What is gross profit?
Gross profit is the difference between income and cost. Taxes are not deducted from these funds. Cost means:
- costs of producing the product: costs of materials, equipment maintenance;
- expenses for purchasing a finished product at the purchase price;
- payment for electricity;
- salary payments.
How is net profit distributed among LLC participants ?
All these indicators constitute technical costs.
IMPORTANT! VP is calculated for a specific period. The time period depends on the company. The resulting figure is indicated in the balance sheet.
Results
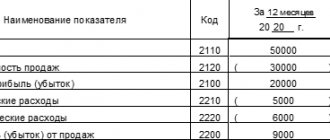
Gross profit is a concept contained in PBU 4/99 and appears in connection with the financial results statement. It is calculated as the difference between sales revenue for main activities and the cost of these sales. At the same time, the cost does not include commercial, administrative and other expenses. The classification of activities as main ones is determined by the accounting policy.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What influences VP?
Gross profit changes under the influence of external circumstances, such as:
- cost of transportation services,
- natural, environmental factors,
- socio-economic environment in which the enterprise operates,
- costs of production resources,
- foreign economic contacts.
What affects the amount of retained earnings (uncovered loss) ?
VP is also influenced by internal factors:
- income from product sales,
- other sources of income: investments, provision of services,
- cost of goods,
- demand for manufactured products, sales figures,
- cost of manufactured goods.
Gross profit is also affected by negative factors possible during the operation of the enterprise:
- overestimated or underestimated cost of products sold;
- low quality of goods;
- disciplinary violations by the company’s employees leading to losses;
- fines and sanctions.
The listed factors can affect the gross profit directly and indirectly. Factors that affect sales income have an indirect influence.
Operating profit margin: checking fixed expenses
Operating profit margin shows how a company is affected by fixed costs. Fixed costs are those that the company incurs regardless of the number of orders, for example, office costs, salaries, advertising.
Operating profit margin is calculated as follows:
Operating profit margin = (Operating profit / Revenue) × 100%.
Operating profit is revenue minus variable and fixed expenses. They count it themselves or look at the OPiU, where they take the proceeds. Let's get back to the examples.
Igor decided to calculate his profitability based on operating profit. In March it was 30%. This is fine.
But from April to August it is already 17%. Igor began to think about what had changed, and remembered that in March he changed the salon at the Marina hairdressing salon for 5,000 rubles. per month to rent a seat in a premium salon for 25,000 rubles.
With data on operating profitability, Igor may think: does he need this salon if the hairdresser in the area had more profit?
If the operating profit margin is falling, then it is necessary to diagnose fixed expenses. Maybe it’s time to give up this luxurious office in Moscow City and reduce someone’s salary.
Operating profit margin: growing - good; falling - check fixed expenses.
Gross profit composition
The VP may include the following financial resources:
- profit from sales of enterprise products and services;
- funds received from rural and logging farms;
- income from the sale of company property: equipment and other objects;
- amounts received from transactions not included in the main list of company activities. For example, a store sells goods. This is his main activity. However, the funds are spent on investments, the income from which is classified as non-operating profit;
- amounts received from the sale of shares.
The vast majority of EP, according to statistics, consists of income received from core activities.
How to view net profit in 1C: Holding Management
The interface and menu sections of the 1C: Holding Management program are somewhat different from 1C: ERP. It is more reminiscent of 1C: Accounting 8.3. Let's look at examples of generating profit reports using the example of the organization TC Megapolis.
Accurate accounting of net profit in holdings based on 1C: Holding Management
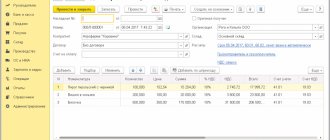
As in 1C:ERP, in order to determine the financial result of the company’s activities and calculate the amount of income tax, in 1C:UH we carry out a list of operations to close the month, for which we go to the “Operations” - “Month Closing” section.
Fig. 11 Closing the month
As a result of regulatory operations, cost accounts determined by the type of activity of the company are closed, and its financial result is determined - profit or loss. “Month Closing”, carried out in December, was supplemented by “Balance Reformation”.
Fig. 12 Closing the month in 1C:UH
Click on the hyperlink of the transactions performed and click on the line - “Calculation of income tax”. The form will display indicators for calculating profit and calculating income tax.
Fig. 13 Indicators for determining profit in 1C:UH
Formula for calculating gross profit
Gross profit is calculated using the formula:
VP = D - (S+W)
The formula includes the following indicators:
- VP – gross profit;
- D – quantity of products sold;
- C – cost of production of goods;
- C – costs of production processes.
VP indicators can be calculated after the product has been produced and sold.
ATTENTION! Typically, gross profit is calculated once a year.
Example
The company produces electric kettles. Production costs are 20,000 rubles, expenses are 10,000 rubles. 500 teapots were sold per day at a cost of 1000 rubles.
Calculations are carried out as follows: revenue per day is calculated. That is, the number of teapots sold is multiplied by their cost. We will receive 500,000 rubles. From this result you need to subtract all costs, which in total amount to 30,000 rubles. From 500,000, 30,000 rubles are deducted. Gross profit will be 470,000 rubles.
Calculation features
The calculation of VP differs in a number of nuances, determined by the type of activity of the enterprise:
- If a company specializes in selling products, it is required to deduct all expenses from revenue, including discounts on goods and returns. The cost of production is subtracted from the amount received. The result of the calculations is the gross profit;
- If an organization specializes in providing services, calculations are usually carried out according to a simplified scheme. Their revenues are deducted from discounts and other expenses. The resulting net profit is also gross profit.
The main stages of the calculation are standard.
Why is gross cost calculation necessary?
Gross profit does not reflect the actual income of a business. This figure includes many unnecessary expenses: advertising, salaries, rent. VP is required for other purposes. This is a narrow, not a general tool. It is used to analyze the production resources of an enterprise. Correctly calculated indicators ensure the achievement of the following goals:
- analysis of the difference between the cost of a product and the income from its sale;
- determining the optimal cost for a product or service;
- competent measures for planning the company’s activities;
- identifying problems and weaknesses of the enterprise.
Based on the analysis of annual VP indicators, it is possible to track the economic growth of the enterprise and the results of optimizing activities.
Methods for generating and planning profits
Profit is the main indicator of the financial and economic activity of an enterprise. It reflects the net income created in the material sphere of production. Profit is both a financial result and a minor element of the financial resources of an enterprise. Profit planning begins after calculating the planned cost of production and sales of products according to the economic elements of costs. However, profit comes in different types, and its size and significance are influenced by a variety of factors. Let's consider the main methods of generating and planning profits.
Profit is the main indicator of the financial and economic activity of an enterprise. In general, profit is defined as the difference between total revenue and total costs, i.e. the difference between income and expenses. Thus, profit reflects the net income created in the material sphere of production.
Types of profit:
- the accounting profit of an enterprise represents the enterprise's revenue from the sale of products minus the costs of producing sold products, adding or excluding income or expenses from non-sales operations;
- Net profit reflects the remaining portion of the company's income. those. this is accounting profit minus taxes on it;
- economic profit - involves obtaining a financial result, perceived as the enterprise’s revenue minus the cost of production.
When developing a profit plan, it should be borne in mind that VAT and excise taxes are not reflected in this plan, since they are collected before profit is generated.
Profit planning begins after calculating the planned cost of production and sales of products according to economic elements of costs, usually for a quarter, since planning for a longer period significantly reduces the accuracy of planned calculations. Gross profit is the amount of profit (loss):
- from sales of products;
- from the sale of fixed assets;
- from the sale of other property (for example, inventory), and also includes income from non-operating operations.
Thus, the financial result of the enterprise is divided into operating and non-operating.
Gross profit (loss) from the sale of products (works, services) is defined as the difference between the proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) at free wholesale prices without VAT, excise taxes and the costs of its production and sale.
When an enterprise uses the method of determining revenue from the sale of products as they are paid for, the gross profit is composed of the amounts received as payment for shipped products to the enterprise’s current account or to the enterprise’s cash desk directly, as well as the amounts indicated when offsetting mutual claims.
Enterprises that determine revenue from sales of products at the time of shipment and presentation of settlement documents to customers reflect gross profit in the amount of the cost of these products indicated in the settlement documents. In this case, the result from the external sale of products from auxiliary and ancillary production of the enterprise is taken into account. If the enterprise could not sell products at prices above cost due to a decrease in their quality or consumer properties (including obsolescence) or if the prevailing prices for this or similar products turned out to be lower than its actual cost. then the actual sales yen of the product is applied (for tax purposes).
Thus, profit is net income expressed in monetary terms, which is the difference between total revenue and total costs. An enterprise makes a profit if sales revenue exceeds the cost of products (works, services) sold. In general, the indicator can be calculated as follows:
Pr = BP - C
where Pr is profit from sales, rub.; C — cost of products sold (work, services), rub.; VR — revenue from the sale of products (services), rub.
The profit value is as follows:
- reflects the final financial result of the enterprise for a certain period;
- performs a stimulating function, manifested in the process of its distribution and use. The content of this function is that profit is both a financial result and a minor element of the financial resources of the enterprise;
- is the main source of revenue generation for budgets at various levels.
The profit generation mechanism is contained in the “Report on Financial Results”.
The net profit of an enterprise is determined by subtracting the amounts of income tax, rental payments, export and import taxes from the balance sheet profit. At the same time, it includes the result of emergency circumstances, calculated as the difference between revenues and expenses associated with these circumstances. When forming net profit, transactions for the payment of fines, penalties and other payments are taken into account, which are paid from the profit remaining at the disposal of the organization after taxation. Net profit is distributed in the following areas:
- for the formation of reserve funds;
- to pay income to founders (participants);
- for the creation of funds for special purposes (accumulation, consumption, social sphere).
An important factor influencing the amount of profit is changes in the volume of production and sales of products (direct relationship).
Let's consider various methods of generating and planning profits.
Direct counting method. This method assumes that profit is determined as the difference between planned revenue and the full cost of production in actual prices with basic deductions. The method is the most common, and it is used to justify the creation of a new or expansion of existing production.
In this method, the main indicator is profit from sales of products, which is calculated for individual types of economic activity. The calculation is carried out using the basic formula for finding profit:
P = Revenue - S/S - Taxes (VAT, excise taxes),
where P is profit from product sales, rub.; С/С — cost price, rub.
This approach is due to the fact that some types of activities are not subject to income and value added tax or have their own calculation percentage. Therefore, the method allows you to accurately and objectively determine the profit of the enterprise.
- Advantages: accuracy and objectivity.
- Disadvantages: labor-intensive; if there is a large range of items, this method becomes impossible to use.
The direct counting method involves determining profit by commodity output and by the volume of products sold by the enterprise.
Thus, profit on commodity output (Ptp) is planned on the basis of cost estimates for production and sales of products, which determines the cost of commodity output for the planned period: Ptp = Ctp - Stp,
where Tstp is the cost of commodity output of the planned period in current selling prices (excluding VAT, excise taxes, trade and sales discounts); Stp, is the total cost of the planning period.
It is also necessary to distinguish the planned amount of profit per commodity output from the profit planned per volume of products sold. Profit on products sold (Prp) is generally calculated using the formula
Prp = Vrp - Srp,
where Vrp is the planned revenue from sales of products at current prices (excluding VAT, excise taxes, trade and sales discounts); CRP is the full cost of products sold in the planned period.
In more detail, based on the volume of products sold in the planning period, profit on products sold is determined by the formula
Prp = Mon + Ptp - Pok,
where Pon is the amount of profit from the balances of unsold products at the beginning of the planning period; Ptp - profit from the volume of output of commercial products in the planning period; Pok - profit from the balance of unsold products at the end of the planning period.
This calculation method is applicable for the enlarged direct method of profit planning, when it is easy to determine the volume of products sold in prices and at cost.
A variation of the direct counting method is the assortment profit planning method. With this method, profit is summed up across all product lines. To the result obtained, profit is added in the balances of finished products that were not sold at the beginning of the planning period.
The normative method involves the formation of profit based on a system of various standards, such as the rate of return on equity capital, the rate of return on the assets of the enterprise, the rate of profit per unit of products sold, etc.
- Advantages: accuracy of calculations, ability to plan and forecast.
- Disadvantages: labor intensive, we will not be able to estimate the price level (possible only with stable production).
The extrapolation method is an analysis of dynamics over several years, identification of general trends in the formation of profit and its forecast for a new planning period.
This method is effective for justifying a feasibility plan or project. The analytical method involves the use of multifactor economic models in the formation and planning of the profit of an industrial enterprise. In the simplest version, the method comes down to establishing the profit of the previous period (analysis), determining its share in the total gross income of the enterprise and per unit of products sold. As a result, by adjusting to take into account changes in production volumes, the planned profit of the enterprise is established.
The analytical method is based on the construction of multifactor models and takes into account the influence of various factors on the results of the enterprise. The method can have a graphical interpretation in the form of profitability graphs, which allow determining the break-even point of the enterprise. The algorithm for determining profit using this method is as follows:
- 1st stage - the profit received by the enterprise for the reporting period is analyzed;
- Stage 2 - the planned change in production volumes is determined;
- Stage 3 - the share of profit in the total amount of income received is established;
- Stage 4 - the planned profit is determined as the product of the planned income of the profit share, taking into account changes in production volumes.
The combined calculation method involves the synthesis of two methods: direct accounting and analytical calculation of enterprise profit.
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
How to increase gross profit?
Gross profit is a dynamic indicator. It constantly changes depending on the company's activities. The following activities help increase VP:
- use of LIFO technique in inventory analysis;
- tax reduction with the help of benefits that the enterprise is entitled to;
- regular write-off of bad debts from the balance sheet;
- optimization of production processes aimed at reducing costs;
- competent pricing policy that takes into account the demand for products and the general market situation;
- improving the quality of equipment to speed up the release of goods and improve their quality. Restoration or acquisition of equipment can be carried out at the expense of shareholder dividends;
- creation of reasonable standards to ensure control over intangible assets.
IMPORTANT! Gross profit is an indicator on the basis of which planning of an enterprise’s activities in the production sector can be carried out.
So. Gross profit is the amount obtained after deducting costs and production costs. Determined by formula. The nuances of the calculation depend on the type of activity of the enterprise. The VP indicator is important for assessing the company's production resources. Is the basis for reasonable pricing. Gross profit is reflected in the financial statements using the appropriate entries established by the Order of the Ministry of Finance.