Is it true that retained earnings are net profits?
Retained earnings are truly net profits that (as the name suggests) were not distributed (divided) among the participants/shareholders of the company.
Net profit is considered to be that part of income from sales and non-sales operations that remains after paying taxes. The decision on how to distribute this income rests solely with the owners. Traditionally, the issue of retained earnings is put on the agenda of the annual meeting of the company's owners. The adopted decision is documented in minutes, which are drawn up following the results of the general meeting of participants/shareholders.
For information on how such a document is drawn up, read the article “Decision on payment of dividends to an LLC - sample and order.”
The main ways of spending retained earnings are considered to be in the following directions:
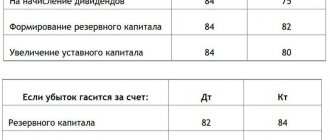
- to pay dividends to participants/shareholders;
- repayment of past losses;
- replenishment (creation) of reserve capital;
- other goals formulated by the owners.
For information about the accounting entries accompanying the accrual, payment and receipt of dividends, read the material “Accounting entries for the payment of dividends”.
The concept of retained earnings
Retained (another name is accumulated) profit is the part of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise after paying taxes, dividends, fines and other obligatory payments.
This concept closely intersects with net profit. If a company has no deferred tax liabilities and no dividends were accrued during the year, then these indicators in the annual reporting coincide. However, retained earnings represent the resulting indicator for the reporting year and for the entire period of the company’s existence, and net profit - only for the reporting period.
This term is interpreted differently in accounting and economic understanding. For an accountant, this is the final result of work, reflected in the reporting on account 84. But it has not yet actually been distributed, since the decision on where to send retained earnings is made by the owners (shareholders) in the period from March 1 to June 30 of the following year. Therefore, in an economic sense, they consider profits for the past year after this date, that is, when the accountant makes all deductions according to the decision of the owners of the enterprise.
Is retained earnings an asset or a liability?
Retained earnings on the balance sheet are, of course, a liability. The value of this indicator indicates the company’s actual debt to its owners, since ideally this profit should be distributed among the participants and invested in the further development of the business.
In fact, the company cannot dispose of retained earnings without the owners making a decision. The loss reflected in line 1370 is also on the passive side of the balance sheet, only this is a negative value, so the number is placed in parentheses.
“How to read a balance sheet (a practical example)?” will help you better understand balance sheet analysis. .
Retained earnings must be reflected on the balance sheet. ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to do this correctly. To do everything right, get trial access to the system and go to the Tax Guide. It's free.
Reflection of retained earnings (uncovered loss) in the financial statements
Retained earnings (uncovered loss) for the reporting year are reflected in line 2400 “Net profit (loss)” of the Statement of Financial Results.
The balance of retained earnings (uncovered loss) is accounted for in line 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” of the Balance Sheet (Appendix No. 1 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n).
Interim dividends paid during the year for which financial statements are prepared are reflected separately (i.e. on a separate line) in the annual balance sheet in the section “Capital and reserves” (in parentheses) (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 19, 2006 N 07-05-06/302).
The movement of retained earnings (uncovered loss) during the reporting period is reflected in the Statement of Changes in Capital (Appendix No. 2 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n).
Still have questions about accounting and taxes? Ask them on the accounting forum.
3. Dynamics of decrease or increase in the volume of retained earnings.
In 2005, compared to 2003, the volume of retained earnings decreased by 71%, and compared to 2004, decreased by 31%. A decrease in profit indicates a deterioration in the ability to replenish working and fixed assets for the organization’s sustainable economic activities.
Balance sheet structure analysis
| Indicators from the balance sheet form No. 1 | Previous years | Reporting year | Changes compared to the reporting year (+,-) | |||||
| thousand roubles. 2003 | % to balance | thousand roubles. 2004 | % to balance | thousand roubles. 2005 year | % to balance | 7-3 | 7-5 | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Assets | ||||||||
| I. Non-current assets | 23451 | 72 | 24952 | 71 | 26651 | 69,31 | -2,69 | -1,69 |
| including: — fixed assets; | 23267 | 71 | 24399 | 70 | 26166 | 68,05 | -2,95 | -1,95 |
| - long-term financial investments | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 2. Current assets | 9200 | 28,18 | 9875 | 28,35 | 11803 | 30,69 | 2,51 | 2,34 |
| including: - reserves; | 8399 | 25,72 | 9034 | 25,94 | 10476 | 27,24 | 1,52 | 1,3 |
| — accounts receivable up to a year; | 645 | 1,98 | 832 | 2,39 | 1089 | 2,83 | 0,85 | 0,44 |
| — short-term financial investments; | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| - cash | 68 | 0,21 | 9 | 0,03 | 238 | 0,62 | 0,41 | 0,59 |
| Balance (I + II) | 32651 | 32651 | 34827 | 34827 | 38454 | 38454 | — | — |
| III. Capital and reserves | 20202 | 61,9 | 23536 | 67,6 | 22933 | 59,64 | -2,26 | -7,96 |
| including: — authorized capital; | 5573 | 17,06 | 5573 | 16 | 5573 | 14,5 | -2,56 | -1,5 |
| - Extra capital; | 22306 | 68,32 | 21193 | 60,85 | 19596 | 51 | -17,32 | -9,85 |
| - Reserve capital; | 2 | 0,006 | 2 | 0,006 | — | — | — | — |
| — retained earnings (uncovered loss] | (7679) | -23,52 | (3232) | -9,28 | (2236) | -5,8 | -29,32 | -15,08 |
| IV Long-term liabilities | 535 | 1,64 | 4871 | 14 | 7014 | 18,24 | 16,6 | 4,24 |
| V. Current liabilities | 11914 | 36,5 | 6420 | 18,43 | 8507 | 22,12 | -14,38 | 3,69 |
| including: - loans and credits; | — | — | 350 | 1,005 | 350 | 0,91 | — | -0,095 |
| - accounts payable | 11914 | 36,5 | 6070 | 17,43 | 8157 | 21,21 | -15,29 | 3,78 |
| Balance (III + IV + V) | 32651 | 32651 | 34827 | 34827 | 38454 | 38454 | — | — |
Retained earnings and uncovered losses - what are they?
As mentioned above, retained earnings are the final income received by the company from its business activities, remaining after the transfer of income taxes and not yet divided (not directed to other purposes) by its owners.
Example 1
Voskhod LLC in 20XX received a profit in the amount of 800,000 rubles and paid income tax in the amount of 160,000 rubles. In line 1370 in the balance sheet liability for the year 20XX, Voskhod LLC should reflect 640,000 rubles. This is retained earnings.
The value in line 1370 of the balance sheet may be equal to that indicated in line 2400 of the financial results report if the company had no profits not distributed by the owners at the beginning of the year and no interim dividends were paid during the year.
What can retained earnings from previous years be used for? The answer to this question is in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Our article “Deciphering the lines of the balance sheet (1230, etc.)” .
As for the uncovered loss, this is the excess of the company's expenses over income at the end of the year.
Example 2
In 20XX, Parus-Trade LLC received revenue from the provision of services and other non-operating income. Their total amount was 400,000 rubles.
The costs associated with conducting the main activity (transportation) are equal to 380,000 rubles. Other company expenses (not taken into account for tax purposes) amounted to another 58,000 rubles. Profit tax was assessed in the amount of RUB 4,000. Parus-Trade LLC has no reserve capital.
This means that at the end of 20XX, after the reformation of the balance sheet, an entry of 42,000 rubles will appear in line 1370 in parentheses. (400,000 – 380,000 – 4,000 – 58,000).
An uncovered loss occurs when the company receives an actual loss and there are no financing reserves. The value entered in the liability side of the balance sheet in parentheses will reduce the total for section 3 of the balance sheet.
Among the main reasons for receiving an uncovered loss are:
- obtaining an actual negative financial result from the company’s activities due to the excess of costs over income;
- changes in accounting policies that had an impact on the financial condition of the company (this is directly stated in paragraph 16 of PBU 1/2008, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 6, 2008 No. 106n);
- errors found in the current year, made in previous years, which affected the financial result (subclause 1, clause 9 of PBU 22/2010, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 28, 2010 No. 63n).
Read more about PBU 1/2008 in the material “ PBU 1/2008 “Accounting policies of the organization” (nuances)” .
Increase in additional capital
You can increase additional capital by revaluing fixed assets or intangible assets (IMA).
According to clause 15 of PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets,” a commercial organization can revalue groups of similar fixed assets at current (replacement) cost no more than once a year (at the beginning of the reporting year). The amount of revaluation of an object of fixed assets as a result of revaluation is credited to the additional capital of the organization. Similar standards for the revaluation of intangible assets are given in clauses 17 and 21 of PBU 14/2007 “Accounting for intangible assets”.
When making this decision, the following must be considered:
— subsequently, fixed assets and intangible assets are revalued regularly. The application of the right to revaluate assets, the procedure and frequency of its implementation are fixed in the accounting policies of the organization;
— on overvalued fixed assets you will have to pay more corporate property tax. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the object of taxation for Russian organizations is movable and immovable property recorded on the balance sheet as fixed assets in the manner established for accounting. The very amount of tax can be accepted as expenses for the purposes of calculating income tax (clause 1, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Taking this into account, the tax overspending will be:
- 1.76% of the amount of increase in additional capital by the amount of revaluation of fixed assets = 2.2% (the maximum rate of tax on property of organizations established by clause 1 of Article 380 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) x (1 - 0.2) (including tax profit rates of 20%);
— to carry out the revaluation of fixed assets or intangible assets, an appraiser’s report will be required.
It is possible to increase the additional capital of an LLC by making contributions to the property of the company by participants on the basis of Art. 27 of the LLC Law.
So, according to paragraphs 1, 3, 4 of Art. 27 of the Law, the participants of the company are obliged, if provided for by the charter, by decision of the general meeting of participants to make contributions to the property of the company. Such an obligation of participants may be provided for by the charter of the company upon its establishment or by introducing amendments to the charter by decision of the general meeting of the company’s participants, adopted unanimously by all participants. Contributions to the company's property are made in money, unless otherwise provided by the company's charter or a decision of the general meeting of participants. Contributions to the company's property do not change the size and nominal value of the participants' shares in the authorized capital of the company.
Contributions made to the property of the LLC are subject to reflection in the additional capital of the company. The procedure for reflecting contributions to the company's property in the financial statements under Art. 27 of the LLC Law is not regulated by law. However, since the list of transactions that form additional capital is open and there are corresponding explanations from the financial department (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 13, 2005 N 07-05-06/107), it is advisable to include these amounts specifically in additional capital.
How retained earnings from previous years are displayed
Retained earnings from previous years are accumulated in account 84. The credit balance of this account is transferred to balance sheet line 1370.
Typically, there should be no movement in the debit of the account during the year, since the distribution of profits traditionally occurs at the end of the year after the annual meeting of the company's owners. But there is also a special case when debit 84 needs to be used during the year. To make sure that you did not miss this very transaction, get free access to ConsultantPlus and go to the Typical Situation.
For information on how data on retained earnings is generated for reflection in the balance sheet (final and interim), read the article “Procedure for compiling a balance sheet (example).”
Retained earnings: problems of accounting and use
Studying the structure of the balance sheet liability allows us to establish one of the possible reasons for the financial instability of an enterprise, which can lead to its insolvency. This reason may be the high share of borrowed funds (over 50%) in the structure of sources of financing economic activities. At the same time, an increase in the share of own sources in the liability currency of the balance sheet indicates increased financial stability and independence of the enterprise from borrowed and raised funds. At the same time, the presence of retained earnings can be considered as a source of replenishment of working capital.
Studying the structure of the balance sheet liability allows us to establish one of the possible reasons for the financial instability of the enterprise, which led to its insolvency. This reason may be the high share of borrowed funds (over 50%) in the structure of sources of financing economic activities. At the same time, an increase in the share of own sources in the liability currency of the balance sheet indicates increased financial stability and independence of the enterprise from borrowed and raised funds. At the same time, the presence of retained earnings can be considered as a source of replenishment of working capital. The assets of the enterprise and their structure are studied both from the point of view of their participation in the production process and from the point of view of assessing their liquidity. The most easily realizable assets include cash and short-term securities; The most difficult to sell assets include fixed assets and other non-current assets.
Pages: 1
Retained earnings of the reporting year
The credit balance at the end of the year according to accounting account 99 is net profit. But in addition to the financial result, this account also reflects some other indicators. You can learn which ones and how not to make mistakes when making transactions from the Typical Situation from K+, having received trial access to the system.
When reforming the balance sheet, it is written off to accounting account 84 (Dt 99 Kt 84) and constitutes retained earnings at the end of the reporting year.
Read about the reformation procedure in the material “How and when to reform the balance sheet?”.
In order to separate the indicators of retained earnings of the current (reporting) year from last year’s, some accountants allocate separate lines 1372 and 1372 in the balance sheet, which respectively reflect the retained earnings of the reporting period and previous years.
The use of retained earnings is the prerogative of the company's owners. And highlighting this financial indicator for different years in the balance sheet is primarily convenient for them. But it is worth keeping in mind that the retained earnings of the past year cannot be fully distributed without taking into account the company’s previous operating results.
IMPORTANT! It must not be allowed that the value of the company’s net assets, after transferring retained earnings of the reporting year for the payment of dividends, becomes less than the size of the company’s authorized capital even if there is a reserve fund. The caution applies to cases where uncovered losses were recorded in previous years. The decision to cover last year's losses from retained earnings of the reporting year is made exclusively by the owners of the company.
But retained earnings for previous years can be distributed by the participants/shareholders of the company not only at the end of the year, but at any time. The main thing is to hold a thematic meeting of all company owners and approve the appropriate decision.
Does an LLC have the right to make incentive payments to employees from retained earnings and how to formalize this, and are they taken into account when calculating the average salary? The answer to this question was prepared by labor inspector in the Nizhny Novgorod region V.I. Neklyudov. Get free trial access to the ConsultantPlus system and get acquainted with the official’s point of view.
Retained earnings - where can it be used and who makes the decision?
An increase in accounts receivable is a negative factor, indicating that the company provides its customers with deferred payment in amounts exceeding the amount of funds received in the form of deferred payments from commercial creditors.
In analyzing the structure of the balance sheet liabilities, we pay attention to the amount of equity capital (authorized capital and accumulated profit). An increase in the share of funds and retained earnings indicates the effective operation of the enterprise.
In the structure of an enterprise's borrowed funds, we pay attention to the share of long-term loans and credits, as they increase the financial stability of the enterprise. An increase in short-term debt means a decrease in turnover.
According to the degree of liquidity, Assets are divided into:
- quickly implemented,
- averagely marketable,
- slow to implement
- difficult to implement.
According to the degree of urgency, Liabilities are divided into:
- short-term,
- mid-term,
- long-term
- permanent.
An enterprise must conduct its financial activities in such a way that the amounts of assets and liabilities of one group coincide. Which in reality is extremely rare.
Therefore, a financial condition in which:
- short-term financial investments, cash and short-term receivables are covered by short-term loans and accounts payable;
- inventories, long-term receivables and non-current assets are covered by the authorized capital, reserves and funds and retained earnings.
To correctly understand the structure of the balance sheet, it is necessary to understand that in different industries the same indicator can mean different results.
It is considered normal for trading enterprises if part of the inventory (goods for resale) is financed through accounts payable or short-term loans.
If such a situation arises at a manufacturing enterprise, this may mean that there is a threat to the solvency of the enterprise due to overstocking and lack of sales of products.
Financiers use the balance sheet to calculate the liquidity ratios, solvency and financial stability of the enterprise, as well as to calculate the net assets of the enterprise.
These ratios are especially important if the company intends to obtain borrowed funds from a credit institution (bank loan).
Balance sheet indicators allow you to create a reliable picture of the financial condition of the enterprise.
Retained earnings: calculation formula
According to general accounting data, retained earnings are a company's net profit after taxes that can be distributed to the company's owners.
Based on global financial practice, retained earnings (hereinafter referred to as RR) are calculated using the following formula:
NPk = NPn + PE – Div,
Where:
NPk - NP at the end of the reporting year;
NPn - NP at the beginning of the reporting period;
PE - net profit remaining after accrual of income tax;
Div - dividends paid in the reporting year based on the NP of previous years.
If you do not have the NP value, then to calculate the NP you can use the following scheme:
- first calculate profit before tax (to determine it, calculate operating profit, which is defined as the difference between operating income and operating expenses);
- then subtract depreciation and interest costs from operating profit;
- Subtract tax from the resulting profit value.
To find out whether it is possible to see the amount of operating profit in the accounting statements, read the article “Which line is operating profit reflected in the balance sheet?”
Indicators for investors
When analyzing the financial condition of a company, investors pay attention to the use of retained earnings. If NP accumulates and is not put into circulation, this state of affairs should seem to suit investors, since they can count on significant dividends.
However, without investment in its activities, the company stops growing, and its income not only does not increase, but may also decrease (due to a drop in competitiveness, high wear and tear of equipment, and for other reasons related to the lack of investment). So a company that accumulates profits but does not invest in its activities cannot be attractive.
At the same time, a company that does not make a profit and does not pay dividends cannot interest investors at all.
The ideal option for investors is a company that invests the funds remaining after paying dividends in its development. Although the owners may decide not to pay dividends and direct the entire volume of NP into circulation.
Results
There is a separate line in the balance sheet to reflect retained earnings (profit remaining after the amount of income tax or net profit has been withdrawn from it). The figure entered into it corresponds to the amount of the entire net profit accumulated over the years of the company’s activity. During the reporting year, the value of retained earnings in accounting relating to this year can be seen in a separate accounting account. Dividends are paid out of net profit.
Sources: Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 6, 2008 No. 106n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How is it formed and what does it include?
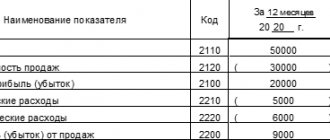
A positive or negative result from the sale of products or the provision of services is reflected in the active-passive account 90 “Sales.” The debit of the account shows the full cost, VAT and other costs. The loan reflects revenue. The final balance is transferred to account 99 “Profits and losses”.
The following entries are made in the accounting book:
- Dt90Kt99 – profit made;
- Dt99Kt90 – loss received.
The operations of the enterprise, which are classified as operating and non-operating, are shown on account 91 “Other income and expenses”.
These include:
- Sale and rental of assets owned by the company;
- Depreciation and revaluation of non-current assets;
- Transactions with foreign currency;
- Investments in business shares of other companies;
- Liquidation and donation of property;
- Income and expenses from transactions with securities.
The postings are as follows:
- Dt91Kt99 – profit made;
- Dt99Kt91 – loss received.
This procedure for writing off the totals for accounts 90 and 91 is called balance sheet reformation. Many economists understand this term as the direct distribution of accumulated profit from account 84.
Similarly, the balance from accounts 76 “Extraordinary income and expenses” (for example, insurance compensation or losses from natural disasters) and 10 “Materials” (the cost of accepted inventory items that are unsuitable for production) is transferred to account 99.
Retained earnings increase when accounting errors are discovered that resulted in overstated expenses. And also in case of unclaimed dividends by shareholders, if more than three years have passed since they were accrued. Accordingly, errors that create an overstatement of income will reduce the accumulated profit.
The components of retained earnings are not always cash in the form of cash or in a checking account (a writedown of fixed assets increases earnings, but does not add cash). This must be taken into account when conducting economic analysis.
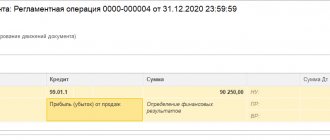
In the last days of the reporting year, the chief accountant writes off the final balance (profit or loss) from account 99 to account 84 “Retained earnings”.
Postings are made:
- Dt99Kt84 – upon receipt of profit;
- Dt84Kt99 – upon receipt of a loss.
After this, account 99 is reset to zero and no transactions are carried out on it until the beginning of the next year. Count 84 is active-passive. Before entering the total amount of accumulated profit into the financial statements, the amount of income tax is subtracted from it (later it can be adjusted).