Accounting for fixed assets under the simplified tax system “income”
“Simplers” who have chosen the object of taxation “income” do not take into account any expenses for tax purposes (clause 1 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore they cannot in any way reduce the tax due to expenses associated with the acquisition of fixed assets.
However, this does not mean that OS objects can be ignored. You will still have to keep records of fixed assets under the simplified tax system “income”. The fact is that the residual value of fixed assets is important as a criterion that allows you to switch to the simplified tax system and apply this particular special regime. All “simplified people” (as well as those who are just planning to switch to the simplified tax system) must comply with it equally, regardless of the chosen object of taxation. The Russian Ministry of Finance drew attention to this in its letter dated September 18, 2008 No. 03-11-04/2/140.
Let us recall that the threshold for the residual value of fixed assets, above which the application of the simplification is impossible, is established in subparagraph. 16 clause 3 art. 346.12 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. From 2022 it will be 150 million rubles. The residual value indicator is calculated according to accounting data.
NOTE! This limitation on the residual value of fixed assets applies to both organizations and individual entrepreneurs (see, for example, letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 2, 2018 No. 03-11-11/78908).
When selling fixed assets, “profitable” “simplified” accounts for the corresponding proceeds in the generally established manner.
More details about this can be found in the material “ Procedure for selling OS under the simplified tax system “income” ” .
IMPORTANT!!! From 01/01/2022, the use of FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” is mandatory for all organizations. Organizations that have the right to conduct simplified accounting (and these often include simplified ones) are exempt from the application of certain points of the new standard. It is necessary to determine the residual (book) value to control the limit on the value of fixed assets based on accounting data, that is, on the basis of FSBU 6/2020.
Fixed assets in KUDIR
Individual entrepreneurs do not keep accounting records, but they are required to record income and expenses in the appropriate accounting book (KUDIR) in the form approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 22, 2012 No. 135n. Organizations also conduct KUDIR. It also reflects the recognition of expenses on acquired fixed assets.
The expenses in question must be recorded in section II of the accounting book. If several fixed assets were acquired during the reporting period, then each of them must be indicated in a separate line of section II.
The fact is that fixed assets may differ in terms of useful life, as a result of which the procedure for writing off expenses for them may be different (we will consider this feature later in the article).
An important aspect of working with fixed assets expenses in the accounting book: the total amount, which reflects the purchase costs taken into account when calculating the tax base of one or more fixed assets, and is indicated in the last line of section II in column 12, must also be entered in column 5, which is located in section I of the accounting book.
It is necessary, as we noted above, to reflect expenses associated with the acquisition of fixed assets under the simplified tax system in equal shares: the corresponding amounts should be recorded in column 11 of Section II of the accounting book.
Accounting for fixed assets under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
Taxpayers using the simplified tax system with the object “income reduced by the amount of expenses” are allowed to take into account expenses when calculating the single tax (subclause 1, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- for the acquisition, construction and production of fixed assets;
- their completion, retrofitting, reconstruction, modernization and technical re-equipment.
You can also read about the accounting procedure and features of taxation of fixed assets under the simplified tax system in this article.
The procedure for accounting for fixed assets under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” is prescribed in subparagraph. 3 and 4 tbsp. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
At what cost to keep fixed assets for the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
The procedure for determining the value in accounting for fixed assets under the simplified tax system depends on when the fixed assets were acquired and put into operation:
- If this happened after the transition to the simplified system, then fixed assets that were acquired/created during the period of being on the simplified tax system are accepted for accounting at their original cost, determined in the manner established by the legislation on accounting (clause 3 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3.10 The procedure for filling out KUDIR, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 22, 2012 No. 135n).
If you have access to K+, check whether you have correctly determined the initial cost of fixed assets. If you don’t have access to K+, get a free trial access and go to the Guide to the simplified tax system.
2. If this happened before the transition to the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses” (clause 3 of article 346.16, clause 2.1 of article 346.25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), the determination of the cost depends on what mode the transition was from:
- with OSNO - at the residual value in the form of the difference between the acquisition price and the amount of depreciation accrued according to the “profitable” rules in accordance with Chapter. 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Unified agricultural tax - at the residual value, determined by the residual value of fixed assets on the date of transition to payment of unified agricultural tax, reduced by the amount of expenses taken into account during the period of application of the agricultural regime;
- when switching from the simplified tax system to “income”, the residual value is not determined.
To learn about the costs of fixed assets for which purposes can be taken into account for the simplified tax system, read the material “For the simplified tax system, expenses only for “production” fixed assets are taken into account .
1C Accounting - accounting of business transactions in detail!
subscribe to blog updates via e-mail
Hello dear readers of the blog-buh blog. Today we will once again get acquainted with another regulatory operation for closing the month , which is in the software product 1C Enterprise Accounting 8 edition 3.0 - it is called “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of OS for the simplified tax system . The 1C ACCOUNTING program allows you to keep records not only under the general taxation system (OSN), but also under the simplified taxation system (USN). I will also note that it can be successfully used to keep records of individual entrepreneurs, but this is a slightly different conversation, so we will put it aside for now. In this article I will talk about some of the features of accounting under the simplified tax system and, using an example, I will tell you why the regulatory operation is used - “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets for the simplified tax system.”
Let me remind you that the site already has a number of articles that are devoted to the issue of closing a month in the 1C BUKH 3.0 program:
- Part 2: “Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26” transactions: detailed analysis of “Closing the month” in 1C ACCOUNTING 3.0
- Part 1: “Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26” transactions: detailed analysis of “Closing the month” in 1C ACCOUNTING 3.0;
- “Adjustment of item cost”;
- “Revaluation of foreign currency funds”;
- “Calculation of trade margin”;
- “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of OS for the simplified tax system”;
- “Write-off of additional expenses for the simplified tax system”;
- “Calculation of shares of write-off of indirect expenses”;
- “Calculation of transport tax”;
- “Calculation of land tax”;
- “Calculation of property tax”;
- “Write-off of deferred expenses”;
- “Repayment of the cost of workwear and special equipment”;
- Accounting for depreciation of fixed assets;
- Exclusion of work in progress from the composition of material costs for the simplified tax system;
- Methods of depreciation of fixed assets in 1C Accounting.
Setting up accounting policies for simplified taxation purposes
Before we begin reviewing the current issue, I would like to talk a little about how to set up 1C ACCOUNTING edition 3.0 to account for the Simplified Taxation System (STS). To do this, let's open the “Accounting Policy” (section of the main menu “Directories and Accounting Settings” in the “Taxi” interface). Set the “Taxation system” switch to “Simplified” and fill out the “STS” tab.
On this tab you need to specify the following fields:
- The date of transition to the simplified tax system is the first day of the year; You can switch to the simplified tax system from another taxation system only from the beginning of the year; I will not fill out this field, since our organization is not switching to the simplified tax system, but has just opened and is starting activities immediately on the simplified tax system;
- Notification of transition to the simplified tax system No. and date - notification of the transition must be submitted to the tax authority before December 31; I also don’t fill it out;
- To control the provisions of the transition period in accordance with clause 1 of Article 346.25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - is established for organizations that, before the transition to the simplified tax system, had a special tax system and used the accrual method when calculating income tax.
- The object of taxation is two options: “income” at a rate of 6% or “income minus expenses” at a rate of 15%. For our example, the second option will be chosen;
- Procedure for recognizing expenses - a table opens in which recognition criteria are set by checkboxes.
- The basic procedure for reflecting advances from the buyer for tax purposes is that if the value “Income of the simplified tax system” is selected, then the advance will be recognized as income for the purposes of the simplified tax system, if the second value is selected, then the advance will not be considered income of the simplified tax system.
I will not go into detail about the remaining bookmarks, since they are individual for each organization and filling them out will not pose any special problems. Let us move on to the issue at hand.
Purchase of fixed assets under the simplified tax system
Let's consider the principle of operation of the regulatory operation “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of OS for the simplified tax system” using the example of an organization that purchases an expensive server and accepts it for accounting as a fixed asset (FP).
| So, to begin with, our organization makes an advance payment to the supplier in the amount of 40,000 rubles. To do this, we generate the document “Write-off from the current account”. Filling out the document itself has no special features in connection with the simplified tax system. I would like to draw your attention to the document postings. In addition to the standard accounting entry Dt 60.02 <- Kt 51 in the amount of 40,000, the program generates movement in the register “Ledger of Income and Expenses (Section I) (1)”. |
In column 6 of this register the amount of our payment is entered - 40,000.
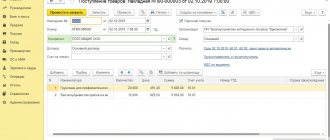
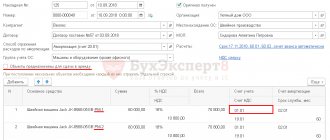
Next, using the document “Receipt of goods and services”, we reflect the purchase of equipment - Server - worth 100,000 rubles. We fill out the document in a standard way, there are no special features in connection with the simplified tax system. It forms a typical posting Dt 08.04 Kt 60.01 in the amount of 100,000 rubles. Also counts the advance payment Dt 60.01 Kt 60.02 – 40,000 rubles. It does not generate additional tax accounting entries.
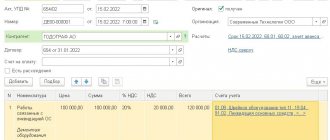
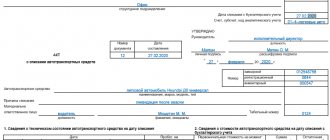
| Now we create the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets” . I wrote in detail about this document and about the depreciation of fixed assets in the article Accounting for depreciation of fixed assets: a detailed description of “Closing the month” in 1C ACCOUNTING 3.0. Therefore, now I will note only those features that relate to the simplified tax system. These features are present on the “Tax accounting (STS)” of the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets”. There are several fields that must be filled in to correctly account for the costs of purchasing this OS in the simplified tax system: |
- Cost (amount of expenses of the simplified tax system) – indicate the total cost of the server 100,000 rubles;
- Date of acquisition – date of the document “Receipt of goods and services” 02/14/2014;
- Useful life – we indicate 36 months;
- The procedure for including the cost in expenses - if we select the option “Include depreciable property” , then the expenses for the purchase of fixed assets will, firstly, be included in Section 2 of the Book of Accounting for Income and Expenses (it is called “II. Calculation of expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets funds and... taken into account when calculating the tax base..."), and, secondly, expenses will be distributed evenly between quarters. If we choose the option “Include in expenses” , then this expense does not fall into Section 2, but only into Section 1 of the Book of Income and Expenses, moreover, the expense will be taken into account in full in one month. We will choose the first option;
- Payment – in this tabular section you must manually indicate the amount and date of prepayment to the supplier for this OS.
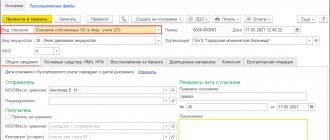
Let's review the document. It will generate a standard accounting entry Dt 01.01 Kt 08.04 – 100,000 rubles, and will also create an entry in the register “Registered payments of fixed assets (STS)”. Based on this register, the month-end closing document “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets for the simplified tax system” . The program took the data for posting from the “Payment” tabular section on the “Tax Accounting (USN)” tab.
Next, we reflect the remaining payment to the supplier in the amount of RUB 60,000. document “Write-off from current account”. I won’t go into detail here.
Since the payment was made after we accepted the OS for accounting, it is necessary to register it for the purposes of the simplified tax system (register “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of OS for the simplified tax system” , which we just looked at). For this, the document “Registration of payment for fixed assets and intangible assets of the simplified tax system” . The link to it is in the “OS and intangible assets” section of the main menu. The document must indicate the fixed asset, payment date and payment amount. Post the document.
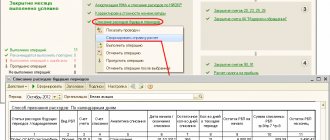
Formation of a routine operation for closing the month “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets for the simplified tax system”
Now we can talk about closing the month. The operation “Recognition of expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets for the simplified tax system” can be generated once a quarter (March, June, October, December), if there are appropriate grounds for formation. In our case, this document will be generated for the first time in March 2014 (OS was purchased and accepted for accounting in February). The operation will be performed every quarter until the end of the year, since in the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets” the cost accounting procedure “ Include depreciable property” was chosen. Let's create a March document and look at the postings.
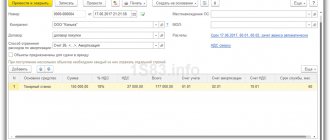
As we can see, the document generated postings in two registers. The first register is “Book of Income and Expenses (Section I)” . In column 7 of this register, 2 entries were made, which correspond to the dates of payment to the supplier for the received equipment (02/10/2014 - advance; 02/16/2014 - the remainder of the debt). The amounts in the column are defined as a quarter (25%) of the amount of payments in order to evenly distribute payments across all 4 quarters of the year. This register determines the completion of Section 1 “Income and Expenses” in KUDiR.
The second register is “Book of Income and Expenses (Section II).” Column 13 of this register is filled with the same values. This register determines the completion of section 2 “Calculation of expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets and ... taken into account when calculating the tax base ...” KUDiR .
That's all!
If you liked this article, you can use the social media buttons to save it to yourself!
Also, don’t forget to leave your questions and comments in the comments !
Let me remind you once again that this was material from the “Closing of the Month” section, all articles of which are located here. To learn about new publications in time, you can subscribe to blog updates via e-mail.
Deadline for writing off fixed assets as expenses
This period also depends on the period of incurring expenses (clause 3 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- If this happened during the period of application of the simplified system, costs for the acquisition (construction, production) of fixed assets, as well as completion, retrofitting, reconstruction, modernization and technical re-equipment of fixed assets are taken into account from the moment these fixed assets are put into operation.
- If expenses were incurred before the transition to a simplified system, the cost of fixed assets with a useful life of up to 3 years inclusive completely reduces the simplified tax during the first calendar year of application of the simplified tax system.
Assets with a useful life of 3 to 15 years inclusive are written off for 3 years:
- 50% of the cost - during the first calendar year of the simplified tax system;
- 30% of the cost - during the second;
- 20% - during the third.
Fixed assets with a useful life of more than 15 years are written off during the first 10 years of application of the simplified taxation system in equal shares of their value.
The useful life of the OS is established on the basis of classification, approved. by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 1, 2002 No. 1, or in accordance with the technical specifications or recommendations of manufacturing organizations, if the OS is not named in the classification (clause 3 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How to take into account fixed assets on the simplified tax system for writing off as expenses
To take an asset into account as an expense, you need to follow the rules for its recognition in accounting and the formation of value (which can be written off in the future).
The cost of an asset in a simplified form is formed in the same way as the initial cost of a fixed asset according to accounting rules. That is, the cost of an object includes the purchase price (creation) and the cost of its delivery, assembly, adjustment and other activities that bring the object into a condition suitable for operation.
Don't forget about payment. If the expenses represent the payment of funds, we take them into account on the date of payment. If obligations are fulfilled differently (for example, by barter), we take into account payment at the time of closing the transaction from both parties.
If an organization uses a simplified accounting procedure, it is also possible to calculate the initial cost of fixed assets in a simplified manner. Let us recall the main points of the simplified order for the OS:
- The price can only include direct expenses for the purchase of an object or its creation (for example, payments to contractors). Other costs (for example, transportation or commissioning) can be taken into account immediately in the expenses of the period in which they were incurred;
- Discounts, bonuses, benefits provided by suppliers can be accepted as income for the period in which they are received, without adjusting the formed cost of capital investments;
- If the seller or contractor has provided a long deferment in payment and interest is not separately specified in the contract, they can not be separated from the contractual cost of the fixed asset. The capital investment includes the entire amount under the contract as if there had been no deferment.
The procedure for writing off fixed assets as expenses
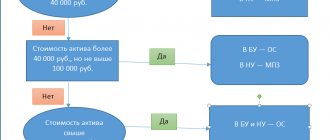
Acquired means of labor under the simplified tax system, as well as under OSNO, for tax purposes are divided into inventories, which are taken into account at a time in costs, and the fixed assets themselves. The guideline here is the cost of the purchased OS, the value of which for the purposes of such division since 2016 is 100,000 rubles. (Clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting for fixed assets under the simplified tax system is carried out according to the following rules:
- Expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets, as well as their completion, additional equipment, reconstruction, modernization and technical re-equipment are taken into account to reduce the tax base for the reporting periods in equal shares (clause 3 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4 of article 5 of the law “On Amendments” dated 06/08/2015 No. 150-FZ).
- Expenses for fixed assets are reflected on the last day of the reporting (tax) period in the amount of amounts paid (subclause 4, clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Expenses can be taken into account only for fixed assets used in carrying out business activities (subclause 4, clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In practice it happens like this:
- the amount to be accounted for in the corresponding year is divided into equal parts according to the number of reporting periods remaining until the end of the year;
- At the end of each quarter, the received portion is expensed, which is recorded in the book of income and expenses.
Read more about the design of this document in this material.
Example
An organization using the simplified tax system purchased and paid for a fixed asset worth RUB 200,000 in July. She can take its cost into account until the end of this year. Since there are 2 reporting periods (III and IV quarters) left from the moment of acquiring the OS until the end of the year, in each of them 100,000 rubles can be written off as expenses. (as of September 30 and December 31, respectively).
How to show write-off of OS in accounting registers
Information that the cost of the operating system is included in expenses is entered into the KUDiR.
To decipher the conditions and procedure for accepting expenses for fixed assets, the book has a special section II. It will need to be filled out for each quarter, on the last day of which they were written off as expenses for fixed assets.
Data from section II is transferred to section I for the corresponding quarter. In the amount accepted as expenses for the quarter, as of its last date. Thus, the result from writing off fixed assets will be summed up with other expenses and taken into account when calculating the advance payment for the quarter or payment for the year.
Write-off of fixed assets purchased with installment payment
If payment for fixed assets occurs in installments (in parts), then expenses are taken into account evenly in the amount of amounts actually paid (subclause 4, clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 25, 2019 No. 03-11-11/73807, dated 17.05 .2011 No. 03-11-06/2/78 and 12/13/2010 No. 03-11-11/287).
Example
An organization purchased a fixed asset worth RUB 555,000 in installments. The parties agreed on the following payment schedule:
- April 30—RUB 225,000;
- July 31—RUB 180,000;
- October 31—RUB 60,000;
- January 15 - 90,000 rub.
In this case, only that part of the cost of fixed assets that the organization will pay this year, that is, 465,000 rubles, can be written off as expenses for the current tax period. (225,000 + 180,000 + 60,000).
Write-offs will occur in the following order:
- RUB 225,000 — in equal shares in the II, III and IV quarters (RUB 75,000 each on June 30, September 30 and December 31);
- 180,000 rub. — equal shares in the third and fourth quarters (90,000 rubles each on September 30 and December 31);
- 60,000 rub. — in the fourth quarter (December 31).
The remaining 90,000 rubles. the organization will take into account next year - also in equal shares of 22,500 rubles. (90,000 rub. / 4) March 31, June 30, September 30 and December 31.
Selling the OS "simplified"
In some cases, when selling fixed assets, recorded expenses will have to be restored. This must be done if the OS implements:
- before the expiration of 3 years from the date of accounting for the costs of its acquisition (for OS with a useful life of up to 15 years);
- before the expiration of 10 years from the date of acquisition (for fixed assets with a useful life of over 15 years).
In this case, the tax base is recalculated for a single tax for the entire period of use of such fixed assets - from the moment they are recorded as expenses until the date of sale (transfer), taking into account the provisions of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In other words, from the tax base it is necessary to remove expenses accounted for according to the rules of the simplified tax system, and include in it depreciation calculated according to the rules of income tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/11/2016 No. 03-03-06/3/20413, dated 04/14/2014 No. 03-11-06/2/16837).
If you use the straight-line depreciation method, you can double-check the accuracy of your calculations with the help of ConsultantPlus experts. Get free trial access to K+ and proceed to the calculation example.
The additional amount of tax is paid to the budget along with penalties (clause 3 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and updated declarations are submitted for the corresponding periods.
Basic limits for the simplified tax system
To work on a simplified basis, entrepreneurs and organizations must comply with the following restrictions:
- the average number of employees is no more than 130 people;
- the amount of income from the beginning of the calendar year is no more than 200 million rubles;
- the residual value of fixed assets is no more than 150 million rubles.
If they are violated, the company will lose the right to use the simplified tax system and will be forcibly transferred to OSNO from the beginning of the quarter in which it exceeded. Already during this period it will be necessary to calculate and pay income tax (personal income tax for individual entrepreneurs) and VAT. It will be possible to return to the simplified version no earlier than in a year. For example, if you lose your right to the simplified tax system in August 2022, you will be able to start working again using the simplified tax system only from January 1, 2023.
We remind you that from 2022, simplified workers must pay tax at increased rates when the amount of income exceeds 150 million rubles and the average number of employees is 100 people.
Read more
Results
When accounting for fixed assets under the simplified tax system, you need to take into account the features discussed in this article and related both to the procedure for determining the value that can be taken into account in expenses, and to the procedure for recognizing expenses. If a fixed asset is sold before the expiration of 3 or 10 years (depending on the useful life) from the moment expenses are recognized, it is important not to forget to recalculate the tax base, submit updated declarations and pay penalties.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 22, 2012 N 135n
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 01.01.2002 N 1
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.