free.
A timely detected violation will lead to fairly high fines, since Law No. 290-FZ, since 2016, fines for violation of cash discipline, or more precisely, liability for non-use of cash registers, have been seriously increased. Administrative liability for non-use of cash registers entails:
- a fine for officials in the amount of 25 to 50% of the settlement amount made without the use of cash register systems, but not less than 10,000 rubles;
- a fine for legal entities in the amount of 75 to 100% of the settlement amount made without the use of cash register, but not less than 30,000 rubles. (clause 2 of article 14.5 of the Administrative Code).
If an organization or individual entrepreneur is caught a second time for not using the cash register, then in the case where the amount of settlements without using the cash register is (including in the aggregate) 1 million rubles. and more, this will entail:
- disqualification of officials for a period of 1 to 2 years;
- suspension of activities for up to 90 days for individual entrepreneurs and organizations (clause 3 of article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Responsibility for violations of cash discipline in 2022 in the form of the use of cash registers that do not meet established requirements, the use of cash register equipment used in violation of the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation and the conditions for its registration and re-registration provides for liability in the form of:
- warning or fine in the amount of 1,500 to 3,000 rubles. for officials;
- warning or fine in the amount of 5,000 to 10,000 rubles. for legal entities (Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, paragraph 15 of Article 7 of Law No. 290-FZ).
Law No. 290-FZ introduced other grounds for holding people accountable for violations in the use of cash register systems. For example:
- for failure to send the buyer a cash receipt or strict reporting form in electronic form or for failure to transfer these documents on paper at the buyer’s request;
- responsibility has been introduced for fiscal operators, cash register manufacturers, and expert organizations.
But even if, at the time of the cash discipline check, the INFS is unable to hold the violator accountable in the form of an administrative fine (due to the expiration of the statute of limitations), there is no need to rejoice. Detection of violations in the use of cash register systems will serve as a reason for closer attention to the taxpayer and, if any other problems are identified in his work, may lead to an early on-site inspection. The clear interest of tax authorities will be caused by the incompleteness and untimely recording of revenue, as well as the identification of inconsistencies between documentary and actual cash balances in the cash register.
You can learn how you can avoid liability for an offense or reduce the fine from the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Follow the link and get trial access to K+ for free.
The fact of issuing large sums of money on account for unreasonably long periods may lead to additional personal income tax assessment on these amounts (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated March 5, 2013 No. 14376/12).
Imposition of sanctions on individual entrepreneurs for violation of cash discipline requirements
For violation of the procedure for conducting cash transactions or handling cash, an individual entrepreneur may be fined in accordance with Art. 15.1 Code of Administrative Offences. The fine is provided in the amount of 4,000 to 5,000 rubles. Sanctions falling within the scope of this article are established by the Tax Authorities (Article 23.5 of the Administrative Code).
The period for imposing administrative punishment is 2 months. An individual entrepreneur brought to justice for the first time may receive a warning. The condition for mitigating the sanction is the provision of evidence of the primary commission of the violation and the absence of damage caused to other persons.
Results
Acceptance of cash proceeds, as a rule, obliges the recipient to have a cash register that issues a document confirming the acceptance of the corresponding amount. Currently, a new type of cash registers - online cash registers - have become mandatory for use. They generate not only cash receipts, but also BSO. Accordingly, the requirements for new cash registers and the documents issued by them have changed.
There are no changes in 2022 regarding the documents generated by the operating cash desk. Just as there are no changes in the authority that checks the state of cash discipline (i.e. compliance with the rules for working with cash), it remains the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate. Despite the limited period for bringing to justice for violations when working with a cash register, the detection of such violations is fraught with consequences in the form of an on-site tax audit.
Administrative liability itself has increased significantly since 2016: the size of fines has increased, the types of liability for non-use of cash registers have been expanded, and in connection with the start of work with a new type of cash register equipment, new grounds for liability have been introduced.
Sources:
- Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making payments in the Russian Federation”
- Directive of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 N 3210-U
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law of December 10, 2003 N 173-FZ “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control”
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What to consider in 2022
When accepting the report, take into account changes in the design of cash receipts and BSO.
From 07/01/2019, the cash register receipt or BSO issued instead includes information about the name of the buyer (organization or individual entrepreneur) and his tax identification number. When preparing documents using the new reporting templates from August 19, 2017, remember:
1. If the accountable person has been given a power of attorney to purchase goods and services in the interests of the organization and he has presented it to the seller, then the seller is obliged to reflect this data in the issued cash receipt.
2. If the seller is not able to reliably establish that an individual is acting in the interests of a certain organization, then he is not obliged to comply with this requirement for issuing a check. In this case, the buyer for the seller is the individual himself. And the cashier's check is issued in the usual manner.
How to keep a cash book
Maintaining a cash book is mandatory for all organizations. No documents or forms can cancel the mandatory requirement for registration of KO-4. Only individual entrepreneurs who keep records of income and expenses or actual indicators under the Tax Code of the Russian Federation have the right to refuse to fill out.
Otherwise, the requirement is the same for everyone. It makes no difference what form of ownership, legal form or taxation system the organization has. You will have to fill out the cash book daily.
Fill out the form at the end of the operating day. The journal records all incoming and outgoing orders issued during the day. The cashier then tallies the total. The entry is recorded in the appropriate column of the form. We examined the filling in detail in the article “Cash book and online cash register: how to do it correctly.” Use this form:
Was it possible to avoid punishment?
As can be seen from the example, it is not enough to correctly register incoming and outgoing cash transactions - it is important to have complete information about the requirements of regulatory documents when carrying out certain business operations, including the restrictions established by law when working with cash.
You can hope that the tax authorities will not have time to check the company during the statute of limitations. However, ignoring legal requirements cannot have a positive impact on the company's reputation.
For more information about liability for tax offenses, see the material “Responsibility for tax offenses: grounds and amount of sanctions”
In order not to miss a profitable deal and not break the law, the company could pay 100,000 rubles in cash. as an advance payment, and transfer the rest of the money from the current account on the first banking day.
If there is a large and varied turnover of cash in a company, it is better for specialists of the financial and (or) accounting service to play it safe in advance - to develop special internal instructions for incoming and outgoing cash transactions. It describes in detail the actions of cashiers in various situations and indicates possible sanctions facing the company if the law is violated. Assign a responsible employee whose responsibilities will include timely updating of cash details when legislation changes. Then cash register work will not cause unnecessary problems and will not cause unplanned expenses.
You can learn how to reduce the fine from the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Follow the link and get trial access to K+ for free.
Control by tax authorities
Previously, control over compliance with discipline was assigned to banks. Now this is entrusted to employees of the Federal Tax Service. Here is what is checked during an on-site audit of cash discipline by tax authorities in 2020:
- making cash settlements with other organizations - to identify over-limit payments;
- the procedure for recording cash at the cash desk, including checking the fiscal memory of cash registers, in order to detect facts of non-receipt (incomplete receipt) of cash to the cash desk;
- the procedure for storing available funds in the cash register and the amount of the balance - to check its compliance with the cash register limit;
- the procedure for issuing cash register checks (or BSO) at the buyer’s request in accordance with Federal regulations. Law of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ.
Main rules
Let's summarize what has been said:
1. Any amount is issued for the report.
2. From August 19, 2017, in order for an employee to receive an accountable payment, an order from the head of the company is sufficient. It is not necessary to write an application.
3. Previously, before submitting a report for the previous amount, an employee could not receive an accountable amount; now the answer to the question: is it possible to issue money for an accountable amount if the employee has not accounted for the previous one? Yes, it is possible.
4. Accountable amounts may be transferred to bank cards.
5. As of August 19, 2017, local acts on settlements with accountable persons have been updated.
Documentation of cash receipts transactions
The receipt of cash at the cash desk is formalized by a cash receipt order (form according to OKUD 0310001).
For more information about it, see “How to fill out a cash receipt order (PKO).”
Upon receipt of the PKO, the cashier:
- Checks for the signature of the chief accountant, accountant or manager - only if it is a paper document.
- Checks the correspondence of the amount of cash entered in numbers with the amount of cash entered in words, as well as the presence of supporting documents.
- Receives money, counts it and checks the amount specified in the order with the amount actually accepted.
- Signs the PKO and affixes a seal (stamp) to the receipt issued to the depositor. If the PKO is electronic, then the cashier sends a receipt at the request of the depositor to his email.
If the amounts do not correspond, and the depositor refuses to add the missing amount, the cashier crosses out the PKO and transfers it to the chief accountant, accountant or manager for re-registration for the actual amount of cash deposited. If the receipt is issued electronically, the cashier makes a note about the need to re-register the PKO.
In the case of capitalization of revenue received using a cash register, the receipt can be issued once for the total amount based on the control tape or strict reporting forms of the online cash register.
Cash discipline for individual entrepreneurs and legal entities
The instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation apply to all business representatives, be it a small enterprise or a large company. However, there are some differences, which we will look at next.
Cash discipline for individual entrepreneurs
For individual entrepreneurs, the procedure for maintaining cash discipline has been significantly simplified. The Central Bank's instruction allows entrepreneurs not to issue receipts and expenditure orders when receiving and issuing money.
In addition, they may not maintain a cash book. An entrepreneur, taking advantage of these benefits, will be able to confirm the receipt of revenue with checks, shift closure reports and strict reporting forms.
It should be remembered that the choice to apply or not to apply these benefits is a right, not an obligation.
In addition, some individual entrepreneurs are exempt from the obligation to use cash registers.
1. Ask our specialist a question at the end of the article. 2. Get detailed advice and a full description of the nuances! 3. Or find a ready-made answer in the comments of our readers.
Thus, until July 1, 2022, entrepreneurs who comply with certain conditions may not use online cash register systems:
- provide services to the population;
- do not have a staff of employees;
- pay UTII or PSN to the budget;
- comply with the room area restrictions;
- They do not sell excisable and marked goods, beer.
Are you switching to an online checkout? We will select a cash register for individual entrepreneurs and LLCs in 5 minutes.
Leave a request and get a consultation.
Cash discipline for legal entities
The rules of cash discipline for legal entities also provide for some relaxations when it comes to small businesses. The criteria for inclusion in this category of “beneficiaries” are incomes of less than 800 million rubles. per year and less than 100 employees. If a commercial legal entity meets these criteria, the condition of storing cash at the cash desk is canceled for it. That is, for such a company the condition for determining the cash limit may not apply. To do this, an internal order must be issued.
Other companies must comply with the entire set of rules and principles described above.
Specifics of violations of cash discipline of LLC
Limited liability companies are the most widely represented organizational and legal form of companies in Russia. For this reason, it is LLCs that most often commit violations of cash discipline.
The most common errors among LLCs are related to exceeding the threshold for cash payments between business entities. This occurs due to an incorrect interpretation of the law, including when an LLC pays under an agreement with individual entrepreneurs (the requirement for limits applies to this situation in full).
General rules for preparing documents for cash transactions
Cash transactions are carried out by a cashier or other employee, to whom the head of the organization or entrepreneur assigns the duties of a cashier. The cashier must familiarize himself with his official rights and responsibilities by signature. If an organization or individual entrepreneur has several cashiers, a senior cashier is appointed. If necessary, the head of the organization or individual entrepreneur can also conduct cash transactions.
NOTE! The cashier is the financially responsible person with whom the corresponding agreement is signed. You can download his example from the link.
All cash documents, including the cash book, can be prepared in paper or electronic form. Documents on paper are drawn up by hand or on a computer and signed by authorized persons. Electronic documents are drawn up using technical means to ensure their protection from unauthorized access, distortion and loss of information. They are signed with electronic signatures in accordance with the requirements of the Law “On Electronic Signatures” dated 04/06/2011 No. 63-FZ.
Cash documents are signed by the chief accountant or accountant (in their absence, by the manager), as well as by the cashier. If the document is electronic, then it is signed with an electronic signature (EDS). The Ministry of Finance believes that when preparing primary accounting documents it is possible to use a simple electronic signature (letter dated July 17, 2017 No. 03-03-06/1/45323). The cashier is provided with a seal (stamp) containing the details confirming the cash transaction, as well as sample signatures of persons authorized to sign cash documents. The cashier is obliged to compare signatures with samples only if the document is not drawn up in electronic form with an electronic signature. In the case of conducting cash transactions and drawing up cash documents by the manager, sample signatures of persons authorized to sign cash documents are not drawn up.
If there is a senior cashier, transactions for the transfer of cash between the senior cashier and cashiers during the working day are reflected by the senior cashier in the book of accounting for received and issued cash.