Profit generation
The process of summing up profits and losses received from operations is called profit formation. Such operations include:
- sales of products;
- activities related to investment;
- non-operating operations,
- sale of the company's fixed assets.
Profit is generated from various sources, the main of which is sales volume, defined as the difference between sales income and the accompanying costs. The amount of profit depends on:
- sales volume;
- product price levels;
- correspondence of the level of costs to the costs incurred.
Sales volume, in turn, depends on competent commercial activity, creating conditions for sales, organizing advertising, successful pricing policy, and commodity production. The optimal level of costs is characteristic of the correct organization of labor, production technology, and technical equipment.
Not the last place in the formation of profit is played by the innovative activity of the enterprise. It ensures the renewal of manufactured competitive products, growth in sales volumes and, accordingly, profits.
Purposes for spending retained earnings
Retained earnings are the financial results obtained for the reporting period (or based on the results of the operation of the enterprise as a whole), which characterizes capital growth.
The decision on what purposes the profit can be spent on is made by the owners of the business - shareholders or founders (subclause 11.1, clause 1, article 48 of the Law “On Joint Stock Companies” dated December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ and clause 1 of Article 28 Law “On LLC” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ). Based on this decision, the accounting department makes appropriate payments. The current accounting legislation speaks about the purposes of spending retained earnings only in the annotation to the 84th account (Order of the Ministry of Finance “On approval of the chart of accounts” dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). Account 84 “Retained earnings” summarizes information about the profit (losses) received by the company for the entire period of its activity.
Learn how to account for retained earnings in accounting from the article “Accounting for retained earnings on account 84 (entries).”
Moreover, by decision of the owners, profit can be directed to:
- For the formation of reserve and other funds.
- To pay off losses from previous years.
- To increase the capital.
- For the payment of dividends.
What can retained earnings from previous years be used for? The answer to this question is in ConsultantPlus. Get trial demo access to the K+ system and access the material for free.
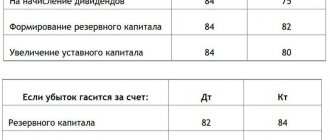
Direct payment of net profit (resulting in a decrease in retained earnings) is allowed only for the payment of dividends. In this case, these expenses do not relate to the expenses of the enterprise, and the 84th account is used in writing off profits:
Dt 84 Kt 75.
For details, see the material “Procedure for paying dividends to founders in an LLC in 2022.”
Other expenses from net profit, for example, on charity, paying bonuses to employees or holding sporting events, according to tax authorities, are illegal and should be taken into account as part of other costs (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated June 19, 2008 No. 07-05-06/138, dated December 19. 2008 No. 07-05-06/260). However, in this case it will be possible to argue with the inspectors. There is positive judicial practice on such issues, for example, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated December 13, 2011 No. F02-5765/11 in case No. A19-1914/2011.
Find out more about the procedure for paying incentives to employees from net profit in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial demo access for free.
If participants decide to use retained earnings for financial investments, for example, place funds in deposit accounts, issue a loan with interest, or purchase shares of a third-party company, then the amount of net profit will not actually decrease, but only its content will change.
Enterprise profit distribution
In a competitive environment, any company not only strives to obtain maximum profit, but also to such a volume that it will make it possible to maintain an acceptable position in the sales market and purposefully develop production. Therefore, it is equally important to correctly distribute profits by correctly implementing the policy of encouraging and generating your own resources.
When distributing profits, companies take into account the state of the market environment, which dictates the need to expand the company's production capacity. Based on this factor, the scale of contributions to funds intended to finance capital investments, increase current assets, introduce new technologies and labor methods, provide R&D, etc. is determined.
The procedure for distribution and use of profits
The company uses the profit received in accordance with current legislation and the provisions enshrined in the constituent documents, adhering to the following profit distribution scheme:
- all taxes and obligatory payments to the budget (for profit, land, vehicles, rental, etc.) are paid from the generated profit;
- from the remaining profit (net) [/anchor] funds are transferred to accumulation and consumption funds (reserve, investment, production development, dividend, social development, material incentives and others provided for by the charter or constituent documents). The standards for contributions to the funds are established by the company with prior agreement with the founders.
With all the variety of approaches to profit distribution, all enterprises are characterized by the same principles of profit distribution - its direction:
- for accumulation, i.e., development of the company (formation and replenishment of reserve and investment funds, investment in management companies of other companies, financial investments for different periods). This part of the profit is reflected in the undistributed block and forms funds;
- for consumption, i.e. distributed profit (payment of dividends, provision of social and material support for personnel, acquisition of shares, etc.)
Thus, profit distribution is a way to implement the developed dividend policy and the policy of forming the company’s own resources.
“Types of profit and distribution of net profit”
1. Types of profit
2. Procedure for distribution of net profit
3. Profitability and its types
Gross profit is defined as the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) excluding VAT and excise taxes and the costs of production and sales of products minus administrative and commercial expenses
Profit from the sale of products (works, services) is defined as the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) without VAT and excise taxes and the costs of production and sales of products
Profit before tax includes:
1. Profit from sales of products (works, services)
2. Other income minus other expenses (see question: income of the organization)
Profit before tax serves as the basis for calculating the tax to be paid to the budget, the rate of which, according to the Tax Code, is 24%
Net profit is defined as the difference between profit before tax and income tax
Monopoly profit is the profit received by monopoly enterprises. The form of realization of monopoly profit is the monopoly price. The lack of competition allows monopolies to receive extremely large profits. Its source is surplus value,
Profit distribution is the process of forming funds and reserves. The procedure for distribution of profits is fixed in the charter and determined by regulations, which are developed by the economic services of the enterprise.
Net profit is subject to distribution at the enterprise .
Enterprises distribute profits independently through the formation of special-purpose funds. The number of funds and their names are determined independently. There are no standards.
The following funds and reserves are formed from net profit:
- accumulation fund , i.e. funds are spent on the creation, implementation and development of new equipment, improvement of technologies, modernization of equipment, reconstruction of existing production, and replenishment of working capital standards. In addition, part of the profits is used to pay interest on overdue bank loans.
- consumption fund, i.e. payment of one-time incentives, benefits to those retiring, pension supplements, financial assistance to all or most employees, bonuses based on the results of work for the year is made
— fund for the development of the social sphere. The funds are spent on the construction of housing, children's institutions and other social facilities. This is a savings fund.
Fines for late and incomplete payment of taxes to the budget are paid from net profit;
- reserve capital - used in unfavorable market conditions - this is insurance capital intended to compensate for losses from business activities, to pay income to investors and creditors if there is not enough profit for these purposes, in case of delay in payments for delivered products, as well as to cover unforeseen expenses without the risk of loss of financial stability.
The formation of reserve capital is voluntary and, in some cases, mandatory.
From January 1, 1996, in accordance with the Law on Joint Stock Companies, it must be at least 15% of the authorized capital (for joint ventures - at least 25% of the authorized capital). Reserve capital is replenished by deductions of at least 5% of net profit.
After the formation of funds and reserves, part of the net profit goes to pay dividends on shares and for charitable purposes.
Distribution and use of enterprise profits
The legislator regulates the distribution of profits in terms of tax revenues to budgets. Determining other areas for spending the remaining part of the profit is the prerogative of the company. The procedure for the distribution and use of profits is necessarily recorded in the constituent documents and approved by the head of the company.
Standards for the distribution of profits are not stipulated by the legislator, but a certain influence, for example, through tax breaks, stimulates the use of profits for capital investments, innovations, charity and other purposes. The legislator limits the size of the reserve fund and regulates the procedure for forming a reserve for doubtful debts. Let's consider some aspects of profit distribution in companies of different organizational and legal forms.
Distribution of profits in LLCs and JSCs
LLC participants have the right to distribute profits or losses received in accordance with Law No. 14-FZ dated 02/08/1998. The net profit of the LLC is distributed by the general meeting of participants, but it does not have the right to make decisions if:
- the management company has not paid;
- the participant's share or part thereof has not been paid;
- there are signs of company insolvency;
- if the value of the LLC's net assets is less than the capital and reserve fund.
The main issues when distributing profits in an LLC may be the following:
- increase in the MC with a proportional increase in the share of participants;
- repayment of losses from previous years;
- dividend payment.
It is possible to increase the authorized capital only after full payment and when such a decision is made by 2/3 of the votes. The part of the profit distributed for the payment of dividends is divided among the participants in proportion to their shares in the management company, unless the charter establishes a different distribution algorithm.
An example of dividend distribution in Dom LLC
The company's participants are three domestic companies with a separate management company:
- LLC "A" - 10%;
- LLC "B" - 40%;
- LLC "V" - 50%.
The charter of Dom LLC states that profits are distributed equally between the participants. According to the decision of the meeting dated March 28, 2018, net profit for 2022 is in the amount of 900,000 rubles. subject to distribution among participants.
Since the distribution of dividends is carried out not proportionally, but equally, each participant is entitled to 300,000 rubles. (900,000 / 3) less tax. If it were carried out in proportion to the shares in the capital company, then the calculation would be as follows:
– LLC “A” - 90,000 rubles. (900,000 x 10%);
– LLC “B” - 360,000 rubles. (900,000 x 40%);
– LLC “V” - 450,000 rubles. (900,000 x 50%).
The procedure for distributing profits in a joint-stock company is regulated by Law No. 208-FZ dated December 26, 1995. According to it, the joint-stock company uses net profit to create funds (including a special fund for the corporatization of employees), increase the authorized capital (by placing additional shares or increasing their value), and paying dividends. Making a decision on the direction of profit of a joint-stock company is the competence of the general meeting of shareholders.
The distribution of dividends is carried out on the basis of the announcement of their payment on outstanding shares, usually accepted based on the results of each quarter. However, the amount of dividends cannot be greater than the amount recommended by the board of directors. A JSC cannot declare the payment of dividends on shares if:
- the management company has not paid;
- shares have not been fully repurchased;
- there are signs of insolvency;
- The value of the LLC's net assets is less than the charter capital and the reserve fund.
The JSC is obliged to create a reserve fund, forming it with mandatory annual contributions (at least 5% of net profit) up to the amount provided for by the charter (at least 5% of the authorized capital).
Example of contributions to the reserve fund of Trio JSC
The joint-stock company received a net profit for 2022 in the amount of RUB 900,000. The authorized capital is 2,000,000 rubles, the reserve fund as of 01/01/2017 was 80,000 rubles. The charter of the joint-stock company establishes the percentage of deductions - 7% of the capital up to the amount of 140,000 rubles. (2,000,000 x 7%).
The amount of deductions should be 63,000 rubles.
(900,000 x 7%), but the total amount of the reserve will be 143,000 rubles. (80,000 + 63,000), i.e. it will exceed the maximum reserve size by 3 thousand rubles. (143,000 – 140,000). Therefore, the amount of 60,000 rubles will be allocated to replenish the fund. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
“Types of profit and distribution of net profit”
1. Types of profit
2. Procedure for distribution of net profit
3. Profitability and its types
Gross profit is defined as the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) excluding VAT and excise taxes and the costs of production and sales of products minus administrative and commercial expenses
Profit from the sale of products (works, services) is defined as the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) without VAT and excise taxes and the costs of production and sales of products
Profit before tax includes:
1. Profit from sales of products (works, services)
2. Other income minus other expenses (see question: income of the organization)
Profit before tax serves as the basis for calculating the tax to be paid to the budget, the rate of which, according to the Tax Code, is 24%
Net profit is defined as the difference between profit before tax and income tax
Monopoly profit is the profit received by monopoly enterprises. The form of realization of monopoly profit is the monopoly price. The lack of competition allows monopolies to receive extremely large profits. Its source is surplus value,
Profit distribution is the process of forming funds and reserves. The procedure for distribution of profits is fixed in the charter and determined by regulations, which are developed by the economic services of the enterprise.
Net profit is subject to distribution at the enterprise .
Enterprises distribute profits independently through the formation of special-purpose funds. The number of funds and their names are determined independently. There are no standards.
The following funds and reserves are formed from net profit:
- accumulation fund , i.e. funds are spent on the creation, implementation and development of new equipment, improvement of technologies, modernization of equipment, reconstruction of existing production, and replenishment of working capital standards. In addition, part of the profits is used to pay interest on overdue bank loans.
- consumption fund, i.e. payment of one-time incentives, benefits to those retiring, pension supplements, financial assistance to all or most employees, bonuses based on the results of work for the year is made
— fund for the development of the social sphere. The funds are spent on the construction of housing, children's institutions and other social facilities. This is a savings fund.
Fines for late and incomplete payment of taxes to the budget are paid from net profit;
- reserve capital - used in unfavorable market conditions - this is insurance capital intended to compensate for losses from business activities, to pay income to investors and creditors if there is not enough profit for these purposes, in case of delay in payments for delivered products, as well as to cover unforeseen expenses without the risk of loss of financial stability.
The formation of reserve capital is voluntary and, in some cases, mandatory.
From January 1, 1996, in accordance with the Law on Joint Stock Companies, it must be at least 15% of the authorized capital (for joint ventures - at least 25% of the authorized capital). Reserve capital is replenished by deductions of at least 5% of net profit.
After the formation of funds and reserves, part of the net profit goes to pay dividends on shares and for charitable purposes.
Profitability is the most important indicator of business efficiency.
The absolute amount of profit characterizes the economic effect, but not efficiency, because this or that amount of profit can be obtained with a larger or smaller amount of funds invested in production. To determine efficiency, it is necessary to compare the financial result with the costs or resources that provided this result.
Profitability is a relative indicator that characterizes the efficiency of an enterprise and the profitability of various types of activities. (production, entrepreneurial, investment).
All profitability indicators can be calculated on the basis of profit before tax, net profit, profit from the sale of products (works, services).
An enterprise is profitable if the proceeds from sales are sufficient not only to cover the costs of production and sales, but also to make a profit.
Profitability indicators can be combined into several groups:
1. Cost profitability or product profitability
2. Sales profitability
3. Return on capital (assets) and its parts
4. Profitability of investment projects.
5. Capital return
Return on production costs shows how much profit an enterprise receives from each ruble of production and sales costs.
Profitability is determined for the enterprise as a whole, workshops and individual types of products.
Profit from sales of products R.costs = * 100% (individual types) cost of individual types of products
Profit from sales of commercial products
P costs = * 100%, where
P - profitability (of all products.) cost of goods sold
2. Return on sales characterizes the efficiency of business activity and shows how much profit the enterprise received from ruble sales.
Profit from product sales
Sales R = *100%
Revenue from product sales
Determined by enterprise, workshops, products.
A decrease in this indicator indicates a decrease in demand for products.
When planning an assortment, they take into account how the profitability of individual types of products will affect the profitability of all products, so the enterprise needs to form an assortment of its products.
Product profitability is affected by cost reduction, material savings, stabilization of calculations, and improvement of the management system.
3. Return on capital is the ability of an enterprise to increase invested capital. It shows the efficiency of use of all property of the enterprise, i.e. how much profit the company will receive per 1 ruble of invested capital.
Return on capital is determined by the ratio of gross, net profit to the average annual cost of invested capital or its individual parts: own (shareholder), borrowed, fixed, working capital.
Return on equity and fixed capital:
PD PE
Rproperty = * 100% or * 100%
capital fixed capital own. capital
where PD is profit before tax; PE – net profit
The return on fixed capital is determined in the same way.
PD PE
Basic capital = *100%, or *100%, capital fixed capital fixed capital
Return on capital serves to determine the efficiency of capital use in different enterprises, since it gives an overall assessment of the profitability of capital invested in production, both own and borrowed.
The size of dividends on shares depends on the level of return on capital. Dividends per share are determined based on the net profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise.
The financial result decreases if the share of equity funds increases and the share of borrowed funds decreases.
4. Return on investment is an indicator of the effectiveness of investments in expanded production and new equipment.
Investment = Amount of profit \ Amount of investment in the project
Return on investment characterizes the size of the increase in profit per one ruble of investment (investment). The coefficient must be compared with bank interest on long-term deposits.
5. Return on fixed assets characterizes the efficiency of using fixed assets.
profit
FR = , where
With o.f.
S.o.f. – average annual cost of fixed assets.
FR - capital return
In foreign practice, profit calculated as a percentage of sales volume or capital is called profit margin (rate).
Profitability indicators are actively used in analysis processes, financial planning, decision-making by potential creditors and investors